WPF/MVVM模式入门教程(二):实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口
引用:https://www.cnblogs.com/flh1/p/12447188.html
1.创建NotifyPropertyChanged类
我们在common文件夹下创建一个名为NotifyPropertyChanged.cs的类,该类继承INotifyPropertyChanged接口主要用于消息通知,当UI里的值发生改变的时候,能够触发相应的改变。
2.创建Model
在Model文件夹下面创建一个FModel.cs,该类为数据模型,存放的是数据的字段。
3.创建ViewModel
在ViewModel文件夹下创建FViewModel.cs,该类为MVVM里最为重要的VM,主要是执行你的后台业务逻辑。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using MVVMtest1.common; using MVVMtest1.Model; namespace MVVMtest1.ViewModel { public class FViewModel: NotifyPropertyChanged { FModel fModel;//View跟Model中间隔着VM,所以要在VM里实例化Model public FViewModel() //构造函数 { fModel = new FModel() { Name="易羽晨"}; } public string Name { get { return fModel.Name; } set { if (fModel.Name!=value) { fModel.Name = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Name");//当字段改变时就通知 } } } } }
需要注意的是,VM要继承第一步创建的NotifyPropertyChanged,只有继承之后才能使用RaisePropertyChanged()方法
4.View的xaml代码
下面的代码是View的页面代码,其中的TextBox控件的Text绑定了Name字段,当Name字段发生改变的时候,该控件显示的内容也将会改变。
5.View的后台代码
在第四步的时候我们定义了页面,但是此时View还没有和ViewModel和Model联系起来,因此我们需要在该View的后代代码(F.xaml.cs)里加入一些东西
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Data; using System.Windows.Documents; using System.Windows.Input; using System.Windows.Media; using System.Windows.Media.Imaging; using System.Windows.Navigation; using System.Windows.Shapes; using MVVMtest1.ViewModel; namespace MVVMtest1 { /// <summary> /// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// </summary> public partial class MainWindow : Window { FViewModel f; public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); f = new FViewModel(); this.DataContext = f;//使View和ViewModel联系在一起 } private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { f.Name = "值发生改变"; } } }
其中的this.DataContext = f;是将Vime和ViewModel联系在了一起,然后我们通过一个按钮点击事件改变Name的值,看看页面的效果是否发生改变。之前说过了,使用MVVM模式的目的就是为了使项目高内聚低耦合,理想状态View的后台代码是不能写按钮点击事件的,但现在只是临时的,下一章将会讲到通过命令的手段实现按钮点击事件,实现低耦合的目标。
6.运行效果
点击按钮前
点击按钮后
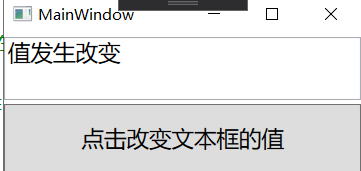
可以看到,我们已经实现了通过NotifyPropertyChanged接口实现了消息的传递,以及UI的更改。下一章将会讲关于命令的内容。
HK




