小波变换 讲解分析 一篇EnglishBlog上的。
FT(Fourier Transform)可以找到频率中包含的信号。
信号信息往往不能从时域信号中看出,而能从频域信号中看出。病理情况在有些时候能够被容易的被检测出来,如果使用频率来分析的话。
除了FT外的transforms: Hillbert transform、 short-time Fourier transform 、 Winger distribution 、 Radon Transform等。
关于傅里叶级数(Fourier coefficients) 和傅里叶变换(Fourier Transform)
- 傅里叶级数:
任何满足狄利克雷收敛条件的周期函数都能用一系列三角函数的和来表示。
- 傅里叶变换:
傅里叶变换从傅里叶级数变换而来,且傅里叶变换的应用不仅限于周期函数,也适用于非周期函数。
傅里叶级数是基于周期为2Π的三角函数系推导出来,其积分域为对称的Π区间,从而推导出特殊形式的傅里叶级数形式,然后将周期拓展到以T为周期,结合欧拉公式变换,将特殊傅里叶级数推广到一般。最后,当周期T趋向于无穷大时,确定出傅里叶变换公式。
FT是一个可逆的变换。FT可以信号在时域信息和频域信息之间进行转换。但每种信息仅包含其对应的特征。
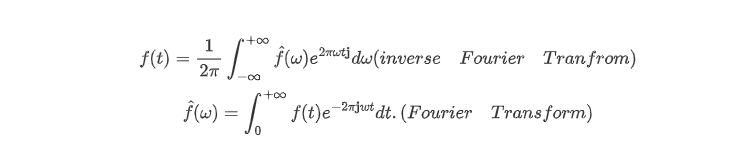
Let's take a closer look at this stationarity concept more closely, since it is of paramount importance in signal analysis. Signals whose frequency content do not change in time are called stationary signals. In other words, the frequency content of stationary signals do not change in time. In this case, one does not need to know at what times frequency components exist, since all frequency components exist at all times!!!
平稳信号
非平稳信号("chirp" signal)
图1.8也是一个非平稳信号,不同时间段(time interval)的频率不一样。
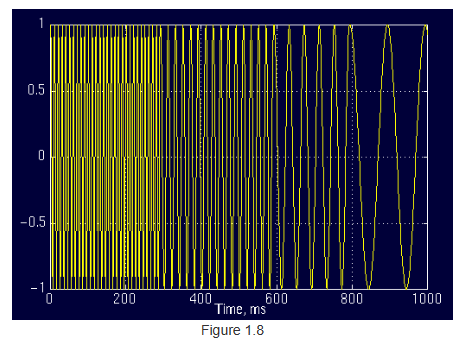
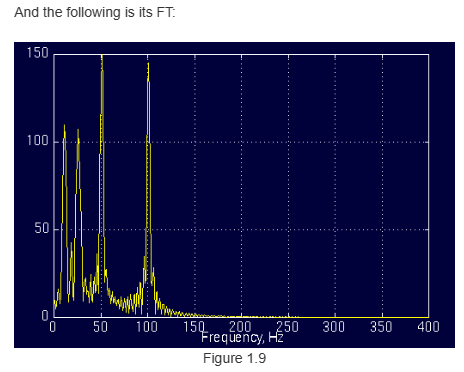
图片中的"涟漪"(ripples)是因为一种频率的波形向另一种频率的波形快速变换所形成的。
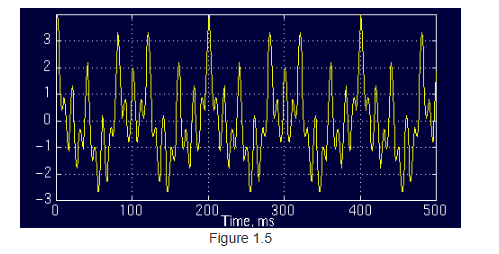
FT对非平稳信号转换不合适,FT仅仅只会将是否有谱信息检测出来,而不能检测谱信息在哪。像ECG、EEG、EMG(electrical activity of the muscles)都是非平稳信号。cite as: Once again please note that, the FT gives what frequency components (spectral components) exist in the signal. Nothing more, nothing less.
