题目

The biomarkers of key miRNAs and target genes associated with acute myocardial infarction
与急性心肌梗死相关的关键miRNAs和靶基因的生物标志物
Submitted:2019.12.23 | Accepted:2020.04.14 | Published:2020.05.13
期刊名称:PeerJ
2021年影响因子 :3.061
题目很规矩,包含两要素,疾病和问题。疾病,急性心肌梗死;问题,揭示潜在的分子标志物。此外,我们还要关注的是此文的目标分子是miRNA。
生信文章中,除了基本的功能基因mRNA,以miRNA,lncRNA作为研究类型的生信文章也有很多,与mRNA生信数据挖掘的套路类似,属于花样翻新。
值得注意的是这篇文章并不是全生信,作者也做了一些湿实验。干湿结合,省去了被reviewer怼没有实验验证的情况。纯生信文章总是会落下不做实验怎能发文章的诟病。如果干湿结合,也能堵住一些人的嘴。
一直以来都传言肿瘤的生信文章容易发,但对非肿瘤来说就很不友好。非肿瘤有利有弊。弊端是数据集少且无临床数据可扒;利处是我们可以把肿瘤生信文章的套路运用到非肿瘤领域中实现降维打击(其实就是灌水)。
摘要

Background. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is considered one of the most prominent causes of death from cardiovascular disease worldwide. Knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying AMI remains limited. Accurate biomarkers are needed to predict the risk of AMI and would be beneficial for managing the incidence rate. The gold standard for the diagnosis of AMI, the cardiac troponin T (cTnT) assay, requires serial testing, and the timing of measurement with respect to symptoms affects the results. As attractive candidate diagnostic biomarkers in AMI, circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) are easily detectable, generally stable and tissue specific. Methods. The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database was used to compare miRNA expression between AMI and control samples, and the interactions between miRNAs and mRNAs were analysed for expression and function. Furthermore, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed. The miRNAs identified in the bioinformatic analysis were verified by RT-qPCR in an H9C2 cell line. The miRNAs in plasma samples from patients with AMI (n = 11) and healthy controls (n = 11) were used to construct receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves to evaluate the clinical prognostic value of the identified miRNAs. Results. We identified eight novel miRNAs as potential candidate diagnostic biomarkers for patients with AMI. In addition, the predicted target genes provide insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying AMI.
背景:急性心肌梗死(AMI)被认为是全球最主要的心血管疾病死亡原因之一。对急性心肌梗死的分子机制的了解仍然有限。需要准确的生物标志物来预测急性心肌梗死的风险,这将有利于管理发病率。诊断急性心肌梗死的金标准,即心肌肌钙蛋白T(CTnT)测定,需要进行一系列检测,而根据症状进行测量的时机会影响结果。作为急性心肌梗死的候选诊断标志物,循环microRNAs(MiRNAs)具有易检出、稳定性好、组织特异性强等特点。 方法:研究方法。利用基因表达数据库比较急性心肌梗死患者和对照组的miRNA表达,并分析miRNAs和mRNAs之间的相互作用,以了解其表达和功能。进一步构建了蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络。在生物信息学分析中鉴定的miRNAs在H9C2细胞系中被RT-qPCR验证。用11例急性心肌梗死患者和11例健康对照血浆中的miRNAs构建受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,评价其临床预后价值。 结果:我们确定了8个新的miRNAs作为急性心肌梗死患者潜在的候选诊断生物标记物。此外,预测的靶基因提供了对急性心肌梗死分子机制的洞察。
前言 INTRODUCTION

Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is the most common cardiac event worldwide and among cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) is a leading threat to human health (Guo et al, 2019). AMI is caused by acute coronary syndrome (ACS), which is induced by plaque ulceration or intravascular thrombosis and thrombotic material after rupture (Li, Zhou & Huang, 2017). Early diagnosis and interventional therapy are important to minimize the damage to cardiac muscle and have the potential to significantly reduce mortality and improve prognosis (Braunwald, 2012). Although the cardiac troponin T (cTnT) assay, the gold standard for diagnosis of AMI, has facilitated the diagnosis of AMI and contributed to lower mortality, it can lead to false positives in patients with chronic but stable coronary artery disease or healthy controls (Braunwald, 2012). Therefore, novel biomarkers with high sensitivity and specificity are urgently needed to allow the early diagnosis of AMI and thereby improve clinical outcomes.
急性心肌梗死(AMI)是世界范围内最常见的心脏事件,在心血管疾病(CVD)中是对人类健康的主要威胁(Guo等人,2019年)。急性心肌梗死是由急性冠脉综合征(ACS)引起的,由斑块溃烂或血管内血栓形成以及血栓形成后的血栓物质引起(Li,Weg&Huang,2017)。早期诊断和介入治疗对于最大限度地减少对心肌的损害非常重要,并有可能显著降低死亡率和改善预后(Braunwald,2012)。虽然心肌肌钙蛋白T(CTnT)是诊断急性心肌梗死的金标准,有助于急性心肌梗死的诊断,并有助于降低死亡率,但在慢性但稳定的冠状动脉疾病患者或健康对照组中,它可能导致假阳性(Braunwald,2012)。因此,迫切需要具有高灵敏度和高特异度的新型生物标志物来早期诊断急性心肌梗死,从而改善临床预后。

microRNAs (miRNAs), which are RNAs containing approximately 20 to 24 nucleotides, do not have the potential to encode proteins but can negatively regulate genes (Cheng et al, 2019). miRNAs restrain protein translation or mRNA degradation by binding to the 30UTRs of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) (Fasanaro et al, 2010). Accumulating studies have revealed that miRNAs are involved in multifarious biological functions, including cell proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation, and exhibit strong correlations with mechanisms of disease, especially in cardiovascular disease (Feinberg & Moore, 2016). miRNAs have been identified as biomarkers of pathological events during the process of AMI (Boon & Dimmeler, 2015). In particular, the knockdown of miR-155 inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in AMI-induced mice, and miR-155 is upregulated by negatively regulating the RNA-binding protein Quaking (QKI) (Guo & Liu, 2019). Cai & Li (2019) found that miR-29b-3p overexpression could protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxiainduced injury by negatively regulating the level of TRAF5, which suggests a potential therapeutic method for AMI. Circulating miRNAs are easily detectable, relatively stable and tissue specific, making them attractive candidate biomarkers (Wang et al, 2010). Enhancing our understanding of the relationships between miRNAs and target genes can help reveal detailed mechanisms and identify novel biomarkers for AMI. In this study, we aimed to identify miRNAs with high clinical applicability for distinguishing patients with AMI from those without.
MicroRNAs(MiRNAs)是含有大约20到24个核苷酸的RNAs,不具有编码蛋白质的潜力,但可以对基因进行负调控(Cheng等人,2019年)。MiRNAs通过与信使RNAs(MRNAs)的30UTRs结合来抑制蛋白质翻译或mRNA降解(Fasanaro等人,2010年)。越来越多的研究表明,miRNAs参与了多种生物学功能,包括细胞增殖、凋亡和炎症,并与疾病机制,特别是在心血管疾病中表现出强烈的相关性(Feinberg&Moore,2016)。MiRNAs已被确定为急性心肌梗死过程中病理事件的生物标志物(Boon&Dimmerer,2015)。特别是,miR-155的敲除抑制了急性心肌梗死诱导的小鼠心肌细胞的凋亡,并且miR-155通过负调控RNA结合蛋白颤动(QKI)而上调(Guo&Liu,2019)。Cai&Li(2019)发现,miR-29b-3p过表达可通过负向调节TRAF5的水平来保护心肌细胞免受缺氧性损伤,这可能是一种潜在的治疗急性心肌梗死的方法。循环中的miRNAs易于检测,相对稳定,并且具有组织特异性,使它们成为有吸引力的候选生物标记物(Wang等人,2010年)。加强我们对miRNAs和靶基因之间关系的理解,有助于揭示详细的机制,并寻找新的急性心肌梗死生物标志物。在这项研究中,我们的目标是确定具有高度临床适用性的miRNAs来区分急性心肌梗死患者和非急性心肌梗死患者。

To that end, we identified circulating miRNAs that are differentially expressed (DE) in AMI by using integrated analysis. Gene expression profiles in AMI were acquired through the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Then, a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network was constructed after a comprehensive analysis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was applied to analyse the diagnostic usefulness of the identified DE-miRNAs and genes. Finally, eight potential miRNAs were identified as significant predictors of AMI. Our study may be helpful for elucidating the mechanisms of AMI pathogenesis and identifying diagnostic biomarkers for AMI.
为此,我们通过综合分析确定了在急性心肌梗死中差异表达的循环miRNAs。通过基因表达总表(GEO)数据库获取急性心肌梗死患者的基因表达谱。然后,通过综合分析,构建了竞争内源RNA(CERNA)网络。应用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析已鉴定的DE-miRNAs和基因的诊断价值。最后,8个潜在的miRNAs被确定为急性心肌梗死的重要预测因子。我们的研究可能有助于阐明急性心肌梗死的发病机制,寻找急性心肌梗死的诊断生物标志物。
材料与方法 MATERIAL AND METHODS
对象 Subjects

Subjects A total of 11 AMI patients and 11 healthy subjects were enrolled from Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University between 2017 and 2018 (Table S2). All of the AMI patients had been diagnosed for the first time and undergone a primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The diagnosis for AMI was made based on the following criteria: (i) acute ischaemic chest pain within 24 h; (ii) electrocardiogram changes (pathological Q wave, ST-segment elevation or depression) and (iii) increases in cardiac biomarkers. The exclusion criteria were selected due to their potential influence on miRNA expression and were as follows: previous history of cardiac disease, tumour, renal insufficiency, surgery within the six previous months, and anticoagulant therapy. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The ethical committee of Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University approved the study numbered QYFYWZLL25621.
选择2017/2018青岛大学附属医院收治的急性心肌梗死患者11例,健康者11例(表S2)。所有急性心肌梗死患者均为首次确诊,并接受了直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)。诊断依据如下:(1)24小时内急性缺血性胸痛;(2)心电图改变(病理性Q波、ST段抬高或压低);(3)心脏生物标志物增加。选择排除标准是因为它们对miRNA表达的潜在影响,如下所示:既往心脏病史、肿瘤史、肾功能不全史、前6个月内的手术史和抗凝治疗史。该研究是根据《赫尔辛基宣言》进行的。青岛大学附属医院伦理委员会批准了这项编号为QYFYWZLL25621的研究。
样本采集和RNA提取 Sample collection and RNA isolation

Blood samples were collected into EDTA tubes before coronary angiography and application of heparin. Serum was obtained after centrifugation at 3,000 g for 10 min at 4 ◦C to remove debris and stored in RNase-free tubes at −80 ◦C at Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University until analysis. All participants were informed of the study details by the ethics committee of the hospital and provided written informed consent. Total RNA from the serum samples was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. For normalization, 25 fmol Caenorhabditis elegans miR-39 (cel-miR-39) (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) was added to each serum sample after the addition of TRIzol, following previous methods
在冠状动脉造影术和肝素应用前,将血样采集到EDTA管中。血清在4◦C下3000g离心10min去除碎屑后,保存在青岛大学附属医院−80◦C无核糖核酸酶试管中,待分析。所有参与者都被医院的伦理委员会告知了研究细节,并提供了书面知情同意。根据制造商的说明,使用TRIzol试剂(Sigma,St.Louis,MO,USA)从血清样本中提取总RNA。在加入TRIzol后,在每个血清样本中加入25fmoL的秀丽线虫miR-39(cel-miR-39)(Qigen,Valencia,CA)进行归一化,按照先前的方法进行。
数据来源 Data Sources

