列表渲染
用 v-for 把一个数组对应为一组元素
我们可以用
v-for指令基于一个数组来渲染一个列表。v-for指令需要使用item in items形式的特殊语法,其中items是源数据数组,而item则是被迭代的数组元素的别名。
<ul id="example-1"> <li v-for="item in items" :key="item.message"> {{ item.message }} </li> </ul>
var example1 = new Vue({ el: '#example-1', data: { items: [ { message: 'Foo' }, { message: 'Bar' } ] } })
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>用 v-for 把一个数组对应为一组元素</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="item in items" :key="item.message"> {{item.message}} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { items: [ { message: '黄子涵是帅哥!'}, { message: '黄子涵是靓仔!'}, { message: '黄子涵真聪明!'}, { message: '黄子涵真厉害!'} ] } }) </script> </body> </html>
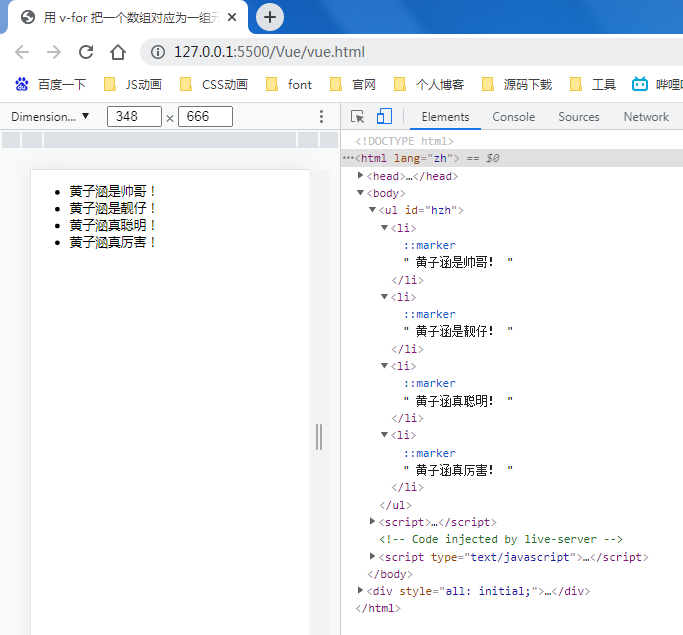
在
v-for块中,我们可以访问所有父作用域的 property。v-for还支持一个可选的第二个参数,即当前项的索引。
<ul id="example-2"> <li v-for="(item, index) in items"> {{ parentMessage }} - {{ index }} - {{ item.message }} </li> </ul>
var example2 = new Vue({ el: '#example-2', data: { parentMessage: 'Parent', items: [ { message: 'Foo' }, { message: 'Bar' } ] } })
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>用 v-for 把一个数组对应为一组元素</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="(item, index) in items"> {{ parentMessage }} - {{ index }} - {{ item.message }} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { parentMessage: '黄子涵', items: [ { message: '黄子涵是帅哥!'}, { message: '黄子涵是靓仔!'}, { message: '黄子涵真聪明!'}, { message: '黄子涵真厉害!'} ] } }) </script> </body> </html>
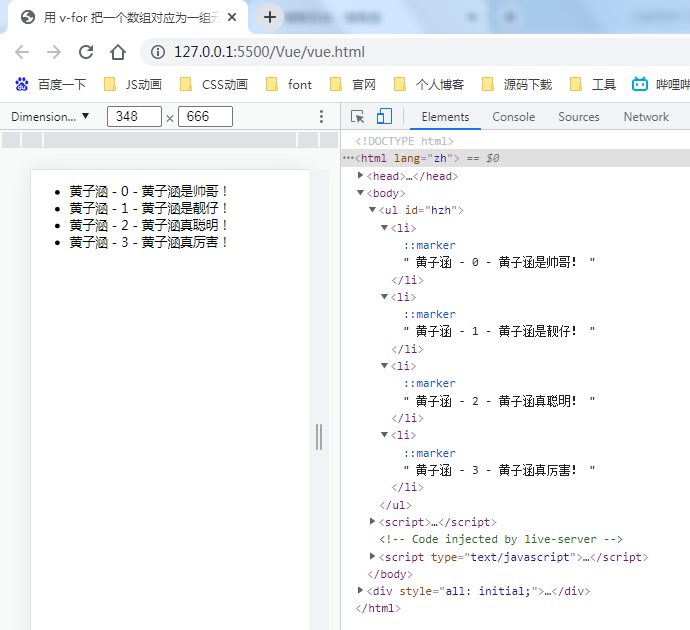
你也可以用
of替代in作为分隔符,因为它更接近 JavaScript 迭代器的语法:
<div v-for="item of items"></div>
