Unity 世界坐标&局部坐标下的旋转
一、旋转方法
在 Unity 中为物体旋转提供了各种 API ,例如 RotateAround、Rotate、LookAt 等方法。但为了避免万向节死锁的问题,一般使用四元数来表示物体的旋转。
四元数的乘法可以看作对一个物体施加两次旋转,最终的旋转角度由这两次旋转的角度决定,旋转的顺序也会对旋转的结果产生影响(Q1*Q2≠Q2*Q1),因为四元数乘法的本质就是矩阵的乘法。
二、世界坐标&局部坐标
物体的坐标分为世界坐标(global)和局部坐标(local)
-
世界旋转坐标(如transform.rotation)表示物体相对于世界坐标系下的旋转角度
-
局部旋转坐标(如transform.localRotation)表示物体相对于父物体坐标系下的旋转角度,如果没有父物体,则局部旋转坐标与世界旋转坐标相同
另外,在 Inspector 面板中 Transform 的值也是物体的局部坐标。
三、世界坐标下的旋转
利用四元数旋转时要记住:旋转轴属于世界坐标系还是物体坐标系是由乘法的顺序决定的。
所以
-
绕本地轴进行旋转时:transform.rotation = transform.rotation * Quaternion;
-
绕世界轴进行旋转时:transform.rotation = Quaternion * transform.rotation;
在这里不需要知道任何本地旋转坐标或者对旋转轴进行坐标系之间的转换。
四、局部坐标下的旋转
