MyBatis-Plus BaseMapper 实现原理
MyBatis-Plus 自定义通用 Mapper 方法
MyBatis-Plus 提供了一些通用的 Mapper 方法,例如insert、update、selectById等。通过让自定义的 Mapper 继承BaseMapper类,我们可以直接调用这些基础的 SQL 方法,而无需自己编写 SQL。
public interface BaseMapper<T> extends Mapper<T> {}
然而,在使用过程中,我们发现提供的方法数量有限。当我们想添加自定义的通用 SQL 方法时,可以参考官方文档中描述的 SQL 注入器。例如,我们可以自定义一个saveBatch方法,用于批量插入数据。
BaseMapper 自定义扩展
MyBatis-Plus 提供了ISqlInjector接口和AbstractSqlInjector抽象类。我们可以通过实现该接口或继承抽象类的方式,注入自定义的 SQL 逻辑。
除了这两个接口外,MyBatis-Plus 还提供了一个默认实现:DefaultSqlInjector。该类中已经包含了一些 MyBatis-Plus 封装的BaseMapper方法。如果我们想进行扩展,可以直接继承这个类并添加自定义的方法。
下面我们在BaseMapper外添加的saveBatch方法,用于批量插入数据:
-
继承
DefaultSqlInjector类,覆盖getMethodList方法。该方法的参数是 Mapper 接口的 Class 类,返回值是List<AbstractMethod>。我们自定义的方法需要实现AbstractMethod。可以参考 MyBatis-Plus 中已实现的一些AbstractMethod方法,仿照编写一个SaveBatch类。public class CustomSqlInjector extends DefaultSqlInjector { @Override public List<AbstractMethod> getMethodList(Class<?> mapperClass) { // 父类的 list 已经包含了 BaseMapper 的基础方法。 List<AbstractMethod> methodList = super.getMethodList(mapperClass); // 添加我们需要增加的自定义方法。 methodList.add(new SaveBatch()); return methodList; } } -
实现
SaveBatch类的逻辑(以下为官方示例)。该逻辑主要用于生成MappedStatement对象。public class SaveBatch extends AbstractMethod { @Override public MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) { final String sql = "<script>insert into %s %s values %s</script>"; final String fieldSql = prepareFieldSql(tableInfo); final String valueSql = prepareValuesSqlForMysqlBatch(tableInfo); final String sqlResult = String.format(sql, tableInfo.getTableName(), fieldSql, valueSql); SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sqlResult, modelClass); return this.addInsertMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, "saveBatch", sqlSource, new NoKeyGenerator(), null, null); } private String prepareFieldSql(TableInfo tableInfo) { StringBuilder fieldSql = new StringBuilder(); fieldSql.append(tableInfo.getKeyColumn()).append(","); tableInfo.getFieldList().forEach(x -> { fieldSql.append(x.getColumn()).append(","); }); fieldSql.delete(fieldSql.length() - 1, fieldSql.length()); fieldSql.insert(0, "("); fieldSql.append(")"); return fieldSql.toString(); } private String prepareValuesSqlForMysqlBatch(TableInfo tableInfo) { final StringBuilder valueSql = new StringBuilder(); valueSql.append("<foreach collection=\"list\" item=\"item\" index=\"index\" open=\"(\" separator=\"),(\" close=\")\">"); valueSql.append("#{item.").append(tableInfo.getKeyProperty()).append("},"); tableInfo.getFieldList().forEach(x -> valueSql.append("#{item.").append(x.getProperty()).append("},")); valueSql.delete(valueSql.length() - 1, valueSql.length()); valueSql.append("</foreach>"); return valueSql.toString(); } } 注意其中的
injectMappedStatement方法返回MappedStatement对象,且方法内部通过调用了父类的addInsertMappedStatement方法构建MappedStatement实例。 -
最后,我们需要将自定义的 Injector 注入 Spring 容器中,以替换默认的 Injector。
@Bean public CustomSqlInjector customSqlInjector() { return new CustomSqlInjector(); } -
验证:
public interface MyBaseMapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T> { int saveBatch(List<T> entityList); } @Mapper public interface TB3Mapper extends MyBaseMapper<Tb3> { } @Test public void test() { List<Tb3> tb3s = Arrays.asList(Tb3.getInstance(), Tb3.getInstance()); tb3Mapper.saveBatch(tb3s); } // 输出日志 ==> Preparing: insert into tb3 (id,f1,f2,f3) values ( ?,?,?,? ),( ?,?,?,? ) ==> Parameters: 38(Integer), 62(Integer), -1546785812(Integer), -16950756(Integer), 24(Integer), 17(Integer), -1871764773(Integer), 169785869(Integer) <== Updates: 2
原理解析
MyBatis-Plus 的工作原理是全面代理了 MyBatis 的一些功能。例如,自动配置转用了MyBatisPlusAutoConfiguration,SqlSessionFactoryBean转用了MyBatisSqlSessionFactoryBean等等。这些 MyBatis 的核心部件都被 MyBatis-Plus 替换,并在其内部定制了逻辑。
要了解 MyBatis-Plus 的工作原理,需要了解 MyBatis 的工作原理。MyBatis 的整体逻辑可以分为两部分:
-
配置文件解析:这个过程包括解析 MyBatis 配置,以及
mapper.xml文件。最终配置都会被解析到一个Configuration对象里面,后面的每个SqlSession也都会包含一个该Configuration对象实例的引用。这个Configuration里面有两个最重要的部分: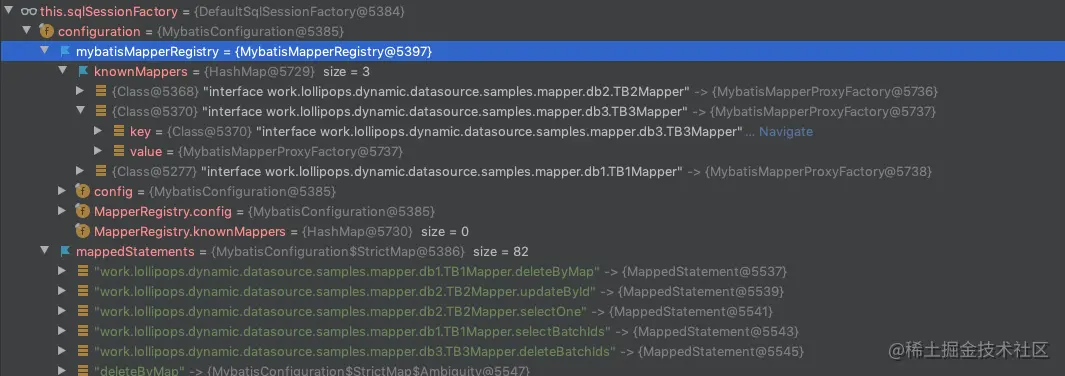
- mappedStatements:存放 mapper 对应的 SQL 信息
- mybatisMapperRegistry.knownMappers:存放 mapper 接口对应的代理类
-
接口的调用:我们接口调用的其实是代理的包装类
MybatisMapperProxy,这个类由上图mybatisMapperRegistry.knownMappers里面展示的MybatisMapperProxyFactory(MyBatis 是MapperProxyFactory)的getObject方法返回。这个代理类里面的主要逻辑就是去Configuration的mappedStatements里面找到对应的 SQL 然后执行。
可以猜到:在Configuration加载的时候,一定有地方将BaseMapper的默认方法对应的 SQL 信息给装载到mappedStatements这个 map 里面去。下面分析这些默认的MappedStatement对象是在哪里进行构建并加入到Configuration中的。
第一步,肯定是自动配置要注入SqlSessionFactory到容器,其通过MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean对象的getObject方法返回,我们跟进MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject():
@Override public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception { if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) { afterPropertiesSet(); } return this.sqlSessionFactory; } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required"); state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null), "Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together"); // 这里才是开始构建 SqlSessionFactory 的 this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory(); }
可以看到,最终会执行到buildSqlSessionFactory()。这块方法的主要逻辑就是解析 XML 配置来创建Configuration对象。我们可以在最下面发现解析我们mapper.xml文件的逻辑:
if (this.mapperLocations != null) { if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) { LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found."); } else { for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) { if (mapperLocation == null) { continue; } try { // 对每一个 mapper.xml 文件进行解析 XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(), targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments()); xmlMapperBuilder.parse(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'"); } } } else { LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified."); }
重点看看xmlMapperBuilder.parse();:
public void parse() { if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); // debug 发现,Configuration 中 mappedStatements 在执行该方法之后,mapper 方法数量就变多了。 bindMapperForNamespace(); } parsePendingResultMaps(); parsePendingCacheRefs(); parsePendingStatements(); }