在 v-for 里使用对象
你也可以用
v-for来遍历一个对象的 property。
<ul id="v-for-object" class="demo"> <li v-for="value in object"> {{ value }} </li> </ul>
new Vue({ el: '#v-for-object', data: { object: { title: 'How to do lists in Vue', author: 'Jane Doe', publishedAt: '2016-04-10' } } })
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>在 v-for 里使用对象</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="value in object"> {{ value}} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { object: { name: '黄子涵', tall: '177cm', tel: 19124896017 } } }) </script> </body> </html>
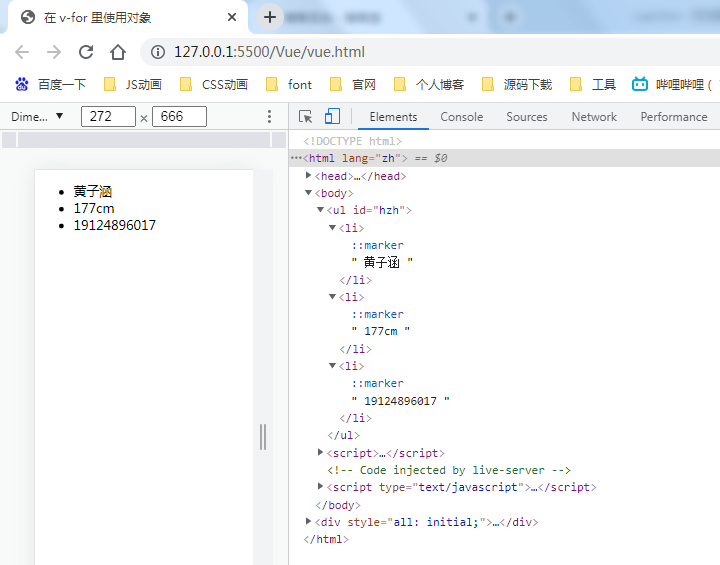
你也可以提供第二个的参数为 property 名称 (也就是键名):
<div v-for="(value, name) in object"> {{ name }}: {{ value }} </div>
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>在 v-for 里使用对象</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="(value, name) in object"> {{ name }} : {{ value }} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { object: { 名字: '黄子涵', 身高: '177cm', 手机号码: 19124896017 } } }) </script> </body> </html>
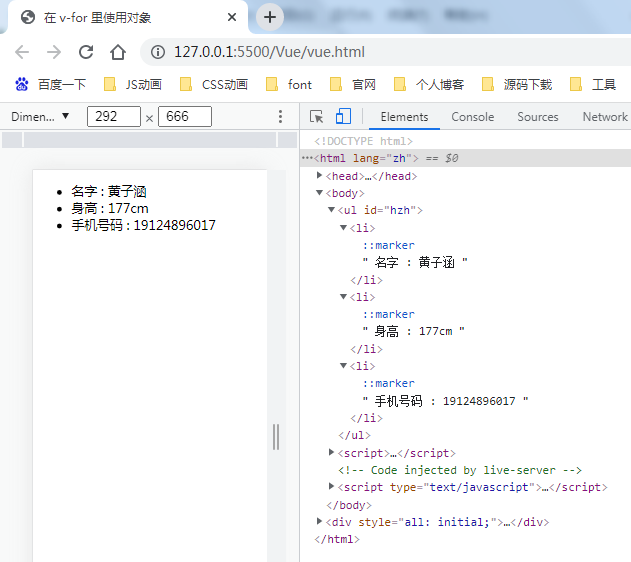
还可以用第三个参数作为索引:
<div v-for="(value, name, index) in object"> {{ index }}. {{ name }}: {{ value }} </div>
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>在 v-for 里使用对象</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="(value, name, index) in object"> {{ index }}.{{ name }} : {{ value }} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { object: { 名字: '黄子涵', 身高: '177cm', 手机号码: 19124896017 } } }) </script> </body> </html>
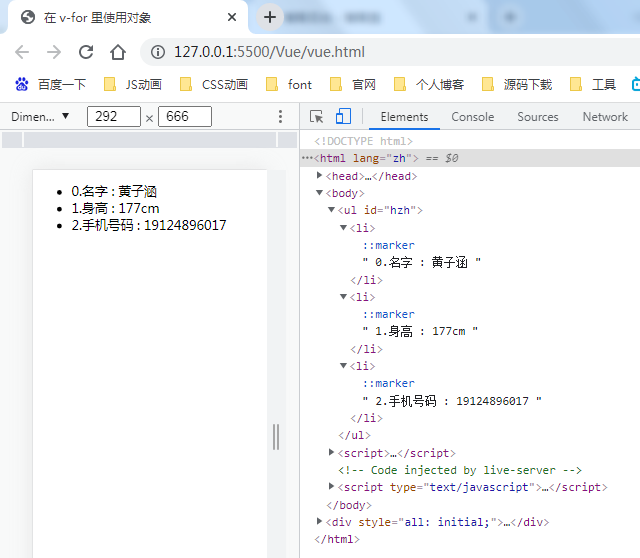
在遍历对象时,会按
Object.keys()的结果遍历,但是不能保证它的结果在不同的 JavaScript 引擎下都一致。