在局部坐标下的旋转操作也是一样的,只有旋转顺序决定了旋转轴属于世界坐标系还是物体坐标系:
-
绕本地轴进行旋转:transform.localRotation = transform.localRotation * Quaternion;
-
绕世界轴进行旋转:transform.localRotation = Quaternion * transform.localRotation;
对于绕本地轴的旋转,在世界坐标以及局部坐标下进行操作的结果是相同的,而绕世界轴旋转时,得到的结果是不一样的。
因为这时物体的旋转实际上可以分为两个过程:
物体本地的旋转(相对于父物体的旋转)+ 父物体的旋转,也就是 transform.rotation = transform.parent.transform.rotation * transform.localRotation。
五、旋转实例
首先创建一个父物体 parentCube,两个子物体 childCube1、childCube2。
1、本地轴旋转
1 using UnityEngine; 2 3 public class QuaternionTest : MonoBehaviour 4 { 5 public Transform childCube1; 6 public Transform childCube2; 7 8 void Update() 9 { 10 Quaternion rotU = Quaternion.AngleAxis(100 * Time.deltaTime, Vector3.up); 11 childCube1.transform.rotation = childCube1.transform.rotation * rotU; 12 childCube2.transform.localRotation = childCube2.transform.localRotation * rotU; 13 } 14 }
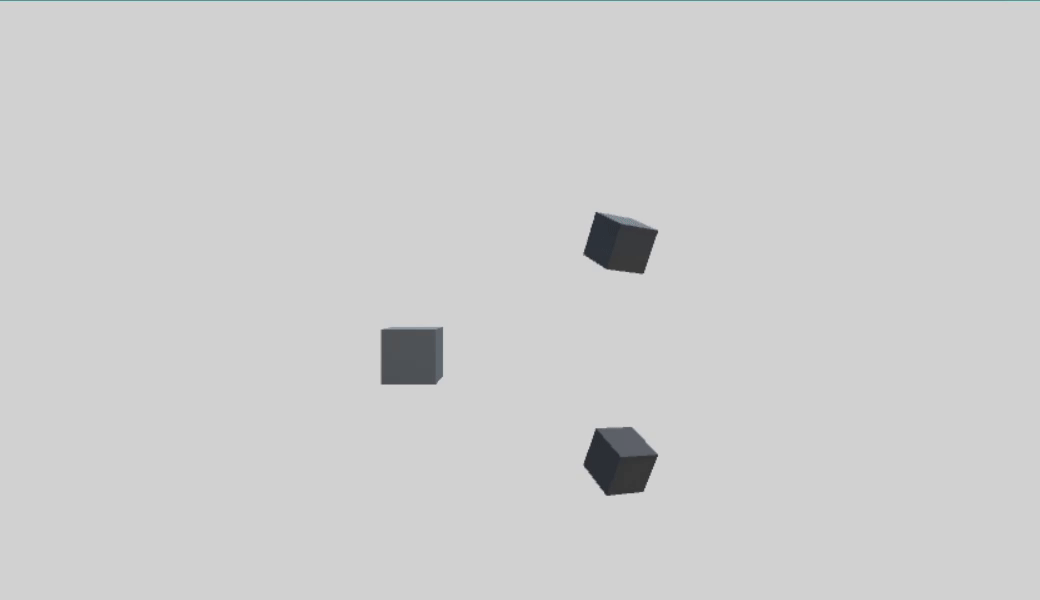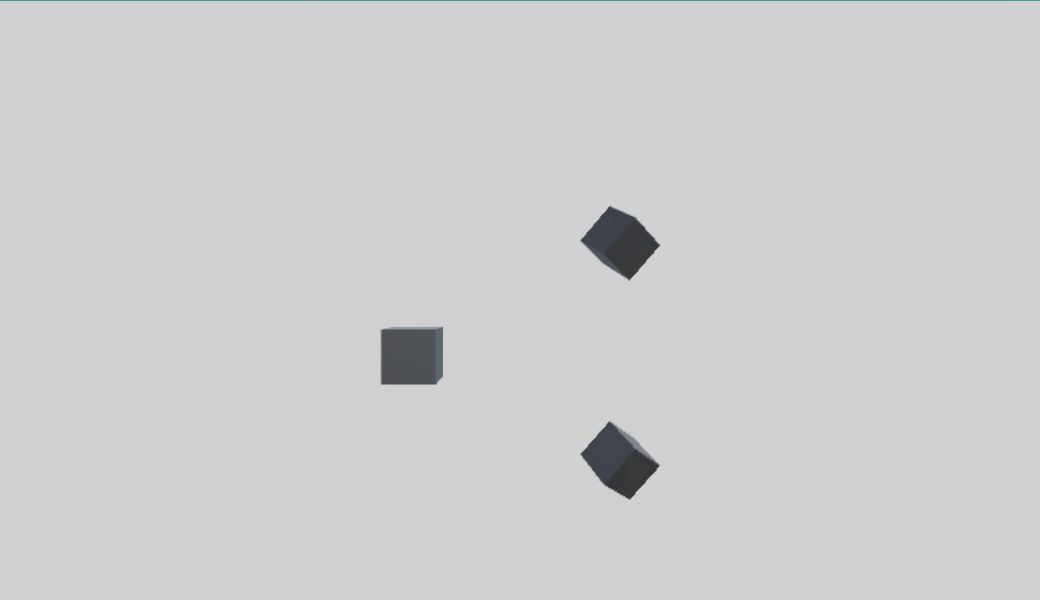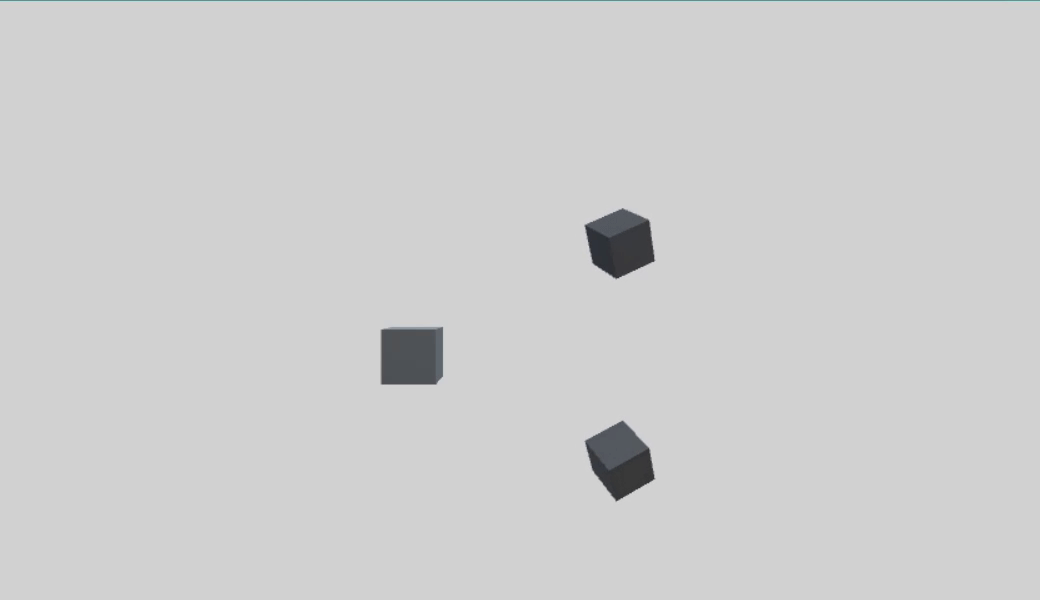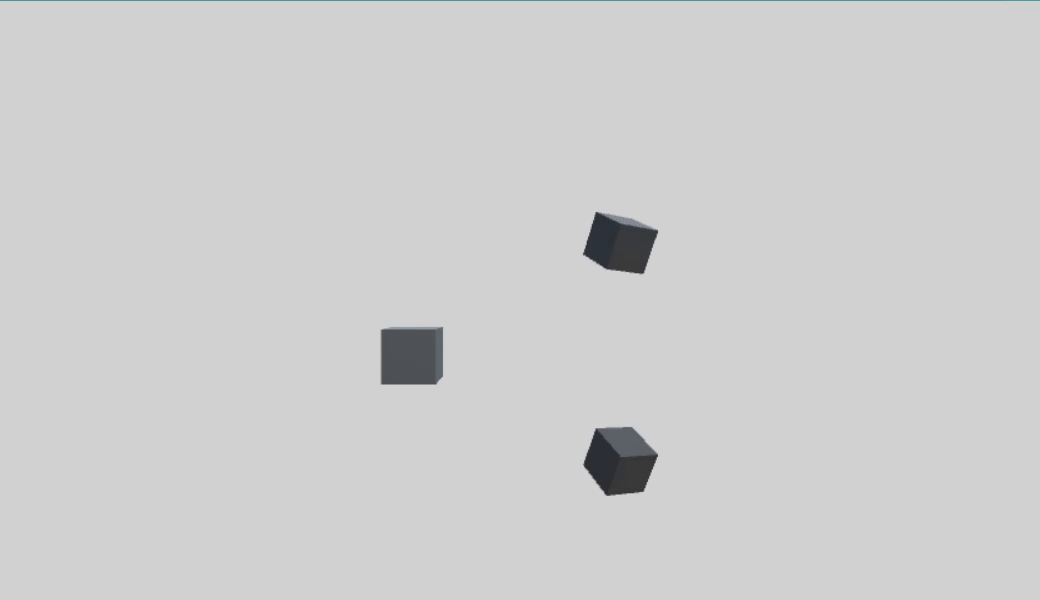
右乘表示物体绕本地轴旋转,所以 childCube 的旋转是绕自身Y轴进行的,parentCube 的旋转并不会对 childCube 旋转产生影响,两种方式旋转相同。
2、世界轴旋转
1 using UnityEngine; 2 3 public class QuaternionTest : MonoBehaviour 4 { 5 public Transform childCube1; 6 public Transform childCube2; 7 8 void Update() 9 { 10 Quaternion rotU = Quaternion.AngleAxis(200 * Time.deltaTime, Vector3.up); 11 childCube1.transform.rotation = rotU * childCube1.transform.rotation; 12 childCube2.transform.localRotation = rotU * childCube2.transform.localRotation; 13 } 14 }

左乘表示物体绕世界轴旋转,在世界坐标下进行旋转的时候无需考虑父物体的旋转角度,导致 childCube1 最终旋转轴是世界坐标系的Y轴。
而在局部坐标下进行旋转的时候可以理解为先将父物体的旋转角度置零,此时 childCube2 绕世界坐标系的Y轴旋转,之后再进行父物体的旋转,这样就会导致物体旋转轴随着父物体改变而改变,换句话说就是物体本身的旋转轴会指向父物体的Y轴。

3、rotation与localrotation的关系
物体的旋转 = 物体相对于父物体的旋转 + 父物体的旋转,即 transform.rotation=transform.parent.transform.rotation * transform.localRotation
1 using UnityEngine; 2 3 public class QuaternionTest : MonoBehaviour 4 { 5 public Transform childCube1; 6 public Transform childCube2; 7 8 void Update() 9 { 10 Quaternion rotU = Quaternion.AngleAxis(200 * Time.deltaTime, Vector3.up); 11 childCube1.transform.rotation = childCube1.transform.parent.transform.rotation * rotU * childCube1.transform.localRotation; 12 childCube2.transform.localRotation = rotU * childCube2.transform.localRotation; 13 } 14 }
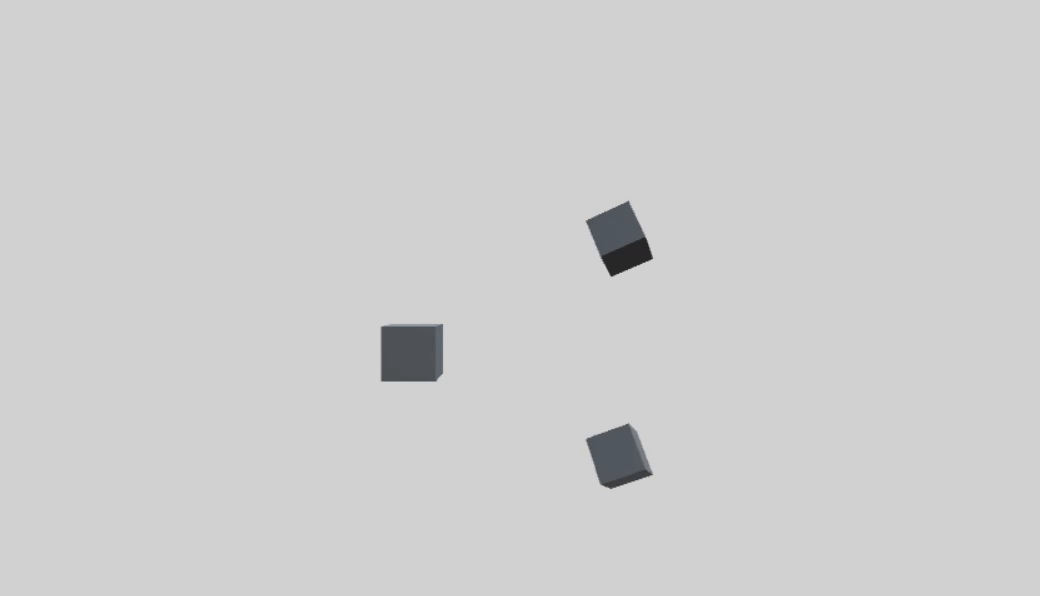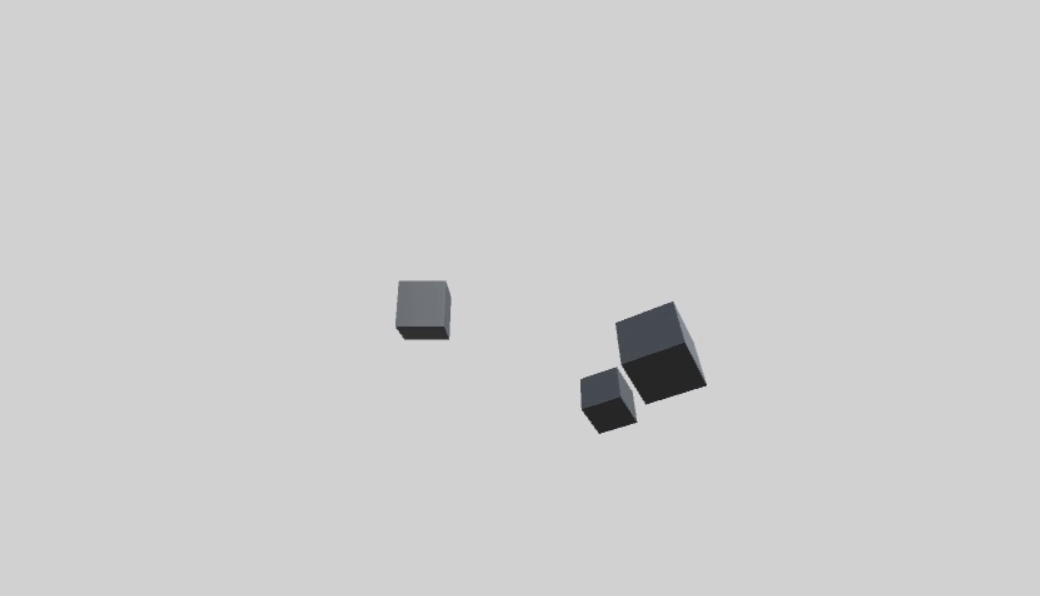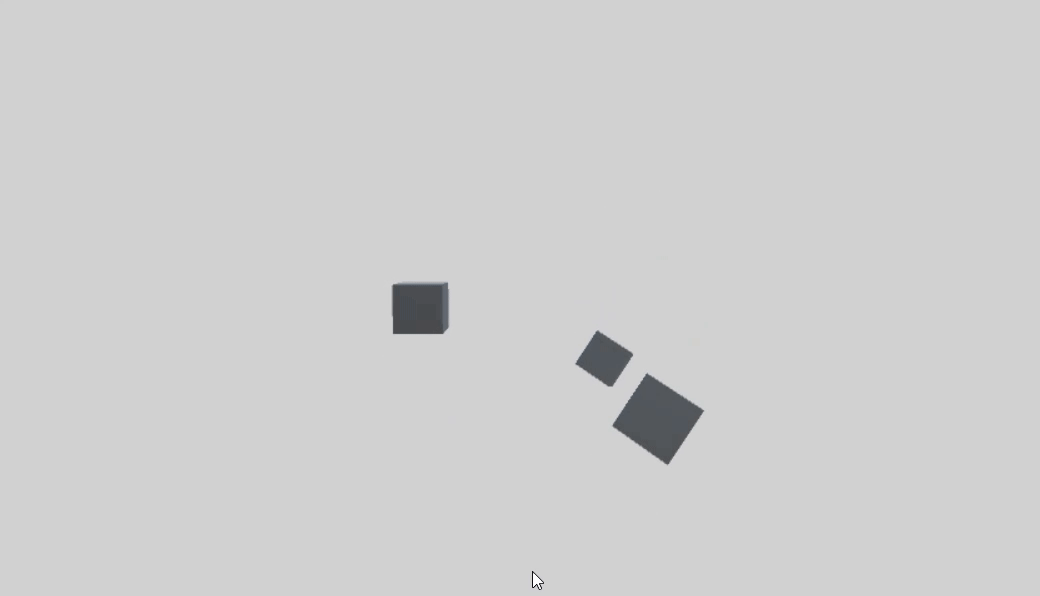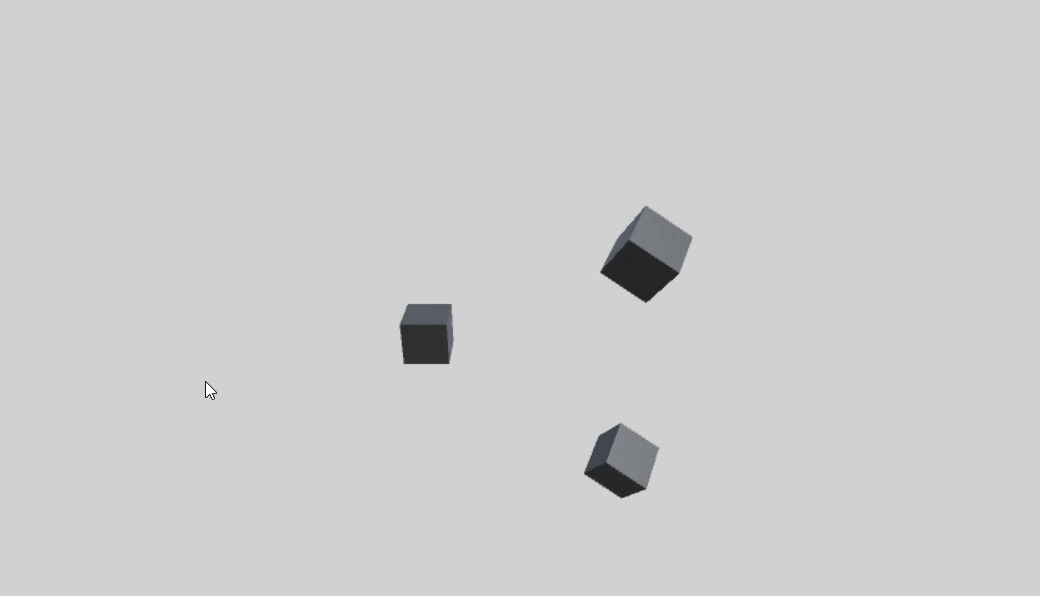
这两个的旋转轴相同,都是父物体的Y轴
六、总结
在使用四元数进行旋转操作的时候要注意乘法的顺序:左乘代表绕世界轴旋转,右乘代表绕本地轴旋转。
在对世界坐标和局部坐标进行右乘时二者会得到相同的结果,而进行左乘时则会得到不同的结果,根本的原因是对局部坐标操作时需要考虑父物体的旋转,而对世界坐标操作时则不需要这种情况。
*** | 以上内容仅为学习参考、学习笔记使用 | ***


