结对编程 四则运算(java)(胡大华 黄绪明)
Github项目地址
https://github.com/yogurt1998/Myapp
项目需求
题目:
实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序
功能
1.使用-n 参数控制生成题目的个数
2.使用-r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围
3.生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数
4. 生成的题目中如果存在形如e1 ÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。
5. 每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
6. 程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。
7.生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件
8.在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件
9. 程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
10. 程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,输入参数如下:
Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt
统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
PSP表格
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
15 |
20 |
|
Development |
开发 |
|
|
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
150 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
30 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
90 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
1000 |
1200 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
90 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
30 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
60 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
40 |
40 |
|
合计 |
|
1535 |
1900 |
设计实现过程
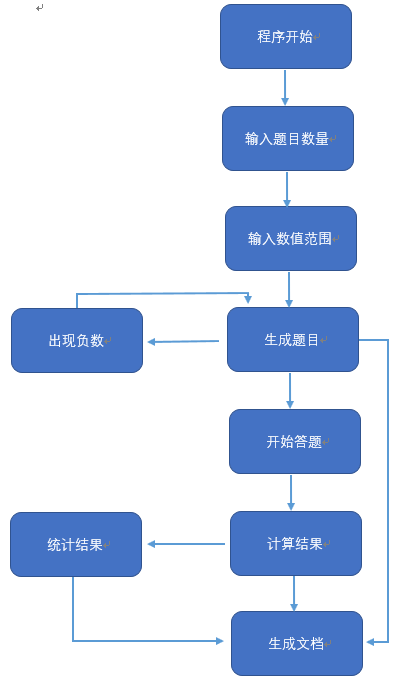
设计思路
先用随机函数得到随机生成题目,为了方便计算转为后缀表达式,用堆栈的方式计算答案,用一个布尔值来判断是否可用。
利用Scanner类获取键盘输入值并判断。
用一个while循环来生成多道题目。
用字符流输入到文件中。
代码说明
1. 用随机函数randon()生产随机数以及运算符组成题目
// 生成四则运算式
public Exercise createFormula(int n) {
String question1 = null;
String num1, num2, num3, num4; // 四个运算数
String char1, char2, char3; // 三个运算符
char1 = randomChar();
char2 = randomChar();
char3 = randomChar();
num1 = (int)(Math.random()*2) == 0 ? Integer.toString((int)Math.round(Math.random()*(n))) : createScore(n);
num2 = (int)(Math.random()*2) == 0 ? Integer.toString((int)Math.round(Math.random()*(n))) : createScore(n);
num3 = (int)(Math.random()*2) == 0 ? Integer.toString((int)Math.round(Math.random()*(n))) : createScore(n);
num4 = (int)(Math.random()*2) == 0 ? Integer.toString((int)Math.round(Math.random()*(n))) : createScore(n);
String question2 = num1 + ' ' + char1 + ' ' + num2;
String question3[] = {question2 + ' ' + char2 + ' ' + num3,
'(' + question2 + ')' + ' ' + char2 + ' ' + num3,
num1 + ' ' + char1 + ' ' + '(' + num2 + ' ' + char2 + ' ' + num3 + ')'};
String question4[] = {question3[(int)(Math.random()*3)] + ' ' + char3 + ' ' + num4,
'(' + question3[(int)(Math.random()*3)] + ')' + ' ' + char3 + ' ' + num4,
num4 + ' ' + char3 + ' ' + '(' + question3[(int)(Math.random()*3)] + ')',
'(' + question2 + ')' + ' ' + char2 + ' ' + num3 + ' ' + char3 + ' ' + num4,
question2 + ' ' + char2 + ' ' + '(' + num3 + ' ' + char3 + ' ' + num4 + ')',
num1 + ' ' + char1 + ' ' + '(' + num2 + ' ' + char2 + ' ' + num3 + ')' + ' ' + char3 + ' ' + num4};
switch ((int)(Math.random()*3)) {
case 0:
question1 = question2;
break;
case 1:
question1 = question3[(int)(Math.random()*3)];
break;
case 2:
question1 = question4[(int)(Math.random()*6)];
break;
default:
break;
}
Exercise exercise = new Exercise(num1, num2, num3, num4, char1, char2, char3, question1);
return exercise;
}
// 分数生成器
public String createScore(int n) {
int upNum, downNum;
do {