The data expression profiles of AMI were searched in the GEO database, and two independent datasets of research on AMI, GSE24591 and GSE31568, were included in our study. Using the genome-wide expression data of miRNAs obtained from the two selected independent cohorts, differential genes were screened according to the control group and AMI group of samples.
在GEO数据库中搜索急性心肌梗死的数据表达谱,并纳入两个独立的急性心肌梗死研究数据集,GSE24591和GSE31568。利用从两个独立队列中获得的miRNAs的全基因组表达数据,根据对照组和急性心肌梗死组样本筛选差异基因。
DEGS的数据预处理与辨识 Data preprocessing and identification of DEGs

GEO2R, which is an interactive web tool that allows comparisons between two groups of samples to analyse almost any GEO series, was used to confirm DEGs between the control group and AMI group. The limma R package was applied by GEO2R and served as the processor to handle the supplied processed data tables. DEGs between the control and AMI groups were screened out according to the criteria p value less than .05 and absolute log fold change greater than 1.
GEO2R是一个交互式网络工具,允许在两组样本之间进行比较,以分析几乎任何GEO系列,用于确认对照组和急性心肌梗死组之间的DEG。GEO2R应用了LIMMA R程序包,并将其用作处理所提供的已处理数据表的处理器。根据标准p值小于0.05,绝对对数折叠变化大于1,筛选出对照组和急性心肌梗死组之间的DEG。
MiRNA-mRNA靶标的分析 Analyses of miRNA-mRNA targets

Investigating the target genes of miRNAs is crucial for identifying the regulatory mechanisms and functions of miRNAs. Herein, we identified 8 DE-miRNAs and then predicted the targets of the DEGs by employing three miRNA-target tools: miRWalk V2.0 database, mirDIP, and miRTarBase. The miRNA targets were screened based on the overlapping results from the three websites. Then, the regulatory networks of the miRNA-mRNA pairs were extracted (based on an expression fold change >2.5 and an FDR <0.05) and visualized using Cytoscape software (Smoot et al, 2011).
研究miRNAs的靶基因对于确定miRNAs的调控机制和功能至关重要。在这里,我们识别了8个DE-miRNAs,然后使用三个miRNA靶标工具:miRWalk V2.0数据库、mirDIP和miRTarBase来预测DEG的靶标。根据三个网站的重叠结果筛选miRNA靶标。然后,提取miRNA-mRNA对的调控网络(基于表达倍数变化>2.5和FDR<0.05),并使用Cytoscape软件进行可视化(Smoot等人,2011年)。
基因本体论(GO)注释和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)路径富集化分析 Gene Ontology (GO) annotation and Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses of the DEGs

GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of the DEGs were performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) (selected with enrichment significance evaluated at p < .05), which revealed the biological processes (BPs), cellular components (CCs), molecular functions (MFs) and pathways associated with the DE-miRNAs.
使用注释、可视化和集成发现数据库(David)(选择具有富集性的数据库,p<0.05)对DEG进行GO注释和KEGG途径富集化分析,揭示了与DE-miRNAs相关的生物学过程(Bps)、细胞成分(CCs)、分子功能(MFS)和途径。
蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络的构建及HUB基因的鉴定 Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network construction and hub gene identification

To gain insights into the interactions of the 591 target genes of the identified miRNAs, a PPI network was constructed and analysed with the STRING tool to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying AMI. Target genes in the PPI network serve as nodes, the lines between two nodes denote associated interactions, and the strengthof the interaction is expressed by the colour of the line. The hub genes, which were defined as genes that play essential roles in the network, were distinguished according to the cutoff criteria of degree calculated by cytoHubba in Cytoscape. The corresponding interactions were visualized using Cytoscape software (http://cytoscape.org/) (Su et al, 2014).
为了深入了解已鉴定的miRNAs的591个靶基因的相互作用,构建了一个PPI网络,并使用STRING工具对其进行分析,以揭示急性心肌梗死的分子机制。PPI网络中的靶基因作为节点,两个节点之间的线条表示关联的相互作用,相互作用的强度由线条的颜色来表示。HUB基因被定义为在网络中起关键作用的基因,根据Cytoscape中的Cell Hubba计算的程度截断标准进行区分。使用Cytoscape软件(http://cytoscape.org/)对相应的互动进行可视化(Su等人,2014年)。
细胞培养与治疗 Cell culture and treatment

The H9C2 cell line was obtained from the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences (Shanghai, China) and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% FBS (ExCell Bio, Shanghai, China) and 1% antibiotics. The cells were cultivated in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37 ◦C. The cells were trypsinised to generate single cell suspensions at 80% confluency. The cells were treated with 2 µM doxorubicin (DOX) for 24 h.
H9C2细胞系取自上海生物科学研究院(上海,中国),在含有10%胎牛血清(Excell Bio,上海,中国)和1%抗生素的Dulbecco's改良Eagle's培养液中培养。细胞在37℃、含5%二氧化碳的潮湿环境中培养,经胰酶消化后产生单细胞悬液,融合度为80%。用2µM阿霉素(DOX)处理细胞24 h。
RT-qPCR分析 RT-qPCR analysis

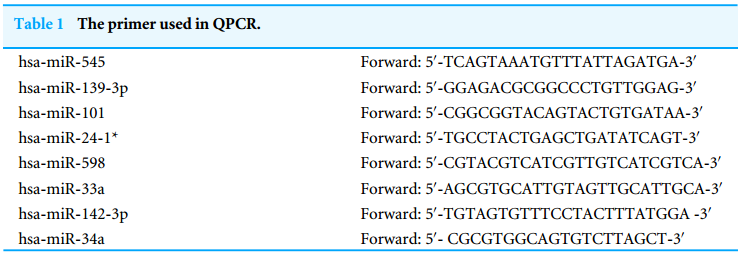
A reverse transcription kit (Takara, Otsu, Japan) was applied to synthesize the cDNA. RT-qPCR was accomplished using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Yeasen, Shanghai, China). The forward primers arepresented in Table 1, and the same reverse primer with the sequence 50-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-30 was used for all miRNAs.
用反转录试剂盒(Takara,Otsu,日本)合成该基因。RT-qPCR采用SYBR Green PCR Master Mix(伊森,上海,中国)。正向引物如表1所示,序列为50-GTGCAGGGGTCCGAGGT-30的相同反向引物用于所有miRNAs。

The average expression levels of serum miRNAs were normalized against cel-miR-39 (Qiagen, Valencia, CA), and the expression of cell-derived miRNAs were normalized against U6 (Takara, Otsu, Japan).
血清miRNAs的平均表达水平与cel-miR-39(Qiagen,Valencia,CA)和细胞来源的miRNAs(U6,Takara,Otsu,日本)的表达标准化。

Fold changes in miRNA expression were calculated using the 2−11Ct method for each sample in triplicate (Chang, Chen & Yang, 2009). Taking the calculation method of miRNA expression in plasma as an example, 11Ct = [(CtmiRNA – Ct cel−miRNA−39)diseased (CtmiRNA-Ct cel−miRNA−39)control]. In brief, with this method, the Ct values from the target miRNA in both AMI and control group are adjusted in relation to the Ct of a normalizer RNA (cel-miR-39), which resulted in 1Ct. In order to compare diseased and control samples, we calculated 11Ct values, which allowed us to determine the magnitude of the difference in miRNA expression. To ensure consistent measurements throughout all assays, for each PCR amplification reaction, three independent RNA samples were loaded as internal controls.
使用2−11CT方法计算每个样本中miRNA表达的倍数变化(Chang,Chen&Yang,2009)。以血浆miRNA表达的计算方法为例,11Ct=[(CtmiRNA-Ct cel−miRNA−39)病态(CtmiRNA-Ct cel−miRNA−39)对照]。简而言之,用这种方法,急性心肌梗死和对照组的靶miRNA的Ct值都相对于归一化RNA(cel-miR-39)的Ct进行调整,从而产生1CT。为了比较患病样本和对照样本,我们计算了11Ct值,这使得我们能够确定miRNA表达差异的幅度。为了确保所有检测过程中的一致性,对于每个PCR扩增反应,三个独立的RNA样本被加载作为内对照。
ROC曲线 ROC curves

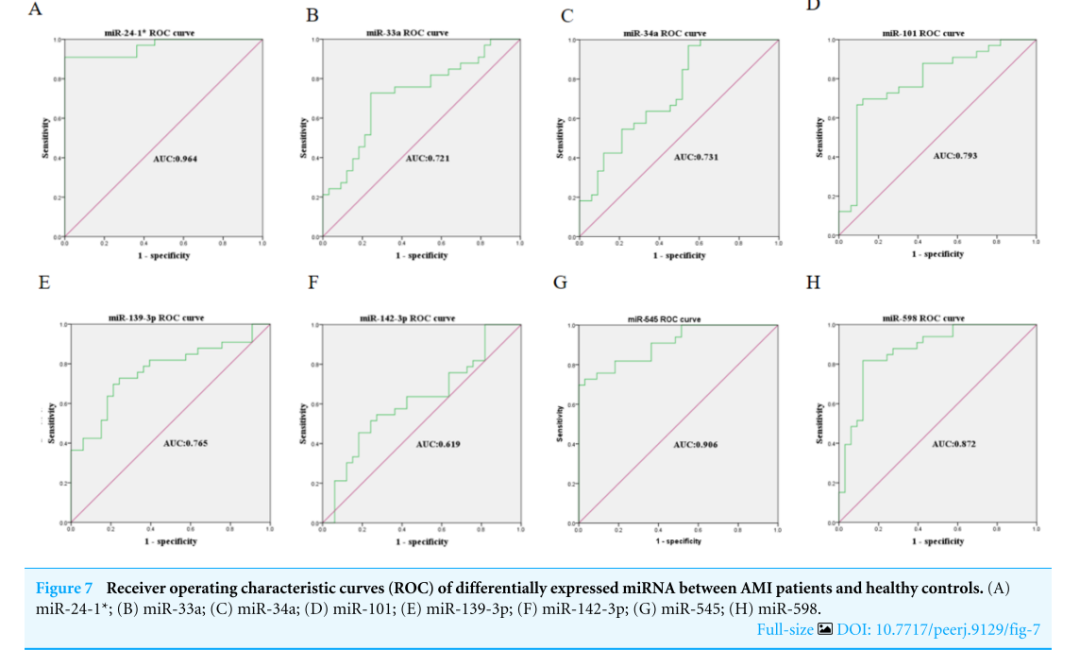
ROC curves were constructed to discriminate AMI patients from control subjects for the plasma miRNAs, and the areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) were analysed to assess the diagnostic accuracy of each identified miRNA. Herein, a normalized miRNA score was used to represent the expression level of the selected miRNA in the AMI group relative to that in the control group (Goren et al, 2012). In brief, we used miRNA scores, which were calculated by subtracting the normalized Ct from 40 and then adjusted by deducting the minimal score, leading to miRNA scores with a lower bound of 0. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 13.0 (Chicago, IL, USA).
构建ROC曲线以区分AMI患者和对照组的miRNAs,并分析ROC曲线下面积(AUC)以评估每个已识别的miRNA的诊断准确性。在这里,标准化的miRNA评分被用来表示所选择的miRNA在急性心肌梗死组中相对于对照组的表达水平(Goren等人,2012年)。简而言之,我们使用miRNA分数,它是通过从40减去归一化的Ct计算出来的,然后通过减去最小分数来调整,导致miRNA分数的下界为0。所有统计分析使用SPSS13.0(芝加哥,伊利诺伊州,美国)进行。
统计分析 Statistical analyses

