NTCPMSG 开源高性能TCP消息发送组件
目前的.net 架构下缺乏高效的TCP消息发送组件,而这种组件是构建高性能分布式应用所必需的。为此我结合多年的底层开发经验开发了一个.net 下的高效TCP消息发送组件。这个组件在异步发送时可以达到每秒160万包,而相同大小的数据包用WCF的TCP模式OneWay 方式发送每秒只能达到5.6万包。
项目首页
功能介绍:
NTCPMSG 组件是基于 .net framework 的开源TCP 消息发送和接收组件。和.net framework 提供的 TcpClient 类比较,这个组件是以包的方式发送消息,不存在沾包的情况。最新发布的1.3.0.0 版本除提供发送 byte[] 数据外,还提供直接发送和接收对象,并提供多种类型的序列化方式供调用者选择。发送模式上,NTCPMSG 提供异步发送和同步发送两种方式。另外相对于 .net framework 自带的 TCP 类,NTCPMSG 提供了 Connection, Disconnection, accept, Receive 等事件,方便调用者对消息发送和接收的各个阶段进行控制。
相比很多通讯组件只能从客户端发送消息到服务器然后接受服务器响应, NTCPMSG 还增加了直接从服务器推送消息给客户端的功能。这个功能对于后台分布式应用的开发也是非常有用的,因为这些分布式应用相互往往是对等的。
NTCPMSG 主要类:
SingleConnection
这个类每次建立1个链接到服务器
主要的方法:
AsyncSend: 这个方法发送异步消息到服务器
SyncSend: 这个方法发送同步消息到服务器
Connect: 这个方法用于和服务器建立连接时调用。这个方法有个 autoConnect 参数,如果这个参数为true,那么SingleConnection 类在和服务器断链后会尝试自动与服务器建链。这个是个比较实用的功能,调用者不需要考虑服务器连接中断后恢复的情况。
主要事件:
ConnectedEventHandler: 这个事件在建立链接成功时触发
ErrorEventHandler: 这个事件在发生错误的情况下触发
RemoteDisconnected: 这个事件在和服务器断链时触发
ReceiveEventHandler: 这个事件当接收到直接从服务器推送过来的消息时触发。
SingleConnectionCable
这个类可以将多个链接绑定到一起和服务器通讯。有用TCP本身是基于滑动窗口协议的,单链路的发送速度受网络时延的影响,这也是TCP比UDP慢的一个原 因。但由于TCP可以提供比UDP可靠的通讯,大部分对可靠性要求较高的系统还是要采用TCP方式发送消息。为了克服网络时延带来的性能下降,通过多链路 同时发送是一个很好的解决方案,因为每个链路都独立维护一个窗口,链路之间是并行发送。实测下来,绑定多链路也确实比单链路的发送速度快很多。所以我一般 推荐用 SingleConnectionCable 这个类连接服务器。
SingleConnectionCable 和 SingleConnection 的主要方法和事件是相同的,这里就不重复介绍了。
NTcpListener
这个类顾名思义是服务器侧用于侦听消息的类。
主要的方法:
AsyncSend: 这个方法推送异步消息到客户端
SyncSend: 这个方法推送同步消息到客户消息,目前版本还没有实现。
Listen: 这个方法用于开始侦听
Close: 这个方法用于关闭侦听
主要事件:
Accepted: 这个事件在客户端建立链接成功时触发
ErrorReceived: 这个事件在发生错误的情况下触发
RemoteDisconnected: 这个事件在和客户端断链时触发
DataReceived: 这个事件当接收到直接从服务器推送过来的消息时触发。
性能报告:
和 WCF 的 TCP 模式比较,相同环境下,发送4字节 byte[] ,异步方式下, NTCMSG 每秒大概发送160万包,CPU占有率60%, WCF 每秒5.6万包,CPU占有率为100%。同步方式下 NTCPMSG 每秒13万包,WCF每秒是2万包。
和 TCPClient 的异步发送比较(TCPClient 发送时不考虑沾包问题,就是连续发送 4字节的 byte[]) , TCPClient 每秒大概可以发送15万包。为什么NTCPMSG 比TCPClient 发送的还要快?这是因为 NTCPMSG 底层做了组包,将多个小包组合成大包批量发送过去。有人会问这样是不是会导致发送不实时呢? NTCPMSG 考虑到了这个实时性的问题,组包是在兼顾实时性的情况下完成的,也就是说如果在一个非常短的时间间隔内如果累计发送的包达到一定阀值才会组包发送,这就很 好的解决的实时发送的问题。
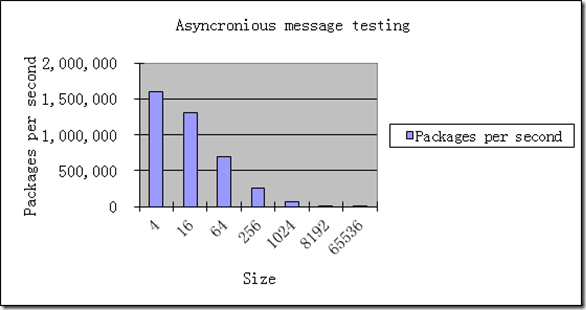
下面图表是 NTCPMSG 自身的性能测试报告:
测试环境: 2台 i5 笔记本,1Gbp 以太网(千兆以太网交换机),客户端用SingleConnectionCable 连接。
异步发送测试
这个测试是发送指定大小的 byte[] 数据,客户机上开两个测试进程模拟两台机器同时发送进行测试。
|
Asyncronious message testing |
|||
|
Size |
Packages per second |
Network usage |
Server CPU |
|
4 |
1,600,000 |
26.00% |
60.00% |
|
16 |
1,300,000 |
33.00% |
60.00% |
|
64 |
700,000 |
44.00% |
60.00% |
|
256 |
260,000 |
58.00% |
50.00% |
|
1024 |
70,000 |
60.00% |
30.00% |
|
8192 |
14,500 |
96.00% |
27.00% |
|
65536 |
1,830 |
97.00% |
30.00% |
同步发送测试
这个测试是发送指定大小的 byte[] 数据,客户机上开四个测试进程(每个进程32个线程并行发送)模拟四台机器同时发送进行测试。
|
Syncronious message testing |
|||
|
Size |
Packages per second |
Network usage |
Server CPU |
|
4 |
130,000 |
4.50% |
35.00% |
|
16 |
120,000 |
5.50% |
43.00% |
|
64 |
118,000 |
10.00% |
38.00% |
|
256 |
90,000 |
20.00% |
60.00% |
|
1024 |
25,000 |
22.00% |
80.00% |
|
8192 |
9,000 |
50.00% |
50.00% |
|
65536 |
1,000 |
50.00% |
15.00% |
不同的序列化方式的测试比较
这个测试是发送一个测试消息对象,客户机上开两个测试进程模拟两台机器同时异步发送进行测试。
|
Compare with different serialization |
|||
|
Serialization |
Packages per second |
Network usage |
Server CPU |
|
Bin |
20,000 |
1.56% |
25.00% |
|
Xml |
13,000 |
1.38% |
40.00% |
|
Json |
16,000 |
1.40% |
60.00% |
|
SimpleBin |
22,000 |
1.64% |
28.00% |
|
Struct |
120,000 |
14.00% |
32.00% |
|
Custom |
320,000 |
9.70% |
30.00% |
这里需要说明一下,为什么前几种序列化方式效率不高,这是因为前几种序列化用到了反射,这个反射极大的消耗了CPU资源。如果要高效的发送,建议用 结构体方式发送或者自定义序列化发送。自定义序列化由于已知要发送的数据结构,不用到发射,发送效率是最高的。从这个测试看自定义序列化,每秒发送30万 包是,服务器的CPU才30%,理论上如果多客户端发送,服务器每秒应该可以最大接收到100万左右的消息。
项目结构
NTCPMSG.sln 这个是 VS2008 下的项目,编译出来是 .net 2.0 的组件
NTCPMSG2010.sln 这个是 VS2010 下的项目,编译出来是 .net 4.0 的组件
ClientTest
这个项目是测试代码的客户端客户端部分。
ServerTest
这个是测试代码的服务器部分
Example
这个是简单的示例代码。可以用于入门学习。
NTCPMSG
这个是组件的核心代码。
示例代码
客户端
