OO前三次博客作业
OO前三次博客作业
前言:前三次作业一共有13道题,第一次作业较为简单,都是一些简单的编程题,涉及到的知识点点比较容易,一些简单的java基本语法,第二次作业一共有五道题,后三道题都是关于年月日的计算,具体来说也比较简单,关键是方法的使用和创建。第三次作业是类的创建,其中以第三题比较难,需要使用到正则表达式,思路上难度适中,关键是对正则表达式的写法。
7-8 判断三角形类型 (20 分)
输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形。
输入格式:
在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。
输出格式:
(1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”; (2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”; (5)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”; (6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”; (7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
50 50 50.0
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Equilateral triangle
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
60.2 60.2 80.56
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Isosceles triangle
结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0.5 20.5 80
结尾无空行
源代码:
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = sc.nextDouble();
double b = sc.nextDouble();
double c = sc.nextDouble();
if (a < 1 || a > 200 || b < 1 || b > 200 || c < 1 || c > 200)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else {
if (a + b <= c || b + c <= a || a + c <= b)
System.out.println("Not a triangle");
else {
if (a == b && b == c)
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
else if ((a == b && a * a + b * b-c * c<0.1) || (a == c && a * a + c * c - b * b<0.1) || (c == b && c * c + b * b - a * a<0.1))
System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
else if (a == b || b == c || c == a)
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
else if (a * a + b * b == c * c || a * a + c * c == b * b || c * c + b * b == a * a)
System.out.println("Right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.println("General triangle");
}
}
}
}
题目分析:这道题没有使用到类,类图就不画了,这道题的思路主要是用if else去一一筛选各个三角形所需要的条件,
这里注意,等腰直角三角形的判断条件是
a == b && a * a + b * b-c * c<0.1
是因为三角形的三条边有精度误差,无法很好的计算出结果。
难度分析:较为简单,知识点重在判断的掌握。
7-4 求下一天 (30 分)
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该日期的下一天。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法。
要求:Main类中必须含有如下方法,签名如下:
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天
输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
1.当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Wrong Format”;
2.当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next date is:年-月-日
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2020 3 10
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Next date is:2020-3-11
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2025 2 10
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
点击查看代码
package com.Javaheima;
import java.util.Scanner;
package com.Javaheima;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = sc.nextDouble();
double b = sc.nextDouble();
double c = sc.nextDouble();
if (a < 1 || a > 200 || b < 1 || b > 200 || c < 1 || c > 200)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else {
if (a + b <= c || b + c <= a || a + c <= b)
System.out.println("Not a triangle");
else {
if (a == b && b == c)
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
else if ((a == b && a * a + b * b-c * c<0.1) || (a == c && a * a + c * c - b * b<0.1) || (c == b && c * c + b * b - a * a<0.1))
System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
else if (a == b || b == c || c == a)
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
else if (a * a + b * b == c * c || a * a + c * c == b * b || c * c + b * b == a * a)
