【神经网络】依存树
主要介绍GCN-Tree模型中依存树的内容。论文中使用的工具来自Standford Parser。
https://www.xfyun.cn/services/semanticDependence 讯飞中文分词平台
http://nlp.stanford.edu:8080/parser/ 这是可以体验功能。
工具包:https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/stanford-dependencies.shtml 教你怎么用stanford dependency parser这个工具代码。
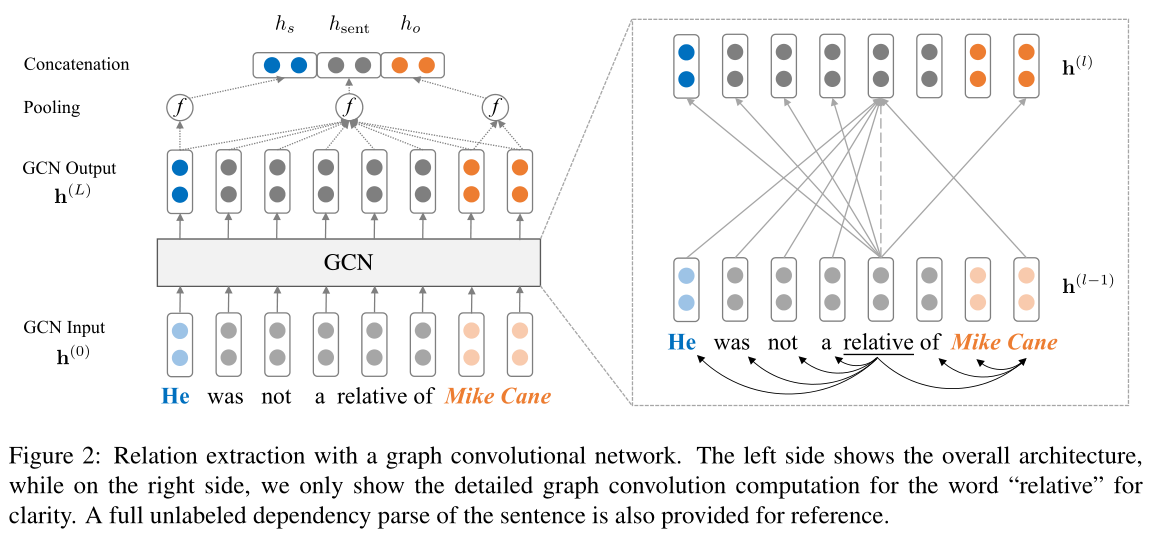
图2:用图卷积网络抽取关系。左侧显示整体架构,而右侧则只显示“relative”一词的详细图卷积计算,以求清晰。本文还提供了一个完整的、未标记的句子依存分析,以供参考。
我们使用论文中的例子还原一下这个解析树:
Your query
Tagging
Parse
(ROOT
(S
(NP (PRP He))
(VP (VBD was) (RB not)
(NP
(NP (DT a) (NN relative))
(PP (IN of)
(NP (NNP Mike) (NNP Cane)))))))
Universal dependencies
nsubj(relative-5, He-1) cop(relative-5, was-2) advmod(relative-5, not-3) det(relative-5, a-4) root(ROOT-0, relative-5) case(Cane-8, of-6) compound(Cane-8, Mike-7) nmod(relative-5, Cane-8)
Universal dependencies, enhanced
nsubj(relative-5, He-1) cop(relative-5, was-2) advmod(relative-5, not-3) det(relative-5, a-4) root(ROOT-0, relative-5) case(Cane-8, of-6) compound(Cane-8, Mike-7) nmod:of(relative-5, Cane-8)
可以看到第5个单词relative作为根节点,nsubj,cop,avvmod,det,root,case,compound,nmod:of作为依赖边关系表示缩写,在论文数据集中标注为$stanford-deprel$
括号前边的项为关系边的出发点,后项为这句子中的第X个单词(head,此单词),head在论文数据集中标注为$stanford-head$
取自数据集中某条数据:

这样可以写出universal dependencies:
nsubj(named-2,He-1)
root(ROOT-0,named-2)
dobj(named-2,one-3)
case(Aziz-7,as-4)
compound(Aziz-7,Shah-5)
compound(Aziz-7,Shah-6)
compound(Aziz-7,Shah-7)
nmod(named-2,Aziz-7)
通过工具验证一下:
Your query
Tagging
Parse
(ROOT
(S
(NP (PRP He))
(VP (VBD named)
(NP (CD one))
(PP (IN as)
(NP (NNP Shah) (NNP Abdul) (NNP Aziz))))))
Universal dependencies
nsubj(named-2, He-1) root(ROOT-0, named-2) obj(named-2, one-3) case(Aziz-7, as-4) compound(Aziz-7, Shah-5) compound(Aziz-7, Abdul-6) obl(named-2, Aziz-7)
Universal dependencies, enhanced
nsubj(named-2, He-1) root(ROOT-0, named-2) obj(named-2, one-3) case(Aziz-7, as-4) compound(Aziz-7, Shah-5) compound(Aziz-7, Abdul-6) obl:as(named-2, Aziz-7)
经验证确实是这样标注的。
两个基本问题
都挺简单的数据结构问题(多叉树的节点问题):
a. 已知一个节点怎么找到它的父(子)节点。
这个就很简单了。自己应该会的。
b. 求两个节点的最短路径
就是找到一个节点,把自己和所有父节点放到一个数组里,再在另一个节点,从本身开始顺着父节点找,直到找到和第一个节点并且存在于第一个数组里,这样,第一个数组从0开始到这个公共节点和第二个节点的从这个节点到自己本身的所有节点就是这俩节点的最短路径。
举个实在例子(意见抽取):

dependency tree是:

![]()
属性之间的最短路径:

注意的是,这个路径上每次经过的线(也就是他们俩的关系),这里的路径就是这个。