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using System.Net; using NTCPMSG.Client; using NTCPMSG.Event; namespace Example { class Client { /// <summary> /// DataReceived event will be called back when server get message from client which connect to. /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="args"></param> static void ReceiveEventHandler(object sender, ReceiveEventArgs args) { switch ((Event)args.Event) { case Event.PushMessage: //Get OneWay message from server if (args.Data != null) { try { Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(args.Data)); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } } break; } } public static void Run(string[] args) { Console.Write("Please input server IP Address [127.0.0.1]:"); string ipAddress = Console.ReadLine().Trim().ToLower(); if (ipAddress == "") { ipAddress = "127.0.0.1"; } try { //************** SingConnection Example ********************** Console.Write("Press any key to start single connection example"); Console.ReadKey(); Console.WriteLine(); //Create a SingleConnection instanace that will try to connect to host specified in //ipAddress and port (2500). SingleConnection client = new SingleConnection(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ipAddress), 2500)); client.ReceiveEventHandler += new EventHandler<ReceiveEventArgs>(ReceiveEventHandler); client.Connect(); Console.WriteLine("AsyncSend: Hello world! I am Single"); //Send an asynchronously message to server client.AsyncSend((UInt32)Event.OneWay, Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello world! I am Single")); int number = 0; try { Console.WriteLine("SyncSend {0}", number); //send a synchronously message to server //send a number with event: Event.Return to server and get the response from server //with the number increased. byte[] retData = client.SyncSend((UInt32)Event.Return, BitConverter.GetBytes(number)); number = BitConverter.ToInt32(retData, 0); Console.WriteLine("Get {0}", number); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } Console.WriteLine("Waitting for 10 seconds to finish simple connection example."); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10000); client.Close(); //************* SingleConnectionCable Example ***************** Console.Write("Press any key to start single connection cable example"); Console.ReadKey(); Console.WriteLine(); //Create a SingleConnectionCable instance that will try to connect to host specified in //ipAddress and port (2500). //by default, SingleConnectionCable will try to connect automatically and including 6 tcp connections. SingleConnectionCable clientCable = new SingleConnectionCable(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ipAddress), 2500)); clientCable.ReceiveEventHandler += new EventHandler<ReceiveEventArgs>(ReceiveEventHandler); clientCable.Connect(); Console.WriteLine("AsyncSend: Hello world! I am Cable {0}", clientCable.CableId); //Send a one way message to server clientCable.AsyncSend((UInt32)Event.OneWay, Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(string.Format("Hello world! I am Cable {0}", clientCable.CableId))); //Send object with bin serialization (By Default) Console.WriteLine("Bin serialization"); clientCable.AsyncSend((UInt32)Event.Bin, "Bin serialization"); while (true) { Console.WriteLine("SyncSend {0}", number); try { //send a number with event: Event.Return to server and get the response from server //with the number increased. byte[] retData = clientCable.SyncSend((UInt32)Event.Return, BitConverter.GetBytes(number)); number = BitConverter.ToInt32(retData, 0); Console.WriteLine("Get {0}", number); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } Console.WriteLine("Quit when you press ESC. Else continue SyncSend."); //Quit when you press ESC if (Console.ReadKey().KeyChar == 0x1B) { clientCable.Close(); return; } } } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); Console.ReadLine(); } } } }
服务器