- wavelet trransform 是一个对STFT(Short-time Fourier transform)的替代品。
视频理解 医学信号处理-小波变换-卢家峰教授课程
STFT不足够
STFT(Short-Time Fourier Transform)简析:
短时傅里叶变换只是在傅里叶变换中加入一个个window,使得每个部分都是均分的。
小波变换的基本使用方法:先是选择基本小波,然后将基本小波平移,缩放,生成一个函数族,构成一个框架,将信号向该框架上投影得到分解信号。选择合适的小波函数,对脑电信号变换,突出需要的特征波形。通过阈值判断,确定是否为待检测的特征波形。
几种很常见的小波:多贝西小波(Signal processing and machine learning for biomedical big data论文上用的就是), Harr小波, Morlet 小波, Mexican hat 小波等。后续看到论文再进行补充
- 高频成分仅需较短的时间长度来呈现(讯号变动快);
- 低频的成分需要较长的时间长度来量测(讯号变动慢)。(STFT,Short Time Fourier Transform)
Sampling方法会Dynamice地调整每个window.
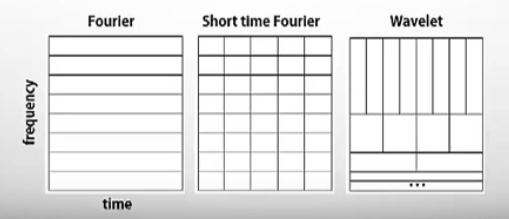
- Wavelet Transform 是一个dynamic 的过程,动态地调整高低频不同窗口(window)的状态(bases)。
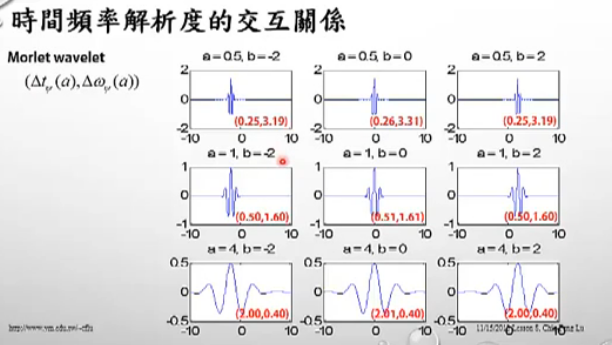
- WaveLet中每个矩形的面积应该是一样的。peak很smooth(相比于STFT)。
连续小波变换(Continus wavelet Transform)
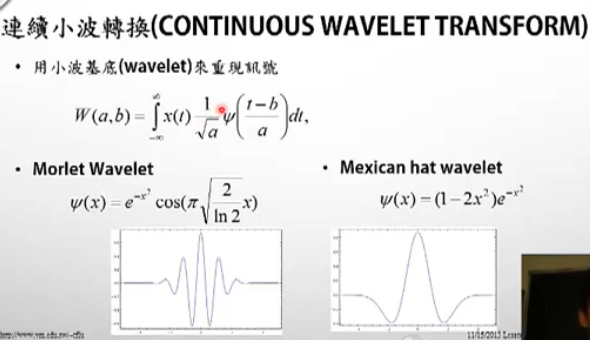
很像window function 的概念,但不是window function.
- 上述函数中的a,b会使小波的形状作出改变,a会使小波进行延展,a的值越大,小波间隔变大,b参数调控小波的平移(translation)。
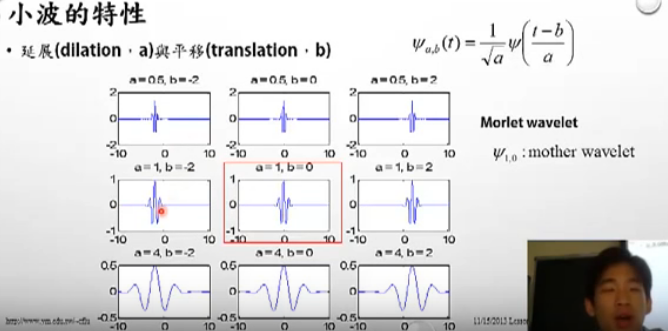
如何去设计小波是关键。使小波去拟合数据的特征
-
使用a和b去调控小波的频率特性;
a大的话,会拉长波段,a小的话,会缩小波段;
b会影响峰值,b越大,峰值越大

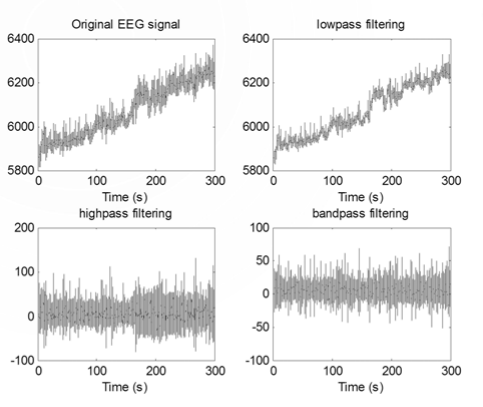
Filter(digital filter)
- 将信号的频谱成分作调整;(对EEG信号中感兴趣的通常在50Hz以下)
HighPass Filter
LowPass Filter
BandPass Filter
波形在三者转换后的变化:
Signal processing and machine learning for biomedical big data算法部分记录
3.1 DataSets
数据集划分,共分五种划分方式:
A,B以眼睛睁闭划分;划分依据:睁闭眼和癫痫的关系
C、D:从海马体到,大脑癫痫发作区相反的位置,C、D均是在未发作时采集;
