python day04 字符串、列表、元组
day04 字符串、列表、元组
复习
1、字符串
-
需要掌握
-
strip,lstrip,rstrip
msg = '****hello*****' msg.strip('*') >>>> hello msg.lstrip('*') >>>> hello***** msg.rstrip('*') >>>> ****hello -
upper,lower
-
startwith,endwith
-
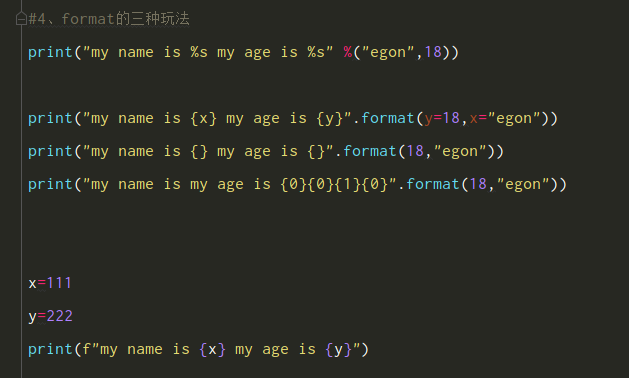
format的三种用法
'my name is {x} my age is {y}'.format(y=18,x='hina') 'my name is {} my age is {}'.format(18,'hina') 'my name is {1} my age is {0}{1}{1}{0}'.format(18,'hina')
-
-
split,rsplit
msg = 'a:b:c:d' msg.split(":",1)>>>>>['a','b:c:d'] msg.rsplit(":",1)>>>>>['a,b,c','d'] -
join
':'.join(['aa','bb','cc']) >>>>'aa:bb:cc' -
replace
msg = 'hello world' msg.replace('l','m') >>>>hemmo wormd msg.replace('l','m',1) >>>>hemlo w orld -
isdigit
msg = '123' msg.isdigit() >>>>True
-
需要了解
# 需要了解的方法 #1、find,rfind,index,rindex,count # msg = "hello egon xxx egon yyy egon zzz" # print(msg.find("egon",0,7)) # print(msg.index("egon")) # print(msg.rfind("egon")) # print(msg.rindex("egon")) # print(msg.find("abcde")) # print(msg.index("abcde")) # print(msg.count("egon")) #2、center,ljust,rjust,zfill # print('egon'.center(50,'*')) # print('egon'.ljust(50,'*')) # print('egon'.rjust(50,'*')) # print('egon'.zfill(50)) # print('egon'.rjust(50,"0")) #3、captalize,swapcase,title msg = "hellO woRld" # print(msg.capitalize()) # print(msg.swapcase()) # print(msg.title()) #4、is数字系列 #5、is其他 # name='egon123' # print(name.isalnum()) #字符串由字母或数字组成 # print(name.isalpha()) #字符串只由字母组成 # # print(name.islower()) # print(name.isupper()) # name=" " # print(name.isspace()) # name ="Hello World" # print(name.istitle()) n1 = b'4' n2 = '4' n3 = '四' n4 = 'Ⅳ' print(n1.isdigit())>>>>True print(n2.isdigit())>>>>True print(n3.isdigit())>>>>False print(n4.isdigit())>>>>False print(n2.isnumeric())>>>True print(n3.isnumeric())>>>True print(n4.isnumeric())>>>True
2、列表类型
-
用途:按位置存储多个值
-
定义方式:在[ ]内用,分割开任意类型元素
所有可以被for循环遍历的类型都可以传给list转化为列表 list({'k1':11,'k2':22}) >>>['k1','k2'] -
常用操作和内置方法
list = [111,222,333,444,555] print(id(list)) list[0]=666 print(id(list)) print(list) # 列表不可以根据不存在的索引赋值 list[7]=777>>>>IndexError:下标超出范围 # 追加 list.append(666) # 插入 list.insert(0,666)>>>>[666,111,222,333,444,555] # 切片 l = [11,22,33,44] l1 = l[:] # 浅拷贝 # 长度 len(l) # 成员运算 in/ not in # 删除 l = [11, 22, 33] del l[0] print(l) >>>>[22, 33] l = [11, 22, 33] l.remove(11) print(l) >>>> [22, 33] l = [11, 22, 33] res = l.pop(0) print(l) print(res) >>>> [22, 33] 11 l = [11, 22, 33] l.reverse() print(l) >>>> [33, 22, 11] # 清空l还存在====l=[] l.clear l = [11, 22, 33] l1 = [44, 55, 66] l.extend(l1) print(l) >>>> [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66] l.index(33,0,1) >>>>ValueError l = ['44', '11', '22', '33', 'x'] l.sort() print(l) >>>> ['11', '22', '33', '44', 'x'] l.sort(reverse=True) >>>> ['x', '44', '33', '22', '11']