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using System.Net; using NTCPMSG.Server; using NTCPMSG.Event; using NTCPMSG.Serialize; namespace Example { class Server { class BinMessageParse : MessageParse { public BinMessageParse() : base(new BinSerializer(), new BinSerializer()) { } public override object ProcessMessage(int SCBID, EndPoint RemoteIPEndPoint, NTCPMSG.MessageFlag Flag, ushort CableId, uint Channel, uint Event, object obj) { Console.WriteLine(obj); return null; } } static BinMessageParse _sBinMessageParse = new BinMessageParse(); /// <summary> /// DataReceived event will be called back when server get message from client which connect to. /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="args"></param> static void ReceiveEventHandler(object sender, ReceiveEventArgs args) { switch ((Event)args.Event) { case Event.OneWay: //Get OneWay message from client if (args.Data != null) { try { if (args.CableId != 0) { Console.WriteLine("Get one way message from cable {0}", args.CableId); } else { Console.WriteLine("Get one way message from {0}", args.RemoteIPEndPoint); } Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(args.Data)); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } } break; case Event.Return: //Get return message from client if (args.Data != null) { try { int fromClient = BitConverter.ToInt32(args.Data, 0); args.ReturnData = BitConverter.GetBytes(++fromClient); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } } break; case Event.Bin: _sBinMessageParse.ReceiveEventHandler(sender, args); break; } } /// <summary> /// RemoteDisconnected event will be called back when specified client disconnected. /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="args"></param> static void DisconnectEventHandler(object sender, DisconnectEventArgs args) { Console.WriteLine("Remote socket:{0} disconnected.", args.RemoteIPEndPoint); } /// <summary> /// Accepted event will be called back when specified client connected /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="args"></param> static void AcceptedEventHandler(object sender, AcceptEventArgs args) { Console.WriteLine("Remote socket:{0} connected.", args.RemoteIPEndPoint); } public static void Run(string[] args) { NTCPMSG.Server.NTcpListener listener; //Create a tcp listener that listen 2500 TCP port. listener = new NTcpListener(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 2500)); //DataReceived event will be called back when server get message from client which connect to. listener.DataReceived += new EventHandler<ReceiveEventArgs>(ReceiveEventHandler); //RemoteDisconnected event will be called back when specified client disconnected. listener.RemoteDisconnected += new EventHandler<DisconnectEventArgs>(DisconnectEventHandler); //Accepted event will be called back when specified client connected listener.Accepted += new EventHandler<AcceptEventArgs>(AcceptedEventHandler); //Start listening. //This function will not block current thread. listener.Listen(); Console.WriteLine("Listening..."); while (true) { System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(5 * 1000); //Push message to client example. foreach (IPEndPoint clientIpEndPoint in listener.GetRemoteEndPoints()) { bool successful = listener.AsyncSend(clientIpEndPoint, (uint)Event.PushMessage, Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("I am from server!")); if (successful) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Push message to {0} successful!", clientIpEndPoint)); } else { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Push message to {0} fail!", clientIpEndPoint)); } } foreach (UInt16 cableId in listener.GetCableIds()) { bool successful = listener.AsyncSend(cableId, (uint)Event.PushMessage, Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(string.Format("Hi cable {0}!", cableId))); if (successful) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Push message to cable {0} successful!", cableId)); } else { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Push message to cable {0} fail!", cableId)); } } } //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(System.Threading.Timeout.Infinite); } } }