博客作业(3)
前言
本次博客是PTA6~8习题总结,侧重于电信计费,循序渐进通过增加功能来增大难度
PTA6
1、 电信计费系列1-座机计费
实现一个简单的电信计费程序:
假设南昌市电信分公司针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式:
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
南昌市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
输入格式:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码除区号外由是7-8位数字组成。
本题只考虑计费类型0-座机计费,电信系列2、3题会逐步增加计费类型。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
注意:
本题非法输入只做格式非法的判断,不做内容是否合理的判断(时间除外,否则无法计算),比如:
1、输入的所有通讯信息均认为是同一个月的通讯信息,不做日期是否在同一个月还是多个月的判定,直接将通讯费用累加,因此月租只计算一次。
2、记录中如果同一电话号码的多条通话记录时间出现重合,这种情况也不做判断,直接 计算每条记录的费用并累加。
3、用户区号不为南昌市的区号也作为正常用户处理。
输出格式:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,
单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯信息单独计费后累加,不是将所有时间累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
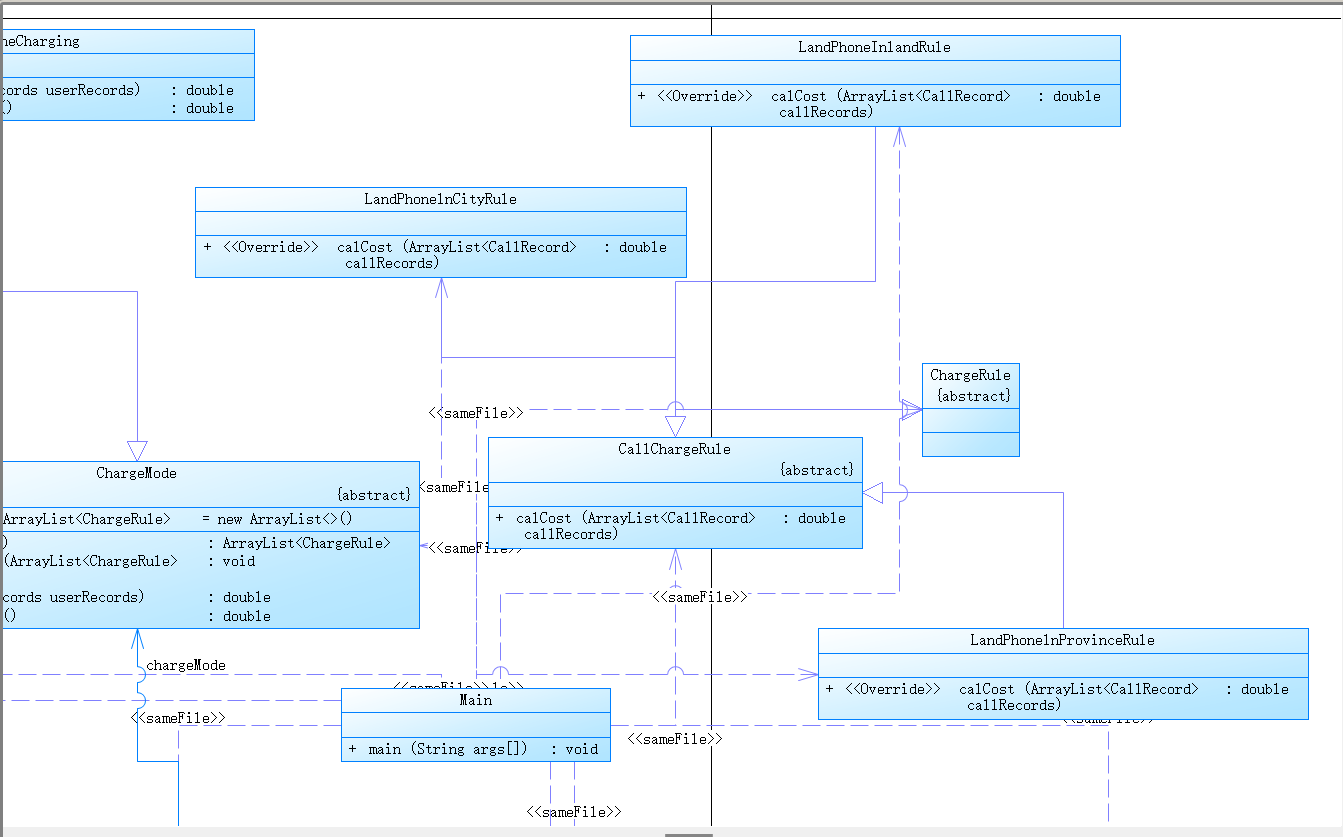
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3,可根据理解自行调整:
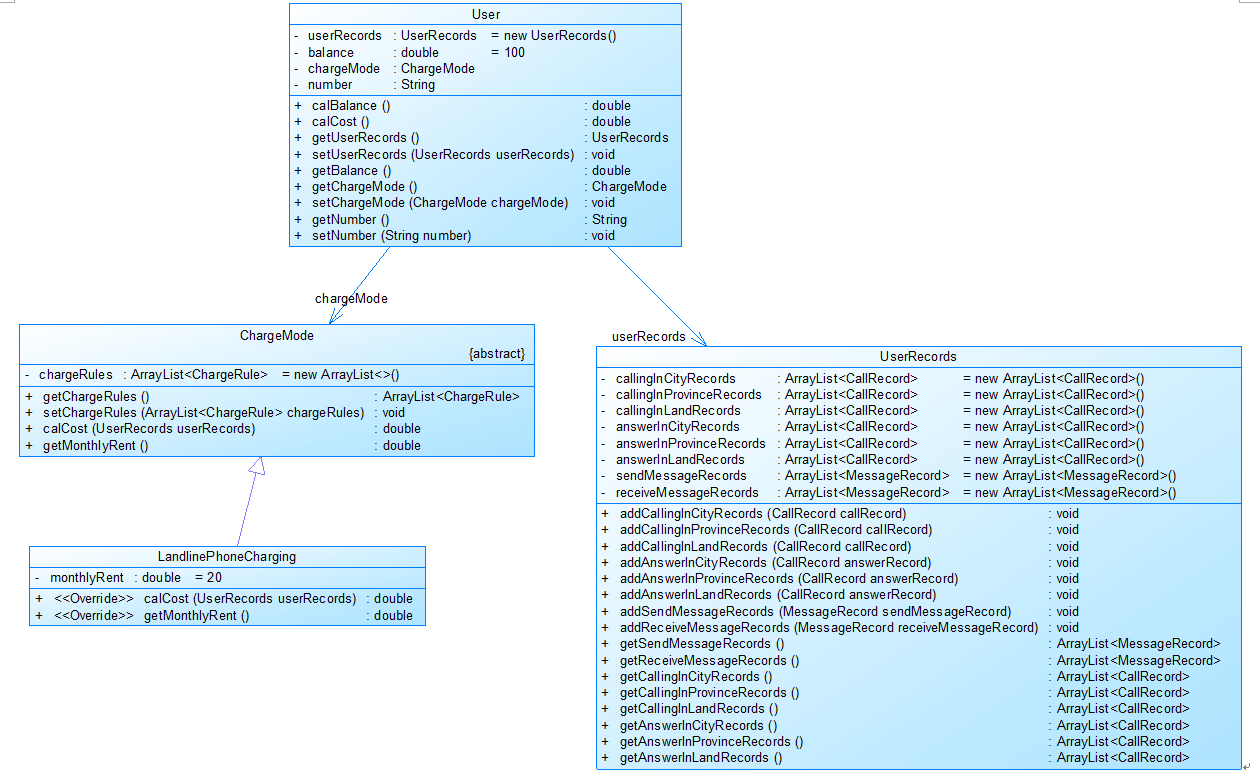
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
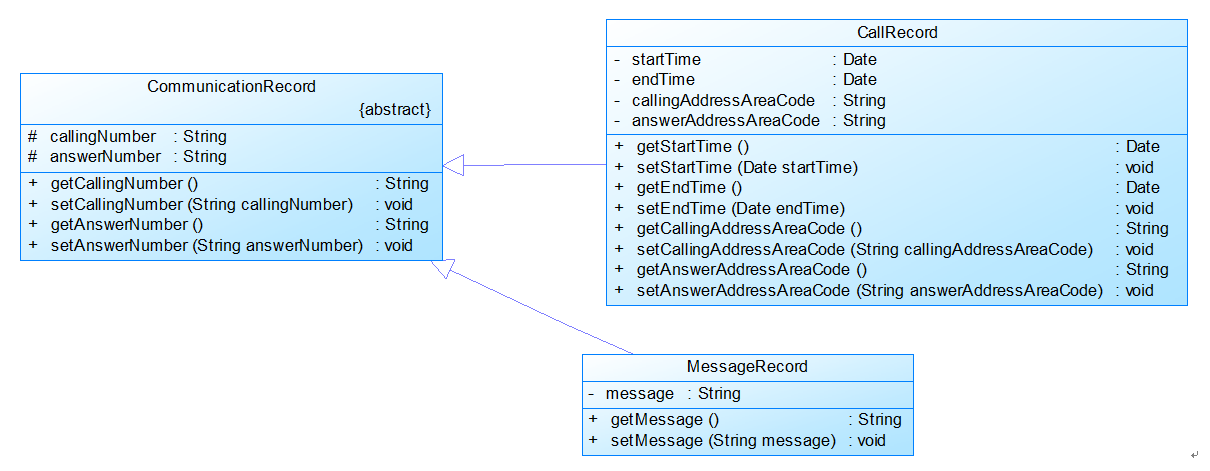
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。
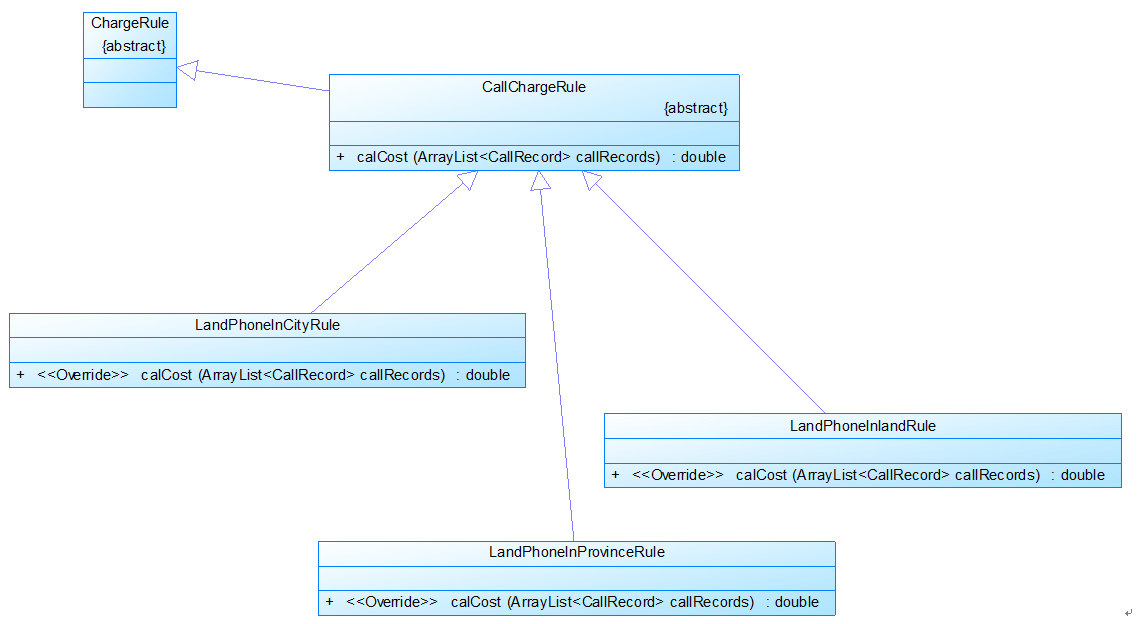
图3
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是
座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
后续扩展说明:
后续题目集将增加手机用户,手机用户的计费方式中除了与座机计费类似的主叫通话费之外,还包含市外接听电话的漫游费以及发短信的费用。在本题的设计时可统一考虑。
通话记录中,手机需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
短信的格式:m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-079186300001 0
t-079186300001 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:25
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
079186300001 3.0 77.0
代码:

import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); ArrayList<User> us = new ArrayList<User>(); DecimalFormat x1 = new DecimalFormat("###.0#"); ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); while(true) { String[] arry = null; Date starttime=null; Date endtime=null; String n=in.nextLine(); if(n.equals("end")) { break;} if(n.matches("u-079[\\d]{1}[\\d]{7,9} 0")||n.matches("u-0701[\\d]{7,9} 0")||n.matches("t-[\\d]{11,12}\\s[\\d]{11,12}\\s[\\d]{4}.[1-12].[1-31]\\s([01]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]:[0-5][0-9]\\s[\\d]{4}.[1-12].