第四次实验
任务1
#include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> void solve(double a, double b, double c); int main() { double a, b, c; printf("Enter a, b, c: "); while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c) != EOF) { solve(a, b, c); // 函数调用 printf("Enter a, b, c: "); } return 0; } void solve(double a, double b, double c) { double x1, x2; double delta, real, imag; if(a == 0) printf("not quadratic equation.\n"); else { delta = b*b - 4*a*c; if(delta >= 0) { x1 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2*a); x2 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2*a); printf("x1 = %f, x2 = %f\n", x1, x2); } else { real = -b/(2*a); imag = sqrt(-delta) / (2*a); printf("x1 = %f + %fi, x2 = %f - %fi\n", real, imag, real, imag); } } }
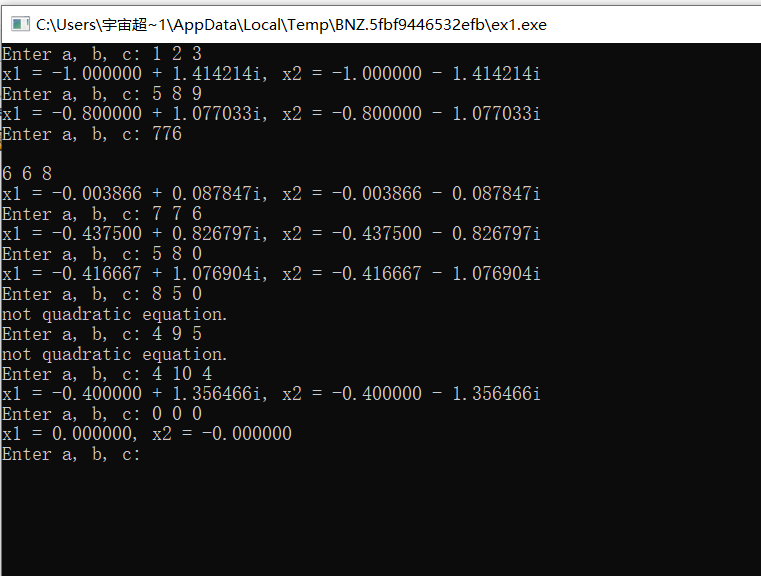
一元二次方程的根,可以设计成函数的返回值返回给主函数 ,只需要更改一下返回值的类型即可。
任务2
//利用局部变量static变量计算阶乘 #include <stdio.h> long long fac(int n); int main(){ int i,n; printf("Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d!=%lld\n",i,fac(i)); return 0; } //函数定义 long long fac( int n) { static long long p=1; p=p*n; return p; }
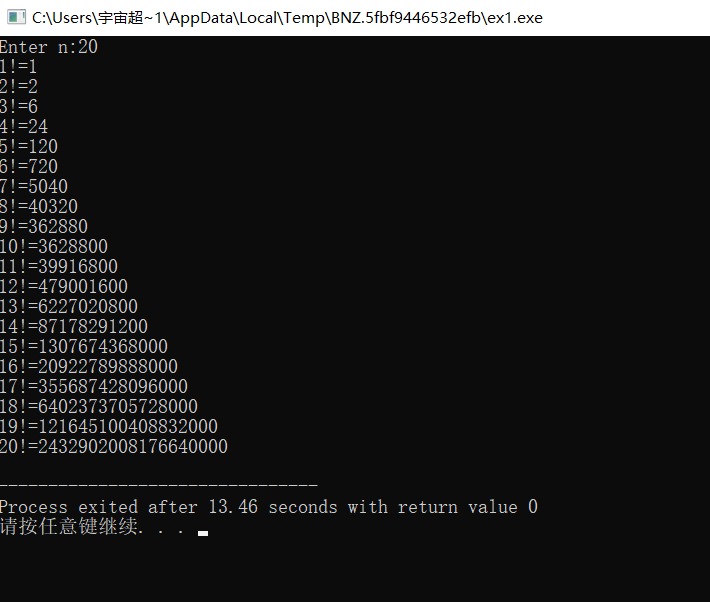
增加一行代码后,程序运行结果如图
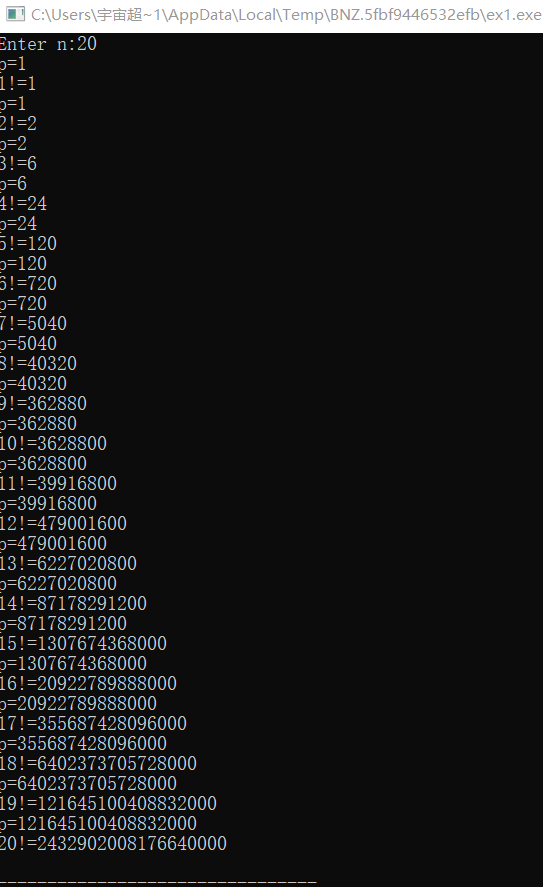
static变量的特性:在赋初始值时只赋值一次,其他次数保留上一次的值,具有继承性
实验任务3
