对顶堆
对顶堆
什么是对顶堆
对顶堆是一种数据结构,它可以动态地维护某一个临界值,如前 \(i\) 个数字的中位数、 前 \(i\) 个数字中第 \(k\) 小的值等。
对顶堆一般适用一个大根堆维护前面某个状态,小根堆维护后面不同的状态(如大于/小于中位数等)。
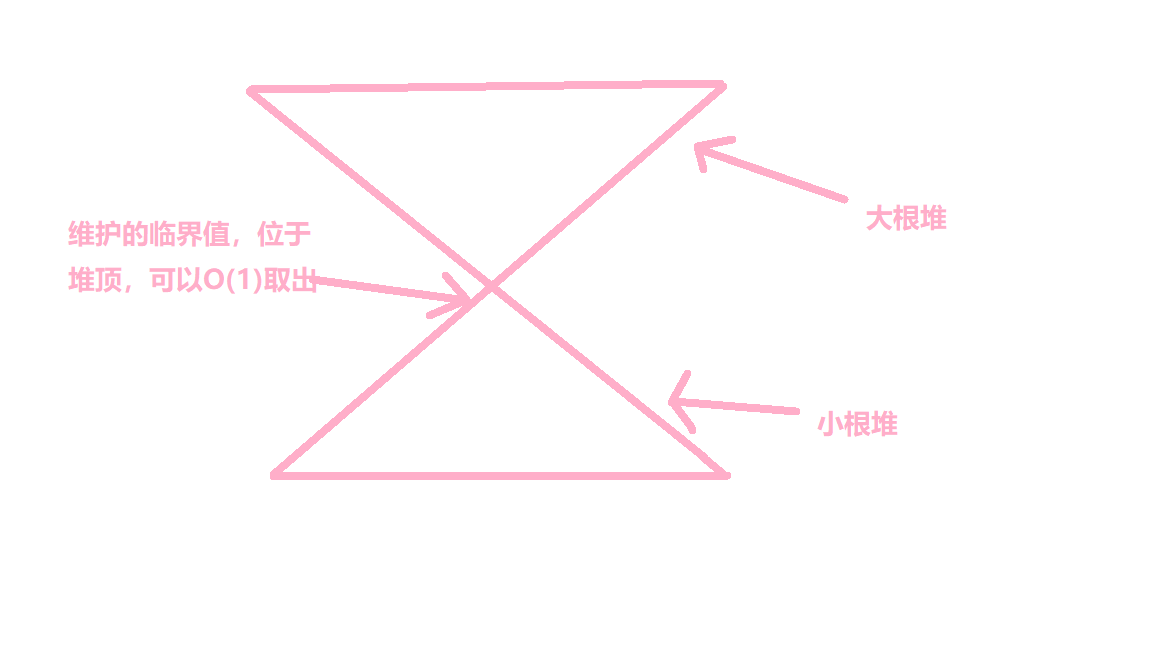
我们只需要调整两个堆的元素数量,即可 \(O(1)\) 地取出需要维护的值。
例题
动态中位数
题意
每次插入一个数字,当序列中数字数量为奇数时,输出序列的中位数。
分析
假设当前序列长度为 \(n\) 。
开一个大根堆来维护当前序列中前 \([1, n / 2]\) 小的元素,再开一个小根堆来维护当前序列前 \([n/2+1, n]\) 小的元素。
那么我们只需要维护大根堆的数量为 \(n/2\) ,即可知道当前序列的中位数为小根堆的堆顶。
每次我们插入一个数字,如果这个数字比中位数小,则插入大根堆里,否则插入小根堆里。
每当我们插入一个数字,如果大根堆的数量大于 \(n / 2\) ,那么把大根堆的最大元素放到小根堆里(堆顶,这也是我们需要两个不同性质的堆的原因)。反之把小根堆的元素放进大根堆里。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int T; cin >> T; while( T -- )
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int> > pre;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > post;
int id, n, write = 0; cin >> id >> n;
cout << id << ' ' << (n + 1) / 2 << endl;
for (int i = 1, x; i <= n && cin >> x; i ++ )
{
if (post.empty() || x >= post.top())
{
post.push(x);
if (post.size() - pre.size() > 1)
{
pre.push(post.top());
post.pop();
}
}
else
{
pre.push(x);
if (pre.size() > post.size())
{
post.push(pre.top());
pre.pop();
}
}
if (i & 1) cout << post.top() << " \n" [++ write % 10 == 0];
}
if (write % 10) cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
黑匣子
题意
有两种操作:
- 向序列中插入一个数字。
- 求出序列中第 \(k\) 小的数字。
\(k\) 初始为 \(0\) ,每次求第 \(k\) 小值都要把 \(k\) 加一。
分析
对顶堆,大根堆维护前 \(k-1\) 小的数字,小根堆维护后面的数字。这样小根堆的堆顶就是第 \(k\) 小的数字。
每次插入操作都至多交换一次堆元素,我们可以放到查询的时候再维护堆的数字,次数与每次操作维护是一样的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
int a[N], q[N], k;
void solve ()
{
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) cin >> q[i];
int pos = 1;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int> > pre;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > post;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (post.empty() || a[i] < post.top()) pre.push(a[i]);
else post.push(a[i]);
// 维护post堆顶为k小数
while (q[pos] == i)
{
++ k;
while(pre.size() < k) pre.push(post.top()), post.pop();
while(pre.size() >= k) post.push(pre.top()), pre.pop();
cout << post.top() << endl;
pos ++ ;
}
}
}
signed main ()
{
cout.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
// int _; for (cin >> _; _ --; ) solve();
solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号