6、注解Annotation
千里之行,始于足下
正文
一、注解的本质:
1、注解,Annotation是JDK5.0引入的新技术。
2、注解的格式:@注释名,还可以添加参数(必要时)
3、注解不是程序本身,但可以对程序作出解释(就这一点,注释和注解的作用类似)
4、注解可以被其他程序读取(比如编译器等等)
5、注解可以给Java包、类型(类、接口、枚举)、构造器、方法、域、参数和局部变量进行注解,相当于给它们添加了一些额外的辅助信息。Java编译器可以根据指令来解释注解和放弃注解,或者将注解放到编译后的生成的class文件中,运行时可用。通过反射机制编程实现对这些元数据的访问。
注:注解的定义方式与接口相似,使用 @interface 关键字来定义注解。
二、元注解:
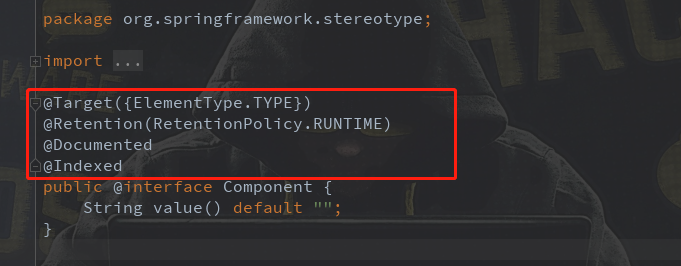
java.lang.annotation
1、@Documented:
指定被标注的注解会包含在javadoc中。
2、@Retention:
指定注解的生命周期(源码、class文件、运行时),其参考值见类的定义:java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy
● RetentionPolicy.SOURCE :
在编译阶段丢弃。这些注解在编译结束之后就不再有任何意义,所以它们不会写入字节码。@Override, @SuppressWarnings都属于这类注解。
● RetentionPolicy.CLASS :
在类加载的时候丢弃。在字节码文件的处理中有用。注解默认使用这种方式。
● RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME :
始终不会丢弃,运行期也保留该注解,因此可以使用反射机制读取该注解的信息。我们自定义的注解通常使用这种方式。
3、@Target:
指定注解使用的目标范围(类、方法、字段等),其参考值见类的定义:java.lang.annotation.ElementType
● ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR :用于描述构造器。
● ElementType.FIELD :成员变量、对象、属性(包括enum实例)。
● ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE: 用于描述局部变量。
● ElementType.METHOD : 用于描述方法。
● ElementType.PACKAGE :用于描述包。
● ElementType.PARAMETER :用于描述参数。
● ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE:用于描述参数
● ElementType.TYPE :用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明。
4、@Inherited:
指定子类可以继承父类的注解,只能是类上的注解,方法和字段的注解不能继承。即如果父类上的注解是@Inherited修饰的就能被子类继承。
三、自定义注解:
1、声明注解:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { String name() default ""; }
2、标记注解:
@Data public class ResponseVO { @MyAnnotation(name = "UUID") private String uuid; @MyAnnotation(name = "姓名") private String name; @MyAnnotation(name = "状态") private String status; }
3、应用:
public class AnnotationWork { /** * 解析字段详情 * * @Return {"name":"姓名","uuid":"UUID","status":"状态"} * */ public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> resultParams = new HashMap<>(); for (Field field : ResponseVO.class.getDeclaredFields()) { MyAnnotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); resultParams.put(field.getName(), annotation.name()); } System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(resultParams)); } }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
2022-08-07 5、基于EasyExcel的导入导出