维护状态
当 Vue 正在更新使用
v-for渲染的元素列表时,它默认使用“就地更新”的策略。如果数据项的顺序被改变,Vue 将不会移动 DOM 元素来匹配数据项的顺序,而是就地更新每个元素,并且确保它们在每个索引位置正确渲染。这个类似 Vue 1.x 的track-by="$index"。
这个默认的模式是高效的,但是只适用于不依赖子组件状态或临时 DOM 状态 (例如:表单输入值) 的列表渲染输出。
为了给 Vue 一个提示,以便它能跟踪每个节点的身份,从而重用和重新排序现有元素,你需要为每项提供一个唯一
keyattribute:
<div v-for="item in items" v-bind:key="item.id"> <!-- 内容 --> </div>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>维护状态</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="hzh"> <div v-for="item in items" v-bind:key="item.id"> {{ items }} </div> </div> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { items: [ '黄子涵是帅哥!', '黄子涵是靓仔!', '黄子涵真聪明!', '黄子涵真厉害!' ] } }) </script> </body> </html>
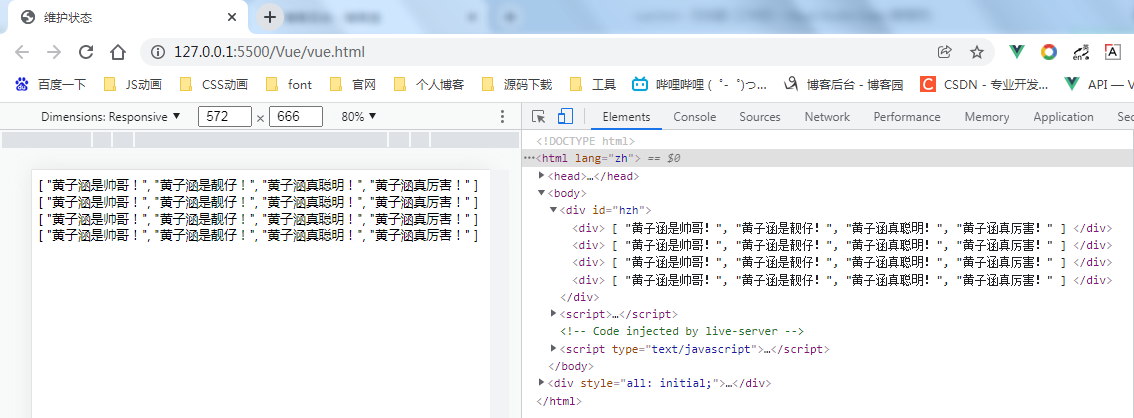
建议尽可能在使用
v-for时提供keyattribute,除非遍历输出的 DOM 内容非常简单,或者是刻意依赖默认行为以获取性能上的提升。
因为它是 Vue 识别节点的一个通用机制,
key并不仅与v-for特别关联。
不要使用对象或数组之类的非基本类型值作为 v-for 的 key。请用字符串或数值类型的值。
数组更新检测
变更方法
Vue 将被侦听的数组的变更方法进行了包裹,所以它们也将会触发视图更新。这些被包裹过的方法包括:
push()pop()shift()unshift()splice()sort()reverse()
你可以打开控制台,然后对前面例子的
items数组尝试调用变更方法。比如example1.items.push({ message: 'Baz' })。
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>变更方法</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="item in items" :key="item.message"> {{item.message}} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { items: [ { message: '黄子涵是帅哥!'}, { message: '黄子涵是靓仔!'}, { message: '黄子涵真聪明!'}, { message: '黄子涵真厉害!'} ] } }) </script> </body> </html>
替换数组
变更方法,顾名思义,会变更调用了这些方法的原始数组。相比之下,也有非变更方法,例如
filter()、concat()和slice()。它们不会变更原始数组,而总是返回一个新数组。当使用非变更方法时,可以用新数组替换旧数组:
example1.items = example1.items.filter(function (item) { return item.message.match(/Foo/) })
