Java 定时任务
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/DD7AngUgYtVui0qqZzKHRw
一、job 定时任务的五种创建方式
1、使用线程创建 job 定时任务
/** * TODO 使用线程创建 job 定时任务 * @author 王松 */ public class JobThread { public static class Demo01 { static long count = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); count++; System.out.println(count); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } } }; Thread thread = new Thread(runnable); thread.start(); } } }
2、使用 TimerTask 创建job定时任务
/** * TODO 使用 TimerTask 创建job定时任务 * @author 王松 */ public class JobTimerTask { static long count = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { TimerTask timerTask = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { count++; System.out.println(count); } }; //创建timer对象设置间隔时间 Timer timer = new Timer(); // 间隔天数 long delay = 0; // 间隔毫秒数 long period = 1000; timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(timerTask, delay, period); } }
3、使用线程池创建 job定时任务
/** * TODO 使用线程池创建 job定时任务 * @author 王松 */ public class JobScheduledExecutorService { public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // task to run goes here System.out.println("Hello !!"); } }; ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); // 第二个参数为首次执行的延时时间,第三个参数为定时执行的间隔时间 service.scheduleAtFixedRate(runnable, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } }
4.Quartz 框架
1.引入maven依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<dependencies>
<!-- quartz -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.quartz-scheduler</groupId>
<artifactId>quartz</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.quartz-scheduler</groupId>
<artifactId>quartz-jobs</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.任务调度类
public class MyJob implements Job { @Override public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException { System.out.println("quartz MyJob date:" + System.currentTimeMillis()); } }
3.启动类
public class JobQuartz { public static void main(String[] args) throws SchedulerException { //1.创建Scheduler的工厂 SchedulerFactory sf = new StdSchedulerFactory(); //2.从工厂中获取调度器实例 Scheduler scheduler = sf.getScheduler(); //3.创建JobDetail, JobDetail jb = JobBuilder.newJob(MyJob.class) //job的描述 .withDescription("this is a ram job") //job 的name和group .withIdentity("ramJob", "ramGroup") .build(); //任务运行的时间,SimpleSchedle类型触发器有效,3秒后启动任务 long time= System.currentTimeMillis() + 3*1000L; Date statTime = new Date(time); //4.创建Trigger //使用SimpleScheduleBuilder或者CronScheduleBuilder Trigger t = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger() .withDescription("") .withIdentity("ramTrigger", "ramTriggerGroup") //.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule()) //默认当前时间启动 .startAt(statTime) //两秒执行一次,Quartz表达式,支持各种牛逼表达式 .withSchedule(CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0/2 * * * * ?")) .build(); //5.注册任务和定时器 scheduler.scheduleJob(jb, t); //6.启动 调度器 scheduler.start(); }
5. springboot 的 @Scheduled 注解
@Component @Configuration //1.主要用于标记配置类,兼备Component的效果。 @EnableScheduling // 2.开启定时任务 public class SaticScheduleTask { @Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?") //3.添加定时任务 //@Scheduled(fixedRate=5000) //或直接指定时间间隔,例如:5秒 private void configureTasks() { System.err.println("执行静态定时任务时间: " + LocalDateTime.now()); } }
5、几个表达式的例子:
0 0 9 * * ?:每天早上9点触发
0 0/30 * * * ?:每30分钟触发一次
0 30 18 ? * MON-FRI:每周一到周五的18:30分触发
0 10 12 1,15 * ?:每月1号、15号的12:10触发
0 0/10 7-8 1,15 * ?:每月1号、15号早上7点到8点每10分钟触发一次
0 15 10 * * ? * 每天10点15分触发
0 15 10 * * ? 2017 2017年每天10点15分触发
0 * 14 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点59分每分触发
0 0/5 14 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点59分(整点开始,每隔5分触发)
0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点59分、18点到18点59分(整点开始,每隔5分触发)
0 0-5 14 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点05分每分触发
0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月最后一周的星期五的10点15分触发
0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三周的星期五开始触发
每隔5秒执行一次:*/5 * * * * ?
每隔1分钟执行一次:0 */1 * * * ?
每天23点执行一次:0 0 23 * * ?
每天凌晨1点执行一次:0 0 1 * * ?
每月1号凌晨1点执行一次:0 0 1 1 * ?
每月最后一天23点执行一次:0 0 23 L * ?
每周星期天凌晨1点实行一次:0 0 1 ? * L
在26分、29分、33分执行一次:0 26,29,33 * * * ?
每天的0点、13点、18点、21点都执行一次:0 0 0,13,18,21 * * ?