#include <stdio.h> //寻找两个整数之间的所有素数(包括这两个素数),把结果保存在bb中,函数返回素数的个数 #define N 1000 int fun(int n,int m,int bb[N]){ int i,j,k=0,s; for(j=n;j<=m;j++) { s=1; for(i=2;i<j;i++) if(j%i==0) { s=0; break; } if(s) bb[k++]=j; } return k; } int main(){ int n=0,m=0,i,k,bb[N]; scanf("%d",&n); scanf("%d",&m); for(i=0;i<m-n;i++) bb[i]=0; k=fun(n,m,bb); for(i=0;i<k;i++) printf("%4d",bb[i]); return 0; }
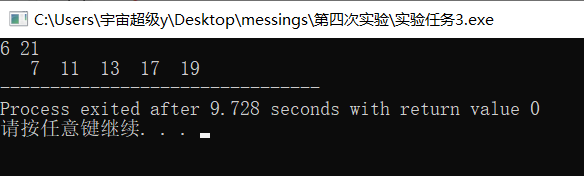
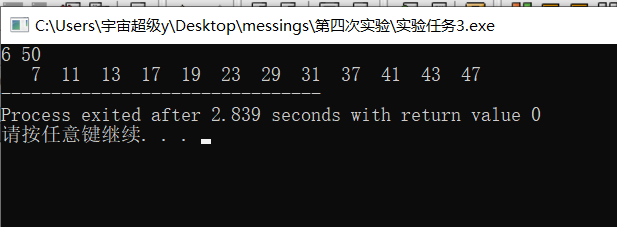
实验任务4
#include <stdio.h>
long long fun(int n);
int main() {
int n;
long long f;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
f = fun(n);
f=f-1;
printf("n = %d, f = %lld\n", n, f);
}
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
long long fun (int n)
{
if(n==0)
return 1;
else return 2*fun(n-1);
return 0;
}
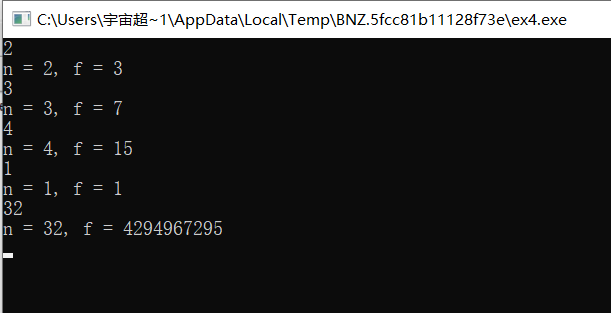
实验任务5
#include <stdio.h> void draw(int n, char symbol); #include <stdio.h> int main() { int n, symbol; while(scanf("%d %c", &n, &symbol) != EOF) { draw(n, symbol); printf("\n"); } return 0; } // 函数定义 void draw(int n,char symbol) { for(int s=1;s<=n;s++) { for(int k=n-s;k>0;k--) printf(" "); for(int k=1;k<=(2*s-1);k++) printf("%c",symbol); printf("\n"); } return; }
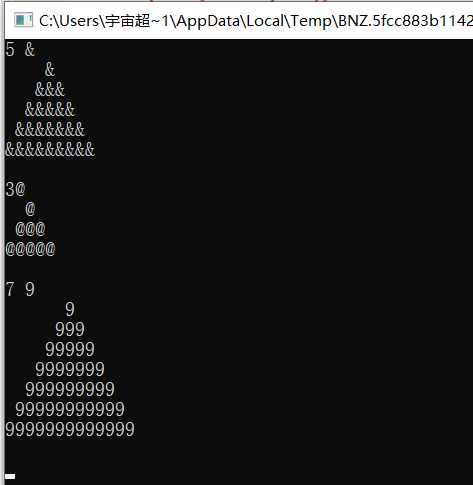
实验总结
学习的新内容:递归函数实现2的n次方,而不是依赖于pow函数。递归 的使用主要在于找到n项与前一项的规律
除了小细节会踩坑以外,还踩了无法统计,自己不能理解不能解释的坑的坑,对于循环结构的把握还是不熟悉
继续加油吧,虽然C语言逻辑性很强,但是加油去理解其背后的奥秘把,C语言YYDS!