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>替换数组</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="item in items" :key="item.message"> {{item.message}} </li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { items: [ { message: '黄子涵是帅哥!'}, { message: '黄子涵是靓仔!'}, { message: '黄子涵真聪明!'}, { message: '黄子涵真厉害!'} ] } }) </script> </body> </html>
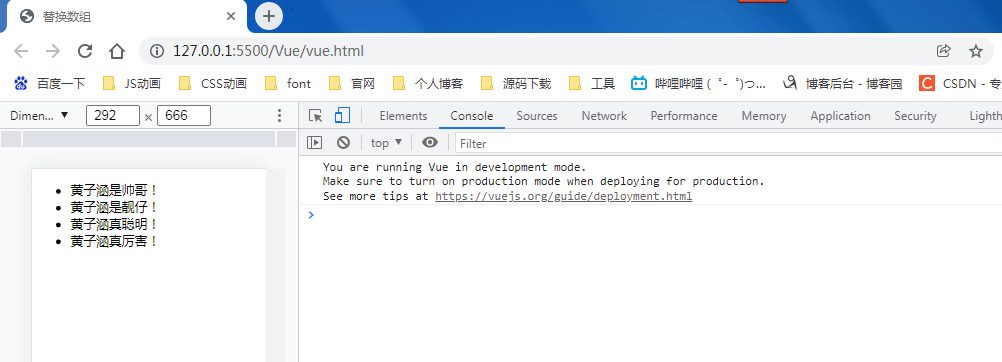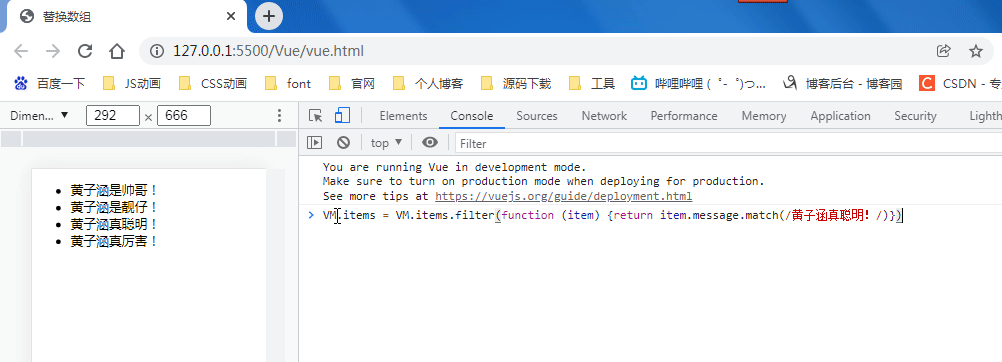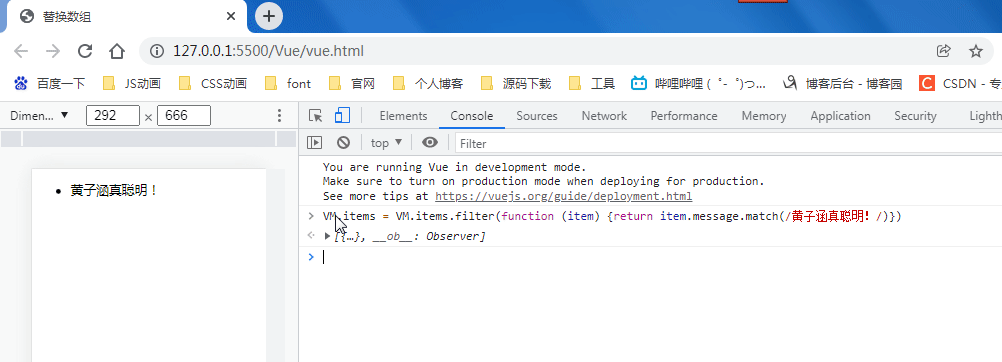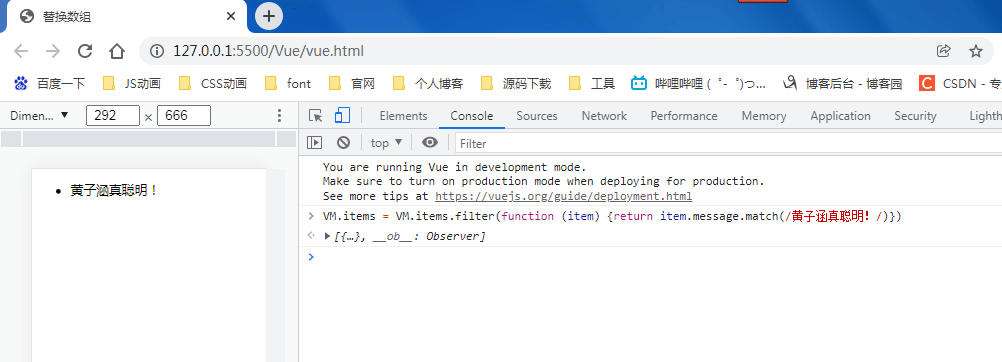
你可能认为这将导致 Vue 丢弃现有 DOM 并重新渲染整个列表。幸运的是,事实并非如此。Vue 为了使得 DOM 元素得到最大范围的重用而实现了一些智能的启发式方法,所以用一个含有相同元素的数组去替换原来的数组是非常高效的操作。
注意事项
由于 JavaScript 的限制,Vue 不能检测数组和对象的变化。深入响应式原理中有相关的讨论。
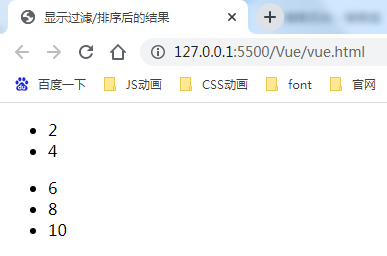
显示过滤/排序后的结果
有时,我们想要显示一个数组经过过滤或排序后的版本,而不实际变更或重置原始数据。在这种情况下,可以创建一个计算属性,来返回过滤或排序后的数组。
例如:
<li v-for="n in evenNumbers">{{ n }}</li>
data: { numbers: [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ] }, computed: { evenNumbers: function () { return this.numbers.filter(function (number) { return number % 2 === 0 }) } }
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>显示过滤/排序后的结果</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <ul id="hzh"> <li v-for="n in evenNumbers">{{ n }}</li> </ul> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { numbers: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] }, computed: { evenNumbers: function() { return this.numbers.filter(function (number) { return number % 2 === 0 }) } } }) </script> </body> </html>
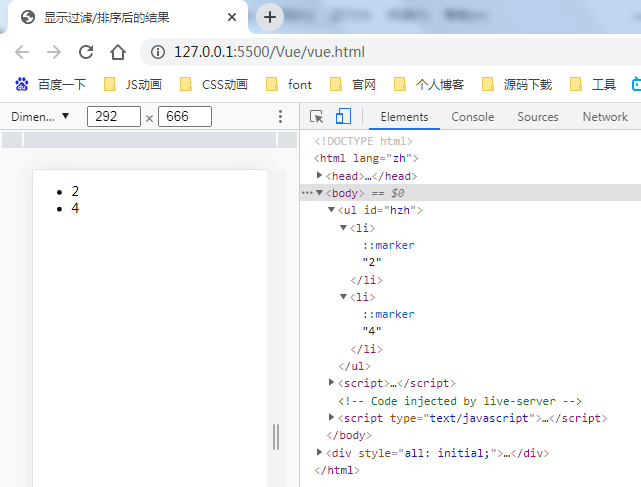
在计算属性不适用的情况下 (例如,在嵌套
