SV Review
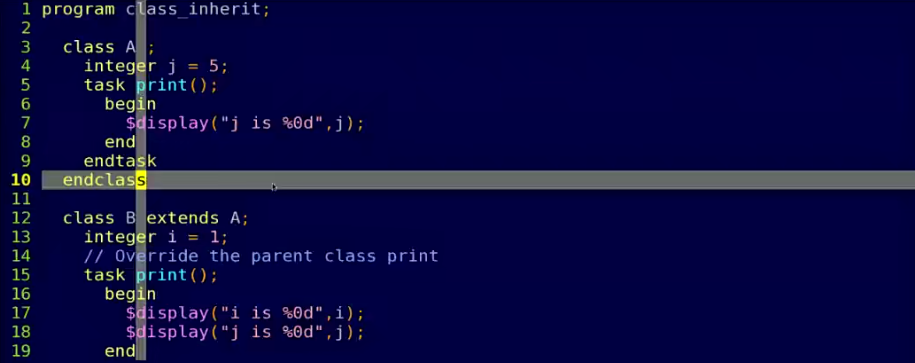
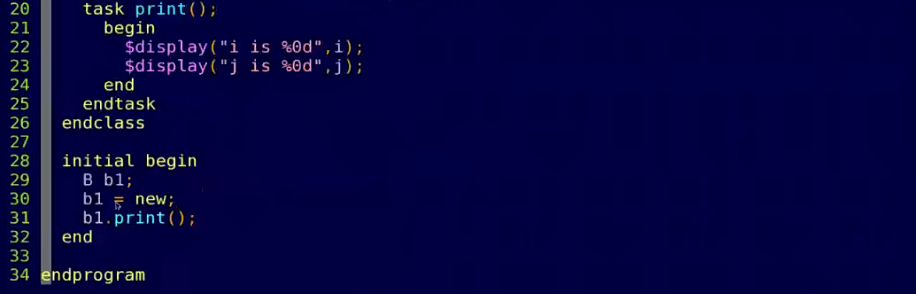
- oop:封装\继承\多态
new()
- new()函数用于申请内存空间并且进行变量的初始化
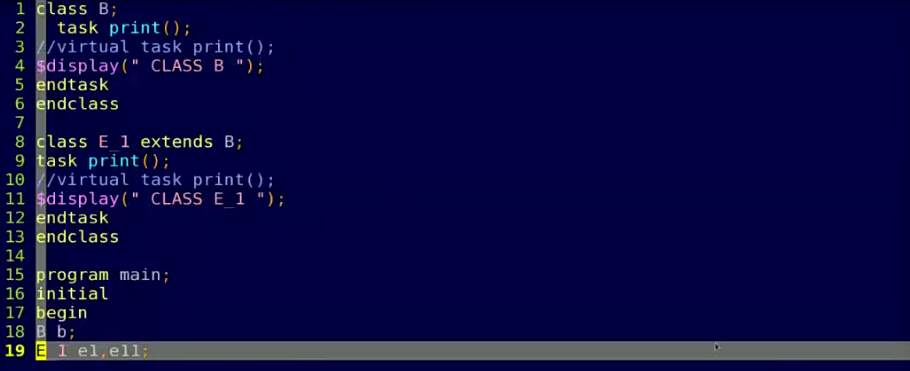
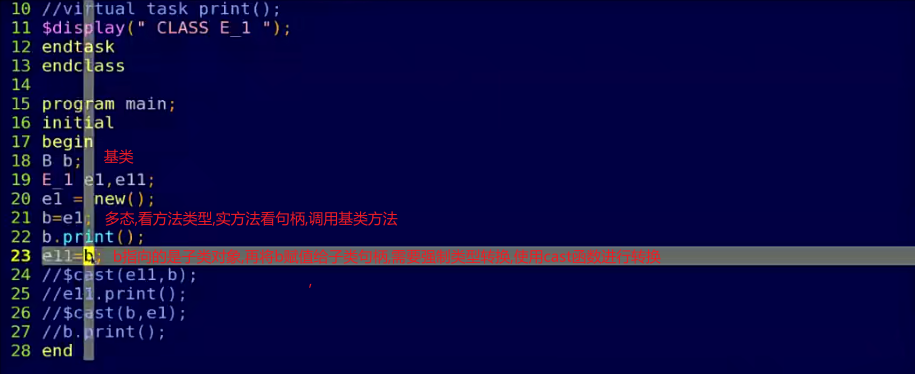
多态
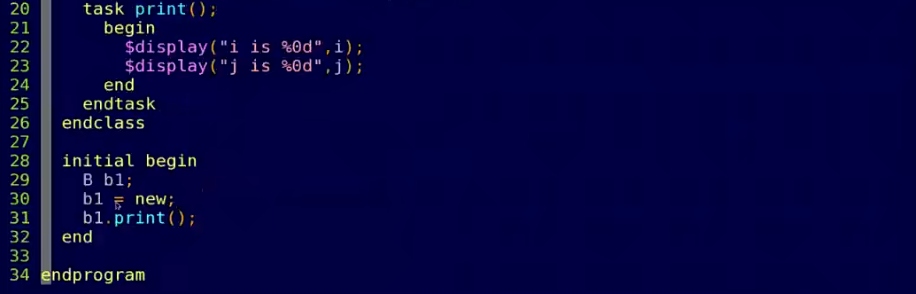
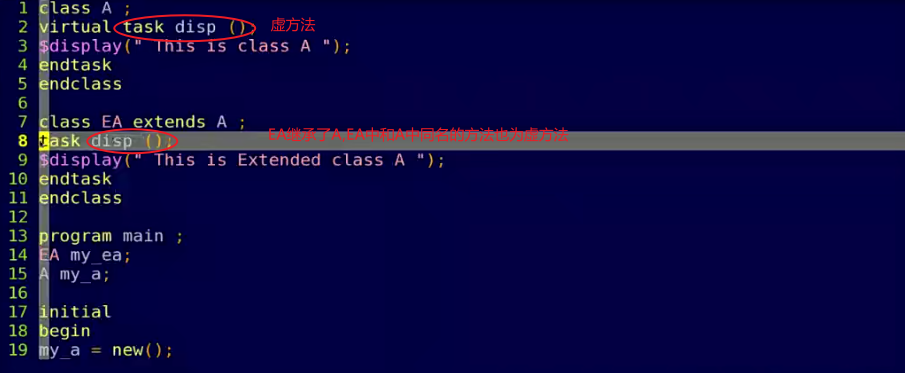
- 父类引用指向子类对象
- 虚方法看对象,实方法看句柄

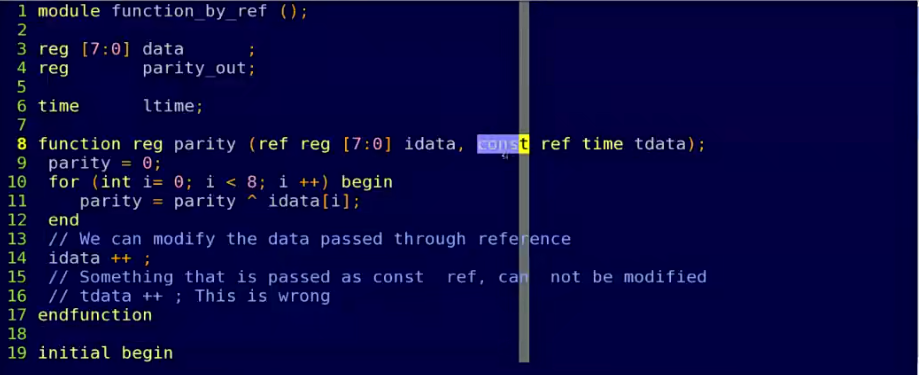
ref参数
ref声明的端口信号,在进行参数传递时,共享同一个变量存储空间,即“引用”传递进来的实参,而不是复制传递的参数。
int array[]= {0,1,2,3,4};
//ref变量指向传入的数组变量的地址,并修改array[1]的值
task change_test(input string name, input int i, ref int array[])
$display("This is a test named %s", name);
array[1] = i;
endtask
change_test("just a test for ref", 6, array);
- 执行函数之后,外部数组中的第2个元素修改为6,如果没有使用ref修饰参数,那么array原数组的元素值是不会发生改变的
- ref相当于一个指针,外部实参传入之后,task中的ref就指向实参的地址,可以直接对于实参地址中的数据进行修改,而不用output修改后的值
- 如果只想引用数组的值,而不想在程序中修改array[],需要加上const关键字修饰,表示该参数不可修改
int array[]= {0,1,2,3,4};
int array_1;
//ref变量添加const关键词,指向传入的数组变量的地址,但是只能在程序中引用其值,不能修改
task change_test(input string name, output int i, const ref int array[])
$display("This is a test named %s", name);
i = array[1];
endtask
change_test("just a test for ref", array_1, array);
SystemVerilog参考手册规定,ref参数只能用于带自动存储的子程序中。即子程序快中的ref变量只能是动态变量(automatic)。
- 通常的参数传递通过复制的方式进行,但是ref之后就会指向地址,提高运算效率,尤其时用于数组
automatic
