python 链表
在C/C++中,通常采用“指针+结构体”来实现链表;而在Python中,则可以采用“引用+类”来实现链表。
节点类:
class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None
链表类:
class Linkedlist: def __init__(self): self.head = None self.tail = None
link_list = LinkedList()
def is_empty(self): return self.head is None
def append(self, data): node = Node(data) if self.head is None: self.head = node self.tail = node else: self.tail.next = node self.tail =node
def iter(self): if not iter.head: return cur = self.head yield cur.data while cur.next: cur = cur.next yield cur.data #先判断是不是空链表,yield head.data 再用while循环遍历
链表的头结点head 和 尾节点tail 都属于node.
insert:先将要插入的节点的next指向之后链表的head,然后将之前链表的next指向 将要插入的节点。
def insert(self, idx, value): cur = self.head cur_idx = 0 if cur is None: raise Exception('That list is and empty list!') while cur_idx < idx-1: cur = cur.next if cur is None: raise Exception('List length less than index!') cur_idx += 1 node = Node(value) node.next = cur.next cur.next = node if node.next is None: self.tail = node
def remove(self, idx): cur = self.head cur_idx = 0 #空指针 if self.head = None: raise Exception('This is an empty list') while cur_idx < idx-1: cur = cur.next #给出的索引大于链表的长度 if cur is None: raise Exception('list length less than index') cur_idx +=1 if idx == 0: #当删除第一个节点时 self.head = cur.next cur = cur.next return if self.head is self.tail: #当只有一个节点时 self.head = None self.tail = None return cur.next = cur.next.next if cur.next is None: #当删除最后一个节点时 self.tail = cur
def size(self): i = 0 cur = self.head if current is None: return 'The list is an empty list' while cur.next is not None: i +=1 cur = cur.next return i
def search(self, item): current = self.head found = False while current is not None and not found: if current.data == item: found = True else: current = current.next return found
1,迭代
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #!/bin/env python # Python2.7 class Node(object): def __init__(self): self.value = None self.next = None def __str__(self): return str(self.value) def reverse_list(head): if not head or not head.next: return head pre = None while head: next = head.next # 缓存当前节点的向后指针,待下次迭代用 head.next = pre # 关键:把当前节点向前指针(pre)作为当前节点的向后指针 pre = head # 把当前指针赋值给 下次迭代 节点的 向前指针 head = next # 作为下次迭代时的(当前)节点 return pre # 返回头指针,头指针就是迭代最后一次的head(赋值给类pre) if __name__ == '__main__': three = Node() three.value = 3 two = Node() two.value = 2 two.next = three one = Node() one.value = 1 one.next = two head = Node() head.value = 0 head.next = one newhead = reverse_list(head) while newhead: print newhead.value newhead = newhead.next
比较形象的图
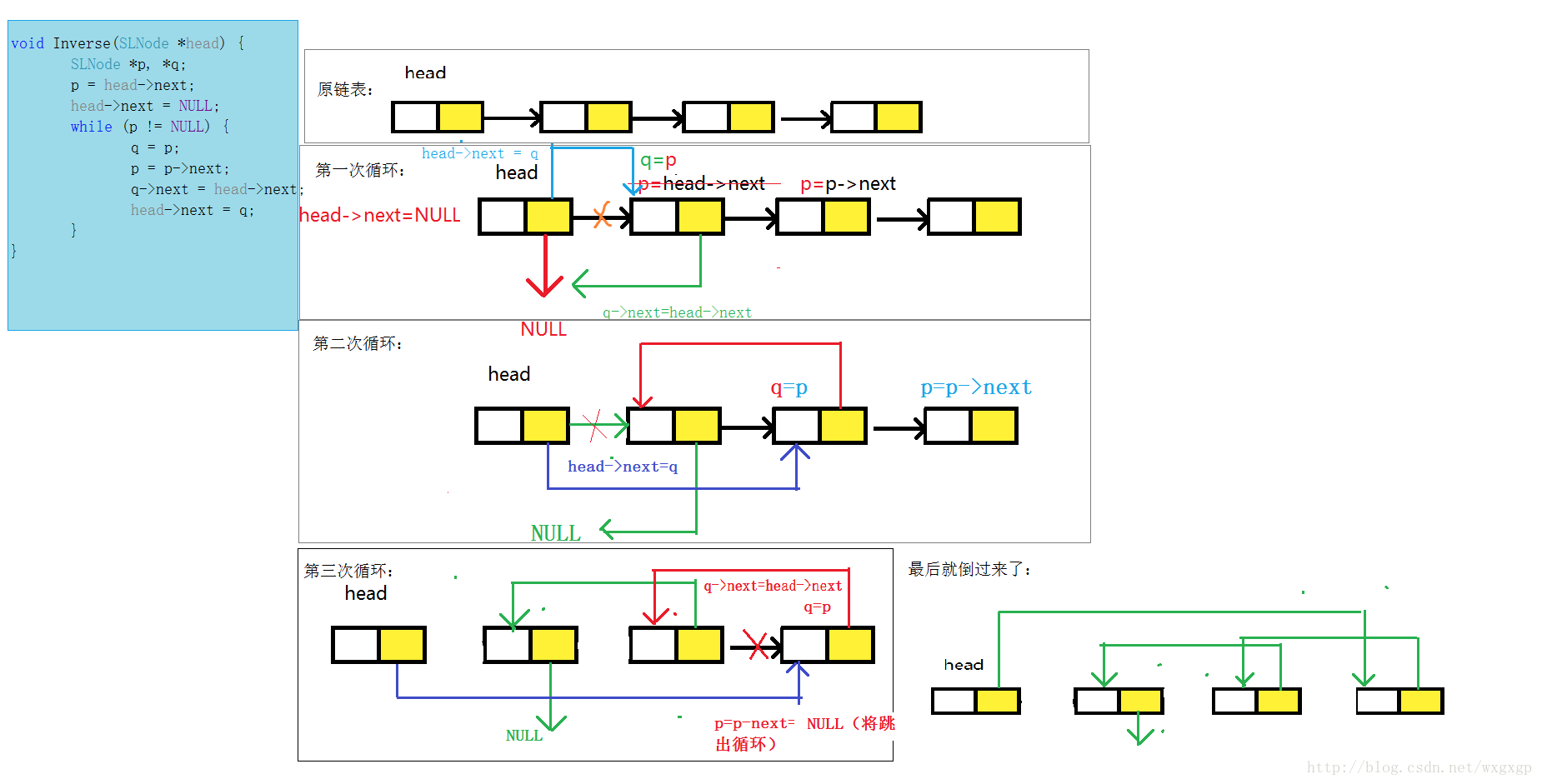
2,递归
# 临界点:head.next为None # 先递归到 把最后一个节点指向 newhead # 然后一步步从后往前逆置 def reverse_recursion(head): if not head or not head.next: return head new_head = reverse_recursion(head.next) head.next.next = head head.next = None return new_head



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号