而bindMapperForNamespace里面,是在执行configuration.addMapper(boundType); 之后方法变多的。这个方法最终调用的是MybatisMapperRegistry.addMapper(),这个方法里面最终会转去调用MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder.parse()方法,将 mapper 的方法加入到mappedStatements中。
@Override public void parse() { // ... try { if (GlobalConfigUtils.isSupperMapperChildren(configuration, type)) { // 执行该步骤之后,新增了 mappestatment parserInjector(); } } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new InjectorResolver(this)); } parsePendingMethods(); }
parserInjector方法如下:
void parserInjector() { GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type); } // GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector public static ISqlInjector getSqlInjector(Configuration configuration) { return getGlobalConfig(configuration).getSqlInjector(); } // getSqlInjector() private ISqlInjector sqlInjector = new DefaultSqlInjector(); // MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration.sqlSessionFactory#sqlInjector this.getBeanThen(ISqlInjector.class, globalConfig::setSqlInjector);
可以看到,通过一连串的方法拿到ISqlInjector实现类。默认是DefaultSqlInjector,但是如果 Spring 中被自行注入了该实现类的话,就会在自动配置的时候,修改为我们自定义的SqlInjector(比如前面的CustomSqlInjector)。
获取到SqlInjector之后,调用其inspectInject方法,CustomSqlInjector继承自DefaultSqlInjector,DefaultSqlInjector继承自AbstractSqlInjector,其中有inspectInject方法。
// DefaultSqlInjector @Override public List<AbstractMethod> getMethodList(Class<?> mapperClass) { return Stream.of( new Insert(), new Delete(), // .... ).collect(toList()); } // AbstractSqlInjector @Override public void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass) { Class<?> modelClass = extractModelClass(mapperClass); if (modelClass != null) { String className = mapperClass.toString(); Set<String> mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration()); if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className)) { // 可以看到这里拿取我们 CustomSqlInjector 返回的 AbstractMethod list,然后循环调用 inject List<AbstractMethod> methodList = this.getMethodList(mapperClass); if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(methodList)) { TableInfo tableInfo = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass); // 循环注入自定义方法 methodList.forEach(m -> m.inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo)); } else { logger.debug(mapperClass.toString() + ", No effective injection method was found."); } mapperRegistryCache.add(className); } } } // AbstractMethod public void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) { this.configuration = builderAssistant.getConfiguration(); this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant; this.languageDriver = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance(); /* 注入自定义方法 */ injectMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo); }
可以看到inspectInject方法调用了getMethodList方法,然后循环getMethodList返回的AbstractMethod集合,调用各项的inject方法。
AbstractMethod的inject最终会调用injectMappedStatement方法,该方法是抽象方法,由子类实现。
比如SaveBatch的injectMappedStatement方法在构建好一个MappedStatement对象需要的元素后,调用AbstractMethod中的addInsertMappedStatement将其加入到Configuration的mappedStatements中。


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端