Student’s t-test was carried out using GraphPad Prism 5 to compare test and control samples. For the analysis of clinical characteristics in AMI patients and control individuals, data were presented as means ± standard deviations (SD) for quantitative variables. Mean values of quantitative variables were evaluated by Student’st-test, or Mann–Whitney U-test when Student’s t-test were not satisfied. p < .05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 13.0 (Chicago, IL, USA).
Student's t检验使用GraphPad Prism 5以比较测试样本和对照样本。为了分析急性心肌梗死患者和对照组的临床特征,数据以量化变量的平均值±标准差(SD)表示。当student t检验不满意时,用student t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验来评估定量变量的平均值。P<0.05被认为是有统计学意义的差异。所有统计分析使用SPSS13.0(芝加哥,伊利诺伊州,美国)进行。
结果 RESULTS
DE-miRNAs的鉴定 Identification of DE-miRNAs

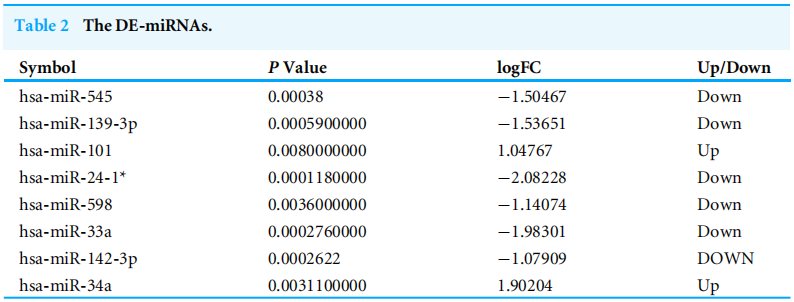
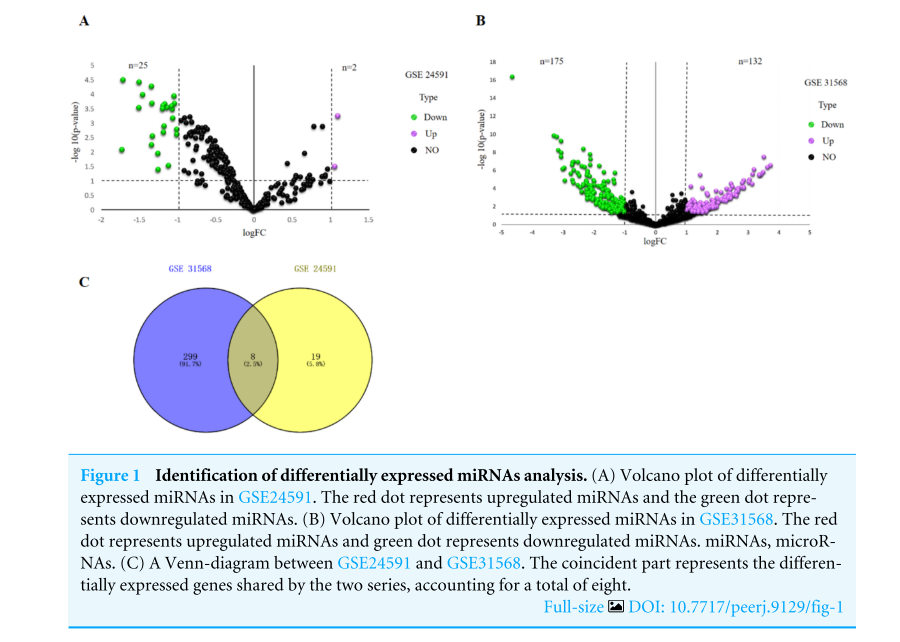
|Log2FC|>1 and p value <.05 were considered as criteria to screen the DE-miRNAs. Among the selected GEO datasets, 27 DE-miRNAs, including 25 downregulated and 2 upregulated genes, were found in the GSE24591 profile (Fig. A), whereas 307 DE-miRNAs, including 132 upregulated and 175 downregulated genes, were found in the GSE31568 profile (Fig. B). The candidate DE-miRNAs generated by the two datasets were intersected using a Venn diagram (Fig. C). All intersecting DE-miRNAs are shown in Table 2 and included hsa-miR-545, hsa-miR-139-3p, hsa-miR-101, hsa-miR-24-1, hsa-miR-598, hsa-miR-33a, hsa-miR-142-3p, and hsa-miR-34a.
|Log2FC|>1和p值<0.05作为筛选DE-miRNAs的标准。在选定的GEO数据集中,在GSE24591图谱中发现了27个DE-miRNAs,其中包括25个下调基因和2个上调基因(图2)。A),而在GSE31568谱中发现了307个DE-miRNAs,包括132个上调基因和175个下调基因(图3)。b)。用维恩图(图2)将两个数据集产生的候选DE-miRNAs相交。c)。所有交叉的DE-miRNA如表2所示,包括hsa-miR-545、hsa-miR-139-3p、hsa-miR-101、hsa-miR-24-1、hsa-miR-598、hsa-miR-33a、hsa-miR-142-3p和hsa-miR-34a。
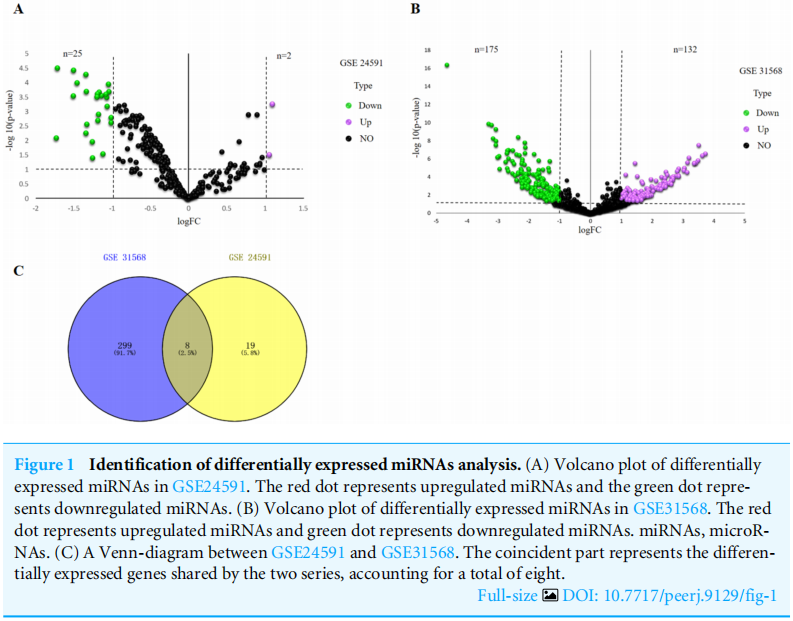
图1差异表达miRNAs分析的鉴定。(A)GSE24591中差异表达miRNAs的火山图谱。红点代表上调的miRNAs,绿点代表下调的miRNAs。(B)GSE31568中差异表达miRNAs的火山图谱。红点代表上调的miRNAs,绿点代表下调的miRNAs。MiRNAs,microRNAs。(C)GSE24591和GSE31568之间的维恩图。重合部分代表两个系列共有的差异表达基因,共占8个。
MiRNA-靶基因相互作用 miRNA-target gene interactions

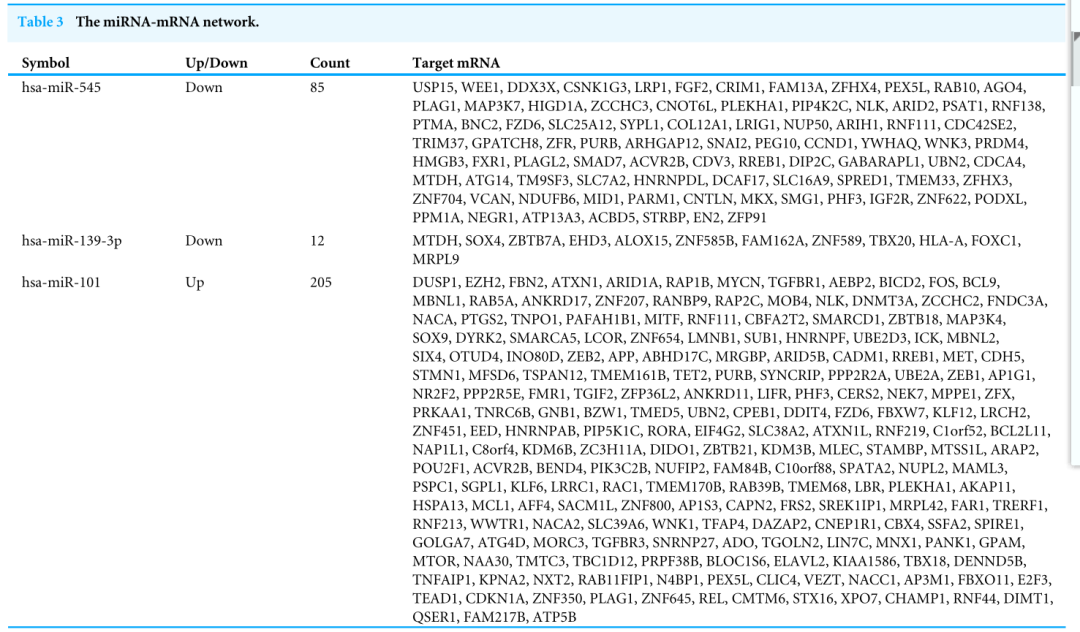
Following data preprocessing and analysis of the three databases, an overlap of 591 gene pairs from eight DE-miRNAs was obtained among the databases. These overlapping pairs were used to predict the target genes that interact with the miRNAs. The predictions were verified by more than four algorithms, including miRDB, RNA22, RNAhybrid, and TargetScan. The network of miRNA-mRNA interactions was visualized in Cytoscape, as shown in Fig. 2, and the target genes are listed in Table 3.
在对三个数据库进行数据预处理和分析后,从8个DE-miRNAs中获得了591个基因对的重叠。这些重叠的对被用来预测与miRNAs相互作用的目标基因。这些预测得到了超过四种算法的验证,包括miRDB、RNA22、RNAhyder和TargetScan。如图2所示,在细胞视角中可视化了miRNA-mRNA相互作用的网络,目标基因如表3所示。
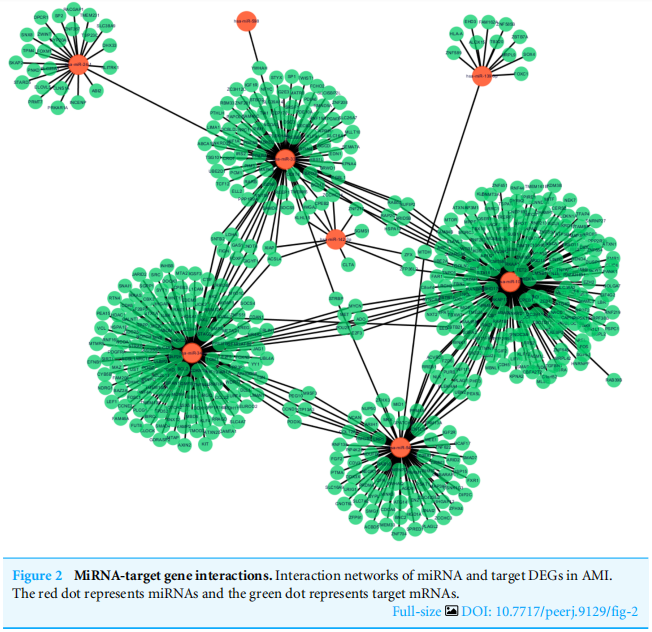
图2 miRNA与靶基因的相互作用。AMI中miRNA和靶点的相互作用网络。红点代表miRNAs,绿点代表靶点mRNAs。
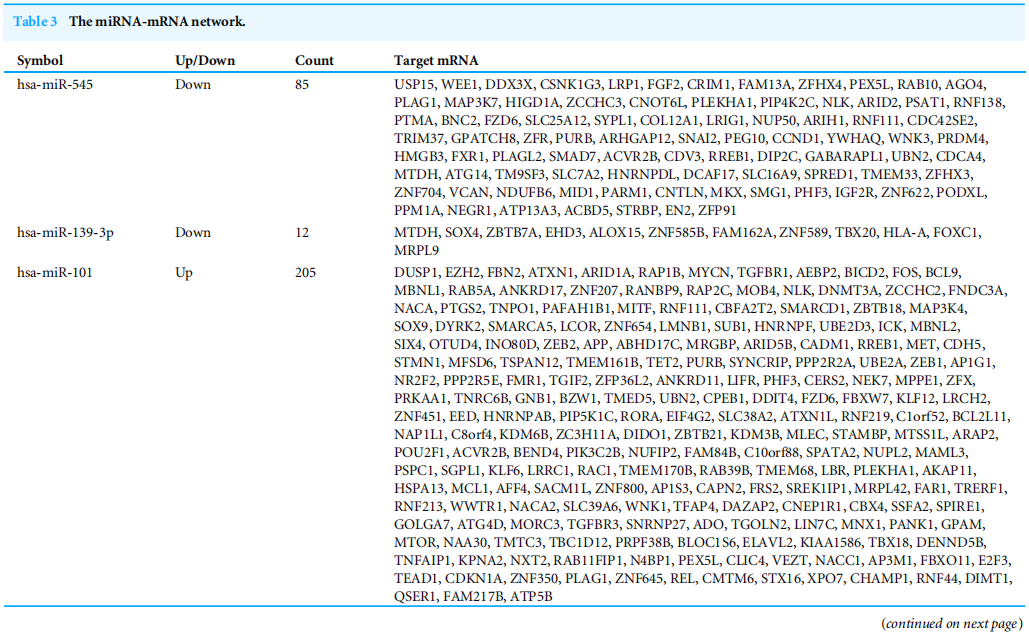
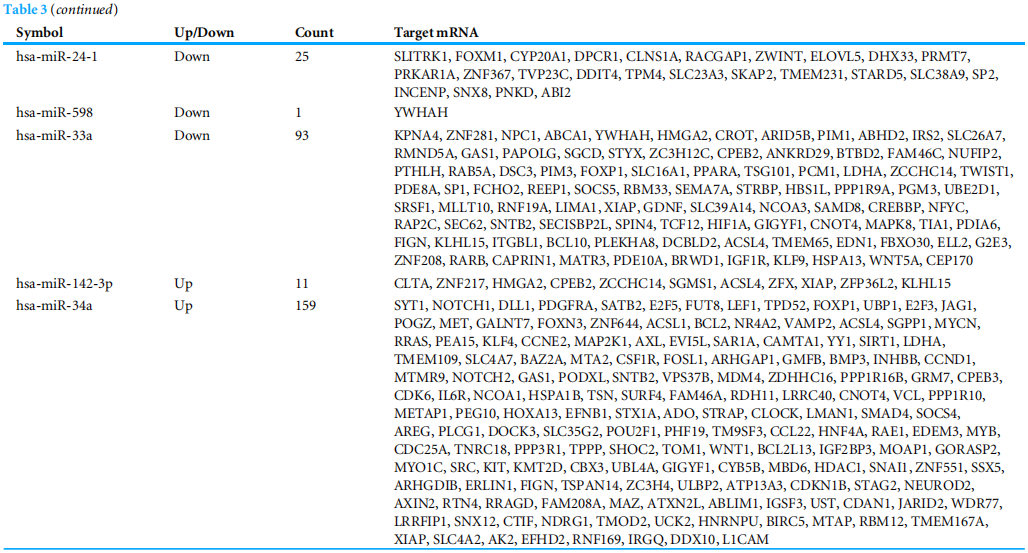
靶基因的富集化分析 Enrichment analyses of the target genes

