Spring Ioc 容器核心概览
Spring Ioc
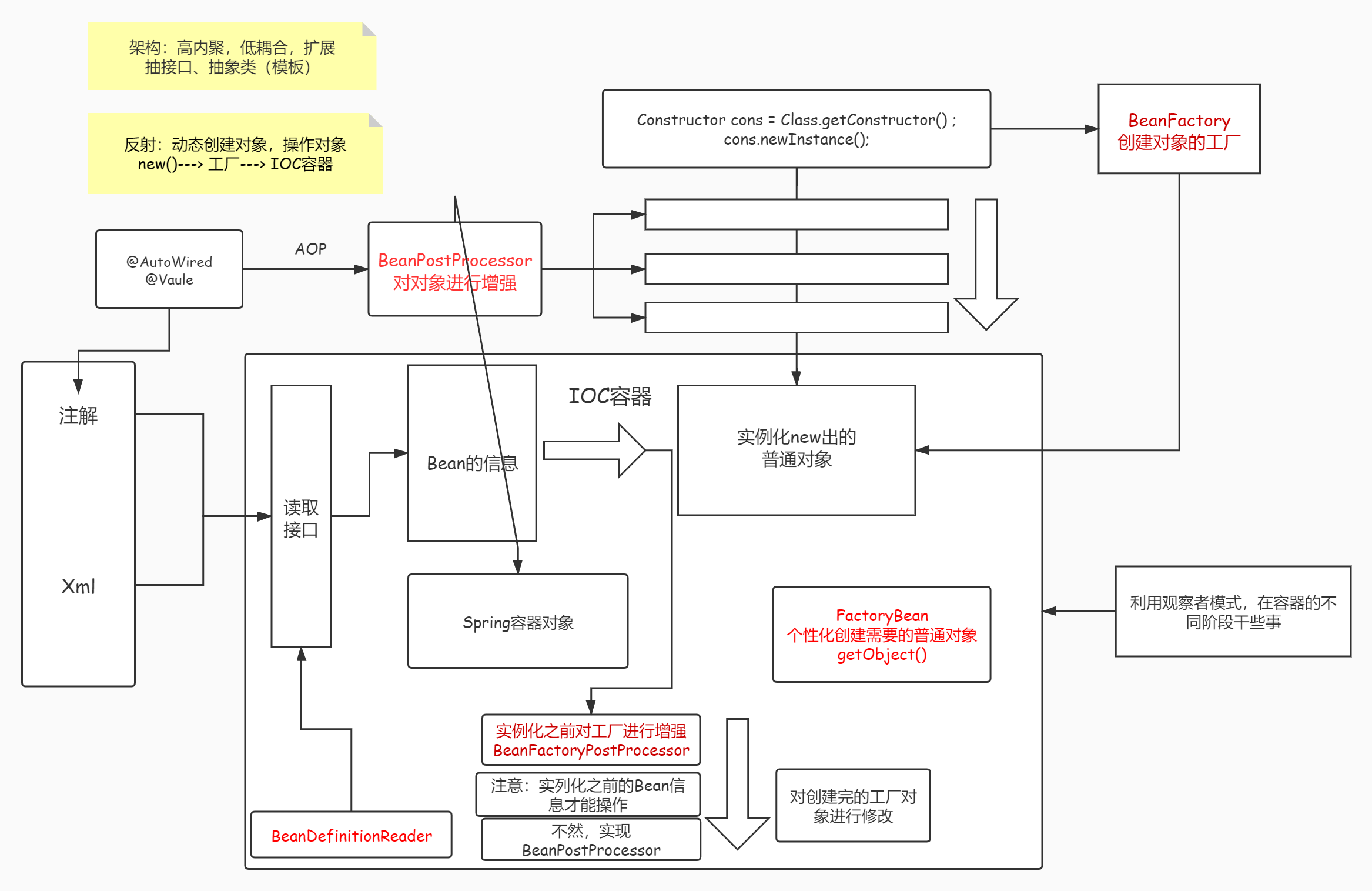
BeanFactory
public interface BeanFactory {
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
- 正常getObject()拿到的是对象,"&"拿到的是产生这个Bean的工厂
Bean生命周期
- Bean生命周期 完整标准顺序如下
- 源码自带说明书
Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is:
- set一堆Aware
- BeanPostProcessors
- InitializingBean 初始化
- 自定义的初始化方法
- BeanPostProcessors
- DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
- DisposableBean destroy
- 自定义销毁方法
BeanNameAware :可以获取容器中bean的名称
BeanFactoryAware:获取当前bean factory这也可以调用容器的服务
ApplicationContextAware: 当前的applicationContext, 这也可以调用容器的服务
MessageSourceAware:获得message source,这也可以获得文本信息
applicationEventPulisherAware:应用事件发布器,可以发布事件,
ResourceLoaderAware: 获得资源加载器,可以获得外部资源文件的内容;
* <li>BeanNameAware's {@code setBeanName}
* <li>BeanClassLoaderAware's {@code setBeanClassLoader}
* <li>BeanFactoryAware's {@code setBeanFactory}
* <li>EnvironmentAware's {@code setEnvironment}
* <li>EmbeddedValueResolverAware's {@code setEmbeddedValueResolver}
* <li>ResourceLoaderAware's {@code setResourceLoader}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ApplicationEventPublisherAware's {@code setApplicationEventPublisher}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>MessageSourceAware's {@code setMessageSource}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ServletContextAware's {@code setServletContext}
* (only applicable when running in a web application context)
* <li>{@code postProcessBeforeInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
* <li>InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* <li>a custom init-method definition
* <li>{@code postProcessAfterInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
<ol>
* <li>{@code postProcessBeforeDestruction} methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
* <li>DisposableBean's {@code destroy}
