线程常见方法
方法
sleep:当前线程暂停
join:将该线程加入到当前线程中,默认是main
setPriority:设置优先级
yield:临时暂停
setDaemon:守护线程
sleep-睡觉
让该线程每运行一次就暂停一秒
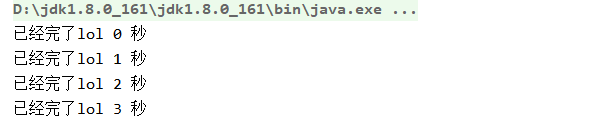
package com.thread.thread4; public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread() { //内部类创建线程对象 public void run() { int seconds = 0; //创建时间变量 while (true) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); //让线程休息1秒钟 }catch(InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.printf("已经完了lol %d 秒 %n", seconds++); //执行一次就+1 } } }; t1.start(); //启动线程 } }
从结果可以看出,每次运行耗时一秒
Join-插队
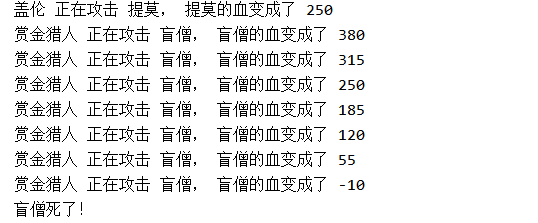
两个线程在一个主线程中同时运行,它的顺序是乱的
使用A.join(),那么就只有等A线程全部运行完了之后,才会运行其他线程
package com.thread.thread5; import com.thread.Hero; public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { final Hero gareen = new Hero(); gareen.name = "盖伦"; gareen.hp = 616; gareen.damage = 50; Hero teemo = new Hero(); teemo.name = "提莫"; teemo.hp = 300; teemo.damage = 30; Hero bh = new Hero(); bh.name = "赏金猎人"; bh.hp = 500; bh.damage = 65; Hero leession = new Hero(); leession.name = "盲僧"; leession.hp = 445; leession.damage = 80; // Thread类实现的Runnable接口 Thread t1 = new Thread() { //创建线程 public void run() { //重新写run方法 while(!teemo.isDead()) { gareen.attackHero(teemo); //调用对象的方法 某某攻击某某 System.out.println("我是t1"); } } }; t1.start(); //代码执行到这里 一直是main线程在执行 try{ //t1线程加入到main线程中来 只有t1线程运行结束 才会继续往下走 t1.join(); }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Thread t2 = new Thread(){ public void run() { while(!leession.isDead()){ bh.attackHero(leession); } } }; //会观察到t1线程运行完成之后 才执行的t2线程 t2.start(); } }
从效果看出,的确t1执行完全才轮到t2上

setPriority-优先级
这个优先级只能说是抢占cpu资源的概率变大了,其他线程来捣乱的几率还是有的
package com.thread.thread6; import com.thread.Hero; public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { final Hero gareen = new Hero(); gareen.name = "盖伦"; gareen.hp = 616; gareen.damage = 50; Hero teemo = new Hero(); teemo.name = "提莫"; teemo.hp = 300; teemo.damage = 30; Hero bh = new Hero(); bh.name = "赏金猎人"; bh.hp = 500; bh.damage = 65; Hero leession = new Hero(); leession.name = "盲僧"; leession.hp = 445; leession.damage = 80; Thread t1 = new Thread() { //创建线程 public void run() { while(!teemo.isDead()) { gareen.attackHero(teemo); } } }; Thread t2 = new Thread() { public void run() { while(!leession.isDead()) { bh.attackHero(leession); } } }; //这个优先级 只能说更大的概率 线程能够抢占到cpu资源 还是有部分的线程会抢占执行 // t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //给线程设置最大优先级别 t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //最小优先级 t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
看到t1的优先级设置到最低,但是在t2执行的时候还是会去捣乱
yield-暂停
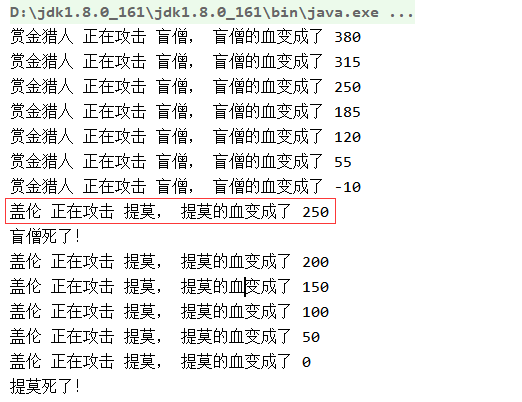
线程2进行暂停操作
package com.thread.thread7; import com.thread.Hero; public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { final Hero gareen = new Hero(); gareen.name = "盖伦"; gareen.hp = 61600; gareen.damage = 50; Hero teemo = new Hero(); teemo.name = "提莫"; teemo.hp = 30000; teemo.damage = 30; Hero bh = new Hero(); bh.name = "赏金猎人"; bh.hp = 50000; bh.damage = 65; Hero leession = new Hero(); leession.name = "盲僧"; leession.hp = 44500; leession.damage = 80; Thread t1 = new Thread() { public void run() { while(!teemo.isDead()) { gareen.attackHero(teemo); } } }; Thread t2 = new Thread() { public void run() { while(!leession.isDead()) { //临时暂停 使得t1可以占用cpu资源 Thread.yield(); //暂停线程 线程的暂停也只能说是一种大概率的暂停 部分线程执行还是会穿插在t1执行过程中 //t1执行完成之后才会完全执行t2 bh.attackHero(leession); } } }; t1.setPriority(5); //设置优先级 t2.setPriority(5); t1.start(); //启动线程 t2.start(); } }
在这里我把t2盲憎给暂停了,但是t1的时候还是会出现t2的,说明暂停只是一种大概率的暂停,和优先级类似

setDaemon-守护进程
守护进程就是像日志一样,我们这个程序执行结束,日志自然就不再记录了。伴随着整个进程的消亡而消亡。或者说守护的东西消失了,自己的使命也就完成了。
package com.thread.thread8; public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(){ public void run() { int seconds = 0; while(true) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.printf("已经完了LOL %d 秒 %n", seconds++); } } }; t1.setDaemon(true); //守护进程开启 这里就是相当于main主线程的守护进程 main执行成功 t1就死翘翘了 //守护进程 从字面意思就是守护 它守护的目标死亡 他的命运就结束了 t1.start(); } }
运行一片空白,这里是将t1线程作为守护线程,那么main主线程完成后,自己就死掉了。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号