v-for循环中) 你可以使用一个方法:
<ul v-for="set in sets"> <li v-for="n in even(set)">{{ n }}</li> </ul>
data: { sets: [[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]] }, methods: { even: function (numbers) { return numbers.filter(function (number) { return number % 2 === 0 }) } }
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>显示过滤/排序后的结果</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="hzh"> <ul v-for="set in sets"> <li v-for="n in even(set)">{{ n }}</li> </ul> </div> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', data: { sets: [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]] }, methods: { even: function (numbers) { return numbers.filter(function (number) { return number % 2 === 0 }) } } }) </script> </body> </html>
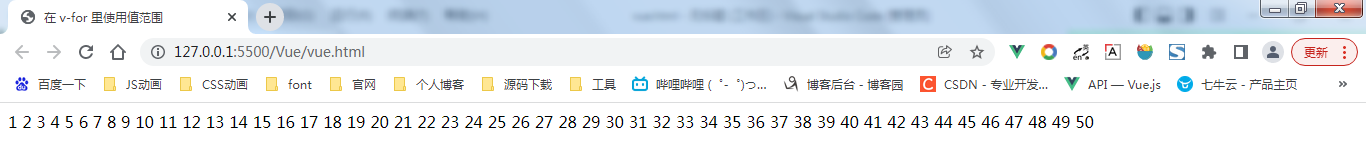
在 v-for 里使用值范围
v-for也可以接受整数。在这种情况下,它会把模板重复对应次数。
<div> <span v-for="n in 10">{{ n }} </span> </div>
点击查看代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>在 v-for 里使用值范围</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="hzh"> <span v-for="n in 50">{{ n }} </span> </div> <script> var VM = new Vue({ el: '#hzh', }) </script> </body> </html>
在 <template> 上使用 v-for
类似于
v-if,你也可以利用带有v-for的<template>来循环渲染一段包含多个元素的内容。比如:
<ul> <template v-for="item in items"> <li>{{ item.msg }}</li> <li class="divider" role="presentation"></li> </template> </ul>
v-for 与 v-if 一同使用
注意我们不推荐在同一元素上使用
v-if和v-for。
当它们处于同一节点,
v-for的优先级比v-if更高,这意味着v-if将分别重复运行于每个v-for循环中。当你只想为部分项渲染节点时,这种优先级的机制会十分有用,如下:
<li v-for="todo in todos" v-if="!todo.isComplete"> {{ todo }} </li>
上面的代码将只渲染未完成的 todo。
而如果你的目的是有条件地跳过循环的执行,那么可以将