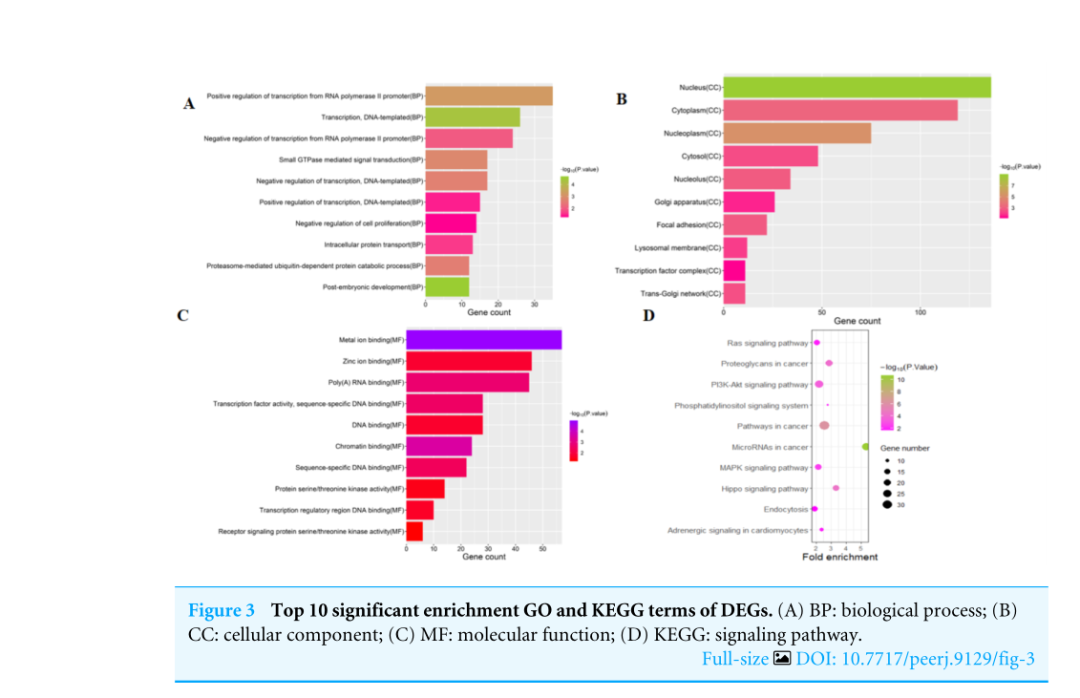
To investigate the functions of the target genes, GO annotation and KEGG pathway analyses of the interacting 591 genes from GSE24591 and GSE31568 were performed utilizing the DAVID online tool. The top 10 GO and KEGG items, including the BPs, CCs, MFs and KEGG pathways that were significantly enriched, are listed in Figs. A–3D. The significantly enriched entries for BPs were positive regulation of transcription from the RNA polymerase II promoter, transcription, and DNA-templated and negative regulation of transcription from the RNA polymerase II promoter (Fig. A). Furthermore, the nucleus, cytoplasm, and nucleoplasm accounted for the majority of the CC terms (Fig. B). The most enriched MFs were functions in metal ion binding, zinc ion binding and poly (A) RNA binding (Fig.3C). In the MF category, the top 10 most highly regulated DE-miRNAs were significantly enriched in the pathways of cancer and the PI3K-Akt pathway. Intriguingly, the enrichment in adrenergic signalling in cardiomyocytes was found to be closely related to AMI (Fig.3D).
为了研究目的基因的功能,利用David Online工具对GSE24591和GSE31568的591个互作基因进行了GO注释和KEGG通路分析。前10个GO和KEGG项,包括BPS、CCS、MFS和KEGG通路显著丰富,如图3所示。A-3D。BP的条目显著丰富是来自RNA聚合酶II启动子的转录的正调控、转录和DNA模板的转录,以及来自RNA聚合酶II启动子的转录的负调控(图3)。a)。此外,细胞核、细胞质和核质占CC术语的大部分(图3)。b)。最丰富的MFS是金属离子结合、锌离子结合和Poly(A)RNA结合功能(图3C)。在MF类别中,调节最高的10个DE-miRNAs在癌症途径和PI3K-Akt途径中显著丰富。有趣的是,心肌细胞中肾上腺素能信号的丰富被发现与急性心肌梗死密切相关(图3D)。
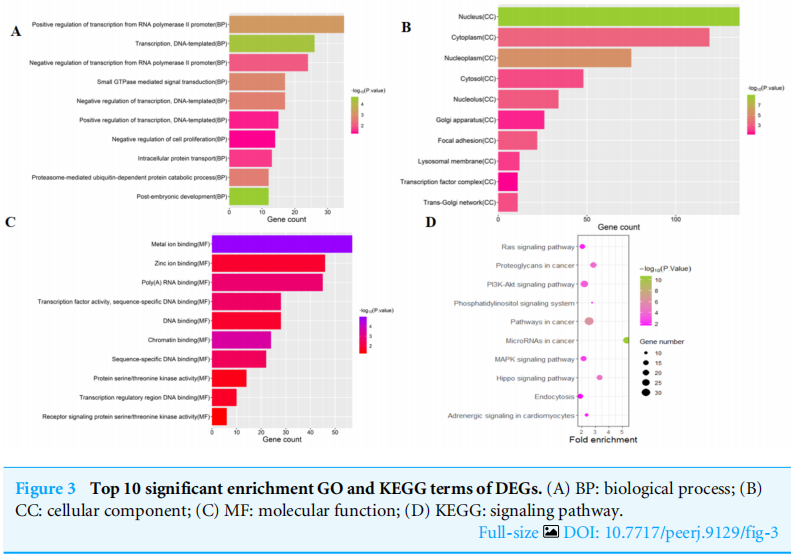
图3 DEGS的10大重要浓缩GO和KEGG术语。(A)BP:生物过程;(B)CC:细胞成分;(C)MF:分子功能;(D)KEGG:信号通路。
PPI网络 PPI network

