java调用python脚本 并传参(根据配置文件获取python文件地址)
方式一:
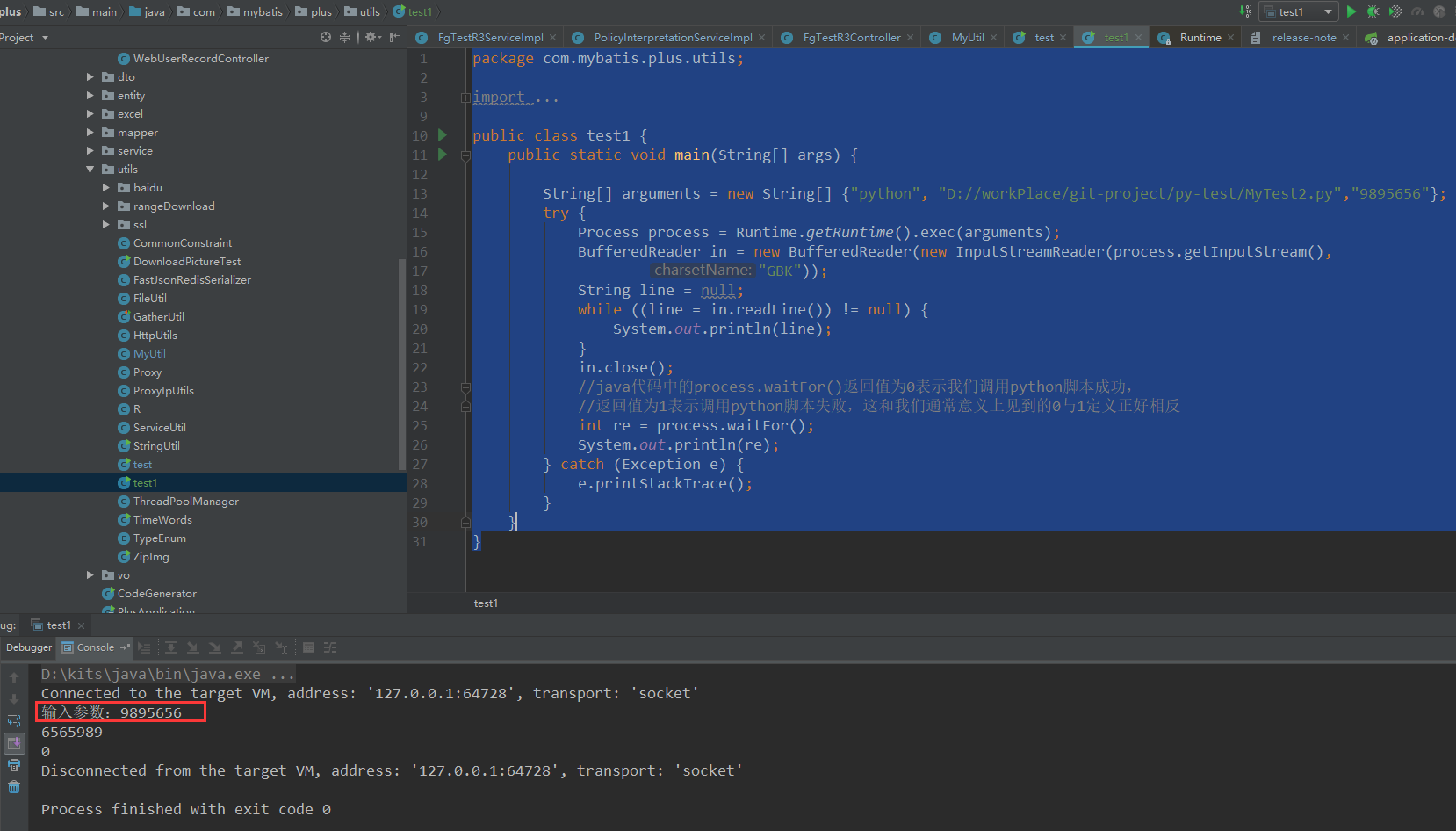
Java代码
package com.mybatis.plus.utils;
import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arguments = new String[] {"python", "D://test.py","9895656"};
try {
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(arguments);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream(),
"GBK"));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
in.close();
//java代码中的process.waitFor()返回值为0表示我们调用python脚本成功,
//返回值为1表示调用python脚本失败,这和我们通常意义上见到的0与1定义正好相反
int re = process.waitFor();
System.out.println(re);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Python
from enum import Enum
import sys
class Solution:
def reverse(self, x: int) -> int:
if x==0:
return 0
strList = []
isPositive = True
if x < 0:
isPositive = False
value = abs(x)
temp = value
while (temp/10.0>0.09):
i = temp%10
strList.append(str(i))
temp = temp//10
join = "".join(strList)
result = int(join)
if result>2147483647:
result=0
if isPositive == False:
result = -result
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
so = Solution()
print("输入参数:"+sys.argv[1])
print(so.reverse(int(sys.argv[1])))
读取配置文件中的数据
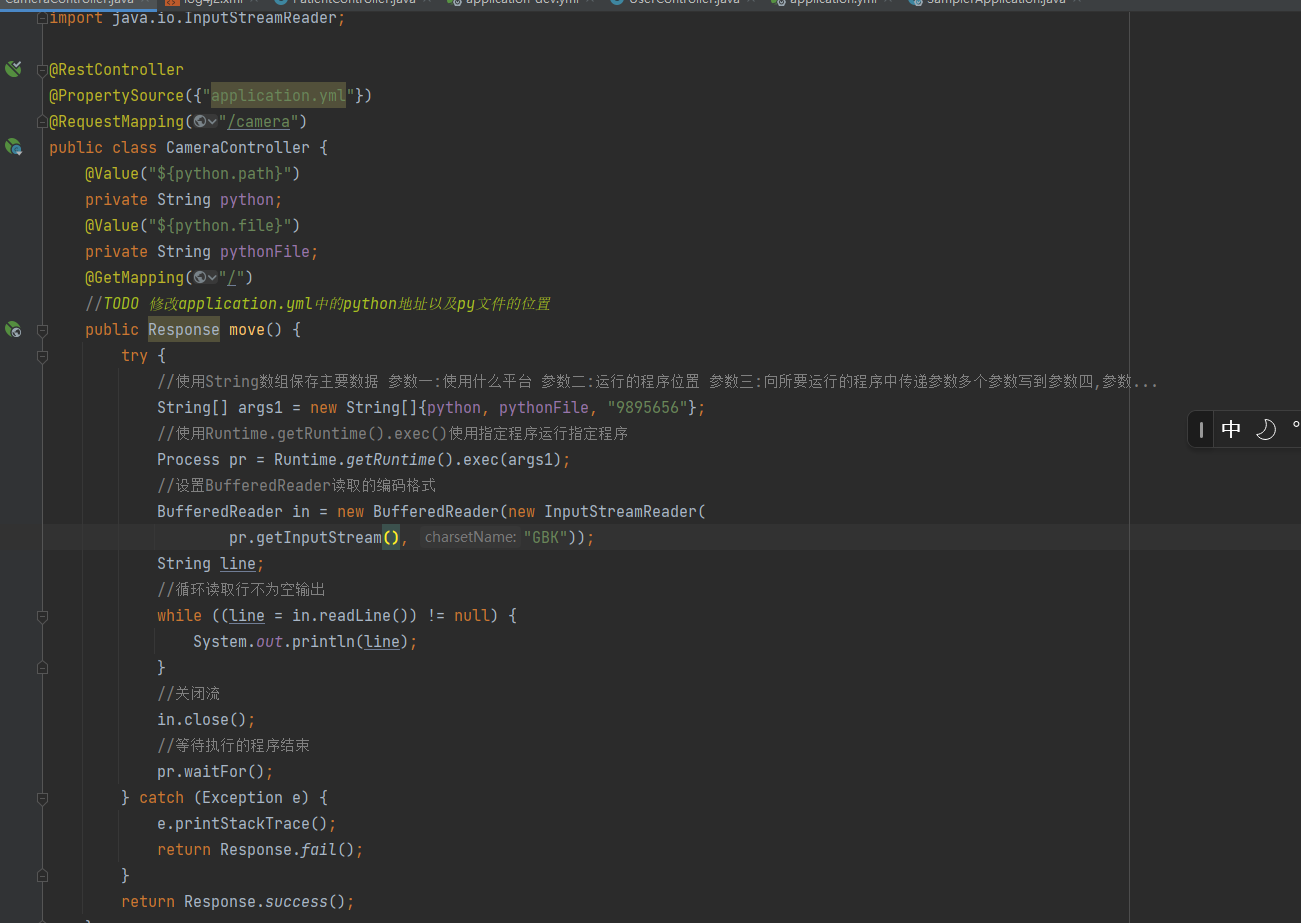
Java代码
import com.mysql.cj.log.Log;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
@RestController
@PropertySource({"application.yml"})
@RequestMapping("/camera")
public class CameraController {
@Value("${python.path}")
private String python;
@Value("${python.file}")
private String pythonFile;
@GetMapping("/")
//TODO 修改application.yml中的python地址以及py文件的位置