v-if置于外层元素 (或<template>) 上。如:
<ul v-if="todos.length"> <li v-for="todo in todos"> {{ todo }} </li> </ul> <p v-else>No todos left!</p>
在组件上使用 v-for
在自定义组件上,你可以像在任何普通元素上一样使用
v-for。
<my-component v-for="item in items" :key="item.id"></my-component>
2.2.0+ 的版本里,当在组件上使用
v-for时,key现在是必须的。
然而,任何数据都不会被自动传递到组件里,因为组件有自己独立的作用域。为了把迭代数据传递到组件里,我们要使用 prop:
<my-component v-for="(item, index) in items" v-bind:item="item" v-bind:index="index" v-bind:key="item.id" ></my-component>
不自动将
item注入到组件里的原因是,这会使得组件与v-for的运作紧密耦合。明确组件数据的来源能够使组件在其他场合重复使用。
下面是一个简单的 todo 列表的完整例子:
<div id="todo-list-example"> <form v-on:submit.prevent="addNewTodo"> <label for="new-todo">Add a todo</label> <input v-model="newTodoText" id="new-todo" placeholder="E.g. Feed the cat" > <button>Add</button> </form> <ul> <li is="todo-item" v-for="(todo, index) in todos" v-bind:key="todo.id" v-bind:title="todo.title" v-on:remove="todos.splice(index, 1)" ></li> </ul> </div>
注意这里的
is="todo-item"attribute。这种做法在使用 DOM 模板时是十分必要的,因为在<ul>元素内只有<li>元素会被看作有效内容。这样做实现的效果与<todo-item>相同,但是可以避开一些潜在的浏览器解析错误。
Vue.component('todo-item', { template: '\ <li>\ {{ title }}\ <button v-on:click="$emit(\'remove\')">Remove</button>\ </li>\ ', props: ['title'] }) new Vue({ el: '#todo-list-example', data: { newTodoText: '', todos: [ { id: 1, title: 'Do the dishes', }, { id: 2, title: 'Take out the trash', }, { id: 3, title: 'Mow the lawn' } ], nextTodoId: 4 }, methods: { addNewTodo: function () { this.todos.push({ id: this.nextTodoId++, title: this.newTodoText }) this.newTodoText = '' } } })



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?