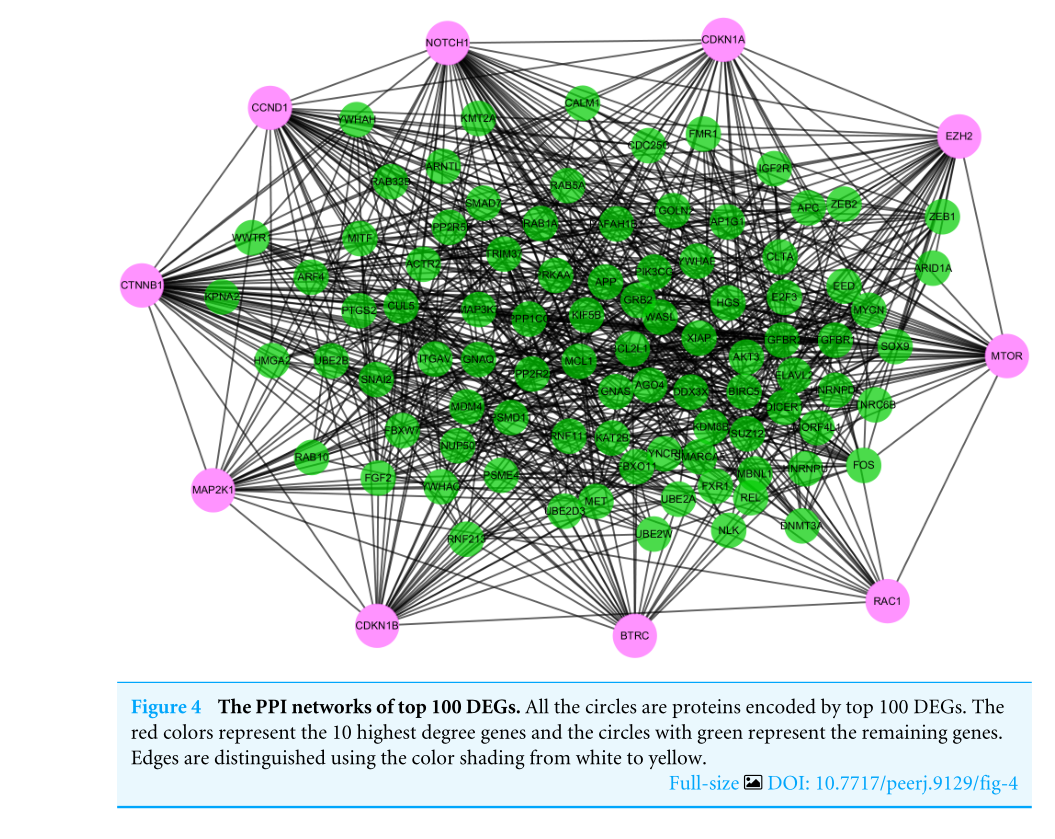
To distinguish the connections among the 591 target genes, we mapped the PPIs using the logical data originating from the STRING database (http://strin g.embl.de/). With degree as the criterion, the top 100 linked DE-miRNAs were identified, as shown in Fig. 4.The network is composed of 100 nodes and 700 edges and has an average local clustering coefficient of .467. The top 10 genes with a high-ranking degree are labelled in purple and associated with much larger circles; all the edges are distinguished based on connection score (Fig. 4).
为了区分591个目标基因之间的联系,我们使用来自字符串数据库)(http://strin g.embl.de/)的逻辑数据绘制了PPI。以度为标准,识别出前100个链接的DE-miRNAs,如图4所示。该网络由100个节点和700个边组成,平均局部聚类系数为.467。排名最高的10个基因用紫色标记,并与更大的圆圈相关联;所有的边缘都基于连接分数来区分(图4)。
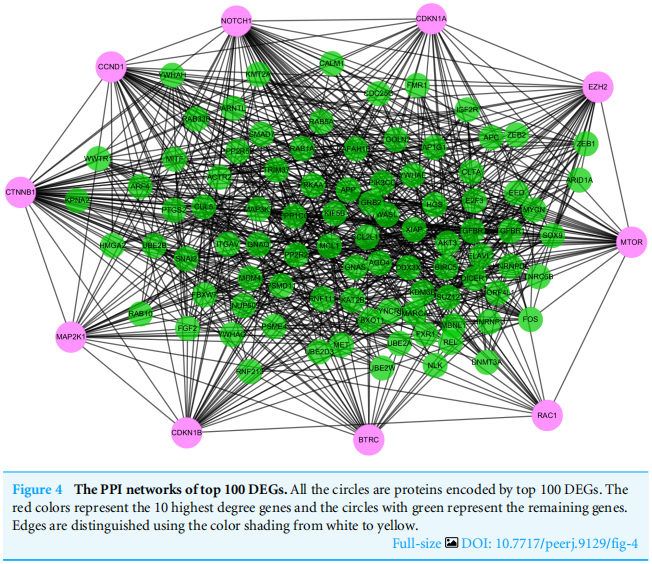
图4 排名前100位的PPI网络。所有的圆圈都是由前100度编码的蛋白质。红色代表10个程度最高的基因,绿色圆圈代表其余基因。边缘通过从白色到黄色的颜色阴影来区分。
HUB基因的生物学分析 Biological analysis of the hub genes

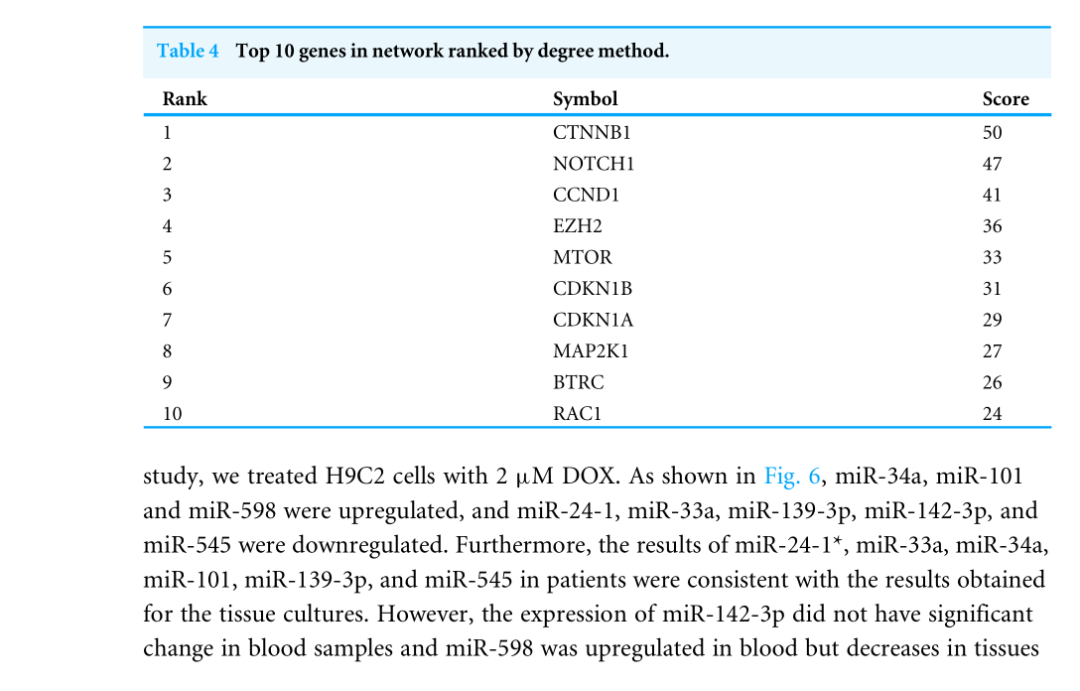
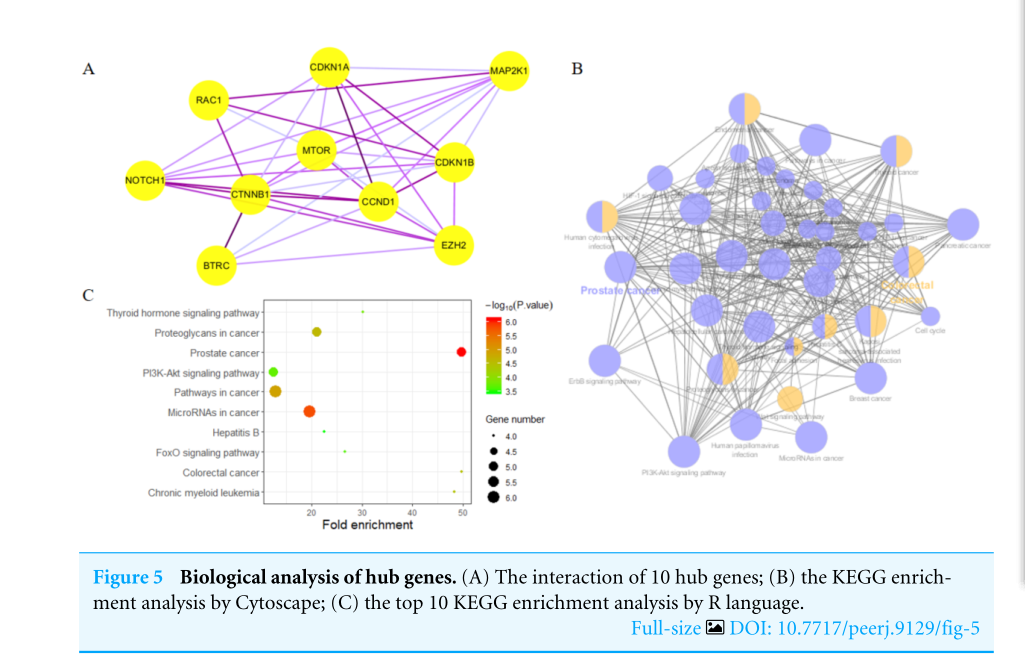
Highly connected proteins in a network are master keys of regulation and are defined as hub proteins (Yu et al, 2017). The hub proteins in the present study included CTNNB1, CCND1, NOTCH1, EZH2, MTOR, BTRC, RAC1, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, and MAP2K1. They were identified by evaluating degree with the Biological Networks Gene Ontology tool (BiNGO) plugin of Cytoscape, which considered the top ten closely related interactions (Table 4); these involved 10 nodes and 35 edges (Fig.5A). Additionally, KEGG analysis was performed on the potential hub genes (Fig.5B), and the top 10 enrichment pathways were identified (Fig.5C).
网络中的高连接蛋白是调控的万能钥匙,被定义为中心蛋白(Yu等人,2017)。本研究中的HUB蛋白包括CTNNB1、CCND1、NOTCH1、EZH2、MTOR、BTRC、RAC1、CDKN1A、CDKN1B和MAP2K1。通过使用Cytoscape的生物网络基因本体论工具(Bingo)插件评估程度来识别它们,该工具考虑了前十个密切相关的交互作用(表4);这些交互涉及10个节点和35个边(图5A)。此外,对潜在的HUB基因进行了KEGG分析(图5B),并确定了前10个浓缩途径(图5C)。
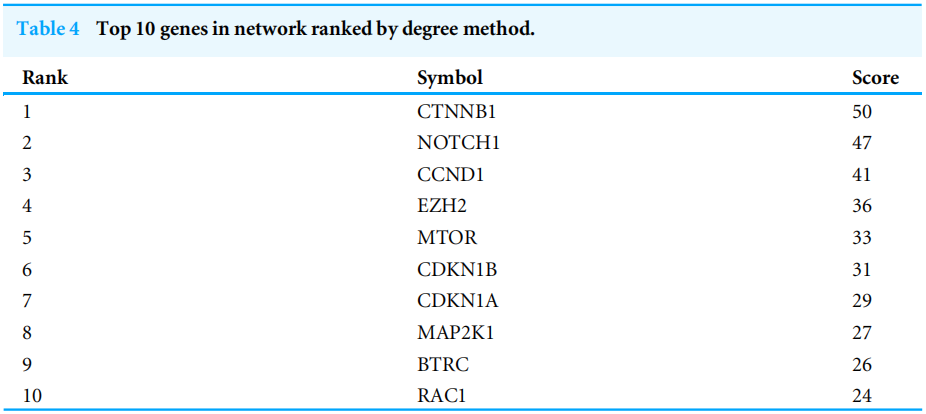
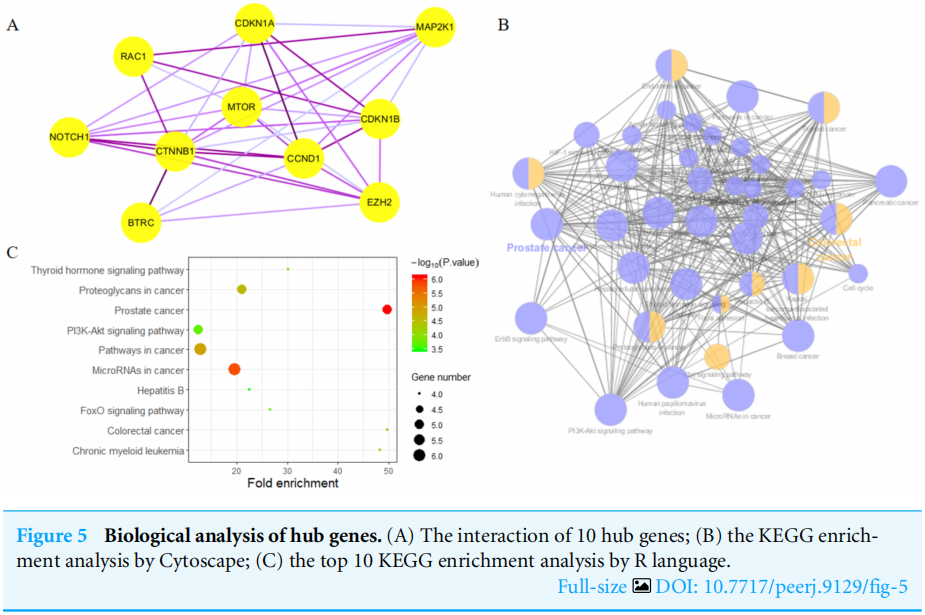
图5 中枢基因的生物学分析。(A)10个HUB基因的相互作用;(B)Cytoscape的KEGG富集度分析;(C)R语言的前10个KEGG富集度分析。
确认已识别的miRNAs Validation of the identified miRNAs