System.out.println("Right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.println("General triangle");
}
}
}
}
public class Main{
//主方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = sc.nextInt();
int month = sc.nextInt();
int day = sc.nextInt();
if (checkInputValidity(year, month, day)) {
nextDate(year,month,day);
} else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型;
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
}
//求输入日期的下一天
public static void nextDate(int year, int month, int day) {
int[] runmouth = new int[]{0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int[] pinmouth = new int[]{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int nextday, nextmonth, nextyear;
if (isLeapYear(year)) {
//判断是否跨月
if (day == runmouth[month]) {
//判断是否跨年
if (month == 12) {
nextday = 1;
nextmonth = 1;
nextyear = year + 1;
} else {
nextday = 1;
nextmonth = month + 1;
nextyear = year;
}
} else {
nextday = day + 1;
nextmonth = month;
nextyear = year;
}
} else {
//判断是否跨月
if (day == pinmouth[month]) {
//判断是否跨年
if (month == 12) {
nextday = 1;
nextmonth = 1;
nextyear = year + 1;
} else {
nextday = 1;
nextmonth = month + 1;
nextyear = year;
}
} else {
nextday = day + 1;
nextmonth = month;
nextyear = year;
}
}
System.out.println("Next date is:" + nextyear + "-" + nextmonth + "-" + nextday);
}
//查看输入的日期是否合理
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year, int month, int day) {
int[] runmouth = new int[]{0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int[] pinmouth = new int[]{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
if (year < 1820 || year > 2020)
return false;
else {
if (month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > 31) {
return false;
} else {
if (isLeapYear(year)) return day <= runmouth[month];
else {
return day <= pinmouth[month];
}
}
}
}
}
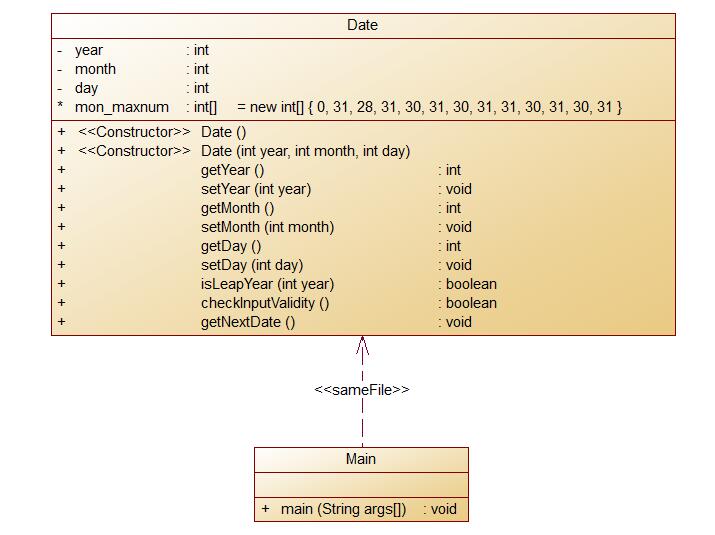
类图

题目分析:这道题我只设置了一个类,但是根据题目写了很多方法。在这里,我着重讲一下我写
的四个方法的思路和构成。首先,isLeapYear()方法,判断是否是闰年,条件是能被四整除或不能被一百整除但被400整除。
7.2
是一个比较简单的闰年的判断。
nextDate(int year, int month, int day) ,这个是求下一天的日期的一个方法,具体的思路:是先写出两个数组,里面分别记载了平年和闰年的各个月的日数,然后定义三个变量,nextday, nextmonth, nextyear,是下一天的年月日。先分两支,判断是平年还是闰年,再判断日期是不是合理,接下来判断是否跨年
if (day == runmouth[month])
如果跨年的话,判断是否跨月
if (month == 12)
如果要跨年的话,就把nextday变为1,nextyear变为1,nextyear自加一
nextday = 1;
nextmonth = 1;
nextyear = year + 1;
如果不跨年的话,检查是否跨月份,跨月份的话,月份就加一,日期为一,
nextday = 1;
nextmonth = month + 1;
nextyear = year;
如果不跨月的话,单单把日期加1就好了;
这道题总体难度偏简单,很容易想到,就是对于条件的判断有一定的难度.
7-2 定义日期类 (28 分)
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
要求:Date类结构如下图所示:
类图.jpg
输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Date Format is Wrong”;
当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next day is:年-月-日
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1912 12 25
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Next day is:1912-12-26
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2001 2 30
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Date Format is Wrong
结尾无空行
源代码
点击查看代码
package com.Javaheima;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Date{
static int year;
static int month;
static int day;
int[] dayNum=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public Date(int year,int month,int day){
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public Date() {
int year,month,day;
}
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
boolean isLeapYear;
