Spring复习-AOP
AOP的概念
AOP,Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程,是对面向对象编程OOP的升华。OOP是纵向对一个事物的抽象,一个对象包括静态的属性信息,包括动态的方法信息等。而AOP是横向的对不同事物的抽象,属性与属性、方法与方法、对象与对象都可以组成一个切面,而用这种思维去设计编程的方式叫做面向切面编程。
AOP思想的实现方案
动态代理技术,在运行期间,对目标对象的方法进行增强,代理对象同名方法内可以执行原有逻辑的同时嵌入执行其他增强逻辑或其他对象的方法。
模拟AOP思想的实现方案
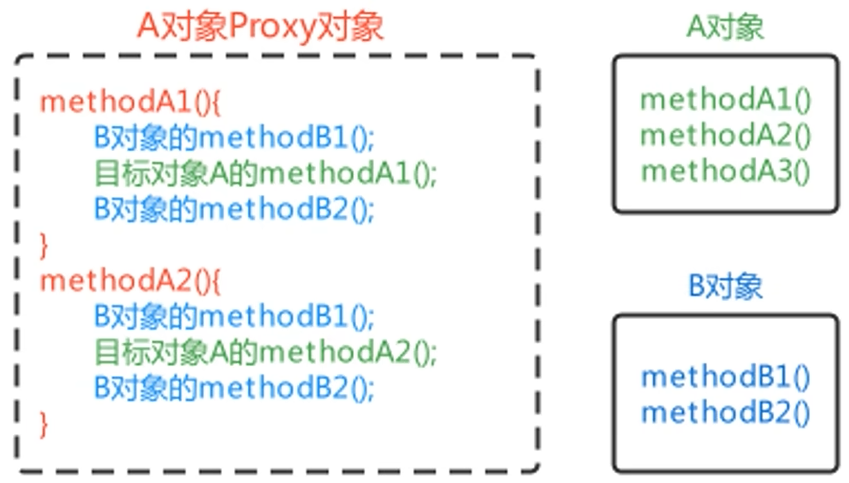
使用B对象的两个方法增强A对象
A对象、B对象
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void show1() {
System.out.println("show1...");
}
@Override
public void show2() {
System.out.println("show2...");
}
}
public class MyAdvice {
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置增强..");
}
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("后置增强..");
}
}
后处理器使用代理对象,通过aware获取applicationContext进而获取bean
public class MockAopBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//判断bean所在路径,进行筛选
if (bean.getClass().getPackage().getName().equals("com.demo.service.impl")) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
(proxy, method, args) -> {
MyAdvice myAdvice = applicationContext.getBean(MyAdvice.class);
myAdvice.beforeAdvice();
Object result = method.invoke(bean,args);
myAdvice.afterAdvice();
return result;
}
);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
A、B、后处理器都加入bean
<bean id="userService" class="com.demo.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.demo.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
<bean class="com.demo.processor.MockAopBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
启动ApplicationContext并获取bean、调用方法即可
前置增强..
show1...
后置增强..
前置增强..
show2...
后置增强..
AOP相关概念

配置AOP
基于xml配置AOP
<aop:config>
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(void com.demo.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.show1())"/>
<!--织入-->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
切点表达式是配置要对哪些连接点(哪些类的哪些方法)进行通知的增强,语法如下:
execution([访问修饰符]返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数))
其中访问修饰符可以省略不写
返回值类型、某一级包名、类名、方法名 可以使用*表示任意;
包名与类名之间使用单点.表示该包下的类,使用双点..表示该包及其子包下的类,
参数列表可以使用两个点..表示任意参数。
AspectJ的通知由以下五种类型

通知方法在被调用时,Spring可以为其传递一些必要的参数

通知方法在被调用时,Spring可以为其传递一些必要的参数

AOP的xml有两种配置方式,如下
1.使用
2.使用
Spring定义了一个Advice接口,实现了该接口的类都可以作为通知类出现
xml方式AOP配置详解
AOP配置的两种语法形式不同点
语法形式不同:
1.advisor是通过实现接口来确认通知的类型
2.aspect是通过配置确认通知的类型,更加灵活
可配置的切面数量不同
1.一个advisor只能配置一个固定通知和一个切点表达式
2.一个aspect可以配置多个通知和多个切点表达式任意组合
使用场景不同:
1.允许随意搭配情况下可以使用aspect进行配置
2.如果通知类型单一、切面单一的情况下可以使用advisor进行配置
3.在通知类型已经固定,不用人为指定通知类型时,可以使用advisor进行配置,例如后面要学习的Spring事务控制的配置
都是动态生成代理对象的方式,一种就是基于JDK的,一种是基于Cglib的
动态代理的实现的选择,在调用qetProxy) 方法时,我们可选用的 AopProxy接口有两个实现类,如上图,这两种


Cglib实现代理的案例
/**
* Cglib代理方式
*/
public class CglibTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//CGlib基于父类(目标类)生成Proxy
Target target = new Target();//需要增强的
MyAdvice4 myAdvice4 = new MyAdvice4();
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(Target.class);//设置父类
enhancer.setCallback((MethodInterceptor) (o, method, objects, methodProxy) -> {
myAdvice4.before();
Object result = method.invoke(target, objects);
myAdvice4.after();
return result;
});
Target proxyObject = (Target) enhancer.create();//生成代理对象
proxyObject.show();
}
}
注解方式开发
配置切面
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice1 {
@Before("execution(void com.demo.service.impl..*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置增强..");
}
}
在xml中开启包扫描和自动代理
<!-- 自动代理 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!-- 包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.demo"></context:component-scan>
注解方式优化的写法:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice1 {
//统一切面配置
@Pointcut("execution(void com.demo.service.impl..*(..))")
public void myPointCut() {}
@Before("myPointCut()")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置增强..");
}
//有异常不执行
@AfterReturning("myPointCut()")
public void returningAdvice() {
System.out.println("returning增强..");
}
//有异常之后的不执行
@Around("myPointCut()")
public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around(前)增强..");
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();//执行方法
System.out.println("around(后)增强..");
return result;
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPointCut()",throwing = "th")
public void throwingAdvice(Throwable th) {
System.out.println("异常为:"+th);
System.out.println("throwing增强..");
}
@After("myPointCut()")
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("后置增强..");
}
}
注解方式开启自动代理:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.demo"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //开启自动代理
public class SpringConfig {
}
三种配置方式:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号