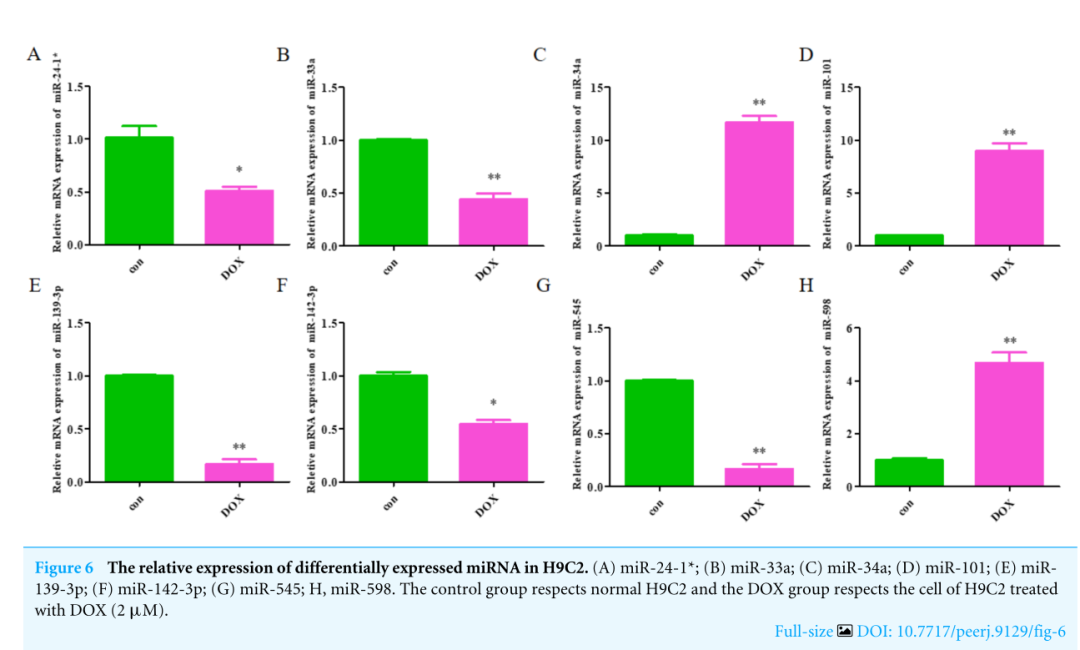
The expression levels of the identified miRNAs were quantified by RT-qPCR in H9C2 cells treated with DOX to verify the results of the bioinformatic analyses. Emerging studies have illuminated the role of cardiomyocyte apoptosis in DOX-induced myocardial damage, which is similar to the proceeding of AMI (Catanzaro et al, 2019). Based on our previous study, we treated H9C2 cells with 2 µM DOX. As shown in Fig. 6, miR-34a, miR-101 and miR-598 were upregulated, and miR-24-1, miR-33a, miR-139-3p, miR-142-3p, and miR-545 were downregulated. Furthermore, the results of miR-24-1*, miR-33a, miR-34a, miR-101, miR-139-3p, and miR-545 in patients were consistent with the results obtained for the tissue cultures. However, the expression of miR-142-3p did not have significant change in blood samples and miR-598 was upregulated in blood but decreases in tissues (Fig. S1). To investigate the efficacy of DE-miRNAs as potential biomarkers of AMI, we performed ROC curve analysis of patients with AMI and patients without AMI. The expression levels of the DE-miRNAs were significantly different between AMI patients and control individuals (Fig. 7). AUC values were used to evaluate the potential of the DE-miRNAs as diagnostic markers. The AUC values of miR-24-1 and miR-545 were greater than .9, and these DE-miRNAs also had the highest accuracies. Moreover, all five miRNAs had high specificity with AUCs>.7 except for miR-142-3p that the accuracy is likely to take place when the AUC above .7 (Catanzaro et al, 2019). These results indicated that the predicted miRNAs, especially miR-24-1 and miR-545, have potential for clinical application.
用RT-qPCR方法检测经DOX处理的H9C2细胞中miRNAs的表达水平,以验证生物信息学分析的结果。新的研究阐明了心肌细胞凋亡在DOX诱导的心肌损伤中的作用,这与急性心肌梗死的过程相似(Catanzaro等人,2019年)。在我们先前研究的基础上,我们用2微米DOX处理H9C2细胞。如图6所示,miR-34a、miR-101和miR-598上调,miR-24-1、miR-33a、miR-139-3p、miR-142-3p和miR-545下调。此外,患者体内miR-24-1*、miR-33a、miR-34a、miR-101、miR-139-3p和miR-545的检测结果与组织培养结果一致。而miR-142-3p在血液中的表达无明显变化,miR-598在血液中表达上调,在组织中表达降低(图4)。S1)。为了探讨DE-miRNAs作为急性心肌梗死潜在生物标志物的有效性,我们对急性心肌梗死患者和非急性心肌梗死患者进行了ROC曲线分析。在急性心肌梗死患者和对照组之间,DE-miRNAs的表达水平有显著差异(图7)。用AUC值评价DE-miRNAs作为诊断标记物的潜力。MiR-24-1和miR-545的AUC值均大于0.9,这些DE-miRNAs的准确度也最高。此外,除miR-142-3p外,所有五种miRNAs都具有高度特异性,AUC>0.7,当AUC超过0.7时,准确性可能发生(Catanzaro等人,2019年)。这些结果表明,所预测的miRNAs,特别是miR-24-1和miR-545,具有临床应用的潜力。
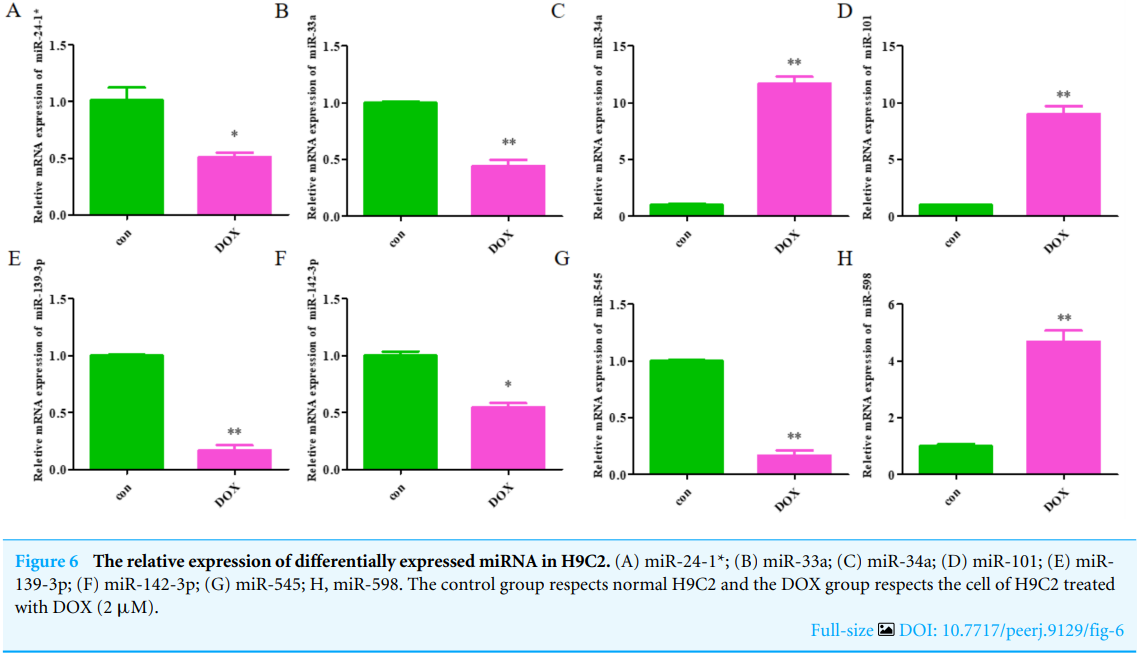
图6 H9C2中差异表达的miRNA的相对表达。(A)miR-24-1*;(B)miR-33a;(C)miR-34a;(D)miR-101;(E)miR139-3p;(F)miR-142-3p;(G)miR-545;H,miR-598。对照组尊重正常的H9C2细胞,DOX组尊重经DOX(2µM)处理的H9C2细胞。
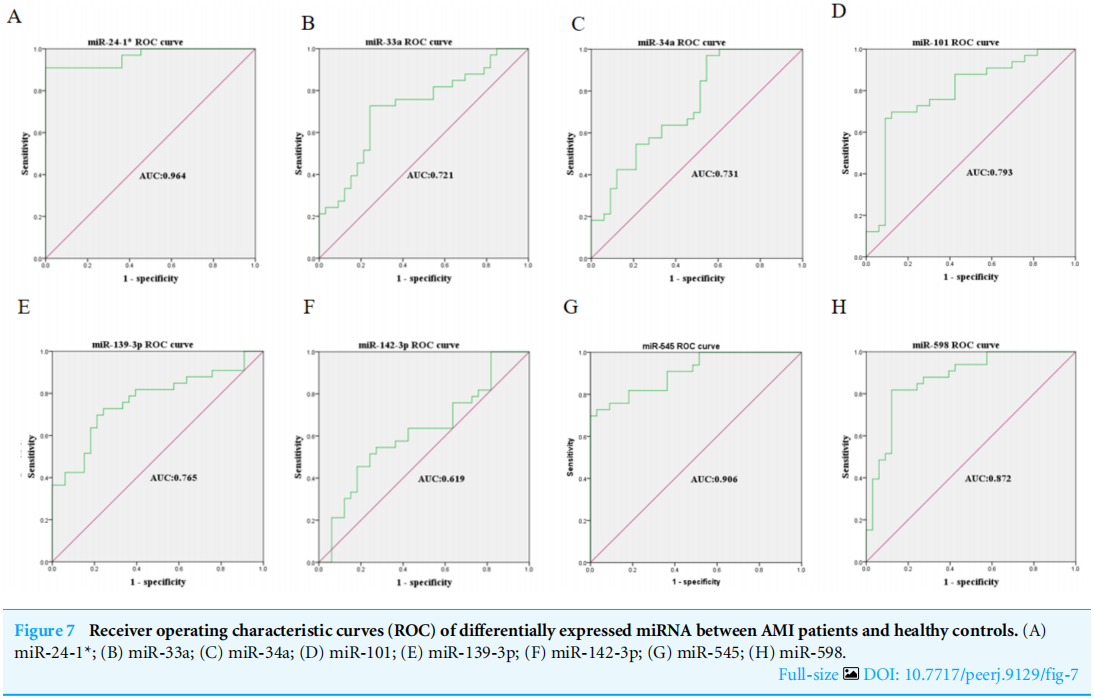
图7 急性心肌梗死患者和健康对照组差异表达miRNA的受体工作特征曲线(ROC)。(A)miR-24-1*;(B)miR-33a;(C)miR-34a;(D)miR-101;(E)miR-139-3p;(F)miR-142-3p;(G)miR-545;(H)miR-598。
与传统预后标志物的关系 Relationships to conventional prognostic markers