* <li>a custom destroy-method definition
* </ol>
FactoryBean
-
一个依赖于BeanFactory,生产个性化Bean的接口,因此它也是synchronization同步的
-
getObjectType() , getObject() 这两个主要方法,在启动的时候进行暴露,甚至在post-processor启动之前
-
@link #getObjectType()} {@link #getObject()} invocations may arrive early in the bootstrap process, even ahead of any post-processor setup. -
A bean that implements this interface cannot be used as a normal bean.
-
A FactoryBean is defined in a bean style
Environment
-
ConfigurableEnvironment -
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer -
@Profile 不同的环境下使用不同的@Configuration配置
-
组合类 StandardEnvironment
-
Environment 应用运行的环境 ,两种表现方式 profiles 、 properties ,使用PropertyResolver接口访问属性
-
Beans信息 在xml 或者 @Profile 注解
-
properties 属性来源有多种途径 JVM , system , JNDI , servlet , ad-hoc Properties objects
-
JVM system properties, system environment variables, JNDI, servlet context parameters, ad-hoc Properties objects, Maps, and so on. -
ApplicationContext 对Bean 进行管理 , 通过EnvironmentAware 或 @Inject 注册
-
使用 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 对xml配置文件的 占位符 ${...} 修改
-
Spring 3.1 注册默认使用 <context:property-placeholder/> 管理
-
@Profile 不同的环境下使用不同的@Configuration配置
-
组合类 StandardEnvironment
ApplicationContext ( 真正的集大成者 )
extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver
-
一个接口代表一个能力的抽象,子接口通过继承父接口,整合了父接口的功能
-
<p>An ApplicationContext provides: * <li>Bean factory methods for accessing application components. * Inherited from {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory}. * <li>The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion. * Inherited from the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader} interface. * <li>The ability to publish events to registered listeners. * Inherited from the {@link ApplicationEventPublisher} interface. * <li>The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization. * Inherited from the {@link MessageSource} interface. -