upNum = (int)Math.round(Math.random()*(n));
downNum = (int)Math.round(Math.random()*(n-1)+1);
} while (upNum / downNum > n);
return upNum > downNum ? upNum / (downNum - upNum % downNum) + "'" + (upNum % downNum) + "/" + downNum
: upNum + "/" + downNum;
}
// 随机运算符
private String randomChar() {
int key = (int)(Math.random()*4);
switch (key) {
case 0:
return "+";
case 1:
return "-";
case 2:
return "×";
case 3:
return "÷";
default:
break;
}
return "";
}
2. 读取和计算题目
1. 将String 类型的题目按运算数、运算符、括号转换为ArrayList<String>;
// String转为list private ArrayList<String> stringsToList(String s) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) { char c = s.charAt(i); if((c >= '0' && c <= '9') || c == '\'' || c == '/') { temp.append(c); } else { String string = temp.toString(); if (!string.isEmpty()) { list.add(string); } temp = new StringBuilder(); } if (i == s.length()-1) { String string = temp.toString(); if (!string.isEmpty()) { list.add(string); } } if (isOperator(c)) list.add(c + ""); if (c == '(' || c == ')') list.add(c + ""); } return list; }
2.将中缀表达式变为后缀表达式
// 中缀表达式转为后缀表达式 private ArrayList<String> changeToPostfixEx(ArrayList<String> list) { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); ArrayList<String> pList = new ArrayList<String>(); int level = -1; for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i) { String aList = list.get(i); if (!sIsOperator(aList) && !aList.equals("(") && !aList.equals( ")")) { pList.add(aList); } else if (aList.equals("(")) { stack.push(aList); level = 0; } else if (aList.equals( ")")){ while (!stack.peek().equals("(")) { pList.add(stack.pop()); } stack.pop(); if (stack.empty()) level = -1; else { level = getLevel(stack.peek()); } } else if (getLevel(aList) > level) { stack.push(aList); if (level != 0) level = getLevel(stack.peek()); } else { while (!stack.empty() && getLevel(aList) <= level) { pList.add(stack.pop()); } stack.push(aList); level = getLevel(stack.peek()); } } while (!stack.empty()) { pList.add(stack.pop()); } return pList; }
3. 计算后缀表达式得到答案
// 计算后缀表达式 private Score calculateHEx(ArrayList<String> list) { boolean beUse = true; // 是否使用 Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); ++i) { if (!sIsOperator(list.get(i))) { stack.push(list.get(i)); } else { Score result = new Score(); String resultS = null; switch (list.get(i)) { case "+": String a1 = stack.pop(); String a2 = stack.pop(); result = addScore(a2, a1); resultS = result.up + "/" + result.down; stack.push(resultS); break; case "-": String a3 = stack.pop(); String a4 = stack.pop(); result = subtractScore(a4, a3); resultS = result.up + "/" + result.down; stack.push(resultS); break; case "×": String a5 = stack.pop(); String a6 = stack.pop(); result = mulScore(a6, a5); resultS = result.up + "/" + result.down; stack.push(resultS); break; case "÷": String a7 = stack.pop(); String a8 = stack.pop(); result = divScore(a8, a7); resultS = result.up + "/" + result.down; stack.push(resultS); break; default: break; } beUse = result.canBeUse; } if (!beUse) break; } Score result = new Score(); result.canBeUse = beUse; if (result.canBeUse) { String endResult = stack.pop(); result.changeScore(endResult); list.add(endResult); simplifyScore(result); } return result; }
4.Score类表示所有的数,并用canBeUse属性表示是否可用。