To further evaluate the potential of circulating miRNAs as cardiac biomarkers, we tested whether the levels of identified miRNAs correlate with troponin T (TnT) level. miR-24-1 and miR-545 were strongly correlated with TnT (r = −0.722, p < 1*10−3and r = −0.57, p = 0.006). miR-101, miR-139-3p, and miR-598 remained correlated with TnT levels in AMI patients (r = −0.444, p = 0.038 for miR-101, r = −0.425, p = 0.048 for miR-139-3p and r = −0.425, p = 0.048 for miR-598). However, miR-33a, miR-34a, and miR-142-3p was not correlated with TnT which showed in Table S3. Combining ROC analysis results, we concluded that miR-24-1 might be the most potential biomarker in AMI.
为了进一步评估循环miRNAs作为心脏生物标志物的潜力,我们测试了已识别的miRNAs水平是否与肌钙蛋白T(TnT)水平相关。MIR-24-1和MIR-545与TnT呈正相关(r=−0.722,p<1×10−3和r=−0.57,p=0.006)。MIR-101、MIR-139-3p和MIR-598与TnT水平呈正相关(MIR-101 r=−0.444,p=0.038;MIR-139-3p r=−0.425,p=0.048;MIR-598 r=−0.425,p=0.048)。然而,如表S3所示,miR-33a、miR-34a和miR-142-3p与TNT没有相关性。结合ROC分析结果,我们认为miR-24-1可能是急性心肌梗死最有潜力的生物标志物。
讨论 DISCUSSION

AMI, commonly referred to as acute heart attack, is generally acknowledged as the outcome of sudden ischaemia that results in insufficient blood supply and a subsequent imbalance between the supply and demand of oxygen induced by cardiomyocyte death (Vogel et al, 2019). AMI is a central contributor to the global disease burden, occurring in 4–10% of people under 45 years, with a massive number of patients still suffering recurrent cardiovascular events after treatment with medication or primary PCI (Tan et al, 2016).Previous studies have identified potential mechanisms and biomarkers for early diagnosis and treatment. Cardiac troponin (cTn) has served as the gold standard for AMI diagnosis and is routinely applied for patients with suspected ACS to rule-in or rule-out AMI (Sandoval et al, 2017). Nevertheless, with the advancing sensitivity of cTn assay, the assay has exceeded the ninety-ninth percentile for stable chronic conditions, weakening its specificity for the diagnosis of AMI (Park et al, 2017). This observation demonstrates that there is an urgent need for the identification of novel diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets with minimal risk of adverse effects and maximum sensitivity and specificity (Cruz et al, 2019). Various investigations have revealed that miRNAs can potentially predict CVDs by modulating the ceRNA network, thus providing a therapeutic option, especially in AMI (Lucas, Bonauer & Dimmeler, 2018). The downregulation of miR-155 expression restrains apoptosis and maintains a proliferative effect in cardiomyocytes by targeting QKI and can thereby serve as a therapeutic marker for MI. Accordingly, strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of AMI could be furnished by analysing correlative data in the GEO database (Cruz et al, 2019) and generating an AMI-associated miRNA-mRNA regulatory network for clinical applications regarding diagnosis, therapy, and prognosis.
急性心肌梗死通常被称为急性心脏病发作,通常被认为是由心肌细胞死亡引起的突然缺血导致血液供应不足和随后的氧供需失衡的结果(Vogel等人,2019年)。急性心肌梗死是全球疾病负担的核心因素,发生在45岁以下的人中有4%-10%,大量患者在接受药物治疗或直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗后仍遭受复发的心血管事件(Tan等人,2016)。以前的研究已经确定了早期诊断和治疗的潜在机制和生物标志物。心肌肌钙蛋白(CTn)已成为诊断急性心肌梗死的金标准,并被常规应用于疑似急性冠脉综合征患者以排除或排除急性心肌梗死(Sandoval等人,2017年)。然而,随着cTn检测灵敏度的提高,该检测已经超过了稳定慢性条件的第99%,削弱了其诊断急性心肌梗死的特异性(Park等人,2017)。这一观察表明,迫切需要确定新的诊断标记物和治疗靶点,使不良反应的风险降至最低,并具有最高的敏感性和特异性(Cruz等人,2019年)。各种研究表明,miRNAs可以通过调节Cerna网络来潜在地预测心血管疾病,从而提供一种治疗选择,特别是在急性心肌梗死(Lucas,Bonauer&Dimmeler,2018)。MiR-155的表达下调通过靶向QKI抑制心肌细胞的凋亡和维持其增殖作用,从而可作为MI的治疗标记物。因此,可以通过分析GEO数据库中的相关数据(Cruz等人,2019年)并为诊断、治疗和预后方面的临床应用生成与AMI相关的miRNA-mRNA调控网络,来提供诊断和治疗AMI的策略。

In this study, 27 DEGs in the GSE24591 dataset and 307 DEGs in the GSE31568 dataset were screened in AMI and control blood samples based on the differential analysis of GEO2R in the GEO database. Furthermore, 8 collective miRNAs (miR-545, miR-139-3p, miR-101, miR-24-1, miR-598, miR-33a, miR-142-3p, and miR-34a) were selected and identified as DE in AMI; there were few common DEGs because the two datasets were independent. An interaction network of miRNAs and mRNAs was constructed by using three websites, miRWalk V2.0, mirDIP, and miRTarBase, and more than 4 online prediction tools, including miRDB, RNA22, RNAhybrid, and TargetScan. In addition, GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of the mRNAs in the ceRNA network were performed. The PPI network, analysed via the STRING database and visualized by Cytoscape software, showed that 591 target proteins and 10 hub genes were significantly closely associated with the miRNAs. The expression validation and ROC analyses of these DE-miRNAs based on the RT-qPCR data supported the above results, which could quantify the diagnostic availability of the identified DE-miRNAs.
在这项研究中,根据GEO数据库中GEO2R的差异分析,在急性心肌梗死和对照血液样本中筛选出GSE24591数据集中的27个DEG和GSE31568数据集中的307个DEG。此外,选择了8个集合miRNAs(miR-545、miR-139-3p、miR-101、miR-24-1、miR-598、miR-33a、miR-142-3p和miR-34a),鉴定为急性心肌梗死中的DE;由于这两个数据集是独立的,所以共同点很少。利用miRWalk V2.0、mirDIP和miRTarBase 3个网站,以及miRDB、RNA22、RNAhyder和TargetScan等4个以上的在线预测工具,构建了miRNAs和mRNAs的相互作用网络。此外,对Cerna网络中的mRNAs进行了GO和KEGG富集性分析。通过字符串数据库分析的PPI网络,通过Cytoscape软件可视化,显示591个目的蛋白和10个HUB基因与miRNAs显著相关。基于RT-qPCR数据的DE-miRNAs的表达验证和ROC分析支持上述结果,可以量化所识别的DE-miRNAs的诊断有效性。

Moreover, among the 8 miRNAs that might exert effects on the development of AMI, miR-34a has been identified in mechanistic studies as a biomarker for AMI. It is highly expressed in adult mice after MI and associated with a thin wall of the left ventricle (LV) (Qipshidze Kelm et al, 2018). Yang et al (2015). found that the suppression of miR-34a facilitated cardiac function following MI partly by modulating the interrelated genes involved in cell proliferation and the cell cycle, including Bcl2, Cyclin D1, and Sirt1, which revealed the potential of miR-34a to boost endogenous repair/regeneration in the adult heart. Additionally, the remaining 7 miRNAs have been shown to regulate cardiac performance. miR-545, the negatively correlated target of HOTAIR, promotes cell apoptosis through the HOTAIR/miR-545/EGFR/MAPK axis (Li et al, 2018). miR-101 has been shown to mitigate the deterioration of cardiac function in post-MI rats (Pan et al, 2012), and it can protect cardiac fibroblasts from hypoxia-induced apoptosis by restraining the TGF-β signalling pathway, as shown by Zhao et al (2015). In contrast, miR33 deteriorates myocardial fibrosis via the inhibition of MMP16 and the stimulation of p38 MAPK signalling (Chen et al, 2018). After I/R, the expression of miR-139-3p increases and is downregulated by Urocortin 1 (Ucn-1), and the overexpression of miR-139-3p promotes the expression of genes involved in cell death and apoptosis (Díaz et al, 2017). miR-24-1 was found to be significantly hypermethylated in ischaemic cardiomyopathy (ISCM) and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and significantly reduced in an ISCM group (Glezeva et al, 2019). Additionally, miR-598 was identified as a significant predictor of heart failure (HF) in a dyspnoea cohort (Ellis et al, 2013), and miR-142-3p sponged by lncRNA TUG1 has been suggested to potentially alleviate myocardial injury (Su et al, 2019). Thus, more mechanistic research is needed to explore the potential functions of the identified miRNAs in AMI. We found that several hub genes and correlative mechanism pathways including Notch1, CTNNB1, RAC1, and MTOR had greater diagnostic potential for AMI. The Notch1 activation pathway manages cardiac AMPK signalling by interacting with LKB1 during myocardial infarction (Yang et al, 2016). Spermidine (SPD) has been suggested to be involved in the cardiac dysfunction induced by MI by promoting autophagy in the AMPK/mTOR pathway (Yan et al, 2019). The inhibition of Annexin A3 (ANXA3) has been reported to accelerate cardiomyocyte maintenance by activating PI3K/Akt signalling in rats with AMI (Meng et al, 2019). RAC1 has been shown to inhibit the death of cardiac myocytes stimulated by hypoxia and modify the phosphorylation levels of PI3K, AKT, MAPK and ERK, which are significant factors of MI (Wang et al, 2017). Overall, we inferred that the 4 hub genes might be regarded as diagnostic biomarkers and recovery monitors in AMI.
此外,在可能影响急性心肌梗死发生发展的8个miRNAs中,miR-34a已被机制研究确定为急性心肌梗死的生物标志物。它在MI后的成年小鼠中高度表达,并与左心室(LV)的薄壁相关(Qipshidze Kelm等人,2018年)。Yang等人(2015)。研究发现,miR-34a的抑制部分通过调节参与细胞增殖和细胞周期的相关基因,包括bcl2、Cyclin D1和Sirt1,促进了MI后的心功能,这揭示了miR-34a促进成人心脏内源性修复/再生的潜力。此外,剩下的7个miRNAs已经被证明可以调节心脏功能。MIR-545是HOTAIR的负相关靶标,通过HOTAIR/miR-545/EGFR/MAPK轴促进细胞凋亡(Li等人,2018年)。如赵等人(2015年)所示,MIR-101已被证明可以缓解心肌梗死后大鼠的心功能恶化(潘等人,2012年),并通过抑制转化生长因子-β信号通路来保护心脏成纤维细胞免受缺氧诱导的细胞凋亡。相反,miR33通过抑制MMP16和刺激p38 MAPK信号转导而恶化心肌纤维化(Chen等人,2018年)。缺血再灌注后,miR-139-3p的表达增加,并被urocortin 1(UCN-1)下调,miR-139-3p的过度表达促进细胞死亡和凋亡相关基因的表达(Díaz等,2017)。在缺血性心肌病(ISCM)和扩张型心肌病(DCM)中,MIR-24-1被发现显著高甲基化,而在ISCM组中显著降低(Glezeva等人,2019年)。此外,在呼吸困难队列中,miR-598被确定为心力衰竭(HF)的重要预测因子(Ellis等人,2013年),而由lncRNA TUG1海绵的miR-142-3p被认为有可能减轻心肌损伤(Su等人,2019年)。因此,需要更多的机制研究来探索已识别的miRNAs在急性心肌梗死中的潜在功能。我们发现包括Notch1、CTNNB1、RAC1和MTOR在内的几个HUB基因及其相关的机制通路对急性心肌梗死具有更大的诊断潜力。Notch1激活通路通过在心肌梗死期间与LKB1相互作用来管理心脏AMPK信号(Yang等人,2016)。亚精胺(Spd)可能通过促进AMPK/mTOR途径中的自噬而参与心肌梗死所致的心功能障碍(Yanet al,2019)。据报道,Annexin A3(ANXA3)的抑制通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路加速了急性心肌梗死大鼠的心肌细胞维护(Meng等,2019)。研究表明,rac1可以抑制缺氧刺激的心肌细胞死亡,并改变PI3K、AKT、MAPK和ERK的磷酸化水平,这些都是MI的重要因素(Wang等,2017)。总体而言,我们推测这4个HUB基因可能被视为急性心肌梗死的诊断生物标志物和康复监测指标。