整合的能力:
- 对于访问应用组件提供BeanFactory
- 加载通用的资源文件 (资源加载器)
- 发布事件,注册监听器
- 解析消息,支持国际化
-
一个父上下文中可以使用整个web应用程序,而每个servlet有自己的子上下文无关其他servlet
-
ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory -
HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory
EnvironmentCapable
-
暴露 Environment getEnvironment();
-
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable -
ConfigurableApplicationContext 继承了ApplicationContext 能力,它重新覆盖了EnvironmentCapable的getEnvironment方法,并且返回的是 ConfigurableEnvironment 事实上 Environment是只读的。ConfigurableEnvironment 是可以被配置的,进行个性定制。
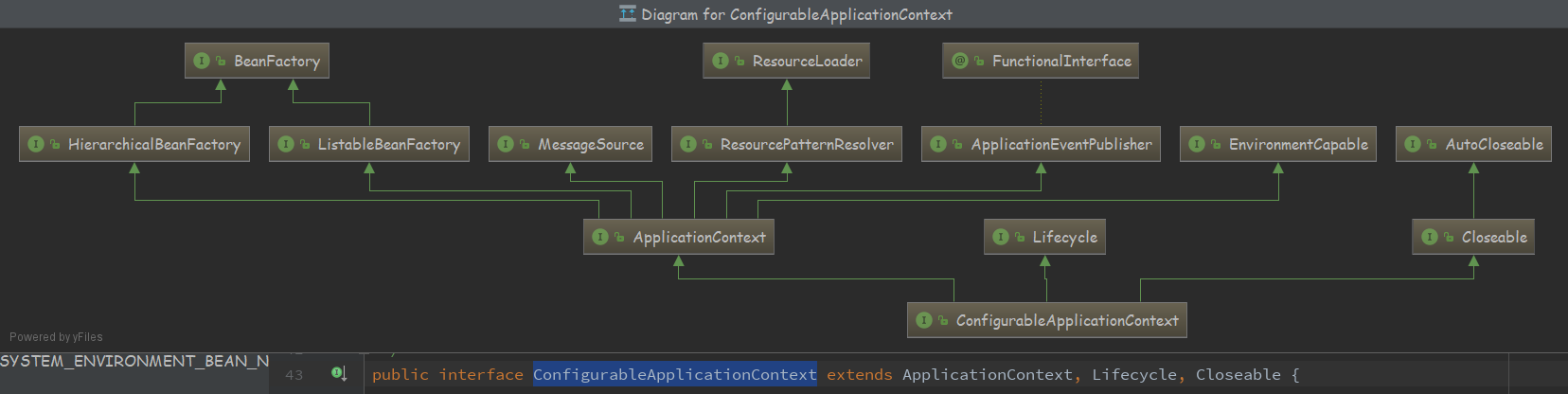
ApplicationEventPublisher
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
- @FunctionalInterface 特点
- 标记在 只有一个抽象方法的 接口上
- 静态方法、默认方法、
- 接口默认继承java.lang.Object ,所以声明Object的方法,不算抽象方法
- 该注解能够更好地让编译器进行检查 ( 不是必须 )
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
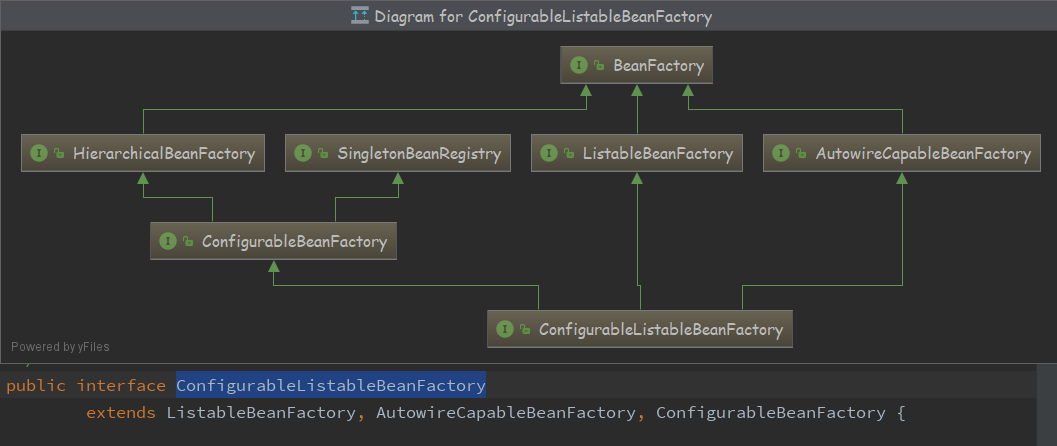
- AutowireCapableBeanFactory
-
拥有自动装配能力,并把这种能力暴露给外部应用的BeanFactory类,需要实现此接口
-
其他框架,利用该接口可以连接和填充Bean实例,且不受Spring控制
-
ApplicationContext通过方法 getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() 可以获取AutowireCapableBeanFactory
-
ListableBeanFactory 扩展BeanFactory ,把所有的Bean实例列举出来,而不是一个个用name去找
-
HierarchicalBeanFactory 分层工厂 (2个方法)
-
//返回工厂的父工厂 BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory(); //这个工厂中是否包含这个Bean boolean containsLocalBean(String name); -
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 集成上图的所有接口的功能,加上自身的可配置性
-
短剑 + 短剑 = 小黄刀 , 黄刀 + 暴风大剑 = 无尽
ResourcePatternResolver
Strategy interface for resolving a location pattern
-
策略接口,解析本地路径的资源
-
策略接口 资源加载器
-
classpath*: 搜索所有jar包
-
classpath: 当前路径搜索
Lifecycle 、SmartLifecycle
- Can be implemented by both components and containers
- 生命周期 在组件和容器中实现 , 将启动/停止信号传播到所有组件,应用到容器
- Can be used for direct invocations or for management operations via JMX.
