比赛链接:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/33186
A.Villages: Landlines
题意:
数轴上有 \(n\) 个点,每个点能覆盖左右长为 \(r\) 的地方,问将所有线段都连接还需多长的线段。
思路:
区间覆盖问题,将所有线段排序之后求值即可。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL n;
cin >> n;
vector < pair<LL, LL> > range;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
LL x, r;
cin >> x >> r;
range.push_back({x - r, x + r});
}
sort(range.begin(), range.end());
LL ans = 0, R = range[0].second;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ){
if (range[i].first > R){
ans += range[i].first - R;
}
R = max(R, range[i].second);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
B.Spirit Circle Observation
SAM,fail 树,虚树
C.Grab the Seat!
模拟
D.Mocha and Railgun
题意:
给定一个圆和一个在圆内的点,从该点以任意角度向圆上发射一个长为 \(2d\) 的电磁炮,问最多能摧毁多长的圆。
思路:
由原点向电磁炮的边界做垂线。
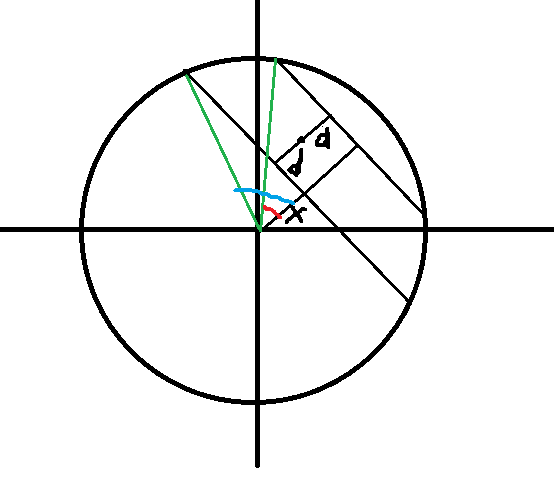
要求的角就是绿色的两条线夹的角,所以先求出红色的角,再求蓝色的角。
设原点距离最近的一个边界的距离为 \(x\)。
以弧度表示就为答案为 \(arccos(\frac{x}{r}) - arccos(\frac{r + 2d}{r})\)。
对该函数求导,得到 \(- \frac{1}{r\sqrt{1 - \frac{x^2}{r^2}}} + \frac{1}{r\sqrt{1 - \frac{(x + 2d)^2}{r^2}}}\)。
导数始终大于 0,所以随着 \(x\) 的增大,答案增大。\(x\) 最大的时候为原点和该点的连线。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
void solve(){
double r, x, y, d;
cin >> r >> x >> y >> d;
double dis = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
double rad = acos((dis - d) / r) - acos((dis + d) / r);
cout << rad * r << "\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(10);
LL T;
cin >> T;
while(T -- ){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
G.Lexicographical Maximum
题意:
输出 1 到 \(n\) 中字典序最大的数。
思路:
如果 \(n\) 除了最后一位都是 9,那这个数的字典序最大。
否则,记 \(n\) 的长度为 \(s\),\(s - 1\) 个 9 的字典序最大。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
LL len = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i ++ ){
if (s[i] != '9'){
string t(len - 1, '9');
cout << t << "\n";
return 0;
}
}
cout << s << "\n";
return 0;
}
I.Chiitoitsu
题意:
打麻将,手中有十三张手牌,保证手中没有相同的三张手牌,每回合可以从牌堆中随机摸一张,然后判断手中有没有七个对子,接着打掉一张牌到弃牌堆(弃牌堆中的牌后续不会抽),每次都采用最优策略。每次询问告诉初始手牌,问抽到七小对的期望是多少。
思路:
概率 \(dp\)。设 \(dp_{i,j}\) 表示手中还有 \(i\) 张单牌,牌堆中还有 \(j\) 张牌,在最优决策下,凑出七小对的期望。
\(i\) 的取值只可能为 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13。
当 \(i\) == 1 时,抽到牌堆中任意对应的三张牌都可以完成,容易得到转移方程 \(dp_{i,j} = 1 + \frac{j - 3}{j}dp_{i,j - 1}\)。
剩余的情况,无法一次完成,需要加上没抽到手牌中单牌对应的牌和抽到这两种情况。
得到转移方程 \(dp_{i,j} = 1 + \frac{j - 3i}{j}dp_{i, j - 1} + \frac{3i}{j}dp_{i - 2, j - 1}\)。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
LL dp[15][130];
LL qp(LL a, LL k, LL p){
LL ans = 1;
while (k){
if (k & 1) ans = ans * a % p;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % p;
}
return ans;
}
LL inv(LL x){
return qp(x, mod - 2, mod);
}
void solve(){
string s;
cin >> s;
LL n = s.size();
map <string, LL> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2){
string t = "";
t += s[i];
t += s[i + 1];
mp[t] ++ ;
}
LL cnt = 0;
for (auto [x, y] : mp)
cnt += (y == 1);
cout << dp[cnt][123] << "\n";
}
void init(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 13; i += 2 ){
for (int j = 1; j <= 123; j ++ ){
if (i == 1){
dp[i][j] = (1 + (j - 3) * inv(j) % mod * dp[i][j - 1] % mod) % mod;
}
else{
dp[i][j] = (1 + ((j - 3 * i) * inv(j) % mod * dp[i][j - 1] % mod + 3 * i * inv(j) % mod * dp[i - 2][j - 1] % mod) % mod) % mod;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
init();
LL T;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i ++ ){
cout << "Case #" << i << ": ";
solve();
}
return 0;
}
J.Serval and Essay
题意:
\(n\) 个论点,当且仅当一个论点的前置论点都被证明的时候它才能被证明,现在已知各论点之间的 \(m\) 条推导关系,可以假设任意一个论点证明,问最多能推导多少个论点。
思路:
建立一个图,可知当一个点入度为 1 的时候,前面那个论点证明之后它就可以被证明,所以可以将这两个点合并。
这里可以用启发式合并的思想,将出度小的那个点合并到出度大的点。因为点的融合过程中,边可能会重复,所以可以用 \(set\) 去存边。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
set <LL> to[N], from[N];
LL n, p[N], sz[N];
LL get(LL x){
return (x == p[x] ? x : (p[x] = get(p[x])) );
}
void unite(LL x, LL y){
x = get(x);
y = get(y);
if (x == y) return;
if (to[x].size() > to[y].size()){
swap(x, y);
}
p[x] = y;
sz[y] += sz[x];
vector < pair<LL,LL> > v;
for (auto t : to[x]){
to[y].insert(t);
from[t].insert(y);
from[t].erase(x);
if (from[t].size() == 1){
v.push_back({y, t});
}
}
for (auto [a, b] : v)
unite(a, b);
}
void init(){
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
to[i].clear();
from[i].clear();
p[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
init();
for (int u = 1; u <= n; u ++ ){
LL k;
cin >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i ++ ){
LL v;
cin >> v;
to[v].insert(u);
from[u].insert(v);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
if (from[i].size() == 1){
unite(i, *from[i].begin());
}
}
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
ans = max(ans, sz[i]);
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
LL T = 1;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i ++ ){
cout << "Case #" << i << ": ";
solve();
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号