public Response move() {
try {
//使用String数组保存主要数据 参数一:使用什么平台 参数二:运行的程序位置 参数三:向所要运行的程序中传递参数多个参数写到参数四,参数...
String[] args1 = new String[]{python, pythonFile, "9895656"};
//使用Runtime.getRuntime().exec()使用指定程序运行指定程序
Process pr = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args1);
//设置BufferedReader读取的编码格式
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
pr.getInputStream(), "GBK"));
String line;
//循环读取行不为空输出
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
//关闭流
in.close();
pr.waitFor();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return Response.fail();
}
return Response.success();
}
}
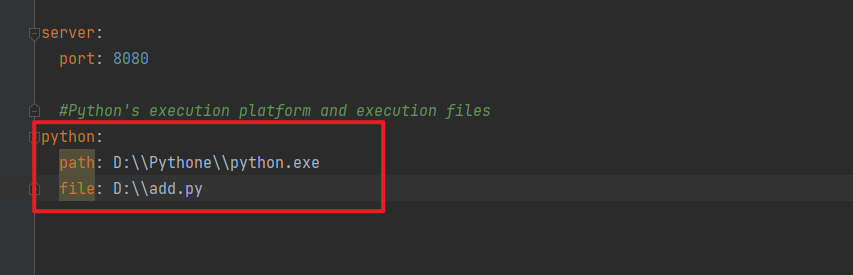
application.yml配置文件
方式二:
此方法需要引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.python</groupId>
<artifactId>jython-standalone</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.python.core.PyFunction;
import org.python.core.PyInteger;
import org.python.core.PyObject;
import org.python.util.PythonInterpreter;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
class SamplerApplicationTests {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
PythonInterpreter interpreter = new PythonInterpreter();
interpreter.execfile("D:\\add1.py");
// 第一个参数为期望获得的函数(变量)的名字,第二个参数为期望返回的对象类型
PyFunction pyFunction = interpreter.get("add", PyFunction.class);
int a = 5, b = 10;
//调用函数,如果函数需要参数,在Java中必须先将参数转化为对应的“Python类型”
PyObject pyobj = pyFunction.__call__(new PyInteger(a), new PyInteger(b));
System.out.println("the anwser is: " + pyobj);
}
}
python代码
def add(a,b):
return a + b


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号