剑指25.复杂链表的复制
题目描述
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针random指向一个随机节点),请对此链表进行深拷贝,并返回拷贝后的头结点。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)
思路
思路1:先复制结点,用next链接,最后根据原始结点的random指针确定该random结点距离头结点的位置,从而对复制结点设置random指针。但是该思路对于n个结点的链表,定位每个节点的random都需要从链表头节点开始经过O(n)步才能找到,所以时间复杂度为O(n^2)。 (时间主要花费在定位节点的random上)
思路2:复制原始结点N创建N’,用next链接。将<N,N'>的配对信息存放入一个哈希表中;在设置random时,通过哈希表,只需要用O(1)的时间即可找到复制结点的random。该方法的时间复杂度为O(n),但空间复杂度为O(n)。 (相当于空间换时间)
思路3:不用辅助空间的情况下,实现O(n)的时间效率。该方法分为三个步骤。
第一步:复制原始链表的任意节点N并创建新节点N',再把N'链接到N的后面
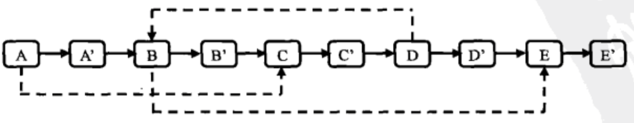
第二步:把复制的节点的random指针指向被复制节点的random指针的下一个节点
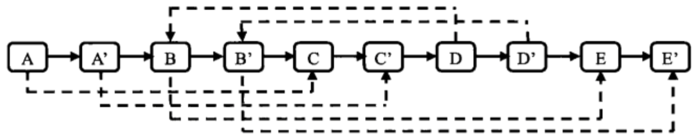
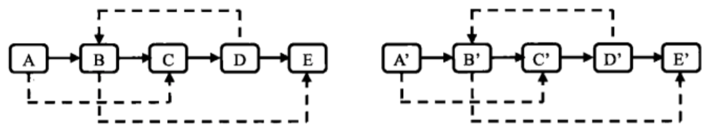
第三步: 拆分成两个链表,奇数位置为原链表,偶数位置为复制链表,注意复制链表的最后一个结点的next指针不能跟原链表指向同一个空结点None,next指针要重新赋值None(判定程序会认定你没有完成复制)
解法1(对应思路3)
/* public class RandomListNode { int label; RandomListNode next = null; RandomListNode random = null; RandomListNode(int label) { this.label = label; } } */ public class Solution { public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) { if (pHead == null) return null; cloneNodes(pHead); // 复制节点 connectRandomNodes(pHead); // 设置random return reconnectNodes(pHead); // 拆分长链表 } // 第一步:复制每个结点,并插入到原始节点的后面 private void cloneNodes(RandomListNode pHead){ RandomListNode currentNode = pHead; while (currentNode != null){ RandomListNode cloneNode = new RandomListNode(currentNode.label); cloneNode.next = currentNode.next; cloneNode.random = null; currentNode.next = cloneNode; currentNode = cloneNode.next; } } // 第二步:根据原节点的random,设置复制节点的random private void connectRandomNodes(RandomListNode pHead){ RandomListNode currentNode = pHead; while (currentNode != null){ if (currentNode.random != null) currentNode.next.random = currentNode.random.next; // 指向原始节点random指向的下一个节点 currentNode = currentNode.next.next; } } // 第三步:将长链表拆分成原始链表和复制链表(根据奇偶位置) private RandomListNode reconnectNodes(RandomListNode pHead){ RandomListNode currentNode = pHead; RandomListNode pCloneHead = pHead.next; while (currentNode != null){ RandomListNode pCloneNode = currentNode.next; if (pCloneNode.next != null){ currentNode.next = pCloneNode.next; pCloneNode.next = currentNode.next.next; }else{ currentNode.next = null; pCloneNode.next = null; } currentNode = currentNode.next; } return pCloneHead; } }
解法2(对应思路2)
/* public class RandomListNode { int label; RandomListNode next = null; RandomListNode random = null; RandomListNode(int label) { this.label = label; } } */ import java.util.HashMap; /* 使用哈希表,时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(N) 需要2次遍历即可 */ public class Solution { public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) { if (pHead == null) return null; HashMap<RandomListNode,RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode>(); RandomListNode currentNode = pHead; // 第一次遍历,新建节点,将<N,N'>的配对信息放到Map中 while (currentNode != null){ map.put(currentNode, new RandomListNode(currentNode.label)); currentNode = currentNode.next; } // 第二次遍历,设置复制节点的属性next和random currentNode = pHead; while (currentNode != null){ RandomListNode cloneNode = map.get(currentNode); // 注意复制链表的最后一个结点的next指针不能跟原链表指向同一个空结点 cloneNode.next = currentNode.next == null ? null : map.get(currentNode.next); cloneNode.random = currentNode.random == null ? null : map.get(currentNode.random); currentNode = currentNode.next; } return map.get(pHead); } }