isLeapYear = ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0);
return isLeapYear;
}
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year, int month, int day) {
boolean checkInputValidity;
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(!isLeapYear(year))
a[2] = 28;
checkInputValidity = (year>=1900&&year<=2000&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=a[month]&&day>0);
return checkInputValidity;
}
public static void getnextDate(int year,int month,int day) {
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0;
if(!isLeapYear(year))
a[2] = 28;
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)) {
if(month==12) {
if(day==a[month]) {
year = year+1;
m = 1;
d=1;
}
else{
m=month;
d =day +1;
}
}
else {//如果不是12月
if(day==a[month]) {
m = month + 1;
d = 1;
}
else{
m=month;
d = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in);
Date rq=new Date();
rq.setYear(x.nextInt());
rq.setMonth(x.nextInt());
rq.setDay(x.nextInt());
rq.getnextDate(rq.getYear(), rq.getMonth(),rq.getDay());
}
}
复杂度分析
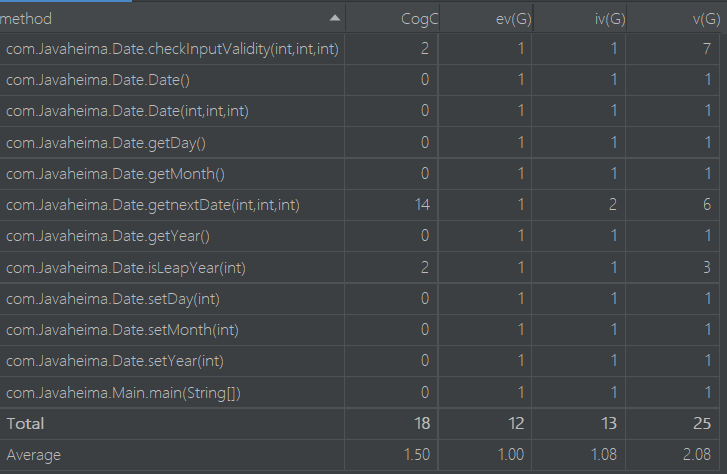
这道题定义了一个Date类,是个日期类,他包括了计算这道题的所有关键点,具体思路:用checkInputValidity判断输入日期的合法性,然后用isLeapyear()判断是否闰年,最后再用nextDate()求下一天
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
boolean isLeapYear;
isLeapYear = ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0);
return isLeapYear;
}
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year, int month, int day) {
boolean checkInputValidity;
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(!isLeapYear(year))
a[2] = 28;
checkInputValidity = (year>=1900&&year<=2000&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=a[month]&&day>0);
return checkInputValidity;
}
public static void getnextDate(int year,int month,int day) {
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0;
if(!isLeapYear(year))//如果不是闰年
a[2] = 28;
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)) {//如果输入的数字合法
if(month==12) {//如果是12月
if(day==a[month]) {//如果是12月的最后一天
year = year+1;
m = 1;
d=1;
}
else{//如果不是12月的最后一天
m=month;
d =day +1;
}
}
else {//如果不是12月
if(day==a[month]) {//如果是该月的最后一天
m = month + 1;
d = 1;
}
else{//如果不是该月的最后一天
m=month;
d = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else//如果输入的数字非法
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
}
}
总体思路没有变化,但是圈复杂度有明显增加。
7-3 一元多项式求导(类设计) (50 分)
编写程序性,实现对简单多项式的导函数进行求解。详见作业指导书。 OO作业3-3题目说明.pdf
输入格式:
在一行内输入一个待计算导函数的表达式,以回车符结束。
输出格式:
1.如果输入表达式不符合上述表达式基本规则,则输出“Wrong Format”。
2.如果输入合法,则在一行内正常输出该表达式的导函数,注意以下几点: 结果不需要排序,也不需要化简;
•当某一项为“0”时,则该项不需要显示,但如果整个导函数结果为“0”时,则显示为“0”;
•当输出结果第一项系数符号为“+”时,不输出“+”;
•当指数符号为“+”时,不输出“+”;
•当指数值为“0”时,则不需要输出“x^0”,只需要输出其系数即可。
输出格式见输入输出示例。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
-2* x^-2+ 5x^12-4x+ 12
结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4*x-3+60*x11-4
结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2*x6-0*x7+5
结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
结尾无空行
源代码:
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String in = sc.nextLine();
String str = in.replace(" ", "");
Str textStr = new Str(str);
if(textStr.check())
textStr.show();
else {
database a = new database();
a.sout();
}
}
}
class database {
private static String a="Wrong Format";
public static void sout(){
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void sout1(BigInteger in){
System.out.print(in);
}
}
class Str {
private String str;
private String rStr;//系数部分
private String iStr;//指数部分
private BigInteger rat;
private BigInteger index;
database db=new database();