属性与评价之间的最短路径:

从这两组最短路径很明显看出谁跟谁更亲近,这也是最短路径的一个应用。
下面介绍在论文模型中如何将输入变为Tree形式表示,这是GCNRelationModel模型中forward过程中使用依赖树的过程:
1 def forward(self, inputs): 2 words, masks, pos, ner, deprel, head, subj_pos, obj_pos, subj_type, obj_type = inputs # unpack 3 l = (masks.data.cpu().numpy() == 0).astype(np.int64).sum(1) #将mask矩阵中的True/Fasle->1/0,记录每个batch有多少个单词 4 maxlen = max(l) 5 6 def inputs_to_tree_reps(head, words, l, prune, subj_pos, obj_pos): 7 head, words, subj_pos, obj_pos = head.cpu().numpy(), words.cpu().numpy(), subj_pos.cpu().numpy(), obj_pos.cpu().numpy() 8 trees = [head_to_tree(head[i], words[i], l[i], prune, subj_pos[i], obj_pos[i]) for i in range(len(l))] 9 adj = [tree_to_adj(maxlen, tree, directed=False, self_loop=False).reshape(1, maxlen, maxlen) for tree in trees] 10 adj = np.concatenate(adj, axis=0) # 这个batch中的多个numpy邻接矩阵,跨行进行拼接 shape = [b,maxlen,maxlen] 11 adj = torch.from_numpy(adj) 12 return Variable(adj.cuda()) if self.opt['cuda'] else Variable(adj) 13 14 #.data用法可以修改tensor的值而不被autograd(不会影响反向传播), 15 # subj_pos,obj_pos均为主语宾语在句子中的位置,#返回距离List :[-3,-2,-1,0,0,0,1,2,3] 16 adj = inputs_to_tree_reps(head.data, words.data, l, self.opt['prune_k'], subj_pos.data, obj_pos.data) 17 h, pool_mask = self.gcn(adj, inputs) #将此batch的adj邻接矩阵,与输入输入到gcn
在第16行,直接输入数据的head,word,l,剪枝路径约束值k,主语、宾语位置信息,调用6~12行的函数生成了此batch的依赖树的邻接矩阵。
方法内部第8行,通过调用head_to_tree( )方法,给batch每句话都生成一棵依赖树。
1 class Tree(object): 2 """ 3 Reused tree object from stanfordnlp/treelstm. 4 stanfordnlp/treelstm重用的树对象 5 """ 6 def __init__(self): 7 self.dist = 0 8 self.idx = 0 9 self.parent = None 10 self.num_children = 0 11 self.children = list() 12 13 def add_child(self,child): 14 child.parent = self 15 self.num_children += 1 16 self.children.append(child) 17 18 def size(self): 19 if getattr(self,'_size'): 20 return self._size 21 count = 1 22 for i in range(self.num_children): 23 count += self.children[i].size() 24 self._size = count 25 return self._size 26 27 def depth(self): 28 if getattr(self,'_depth'): 29 return self._depth 30 count = 0 31 if self.num_children>0: 32 for i in range(self.num_children): 33 child_depth = self.children[i].depth() 34 if child_depth>count: 35 count = child_depth 36 count += 1 37 self._depth = count 38 return self._depth 39 40 def __iter__(self): 41 yield self 42 for c in self.children: 43 for x in c: 44 yield x 45 46 def head_to_tree(head, tokens, len_, prune, subj_pos, obj_pos): 47 """ 48 Convert a sequence of head indexes into a tree object. 