- 如果变量被声明为automatic,那么进入该方法后,就会自动创建,离开该方法后,就会被销毁;
- static则是在仿真开始时就会被创建,直到仿真结束,可以被多个方法/进程共享。
例1
function automatic int auto_cnt(input a);
int cnt = 0;
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
$display("@1 auto_cnt = %0d", auto_cnt(1));
$display("@2 auto_cnt = %0d", auto_cnt(1));
# @1 auto_cnt = 1 // 定义为automatic方法,每次执行销毁变量
# @2 auto_cnt = 1
例2
function automatic int auto_static_cnt(input a);
static int cnt = 0;
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
$display("@1 auto_static_cnt = %0d", auto_static_cnt(1));
$display("@2 auto_static_cnt = %0d", auto_static_cnt(1));
// 定义为static变量,仿真开始创建,直到仿真结束
# @1 auto_static_cnt = 1
# @2 auto_static_cnt = 2
例3
function static int static_cnt(input a);
static int cnt = 0;
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
$display("@1 static_cnt = %0d", static_cnt(1));
$display("@2 static_cnt = %0d", static_cnt(1));
# @1 static_cnt = 1
# @2 static_cnt = 2
- static的function隐含其中的变量就是static,因为我们对cnt进行了初始化,所以必须明确指出其是static还是automatic。
例4
function static int static_auto_cnt(input a);
automatic int cnt = 0;
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
$display("@1 static_auto_cnt = %0d", static_auto_cnt(1));
$display("@2 static_auto_cnt = %0d", static_auto_cnt(1));
# @1 static_auto_cnt = 1
# @2 static_auto_cnt = 1
- 方法是static的,但是如果我们把变量定义为automatic,每次结束方法就会销毁该变量。