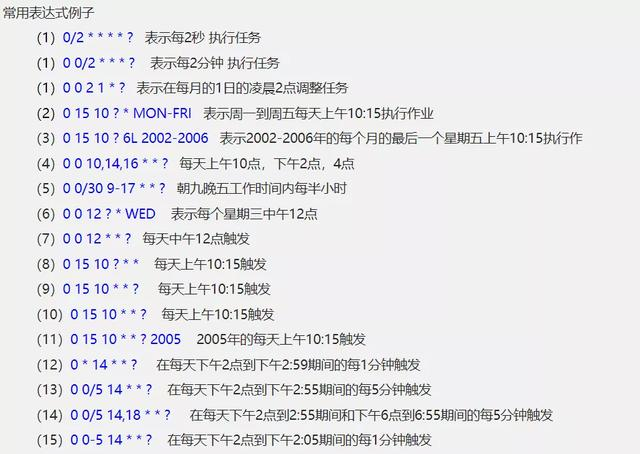
0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点
0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时
0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点
"0 0 12 * * ?" 每天中午12点触发
"0 15 10 ? * *" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ?" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? *" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? 2005" 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
"0 * 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
"0 0/5 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
"0 0/5 14,18 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
"0 0-5 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
"0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED" 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
"0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI" 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 15 * ?" 每月15日上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 L * ?" 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
我们可以通过一些Cron在线工具非常方便的生成,比如http://www.pppet.net/等。
0 0/30 * * * ?:每30分钟触发一次
0 30 18 ? * MON-FRI:每周一到周五的18:30分触发
0 10 12 1,15 * ?:每月1号、15号的12:10触发
0 0/10 7-8 1,15 * ?:每月1号、15号早上7点到8点每10分钟触发一次
0 15 10 * * ? * 每天10点15分触发
0 15 10 * * ? 2017 2017年每天10点15分触发
0 * 14 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点59分每分触发
0 0/5 14 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点59分(整点开始,每隔5分触发)
0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点59分、18点到18点59分(整点开始,每隔5分触发)
0 0-5 14 * * ? 每天下午的 2点到2点05分每分触发
0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月最后一周的星期五的10点15分触发
0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三周的星期五开始触发
每隔5秒执行一次:*/5 * * * * ?
每隔1分钟执行一次:0 */1 * * * ?
每天23点执行一次:0 0 23 * * ?
每天凌晨1点执行一次:0 0 1 * * ?
每月1号凌晨1点执行一次:0 0 1 1 * ?
每月最后一天23点执行一次:0 0 23 L * ?
每周星期天凌晨1点实行一次:0 0 1 ? * L
在26分、29分、33分执行一次:0 26,29,33 * * * ?
每天的0点、13点、18点、21点都执行一次:0 0 0,13,18,21 * * ?
0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点
0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时
0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点
"0 0 12 * * ?" 每天中午12点触发
"0 15 10 ? * *" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ?" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? *" 每天上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? 2005" 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
"0 * 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
"0 0/5 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
"0 0/5 14,18 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
"0 0-5 14 * * ?" 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
"0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED" 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
"0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI" 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 15 * ?" 每月15日上午10:15触发
"0 15 10 L * ?" 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
我们可以通过一些Cron在线工具非常方便的生成,比如http://www.pppet.net/等。
理解ScheduledExecutorService中scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay的区别
1.scheduleAtFixedRate
每间隔一段时间执行,分为两种情况:
当前任务执行时间小于间隔时间,每次到点即执行;
/** * 任务执行时间(8s)小于间隔时间(10s) */ public class ScheduleTest { static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1); public static void main(String[] args) { scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: " + new Date()); try { Thread.sleep(8000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("End : scheduleAtFixedRate: " + new Date()); } }, 0, 10 , SECONDS); } } output: Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:00 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:08 CST 2019 Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:10 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:18 CST 2019 Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:20 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:28 CST 2019 Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:30 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:36:38 CST 2019 ... 程序启动时间是14:36:00,以后每间隔10s执行一次(即14:36:10、14:36:20、14:36:30等)。
当前任务执行时间大于等于间隔时间,任务执行后立即执行下一次任务。相当于连续执行了。
/** * 任务执行时间(12s)大于间隔时间(10s) */ public class ScheduleTest { static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1); public static void main(String[] args) { scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: " + new Date()); try { Thread.sleep(12000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("End : scheduleAtFixedRate: " + new Date()); } }, 0, 10 , SECONDS); } } output: Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:13 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:25 CST 2019 Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:25 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:37 CST 2019 Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:37 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:49 CST 2019 Start: scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:30:49 CST 2019 End : scheduleAtFixedRate: Sun Apr 28 14:31:01 CST 2019 程序启动时间是14:30:13,按理说应该每间隔10s执行一次(即14:30:23、14:30:33等),但由于任务执行时间长于10s,下一次的任务要开始的时候发现上次的任务还没有完成,因此阻塞等待,一旦发现上次的任务完成,就马上启动。表现出来就是任务延时启动,最终的效果就是连续执行。
2.scheduleWithFixedDelay(推荐使用)
每当上次任务执行完毕后,间隔一段时间执行。不管当前任务执行时间大于、等于还是小于间隔时间,执行效果都是一样的。
/** * 任务执行时间(8s)小于间隔时间(10s) */ public class ScheduleTest { static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1); public static void main(String[] args) { scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: " + new Date()); try { Thread.sleep(12000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: " + new Date()); } }, 0, 10 , SECONDS); } } output: Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:27:59 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:28:07 CST 2019 Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:28:17 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:28:25 CST 2019 Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:28:35 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:28:43 CST 2019 Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:28:53 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:29:01 CST 2019 ... 可以看出每个End后,等待了10秒,才启动下一次Start。
/** * 任务执行时间(12s)大于间隔时间(10s) */ public class ScheduleTest { static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1); public static void main(String[] args) { scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: " + new Date()); try { Thread.sleep(12000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: " + new Date()); } }, 0, 10 , SECONDS); } } output: Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:26:29 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:26:41 CST 2019 Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:26:51 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:27:03 CST 2019 Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:27:13 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:27:25 CST 2019 Start: scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:27:35 CST 2019 End : scheduleWithFixedDelay: Sun Apr 28 14:27:47 CST 2019 ... 可以看出每个End后,等待了10秒,才启动下一次Start。
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi666/p/10783879.html
故乡明


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号