[1-31]\\s([01]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9]:[0-5][0-9]")) { arry=n.split("-| "); if(arry[0].equals("t")) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); String answerareaCode,callareaCode;//接听区号;拨打区号 callareaCode = arry[1].substring(0, 4);//赋值 answerareaCode = arry[2].substring(0, 4);//赋值 callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(callareaCode); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(answerareaCode); callRecord.setCallingNumber(arry[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(arry[2]); SimpleDateFormat time = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); try { starttime = time.parse(arry[3]+" "+arry[4]); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { endtime = time.parse(arry[5]+" "+arry[6]); } catch (ParseException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } callRecord.setStartTime(starttime);//开始时间 callRecord.setEndTime(endtime);//结束时间 callRecords.add(callRecord);//添加用户记录 } if(arry[0].equals("u")){ String areaCode; CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); LandlinePhoneCharging lip = new LandlinePhoneCharging();//座机 boolean decide = true; areaCode = arry[1].substring(0, 4); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(areaCode); for(User user : us) { if(user.getNumber().equals(arry[1])) decide=false; } if(decide==true) { User u = new User(lip,arry[1]); us.add(u); } } } } for(int i=0;i<us.size();i++) { UserRecords u=new UserRecords(); for(int j=0;j<callRecords.size();j++) { CallRecord a=callRecords.get(j); String callnumber=a.callnumber; if(us.get(i).number.equals(callnumber)) { if(a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("0791"))u.addCallingInCityRecords(a); else if(a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("0701"))u.addCallingInProvinceRecords(a); else if(a.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("079[0-9]"))u.addCallingInProvinceRecords(a); else u.addCallingInLandRecords(a); } } us.get(i).setUserRecords(u); } Collections.sort(us,new Comparator<User>() { @Override public int compare(User o1, User o2) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub double x=Double.parseDouble(o1.getNumber()); double y=Double.parseDouble(o2.getNumber()); return (int) (x-y); } }); for(User u : us) { double cost=Double.parseDouble(x1.format(u.calCost())); double balance=Double.parseDouble(x1.format(u.calBalance())); System.out.println(u.getNumber()+" "+cost+" "+balance); } in.close(); } } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { public abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords); } class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord{ Date startTime; Date endTime; String callingAddressAreaCode; String answerAddressAreaCode; String callnumber; String answernumber; Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } void setStartTime(Date starttime2) { this.startTime=(Date) starttime2; } Date getEndTIme() { return endTime; } void setEndTime(Date endtime2) { this.endTime=(Date) endtime2; } String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode=callingAddressAreaCode; } String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode=answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingNumber(String string) { this.callnumber=string; } public void setAnswerNumber(String string) { this.answernumber=string; } } abstract class ChargeMode { private ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules= new ArrayList<>(); public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getChargeRule(){ return chargeRules; } public void setChargeRules(ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules) { this.chargeRules= chargeRules; } public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); abstract double getMonthlyRent() ; } abstract class ChargeRule { } class CommunicationRecord { private String callingNumber; private String answerNumber; public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber=callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumber() { return answerNumber; } public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber) { this.answerNumber=answerNumber; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { double monthlyRent = 20; public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sum = 0.0; LandPhoneInlandRule p1 = new LandPhoneInlandRule(); LandPhonelnCityRule p2 = new LandPhonelnCityRule(); LandPhonelnProvinceRule p3 = new LandPhonelnProvinceRule(); double sum1= sum+p1.calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()); double sum2=sum+p2.calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()); double sum3=sum+p3.calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()); return sum1+sum2+sum3; } public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0.0; for(int i=0;i<callRecords.size();i++) { double s = callRecords.get(i).getEndTIme().getTime()-callRecords.get(i).getStartTime().getTime(); s=s/1000.0/60;//分钟 if(s%1==0) { sum+=s*0.6; } else { double a=s%1; s=s-a+1; sum+=s*0.6; } } return sum; } } class LandPhonelnCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<callRecords.size();i++) { double s = callRecords.get(i).getEndTIme().getTime()-callRecords.get(i).getStartTime().getTime(); s=s/1000.0/60;//分钟 if(s%1==0) { sum+=s*0.1; } else { double a=s%1; s=s-a+1; sum+=s*0.1; } } return sum; } } class LandPhonelnProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<callRecords.size();i++) { double s = callRecords.get(i).getEndTIme().getTime()-callRecords.get(i).getStartTime().getTime(); s=s/1000.0/60;//分钟 if(s%1==0) { sum+=s*0.3; } else { double a=s%1; s=s-a+1; sum+=s*0.3; } } return sum; } } class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord { String message; String getMessage() { return message; } void setMessage(String message) { this.message=message; } } class User { UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); double balance = 100; ChargeMode chargeMode; String number; User(ChargeMode chargeMode,String number){ this.chargeMode=chargeMode; this.number=number; } double calBalance() { double a = balance-(calCost()+chargeMode.getMonthlyRent()); return a; } double calCost() { double s =chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); return s; } UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords=userRecords; } double getBalance() { return balance; } ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } String getNumber() { return number; } void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } class UserRecords { ArrayList<CallRecord>callinglnCityRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>callinglnProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>callinglnLandRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerlnCityRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerlnProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerlnLandRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<MessageRecord>sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<MessageRecord>(); ArrayList<MessageRecord>receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<MessageRecord>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords (CallRecord callRecord) { callinglnCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords (CallRecord callRecord) { callinglnProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords (CallRecord callRecord) { callinglnLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords (CallRecord