public Str(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
String termStr = "([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?";
String wholeStr = "(([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?)+";
String constNum = "[+-]?[0-9]+";
public boolean check() {
return Pattern.matches(wholeStr, str);
}
public void show() {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(termStr);
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);
if (Pattern.matches(constNum, str)) {
System.out.println("0");
System.exit(0);
} else {
int flag = 0;
while (m.find()) {
rStr = m.group(1);
iStr = m.group(4);
if (rStr != null) {
rat = new BigInteger(rStr);
if (m.group(2) != null && m.group(2).startsWith("-")) {
rat = BigInteger.valueOf(-1);
} else if (m.group(2) != null && m.group(2).startsWith("+")) {
rat = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
}
} else {
rat = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
if (m.group() != null && m.group().startsWith("-")) {
rat = BigInteger.valueOf(-1);
} else if (m.group() != null && m.group().startsWith("+")) {
rat = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
}
}
if (iStr != null) {
index = new BigInteger(iStr);
rat = rat.multiply(index);
index = index.subtract(new BigInteger("1"));
if (rat.compareTo(new BigInteger("0")) > 0 && flag == 1)
System.out.print("+" + (rat.equals(new BigInteger("-1")) ? "-x" : rat + "*x") + (index.equals(new BigInteger("1")) ? "" : ("^" + index)));
else {
flag = 1;
System.out.print((rat.equals(new BigInteger("-1")) ? "-x" : rat + "*x") + (index.equals(new BigInteger("1")) ? "" : ("^" + index)));
}
} else if (m.group(2) != null) {
flag = 1;
db.sout1(rat);
}
}
}
}
}
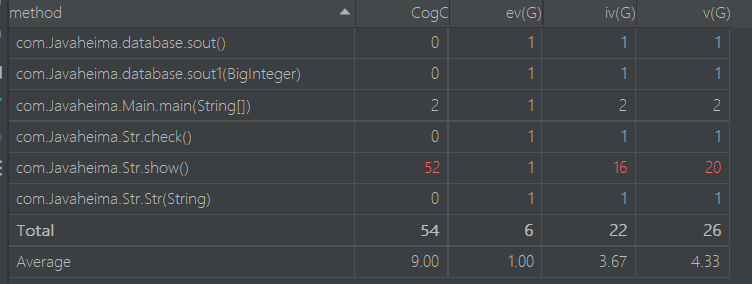
题目分析:
这道题这是这三次作业中最难的,也是我耗时最多的一道题,这道题的主要难度的是检验表达式的合法性的检测,本来想学我室友一样的一点一点的补起来,但是最后俩个测试点始终过不去,于是我去学了一手正则表达式了,并且慢慢的补起来了。
求导方法还是比较简单的
{新系数=旧系数×旧指数
{新指数=旧指数−1
第一步去掉字符串内的空格:
String express = initExpress.replaceAll("\\s", "");
这是我的正则判断试:
String termStr = "([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?";
String wholeStr = "(([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?)+";
String constNum = "[+-]?[0-9]+";
第一个可以判断一个简单多项式的各个系数和指数相,第二个可以判断输入的合法性,第三个可以检验常数项。
public boolean check() {
return Pattern.matches(wholeStr, str);
}
这个方法可以检验代码的合法性,输入是否符合格式。
public void show()
这个方法是这道题的精华所在,也是得出结果的一个方法。
具体就是通过判断来确立各个情况但也是较多面向过程的思路,所以,思路比较复杂,可以看到代码的复杂度也很高。
三·踩坑心得
心得一:第一次作业的最后一道题,没有考虑精度,对于等腰直角三角形的直角判断使用的是两边平方值和等于第三边的平方,但是对于很多数字,int类型是不能满足精度的,所以都使用的是0.01的精准度。
心得二:第二次作业的第四题,需要考虑的是比较多要一一排除多种特殊情况。
心得三:第三次作业的最后一道题,一开始在一点一点的试着排除格式
当指数和系数都存在:
[+-]?[0-9]+\\*x\\^[+-]?[0-9]+
兼容无前导0
[+-]?[1-9][0-9]*\\*x\\^[+-]?[1-9][0-9]*
兼容系数不存在:
([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?\\*?x\\^[+-]?[1-9][0-9]*
兼容指数不存在:
([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?\\*?x(\\^[+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?
兼容常数项:
([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?(\\*?x(\\^[+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?)?
给指数部分加上()方便提取:
([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?(\\*?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?
四、改进建议
对于第三次作业的一元多项式求导,有太多面向过程的做法,冗余代码过多,复用性低,不利于后期改进,难度大。
优化:设计各个不同的类,将表达式分解成项,对项进行处理,利于运算,利于合并同类项,降低程序耦合度。
五、总结
学到了什么:通过这三次的学习和练习,学习了Java基本语法的使用,强化了面向对象的思想,第一次学习了正则检测的使用。
进一步学习:不停留在基本语法,不一直保留面向过程的思想,开始了解各种开发框架和管理工具。
课程建议:课程自由度高,java学习很有趣,给学生充分的自学时间也很多,作业循序渐进,梯度适中,感觉很有挑战性,没必要修改。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号