49 将head索引序列转换为tree对象 50 """ 51 tokens = tokens[:len_].tolist() 52 head = head[:len_].tolist() 53 root = None 54 55 if prune < 0: #不进行剪枝 56 nodes = [Tree() for _ in head] #多少个单词,就有多少个节点nodes 57 58 for i in range(len(nodes)): 59 h = head[i] 60 nodes[i].idx = i 61 nodes[i].dist = -1 # just a filler 62 if h == 0: 63 root = nodes[i] 64 else: 65 nodes[h-1].add_child(nodes[i]) #nodes[h-1]出边指向->当前节点,对应standford标注 66 else: #进行剪枝 67 # find dependency path 68 subj_pos = [i for i in range(len_) if subj_pos[i] == 0] #subj_pos为0的部分实际上是实体,返回主语实体的下标[3,4,5] 69 obj_pos = [i for i in range(len_) if obj_pos[i] == 0] 70 71 cas = None 72 73 subj_ancestors = set(subj_pos) 74 for s in subj_pos: #遍历主语实体的每一个下标 75 h = head[s] 76 tmp = [s] 77 while h > 0: #head如果不是root 78 tmp += [h-1] #tmp存储当前节点s与发射边节点(head,s),以及发射边节点的祖先 79 subj_ancestors.add(h-1) 80 #subj_ancestors存储主语实体下标除root之外的所有发射边节点,以及发射边节点的祖先,一直到找到root根节停止 81 h = head[h-1] 82 83 if cas is None: 84 cas = set(tmp) #第一次遍历cas是空的,把第一个下标节点对应的所有祖先加入 85 else: 86 cas.intersection_update(tmp) #第二三次遍历就调用intersection_update取交集,最后保留几个主语实体节点的公共祖先 87 88 obj_ancestors = set(obj_pos) 89 for o in obj_pos: 90 h = head[o] 91 tmp = [o] 92 while h > 0: 93 tmp += [h-1] 94 obj_ancestors.add(h-1) 95 h = head[h-1] 96 cas.intersection_update(tmp) #cas再与宾语实体节点的公共祖先取交集 97 98 # find lowest common ancestor 99 if len(cas) == 1: #只有一个公共节点那么LCA就是它 100 lca = list(cas)[0] 101 else: 102 child_count = {k:0 for k in cas} 103 for ca in cas: 104 if head[ca] > 0 and head[ca] - 1 in cas: #ca的祖先不是根节点 and ca的祖先在cas这堆祖先节点中 105 child_count[head[ca] - 1] += 1 #ca的祖先加一个孩子,那个孩子就是ca 106 107 #LCA(Least Common Ancestors) 108 # the LCA has no child in the CA set 109 for ca in cas: #很容易理解,公共祖先树中没孩子的‘叶子’肯定是所有实体节点的lCA 110 if child_count[ca] == 0: 111 lca = ca 112 break 113 114 path_nodes = subj_ancestors.union(obj_ancestors).difference(cas) 115 #主语树(含祖先)与宾语树(含祖先)取并集,再去掉公共祖先节点 116 path_nodes.add(lca) #再加上最低公共祖先,LCA树构造完成了 117 118 # compute distance to path_nodes 119 dist = [-1 if i not