E:癫痫发作时,海马体的情况。
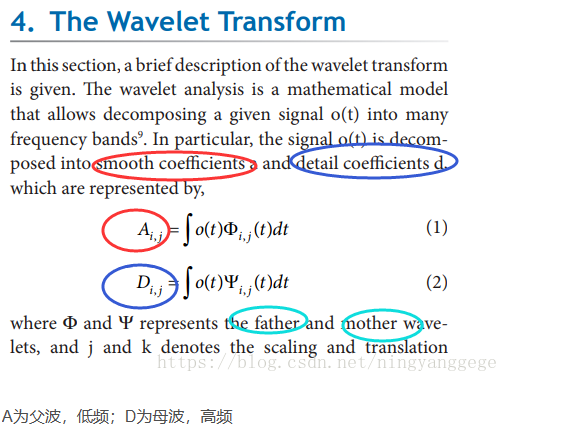
3.2 WaveLet
使用小波变换函数对数据进行时频域划分,低时(lower scale)有高频信息,高时(high scale)有低频成分信息。
使用多贝西基本小波(db_4)作为基本波,然后使用。
Approxiamtion coeffcients (低频系数)
Detail Coeffcients(高频系数)

3.3 Arithmetic coding
算数编码:先得到每个字符对应的频率,首先从(0,1]的区间里进行划分,以第一个字符的频率p_1做如下划分:[0,p_1], 然后依[0,p_1]为原区间,以第二个字符的频率再对[0,p_1]区间进行划分,依次类推。假设编码序列为(x_1 ,x_2 ,x_3 ,x_3 ,x_4)编码结果即如下:
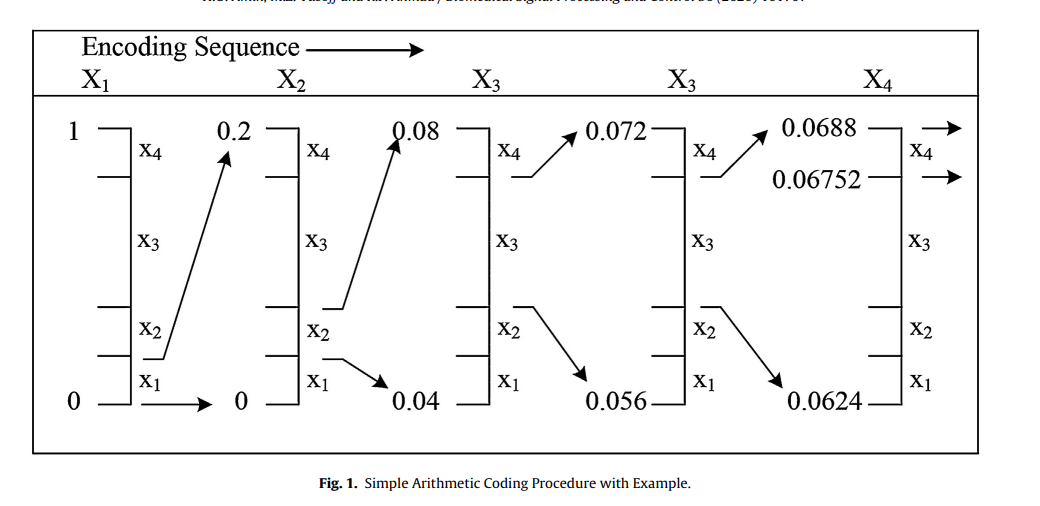
First, the complete sequence is considered to occupy the entire half open interval [0, 1). This interval is subdivided into four parts based on the probabilities of the source symbols. The first symbol of the sequence (x1) is associated with subinterval (0, 0.2); the sequence interval is narrowed to [0, 0.2). The subinterval[0, 0.2) is then stretched to the full height of the entire half-open interval [0, 1) and labeled with end points that hold narrowed range values [0, 0.2). Again, the narrowed range [0, 0.2) is then subdivided according to the original source symbol probabilities, whose process continues with the next symbol. Accordingly, x2 contracts to (0.04, 0.08), x3 narrows to (0.056, 0.072), and so on until the last symbol. The last symbol is used as a special indicator marking the end of the sequence, which narrows the range to (0.06752, 0.0688). At this point, any number with an interval, say 0.068, can represent the entire sequence.