answerRecord) { answerlnCityRecords.add(answerRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords (CallRecord answerRecord) { answerlnProvinceRecords.add(answerRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords (CallRecord answerRecord) { answerlnLandRecords.add(answerRecord); } public void addSendMessageRecords (MessageRecord sendMessageRecord) { sendMessageRecords.add(sendMessageRecord); } public void addReceiveMessageRecords (MessageRecord receiveMessageRecord) { receiveMessageRecords.add(receiveMessageRecord); } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords (){ return this.sendMessageRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords (){ return this.receiveMessageRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords (){ return this.callinglnCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords (){ return this.callinglnProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords (){ return this.callinglnLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords (){ return this.answerlnCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords (){ return this.callinglnProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords (){ return this.callinglnLandRecords; } }
类图:


小结:因为是第一次接触电信计费相关问题,规则了解不熟练,所以写的时候很费劲,功能不全面或者不正确,有很多逻辑上的错误,变量很多,有时候一天写不完,第二天再去看的时候就会网点有些变量名,需要对前一天的代码进行复习,往往在这个过程中可能会解决掉之前困惑自己的问题。
2、多态测试
定义容器Container接口。模拟实现一个容器类层次结构,并进行接口的实现、抽象方法重写和多态机制测试。各容器类实现求表面积、体积的方法。
定义接口Container:
属性:
public static final double pi=3.1415926;
抽象方法:
public abstract double area();
public abstract double volume();
static double sumofArea(Container c[]);
static double sumofVolume(Container c[]);
其中两个静态方法分别计算返回容器数组中所有对象的面积之和、周长之和;
定义Cube类、Cylinder类均实现自Container接口。
Cube类(属性:边长double类型)、Cylinder类(属性:底圆半径、高,double类型)。
输入格式:
第一行n表示对象个数,对象类型用cube、cylinder区分,cube表示立方体对象,后面输入边长,输入cylinder表示圆柱体对象,后面是底圆半径、高。
输出格式:
分别输出所有容器对象的表面积之和、体积之和,结果保留小数点后2位。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4
cube
15.7
cylinder
23.5 100
cube
46.8
cylinder
17.5 200
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
56771.13
472290.12