例5
function int def_cnt(input a);
static int cnt = 0;
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
$display("@1 def_cnt = %0d", def_cnt(1));
$display("@2 def_cnt = %0d", def_cnt(1));
- 任何隐含为static的方法,如果我们需要对其中的变量进行初始化,一定要指定其是static还是automatic的,否则会报error:
(vlog-2244) Variable 'cnt' is implicitly static. You must either explicitly declare it as static or automatic
# or remove the initialization in the declaration of variable.
例6
function int def_cnt_auto(input a);
automatic int cnt = 0;
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
$display("@1 def_cnt_auto = %0d", def_cnt_auto(1));
$display("@2 def_cnt_auto = %0d", def_cnt_auto(1));
# @1 def_cnt_auto = 1
# @2 def_cnt_auto = 1
例7
int cnt = 0;
function automatic int auto_cnt(input a);
cnt += a;
return cnt;
endfunction
auto_cnt(1);
$display("@1 auto_cnt = %0d",cnt );
auto_cnt(1);
$display("@2 auto_cnt = %0d", cnt);
# @1 auto_cnt = 1
# @2 auto_cnt = 2
- 外部变量默认还是static的
- static修饰函数内部变量默认是static类型变量
- static修饰函数内部变量进行初始化需要指出是static还是automatic类型
- static函数内部变量声明为automatic类型,每次方法结束后会被销毁
- 隐含为static的方法,为其中的变量进行赋值的时候必须指明函数的类型是不是static
- class中的方法默认是automatic的
- module\interface\program中的task和function默认是static的
- automatic方法中的变量默认是automatic类型
- 变量没有初始化就看方法的类型是static还是automatic
cast(des,src) - 强制类型转换