剑指Offer_#55 - I_二叉树的深度
剑指Offer_#55 - I_二叉树的深度
Contents
题目
输入一棵二叉树的根节点,求该树的深度。从根节点到叶节点依次经过的节点(含根、叶节点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。提示:
节点总数 <= 10000
思路分析
方法1:自底向上
求整棵树的深度这个问题,可以分解为求当前节点左右子树深度的子问题,即存在递推关系:
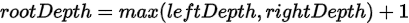
所以可以用递归解决。
终止条件:
当前访问到节点是null,深度看作0。
递推过程:
- 求左右子树深度leftDepth,rightDepth。
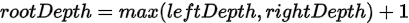
自底向上的递推是通过递归函数的返回值传递信息,即把max(leftDepth,rightDepth) + 1用返回值返回到父递归函数。
方法2:自顶向下
与自底向上的思路不同,自顶向下的思路是相反的。
- 自底向上:先得出左右子树的深度,再得出根节点的树的深度。
- 自顶向下:先得出根节点的层数,再得出根节点左右子树所在的层数。
自顶向下的递推需要通过函数参数来传递信息,即把当前节点的深度+1用参数传递给子递归函数。
解答
解答1:自底向上
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth) + 1;
}
}解答2:自顶向下
class Solution {
private int maxDepth = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
recur(root, 1);
return maxDepth;
}
private void recur(TreeNode root,int depth){
//如果是null,终止递归
if(root == null) return;
//如果root是叶子节点,更新最大值
if(root.left == null && root.right == null)
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth,depth);
//向下递推,需要给出depth参数
recur(root.left,depth + 1);
recur(root.right,depth + 1);
}
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号