in path_nodes else 0 for i in range(len_)]#LCA树中的节点被标记为0,其他节点标记为-1 120 121 for i in range(len_): 122 if dist[i] < 0: #如果不是LCA的节点 123 stack = [i] 124 while stack[-1] >= 0 and stack[-1] not in path_nodes:# 125 stack.append(head[stack[-1]] - 1) #stack存储节点i以及他的祖先们,直到最高的祖先在path_nodes中 126 127 if stack[-1] in path_nodes: #如果节点i的最高祖先在LCA中 128 for d, j in enumerate(reversed(stack)): #stack存储的路径反序i<-B<-A 变成 A->B->i 129 dist[j] = d #dist[A] = 0 ,dist[B] = 1,dist[i] = 2,显然dist表示了各个节点到LCA树的距离 130 else: 131 for j in stack: #这部分节点说明与LCA没有边连接到,与LCA的距离自然是无穷大 132 if j >= 0 and dist[j] < 0: 133 dist[j] = int(1e4) # aka infinity 134 135 highest_node = lca 136 nodes = [Tree() if dist[i] <= prune else None for i in range(len_)] #剪枝 prune<=k,满足要求的节点Tree(),不满足要求的为None 137 138 #遍历一遍nodes,将LCA树创建好 139 for i in range(len(nodes)): 140 if nodes[i] is None: 141 continue 142 h = head[i] 143 nodes[i].idx = i 144 nodes[i].dist = dist[i] 145 if h > 0 and i != highest_node: 146 assert nodes[h-1] is not None 147 nodes[h-1].add_child(nodes[i]) 148 149 root = nodes[highest_node] 150 151 assert root is not None 152 return root
再调用tree_to_adj( )方法(第9行),将每棵依赖树转换为邻接矩阵。
1 def tree_to_adj(sent_len, tree, directed=True, self_loop=False): 2 """ 3 Convert a tree object to an (numpy) adjacency matrix. 4 把一个树对象转为邻接矩阵 5 """ 6 ret = np.zeros((sent_len, sent_len), dtype=np.float32) 7 8 queue = [tree] #树LCA根节点入队 9 idx = [] 10 while len(queue) > 0: 11 t, queue = queue[0], queue[1:] 12 13 idx += [t.idx] #LCA树的节点编号 14 15 for c in t.children: #t节点有孩子c节点,所以t到c有临界边 16 ret[t.idx, c.idx] = 1 17 queue += t.children #孩子节点入队遍历 18 19 if not directed: #这个参数关键决定是双向还是单向图 20 ret = ret + ret.T 21 22 if self_loop: #节点到自身循环边 23 for i in idx: 24 ret[i, i] = 1 25 26 return ret
最后将依赖树邻接矩阵做合适处理可以输入gcn当中了。
参考:
详解依存树的来龙去脉:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27590277/article/details/88345017
Standford依存句法详细解释:http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=IfW-hkMfPuK29t49Wa_nO2UAMpP2oGYCUAZuY5PrHHIQHsIm5moH82DMbTA521PMhCC4svgGRSgUTaSkHktw5Ru6RQCCRjwuHfkNVB3mcum
numpy库数组拼接np.concatenate:https://www.cnblogs.com/shueixue/p/10953699.html
PyTorch中Variable变量:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19329785/article/details/85029116



