设计模式之抽象工厂模式-我生产的是一个家族!
抽象工厂模式
一、抽象工厂模式的概念
抽象工厂模式可以向客户端提供一个接口, 使得客户端在不必指定产品的具体类型的情况下, 能够创建多个产品族的产品对象。
工厂模式只能生产一种产品,抽象工厂模式是生产一族产品。
二、抽象工厂模式使用场景
1、在不指定具体的产品情况下,创建多个产品族中的产品对象。
三、抽象工厂模式构建方法
1、构建抽象工厂类
抽象工厂类是抽象工厂模式的核心, 包含对多个产品结构的声明,其他所有的工厂类都必须实现该类中的对外接口。
2、构建具体工厂类
具体工厂类用于实现抽象工厂中的对外接口,包含对象创建的逻辑实现,负责实例化某个产品族中的产品对象。
3、构建抽象产品类
抽象工厂模式所创建的所有产品对象的父类,它负责描述所有实例所共有的公共接口。
4、构建具体产品类
抽象工厂模式所创建的具体产品实例化对象。
四、抽象工厂模式的示例
// AbFactory.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 水果基类
class Fruit
{
public:
Fruit() {};
~Fruit() {};
virtual void printName()
{
cout << "My name is Fruit." << endl;
}
};
// 具体水果-北京香蕉
class BeiJingBanana : public Fruit
{
public:
BeiJingBanana() {};
~BeiJingBanana() {};
void printName()
{
cout << "My name is BeiJingBanana." << endl;
}
};
// 具体水-北京苹果
class BeiJingApple : public Fruit
{
public:
BeiJingApple() {};
~BeiJingApple() {};
void printName()
{
cout << "My name is BeiJingApple." << endl;
}
};
// 具体水果-南京香蕉
class NanJingBanana : public Fruit
{
public:
NanJingBanana() {};
~NanJingBanana() {};
void printName()
{
cout << "My name is NanJingBanana." << endl;
}
};
// 具体水-南京苹果
class NanJingApple : public Fruit
{
public:
NanJingApple() {};
~NanJingApple() {};
void printName()
{
cout << "My name is NanJingApple." << endl;
}
};
// 抽象工厂类
class Factory
{
public:
Factory() {};
~Factory() {};
virtual Fruit *CreatBananaFruit()
{
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
pFruit = new Fruit();
return pFruit;
}
virtual Fruit *CreatAppleFruit()
{
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
pFruit = new Fruit();
return pFruit;
}
};
// 北京工厂类
class BeiJingFactory : public Factory
{
public:
BeiJingFactory() {};
~BeiJingFactory() {};
virtual Fruit *CreatBananaFruit()
{
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
pFruit = new BeiJingBanana();
return pFruit;
}
virtual Fruit *CreatAppleFruit()
{
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
pFruit = new BeiJingApple();
return pFruit;
}
};
// 南京工厂类
class NanJingFactory : public Factory
{
public:
NanJingFactory() {};
~NanJingFactory() {};
virtual Fruit *CreatBananaFruit()
{
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
pFruit = new NanJingBanana();
return pFruit;
}
virtual Fruit *CreatAppleFruit()
{
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
pFruit = new NanJingApple();
return pFruit;
}
};
#define DELETE_PTR(p) {if(p!=nullptr){delete (p); (p)=nullptr;}}
int main()
{
cout << "------------AbstractFactory------------" << endl;
Factory *pFactory = nullptr;
Fruit *pFruit = nullptr;
// 北京水果
cout << "-------北京水果--------" << endl;
pFactory = new BeiJingFactory();
pFruit = pFactory->CreatBananaFruit();
pFruit->printName();
pFruit = pFactory->CreatAppleFruit();
pFruit->printName();
DELETE_PTR(pFruit);
DELETE_PTR(pFactory);
// 南京水果
cout << "-------南京水果--------" << endl;
pFactory = new NanJingFactory();
pFruit = pFactory->CreatBananaFruit();
pFruit->printName();
pFruit = pFactory->CreatAppleFruit();
pFruit->printName();
DELETE_PTR(pFruit);
DELETE_PTR(pFactory);
std::cout << "Hello World!\n";
getchar();
}
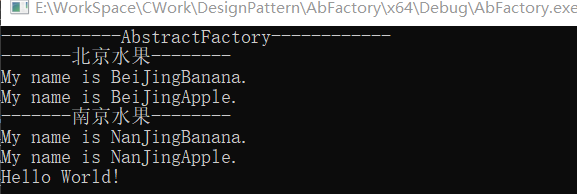
程序输出结果:
五、抽象工厂模式的优缺点
优点:
1、只需要知道是哪个工厂,不需要知道具体是哪种产品,就可以创建某种产品,封装了产品的创建。
2、模式灵活性更强,可以支持不同类型的产品创建。
3、可以非常方便的使用一族产品中的不同类型的产品。
缺点:
1、结构臃肿,如果产品类型或者产品族类型比较多的话,会非常难于管理。
2、每次添加一组产品,所有的工厂类都必须添加一个方法,这样违背了开放-封闭原则,一般适用于产品组合产品或者产品族变化不大的情况。
能力有限,如有错误,多多指教。。。
本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许请勿转载!作者:ISmileLi



