比赛链接:
https://codeforces.com/contest/1598
A. Computer Game
题目大意:
由 1 和 0 组成的 2 行 \(n\) 列的地图,可以移动到 0 的格子,不能去 1 的格子,从(1, 1)出发,每一次都可以移动到周围的八个格子(不能移出地图),判断能不能到达(2, \(n\))。
思路:
显然,不能抵达终点的情况就是两行都是 1 的时候。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define fi first
#define LL long long
#define se second
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1;
LL T = 1, n;
string a, b;
void solve(){
cin >> n >> a >> b;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] == '1' && b[i] == '1'){
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
cout << "YES\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
B. Groups
题目大意:
有 \(n\) (为偶数)个学生周一到周五的日程表,0 表示学生该日没空,1 表示有空,判断能不能将所有学生分成两组去上课,两组的学生数量要相同且他们在同一天都有空,但是两组有空的那一天要不同。
思路:
假设 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 分别为两组有空的那天,因为组合数很少,所以直接 暴力 跑出来。然后遍历所有学生,统计能不能找出两组这样的学生来。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define fi first
#define LL long long
#define se second
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1;
LL T = 1, n;
int a[1010][10];
string s;
void solve(){
scanf("%lld", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++)
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
for (int x = 1; x <= 5; x++){
for (int y = x + 1; y <= 5; y++){
int s1 = 0, s2 = 0, s3 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if (a[i][x] && a[i][y]) s3++;
else if (a[i][x]) s1++;
else if (a[i][y]) s2++;
}
if (s1 * 2 <= n && s2 * 2 <= n && s1 + s2 + s3 == n){
cout << "YES\n";
return;
}
}
}
cout << "NO\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
C. Delete Two Elements
题目大意:
给了长为 \(n\) 的整数序列,假设 \(k\) 是它的平均值,平均值可能是小数,计算去掉其中两个数 \(a_i 和 a_j (i < j)\) 之后序列的平均值不变的情况有几种。
思路:
假设 \(sum\) 是序列值的总和,去掉的数分别是 \(a_i\) 和 \(a_j\),那么可以得到 \(a_i\) + \(a_j\) = 2 * \(k\) = 2 * \(sum / n\),也就是 \((a_i + a_j) * n\) = 2 * \(sum\)。
我们可以先由小到大排序整个序列,那么对于 \(a_i\) 而言,满足条件的只能在它后面找,直接 二分 查找大于等于 \(2 * sum / n - a_i\) 的数即可,所有等于这个值的数的组合都是可以的。计算组合总数的话可以通过 \(map\) 去实现。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define fi first
#define LL long long
#define se second
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1;
LL T = 1, n, a[N];
string s;
void solve(){
scanf("%lld", &n);
map <LL, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
mp[a[i]]++;
}
LL sum = 2 * accumulate(a + 1, a + n + 1, 0LL), ans = 0;
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int p = lower_bound(a + i + 1, a + n + 1, sum / n - a[i]) - a;
mp[a[i]]--;
if ( (a[i] + a[p]) * n == sum) ans += mp[a[p]];
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
D. Training Session
题目大意:
有 \(n\) 个问题,\(a_i\) 和 \(b_i\) 分别是问题的主题和难度,不会出现主题和难度相同的题目,找其中的三个问题,让它们满足主题全部不一样或者难度全部不一样,计算符合条件的三个问题的组合有几种。
思路:
反一下考虑,不求满足条件的组合数,而是求总数减去不符合条件的数量。
对于 \(n\) 个数,总共有 \(n * (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 6\) 种可能的组合。
假设某问题的主题是 \(a\),难度是 \(b\),那么和它组合起来不符合条件的问题可以是主题相同或者是难度相同。
设主题为 \(a\) 的问题的数量是 \(ca\),难度是 \(b\) 的问题的数量是 \(cb\),那不符合条件的组合数就是 \((ca - 1) * (cb - 1)\)。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define fi first
#define LL long long
#define se second
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1;
LL T = 1, n;
void solve(){
cin >> n;
vector <LL> a(n), b(n), ca(n + 1), cb(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%lld%lld", &a[i], &b[i]);
ca[a[i]]++, cb[b[i]]++;
}
LL ans = n * (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 6;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ans -= (ca[a[i]] - 1) * (cb[b[i]] - 1);
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main(){
cin >> T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
E. Staircases
题意:
\(n * m\) 的矩阵,每个格子有两个状态,释放或者锁住。
当一条路径满足以下三个条件时,被称作楼梯:
1.从释放的节点出发,到达释放的节点。
2.路径上只经过释放的节点。
3.符合下列两种移动方式。
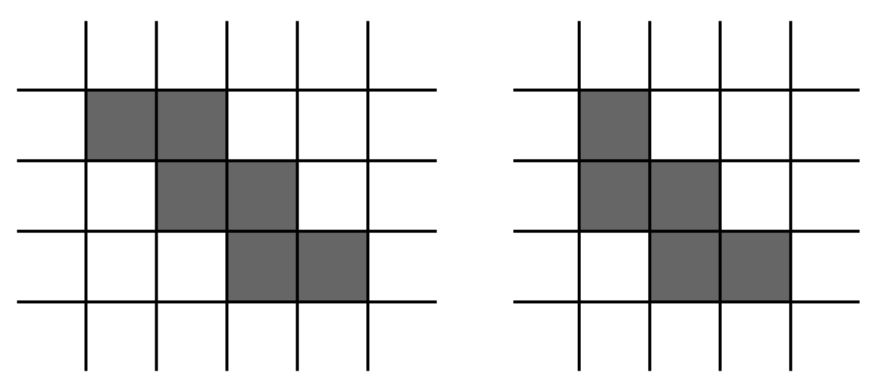
具体可以看题目。
初始所有的格子都是释放的,\(q\) 次询问,每次翻转指定的格子的状态,然后输出矩阵中楼梯总数。
思路:
定义 \(dp[i][j][0]\) 表示从右边过来的路径总数,\(dp[i][j][1]\) 表示从上面下来的路径总数。
每次修改一个格子,可以发现,它会更改右下角的部分格子的状态,可以通过 \(dfs\) 去修改,而修改的时间复杂度是 \(O(n)\) 的。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
LL n, m, q, x, y, dp[N][N][2], sum, a[N][N];//0表示右过来,1表示上下来
void dfs(LL x, LL y, LL f){
if (x > n || y > m) return;
sum -= dp[x][y][f];
if (a[x][y]) dp[x][y][f] = 0;
else if (f) dp[x][y][f] = dp[x - 1][y][0] + 1;
else dp[x][y][f] = dp[x][y - 1][1] + 1;
sum += dp[x][y][f];
if (f) dfs(x, y + 1, 0);
else dfs(x + 1 , y, 1);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ){
dp[i][j][0] += dp[i][j - 1][1] + 1;
dp[i][j][1] += dp[i - 1][j][0] + 1;
sum += dp[i][j][0] + dp[i][j][1];
}
}
LL cnt = n * m;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ){
cin >> x >> y;
a[x][y] ^= 1;
cnt += (a[x][y] ? -1 : 1);
dfs(x, y, 0);
dfs(x, y, 1);
cout << sum - cnt << "\n";
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号