import java.util.ArrayList; import javax.naming.InitialContext; public class Score { int up; int down; boolean canBeUse = true; // ËãʽÊÇ·ñ¿ÉÓà public Score() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public void changeScore(String s) { boolean isBig = false; boolean isHave = false; ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) { char c = s.charAt(i); if (c == '/') isHave = true; if (c == '\'') isBig = true; if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { temp.append(c); } else { list.add(temp.toString()); temp = new StringBuilder(); } if (i == s.length() - 1) { if (!temp.toString().isEmpty()) { list.add(temp.toString()); } } } if (list.isEmpty()) { canBeUse = false; } else { if (!isBig && !isHave) { this.up = Integer.parseInt(list.get(0)); this.down = 1; } else if (isBig) { this.up = Integer.parseInt(list.get(0)) * Integer.parseInt(list.get(2)) + Integer.parseInt(list.get(1)); this.down = Integer.parseInt(list.get(2)); } else if (isHave && !isBig){ this.up = Integer.parseInt(list.get(0)); this.down = Integer.parseInt(list.get(1)); } } } }
3. IO输出
用fileWrite()和BufferWrite();
public class IO { public void writeExercise(String context, int flag) { File exerFile = new File("D:\\test\\Exercise.txt"); File answerFile = new File("D:\\test\\Answer.txt"); if (flag == 0) { writeIn(context, exerFile); } else { writeIn(context, answerFile); } } private void writeIn(String context, File file) { FileWriter fileWriter; BufferedWriter brout; try { fileWriter = new FileWriter(file, true); brout = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter); brout.write(context); brout.flush(); brout.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4. 主函数
import java.util.Scanner; import javax.swing.CellEditor; public class main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String order = null; int exNum = 0, valueNum = 1; while (valueNum <= 1) { System.out.println("输入命令:1. 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数 2. 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); if (scanner.hasNext()) { order = scanner.next(); } if (scanner.hasNextLine()) { if (order.equals("-n")) { exNum = scanner.nextInt(); } else if (order.equals("-r")) { valueNum = scanner.nextInt(); } else { System.out.println("请输入正确的命令参数:1. 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数 2. 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围"); } } if (valueNum <= 1) { System.err.println("请输入正确的命令参数:1. 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数 2. 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围"); } } int i = 0; int j = 0; IO io = new IO(); while (j < exNum) { Func func = new Func(); Exercise exercise = func.createFormula(valueNum - 1); Score answer = func.calculateExercise(exercise.aQuestion); String endAnswer = null; if (answer.canBeUse) { if (answer.down == 1) { endAnswer = answer.up + ""; io.writeExercise(++j + ". " + exercise.aQuestion + " = " + "\r\n", 0); io.writeExercise(j + ". " + endAnswer + "\r\n", 1); } else if (answer.up > answer.down) { endAnswer = answer.up / (answer.down - answer.up % answer.down) + "'" + answer.up % answer.down + "/" + answer.down; io.writeExercise(++j + ". " + exercise.aQuestion + " = " + "\r\n", 0); io.writeExercise(j + ". " + endAnswer + "\r\n", 1); } } else { continue; } } } }
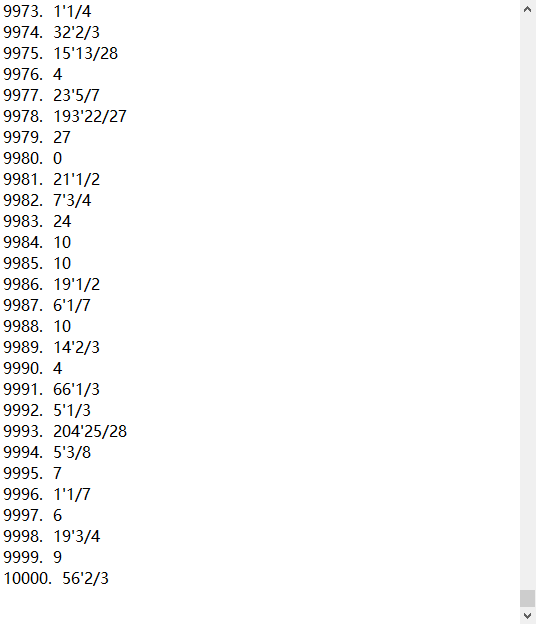
测试运行
题目:

答案:
项目小结
此次的结对编程,胡大华同学负责表达式的生成、计算,程序框架的设计,我负责IO生成文件、编写博文。
刚拿到题目的时候,我们的对题目只有一点模糊的想法,经过不断地写代码实现,逐渐发现不同的问题,遇到过各种问题和BUG,经过不断的学习和查找资料,最终解决问题。
这次的结对编程,让我体会到了合作的力量,同时也认识到了自己数据结构方面知识的不足,今后会多加学习这方面的知识,完善自己的不足。