There are several limitations to our present study. The number of samples we obtained from GSE24591 and GSE31568 was small, generating some bias when analysing the DE-miRNAs, and more blood samples are needed for validation with RT-qPCR in further research. In addition, the functions and molecular mechanisms of genes are very complicated, and predictions based only on bioinformatics need cellular and animal experiments for verification.
我们目前的研究有几个局限性。我们从GSE24591和GSE31568获得的样本数量较少,在分析DE-miRNAs时会产生一定的偏差,在进一步的研究中需要更多的血液样本来验证RT-qPCR。此外,基因的功能和分子机制非常复杂,仅基于生物信息学的预测需要细胞和动物实验来验证。
结论 CONCLUSIONS

Based on GEO database analysis, bioinformatic analysis, and experimental verification, we not only identified eight significant DE-miRNAs in AMI but also detected 10 hub genes that may serve as potential biomarkers of AMI. Our findings might provide reliable candidate biomarkers for the precise diagnosis and individualized treatment of AMI and the development of further clinical applications in AMI.
基于GEO数据库分析、生物信息学分析和实验验证,我们不仅确定了8个在急性心肌梗死中有意义的DE-miRNAs,还检测到了10个可能作为急性心肌梗死潜在生物标志物的HUB基因。我们的研究结果可能为急性心肌梗死的准确诊断和个体化治疗以及进一步的临床应用提供可靠的候选生物标志物。
实验思路
| 实验思路 | 研究流程 | 研究结果 | 可视化形式 | |
| 干实验 | 从GEO下载数据 | GSE24591,SE31568 | ---------- | |
| 挑 | 差异分析,取交集 |
GSE24591:27个DE-miRNAs GSE31568:307个DE-miRNAs 取交集:8个DE-miRNAs |
GSE24591:火山图 GSE31568:火山图 交集展示:韦恩图、列表 |
|
| 联 | 用8个DE-miRNAs预测靶基因 | miRDB、RNA22、RNAhybird、TargetScan:591个靶基因 | Cytoscape将结果可视化
并将靶基因用列表展示 |
|
|
圈 |
591个靶基因GO、KEGG富集分析 | ---------- | GO:条形图*3
KEGG:柱形图 |
|
|
联 |
591个靶基因做PPI网络 |
找出排名前100的靶基因,并选出其中10个Hub基因 |
PPI网络图 |
|
|
圈 |
10个Hub基因的生物学分析 | 10个HUB基因的相互作用 KEGG富集分析 | 相互作用:PPI网络图
KEGG富集分析:网络图,气泡图 |
|
| 靠 | 血清样本测序 | 血清样本测序看8个DE-miRNAs差异表达 | 8个ROC曲线 | |
|
湿实验 |
细胞实验:RT-qPCR | 细胞系看8个DE-miRNAs差异表达:找到2个最佳miRNA |
细胞RT-qPCR:柱形图对比 |
|
|
|
与传统预后标志物的关系 | 与肌钙蛋白T(TnT)水平做相关性:确定出1个最佳miRNA | ---------- | |
干实验
Part1 挑
作者选用了GSE24591和GSE31568两个数据集。分别做差异表达基因分析,即疾病组 vs 正常组,并将结果可视化。
A图和B图即是两个数据集的可视化结果。文章结果采用的是火山图,筛选条件是LogFC绝对值大于1且p值小于0.05。
C图是A、B两图取交集的结果,共有8个miRNA,用韦恩图展示的结果。
作者还把这8个miRNA用表列举了出来,即是Table2的结果。将挖掘出来的差异基因、关键信息进一步图表化、具体化,也是一种凑数据图表的方式。
Part2 联
如果目标分子是功能基因,那这一部分其实应该是功能聚类。但文章的研究对象是miRNA,所以这一步换位“联”。作者用miRNA预测靶基因,采用的是miRDB、RNA22、RNAhybird、TargetScan,并用Cytoscape将结果可视化。结果显示8个miRNA共有591个靶基因。
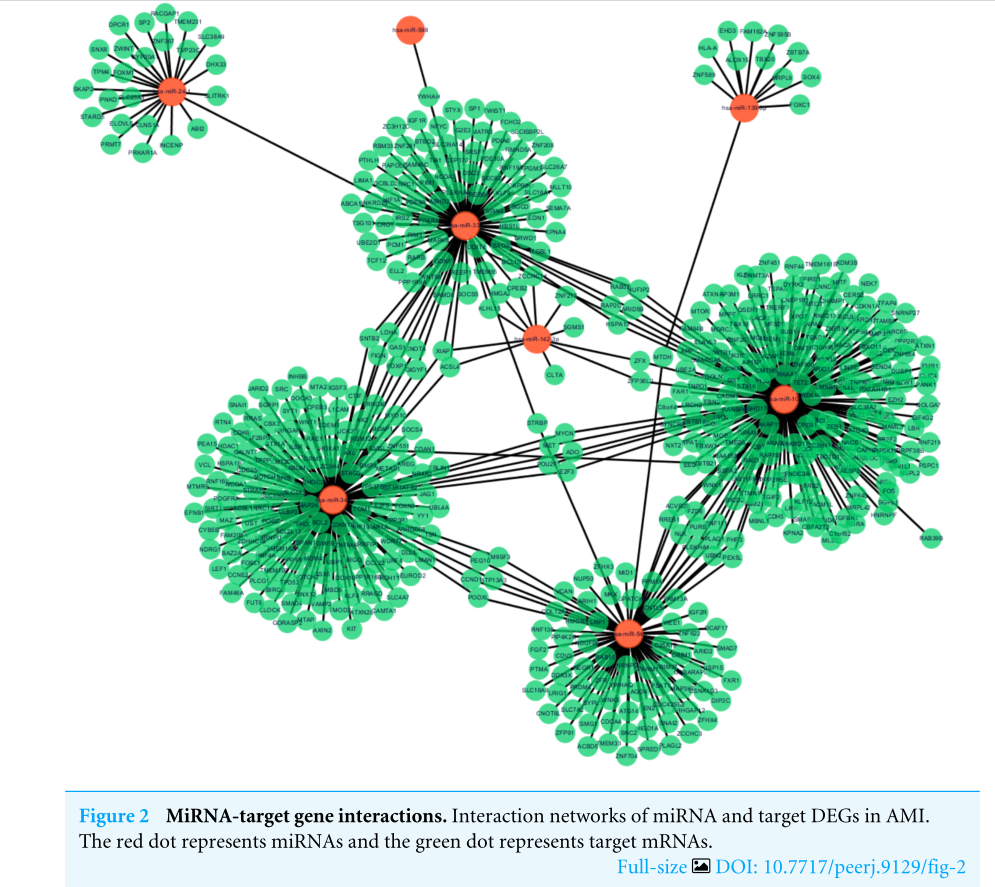
同样,作者把结果用表格展示出来了,即Table3的结果。
miRNA预测靶基因的常用数据库总结:
1. TargetScan数据库(http://www.targetscan.org/mamm_31/)TargetScan主要通过Total contextscore对检索结果进行评分,它代表所有位点context score 加和,数值越低,结合可能性越大。此外,TargetScan通过Aggregate Pct 对miR保守性进行估计,数值越高,结合可能性越大。
2. TarBase数据库(http://microrna.gr/tarbase/)是一个有实验支持的miR靶基因数据库;主要包括人、鼠、猿、鸡等多个物种的数据。
3. starbase数据库(http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/)(现在叫ENCORI)是中山大学开发的miR综合数据库,功能非常强大,提供包括23个物种的700多个datasets的CLIP-seq数据,100个datasets的降解组测序数据,32个癌种的RNA-seq数据,样本数超过10800个,信息量非常大。
4. miRWalk数据库(http://zmf.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/apps/zmf/mirwalk2/)是一个交叉预测网站,既可以通过miRNA预测靶基因,也可以通过gene预测与之结合的miRNA;不仅支持对一个miRNA或gene的预测,也支持多个miRNA或gene同时预测。这些数据库我们往往是将预测的靶基因取交集作为最后的结果。
Part3 圈
作者将Figure2中预测的591个靶基因拿来做功能聚类,即做GO/KEGG分析。GO分析工具为David,出的结果是柱状图,而KEGG分析采用是R包clusterProfiler,出的结果是气泡图。所有的结果展示的均是Top10的富集结果。
1. Metascape数据库(http://metascape.org/gp/index.html) 是提供基因注释和富集分析的门户网站,帮助生物学家理解一个或多个基因列表;可以作为大量基因背景调研和初步筛选的辅助工具。Metascape在首页说“它是一个超过DAVID的分析数据库”。它的优势主要体现在以下几个方面。如操作简单,新手更容易上手;结果呈现美观,报告下载方便;覆盖面广泛;在线;数据更新快;
2. WebGestalt(http://www.webgestalt.org/)支持12个物种,多种数据库和平台的354基因标识符,以及来自公共数据库和模型计算的321251个功能注释集。WebGestalt也可以分析来自公共其他数据库的基因名和实验数据,还可以进行磷酸激酶位点的富集分析。WebGestalt支持ORA、GSEA和NTA三种富集分析法。尤其是GSEA分析,可谓是良心出品。大大省去下载GSEA软件以及分析时经常报错的烦恼。但GSEA分析结果是黑白的,其实影响也不大。
Part4 联
Figure4,这一步,作者将Figure2中的591个靶基因作PPI网络分析,采用的是String在线工具,并用Cytoscape中的插件CytoHubba将结果可视化。结果展示了得分前10的关键分子,即Hub基因。同样,将10个关键基因用表格列举了出来。即为Table4的结果。
Part5 圈
Figure5,“聚类分析”,即先获得的基因列表或基因表达矩阵,然后把具有相似功能的基因放到一起,和生物学表型相关联,对生物学功能/相关的通路或机制进行预测分析。针对Figure4中的Top10 genes做KEGG分析,和Figure3如出一辙。只不过作者采用的是Cytoscape和clusterprofiler包的R包进行分析,出的图是气泡图,非常直观。
Part6 靠
Figure7,“靠”,即联系临床。作者在这里用的是ROC曲线。ROC曲线,可谓Biomaker的标配,可用SPSS绘制。初学者可以直接关注AUC数值。一般来说,AUC应大于0.5。若AUC在0.5~0.7,说明此指标诊断价值低;若AUC在0.7~0.9,说明此指标诊断价值中;若AUC在0.9~1,说明此指标诊断价值高。文章结果显示miR-24-1,AUC为0.964,诊断价值高。
以上就是干实验部分。包含“挑”、“圈”、“联”“靠”4部分,其中“圈”和“联”使用了2次。其实,继续拓展一下,我们也可以做ceRNA机制,即根据miRNA分别预测lncRNA和mRNA,然后建立一个lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA的ceRNA调控网络。常用的根据miRNA预测lncRNA的数据库,如LncBase 。
LncBase数据库(https://dianalab.e-ce.uth.gr/html/diana/web/index.php?r=lncbasev2,https://diana.e-ce.uth.gr/lncbasev3/home)是DIANA-Tools数据库的一个版块,记录lncRNA与miRNA相互作用的数据库,旧版本为v2,目前最新版本为v3。分为实验证据支持和软件预测两部分。
湿实验
Figure6,细胞实验。验证8个miRNA在疾病组中高表达。总结来说,包含“模”、“法”、“标”三个部分
分组:急性心肌梗死vs 正常组
模型:Dox诱导的心肌梗死细胞模型
法:检测方法,为RT-PCR
标:即八个miRNA
好了,湿实验就结束了。到此,整篇文章也结束了。
最后再来做个总结,文章属于干湿结合。干实验包含“挑”(Figure1)“圈”(Figure3,5)“联”(Figure2,4) “靠”(Figure7);湿实验包含细胞实验(Figure6)。