队列:先进先出
堆栈:后进先出
3、元组类型
-
用途
-
定义方式:在()内用逗号分隔开多个任意类型的元素
x = (10,) # x = tuple(...) # tuple可以把任意能够被for循环遍历的类型转化为元组 -
元组的常用操作+内置方法
t = (11,22,33,44) # 1.索引 print(t[0]) # 2.切片 t[0:3] # 3.长度 len(t) # 4.成员运算 in 和 not in # 5.循环
总结:存多个值,有序,不可变
列表存的是索引与对应值得内存地址的绑定关系
t = (111,222,333,[444,555])
t[-1][0]=666
print(t)
>>>>
(111,222,333,[666,555])
l = [111, 222, 333]
print(id(l))
l[0] = 444
print(id(l))
print(l)
>>>>
2310692163328
2310692163328
[444, 222, 333]
t = (111, 222, 333, [44, 555])
print(id(t[0]), id(t[1]), id(t[2]), id(t[3]))
t[-1][0] = 666
print(id(t[0]), id(t[1]), id(t[2]), id(t[3]))
print(t)
>>>>
2626267207472 2626267211088 2626275091888 2626275397248
2626267207472 2626267211088 2626275091888 2626275397248
(111, 222, 333, [666, 555])
4、字典类型
-
用途
-
定义方式:在{}内用逗号分隔多个元素,每个元素都是key:value的格式,其中value可以是任意类型,而key必须是不可变类型,通常是str类型,而且key不能重复
dict数据类型转换
info = [('k1',111),('k2',222),('k3',333)] dic = dict(info) print(dic) >>>> {'k1': 111, 'k2': 222, 'k3': 333} print(dict(x=1,y=2,z=3)) >>>> {'x': 1, 'y': 2, 'z': 3} -
长度:len(dict)
-
成员运算 in 和 not in: 以key为主
-
删除
dic = {'name':'hina','age':18} # 单纯的删除 del dic['name'] print(dic) # 取走 v = dic.pop('name') print(v) print(dic) >>>> hina {'age': 18} dic = {'name':'hina','age':18} v = dic.popitem() print(v) >>>> ('age', 18) -
keys,values,items
dic = {'name':'hina','age':18} print(dic.keys()) print(dic.values()) for k,v in dic.items(): print(k,v) >>>> dict_keys(['name', 'age']) dict_values(['hina', 18]) name hina age 18 -
get:dic.get('key')与dic['key']相似,不同点在于若dic中没有key则dic['key']会报错
-
其他
dic = {'name':'hina','age':18} dic.update({'gender':'male',"age":20}) print(dic) >>>> {'name': 'hina', 'age': 20, 'gender': 'male'} print({}.fromkeys(['name', 'age', 'gender'],None)) >>>> {'name': None, 'age': None, 'gender': None} v = dic.setdefault('name','xxx') # 等价于下面的代码,返回值为dic中name对应的值 if 'name' not in dic: dic['name'] = 'xxx'
总结:存多个值,可变,字典本身不可变
for i in enumerate([1,2,3,4,5,'xxx','yyy']):
print(i)
>>>>
(0, 1)
(1, 2)
(2, 3)
(3, 4)
(4, 5)
(5, 'xxx')
(6, 'yyy')
for j in zip(['a','b','c','d'],('A','B','C','D','E')):
print(j)
>>>>
('a', 'A')
('b', 'B')
('c', 'C')
('d', 'D')


