Data Structure and Algorithms Analysis in C Note (I)
Four basic rules of recursion:
- Base cases
- Making progress
- Design rules: Assume that all recursive calls work.
- Compound Interest Rule: Never duplicate work by solving the same instance of a problem in separate recursive calls.
Two most common ways of proving statements: by induction and by contradiction.
Modular Arithmetic:
A is congruent to B modulo N, written A ≡
B if N divides A – B(The remainder is the same when either A or B is divide by N.).
The term procedure refers to a function that returns void.
[X] is the largest integer that is less than or equal to X.
log X < X for all X > 0; log2 = 1; log1024 = 10; log1048576 = 20.
Positive Constants: c, n0. Precondition: N >= n0
- T(N) = O(f(N)) such that T(N) <= cf(N)
- T(N) = Ω(g(N)) such that T(N) >= cg(N)
- T(N) = Θ(h(N)) if and only if T(N) = Θ(h(N)) and T(N) =Ω(h(N))
- T(N) = o(p(N)) if T(N) = O(p(N)) and T(N) ≠ Θ(h(N))
Rule 1:
If T1(N) = O(f(N)) and T2(N) = O(g(N)), then
- T1(N) + T2(N) = max(O(f(N)), O(g(N))
- T1(N) * T2(N) = O(f(N) * g(N))
log平方——log-squared; N——Linear;
2的n次方——exponential; N的2次方——quadratic;
N的3次方——cubic; k次多项式——polynomial of degree k.
Rule 2:
If T(N) is polynomial of degree k, then 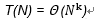
Rule 3:
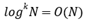 for any constant k.
for any constant k.
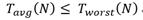
Generally, the quantity required is the worst-case time.
Efficient Algorithms: Time to read the input > Time required to solve the problem.
Big-Oh is the upper bound; Ω is a lower bound.
General rules:
-
For loops: Running time = statements inside the for loop (including tests) * the number of iterations
/* Ignore the costs of calling the function and returning. */
- Nested for loops: Analyze inside out.
-
If / Else:
if (Condition) S1; else S2;
The running time <= The running time of the test + the larger of S1/S2
If there are function calls, these must be analyzed first.
When recursion is properly used, it's difficult to convert the recursion into a simple loop structure.
Don't compute anything more than once.
Divide and Conquer Strategy:
- Divide part: to split the problem into 2 roughly equal subproblems.
- Conquer stage: patch together the 2 solutions of the subproblems to arrive at a solution for the whole problem.
An algorithm is O(logN) if it takes constant O(1) time to the problem size by a fraction (usually 1/2); if constant time is required to merely reduce the problem by a constant amount, then the algorithm is O(N).
Theorem: If M > N, then M mod N < M/2.
Checking your analysis:
- Code up the program and observe the running time.
-
Verify some program is O(f(N)) is to compute the T(N)/f(N) for a range of N.
Computed Value : N+ (f(N) is tight), 0 (overestimate), ∞ ( wrong/underestimate)
Overestimate?
- Needs to be tightened
- Significantly less than the worst running time and no improvement in the bound is possible.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号