- 可以被直接调用或通过JMX进行管理(Jconsole)
- SmartLifecycle provides sophisticated integration with the application context's startup and shutdown phases.
- SmartLifecycle 提供应用上下文 更复杂的 启动 ,关闭阶段。
ConfigurableApplicationContext
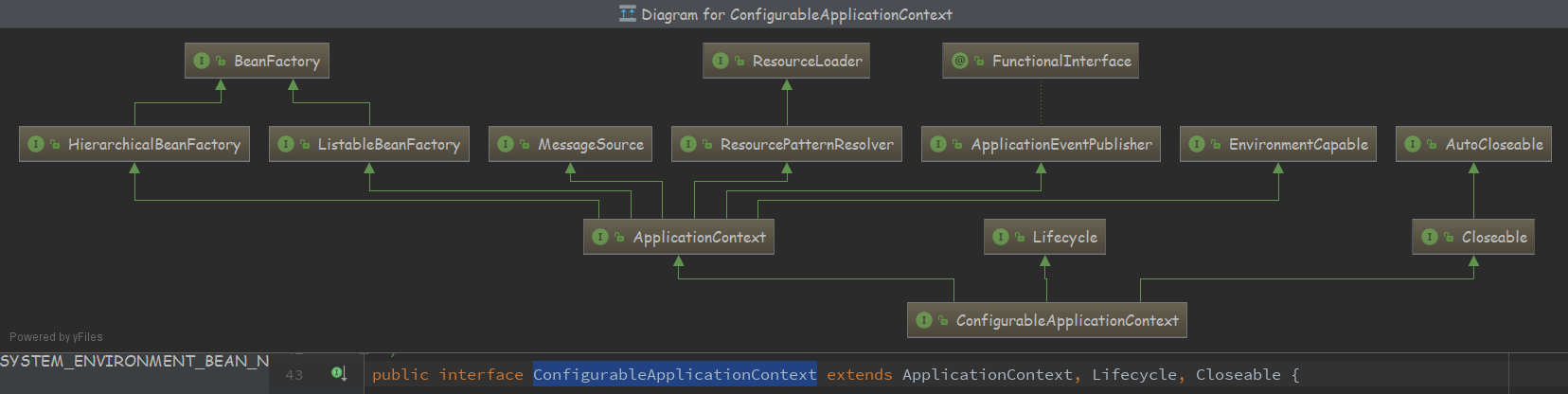
ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
- ConfigurableApplicationContext 继承 ApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext
abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
-
抽象类 --> 模板方法设计模式,具体的子类来实现抽象方法
-
an ApplicationContext is supposed * to detect special beans defined in its internal bean factory: * Therefore, this class automatically registers BeanFactoryPostProcessors BeanPostProcessors ApplicationListeners -
应用上下文在内部BeanFactory检测特定的Beans,将 BeanFactoryPostProcessors、 BeanPostProcessors 、ApplicationListener 这些Beans注册进上下文中
-
MessageSource 也作为Bean 在上下文中,ApplicationEventMulticaster 也一样作为Bean
-
Implements resource loading through extending DefaultResourceLoader (extends DefaultResourceLoader)
重点:更新应用上下文
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~