CAD(Computer Aided Diagnostic)基本流程
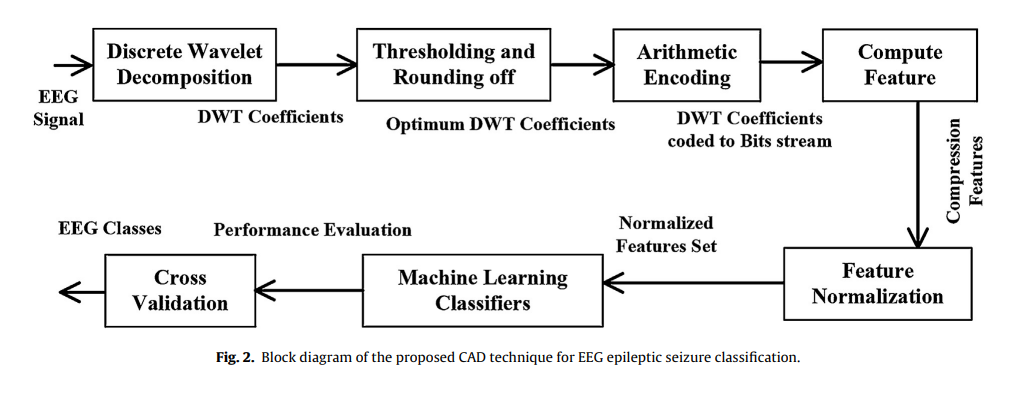
***1 Wavelet Decomposition ***
*** Decomposition of EEG signals via discrete wavelet transform.***
*** Apply threshold to coefficients such that reconstructed signal energy remains ∼99%, rounded to the nearest integer.***
*** 2 Feature Computation ***
***Encode DWT coefficients using Arithmetic coding. ***
Compute compression features. Standardize extracted features.
*** 3 Feature Classification ***
Classify features using machine-learning classifiers.
*** Evaluate performance via k-fold cross-validation and EEG classification results***
Daubechies wavelet
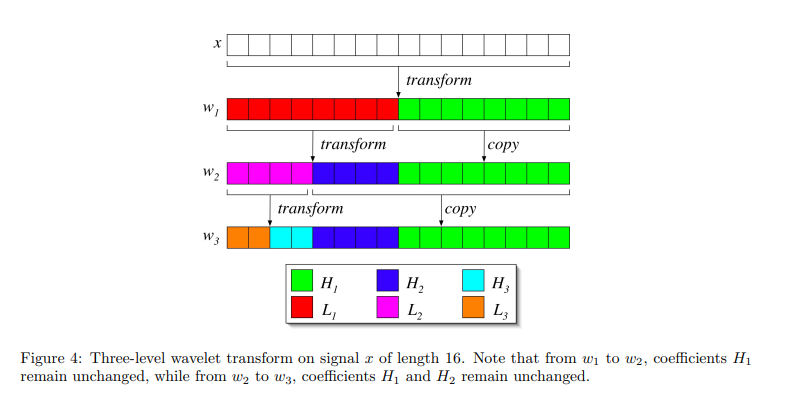
WaveLet Transform
One_dimensional wavelet transform and level-3 transfrom
Relationship between Low pass filter h and High pass filter g

Harr wavelet (use Harr filter)
low pass form:
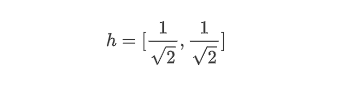
high pass form
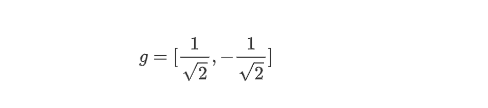
Daubechies-4 wavelet's low pass filter
$$
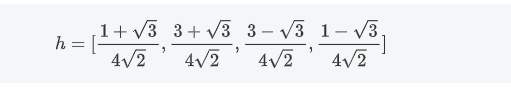
$$
或许可以从PywaveLets上找到灵感。
小波变换
用于处理EEG信号的通常是离散小波变换,即将伸缩银子和平移银子离散化,其优点是计算量少,但从分辨率的角度来看,离散小波变换较之于连续小波变换对频带的发呢姐较粗糙,
关于小波变换拟合数据:
先是选择基本小波,然后将基本小波平移,缩放,生成一个函数族,构成一个框架,将信号向该框架上投影得到分解信号。选择合适的小波函数,对脑电信号变换,突出需要的特征波形。通过阈值判断,确定是否为待检测的特征波形。
@IAI-AHU-Threemen-ZL