代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner i=new Scanner(System.in); int n=i.nextInt(); Container c[]=new Container[n]; String name=null; for(int a=0;a<n;a++){ name=i.next(); if(name.equals("cube")){ c[a]=new Cube(i.nextDouble()); } else if(name.equals("cylinder")){ c[a]=new Cylinder(i.nextDouble(),i.nextDouble()); } } System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",Container.sumofArea(c))); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",Container.sumofVolume(c))); } } interface Container{ public static final double pi=3.1415926; public abstract double area(); public abstract double volume(); static double sumofArea(Container c[]){ double sum=0; for(int b=0;b<c.length;b++){ sum+=c[b].area(); } return sum; } static double sumofVolume(Container c[]){ double sum=0; for(int d=0;d<c.length;d++){ sum+=c[d].volume(); } return sum; } } class Cube implements Container{ double e; Cube(double e){ this.e=e; } public double area(){ return e*e*6; } public double volume(){ return e*e*e; } } class Cylinder implements Container{ double R; double h; Cylinder(double R,double h){ this.R=R; this.h=h; } public double area(){ return 2*(pi*R*R)+(2*pi*R*h); } public double volume(){ return pi*R*R*h; } }
类图:
小结:代码部分没有遇到什么问题,刚开始的时候没有注意到已经给定了pi的值,用了Math.PI,答案错误,重新进行了审题并改正。因为要计算综合,本来是想直接加在一起,突然发现不确定容器的数量,所以用Container类定义了一个动态数组对象,用来储存输入值,用循环进行总和的计算。生成类图的时候只有两个框框,因为Cube和Cylinder均实现自Container接口。
PTA7
1 、电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费
实现南昌市电信分公司的计费程序,假设该公司针对手机和座机用户分别采取了两种计费方案,分别如下:
1、针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式(与电信计费系列1内容相同):
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
假设本市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
2、针对手机用户采用实时计费方式:
月租15元,市内省内接电话均免费,市内拨打市内电话0.1元/分钟,市内拨打省内电话0.2元/分钟,市内拨打省外电话0.3元/分钟,省内漫游打电话0.3元/分钟,省外漫游接听0.3元/分钟,省外漫游拨打0.6元/分钟;
注:被叫电话属于市内、省内还是国内由被叫电话的接听地点区号决定,比如以下案例中,南昌市手机用户13307912264在区号为020的广州接听了电话,主叫号码应被计算为拨打了一个省外长途,同时,手机用户13307912264也要被计算省外接听漫游费:
u-13307912264 1
t-079186330022 13307912264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
输入:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,含手机和座机用户
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题在电信计费系列1基础上增加类型1-手机实时计费。
手机设置0或者座机设置成1,此种错误可不做判断。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
输入格式增加手机接打电话以及收发短信的格式,手机接打电话的信息除了号码之外需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:
t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:
t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
输出:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯、短信信息均单独计费后累加,不是将所有信息累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
本题只做格式的错误判断,无需做内容上不合理的判断,比如同一个电话两条通讯记录的时间有重合、开户号码非南昌市的号码等,此类情况都当成正确的输入计算。但时间的输入必须符合要求,比如不能输入2022.13.61 28:72:65。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3:
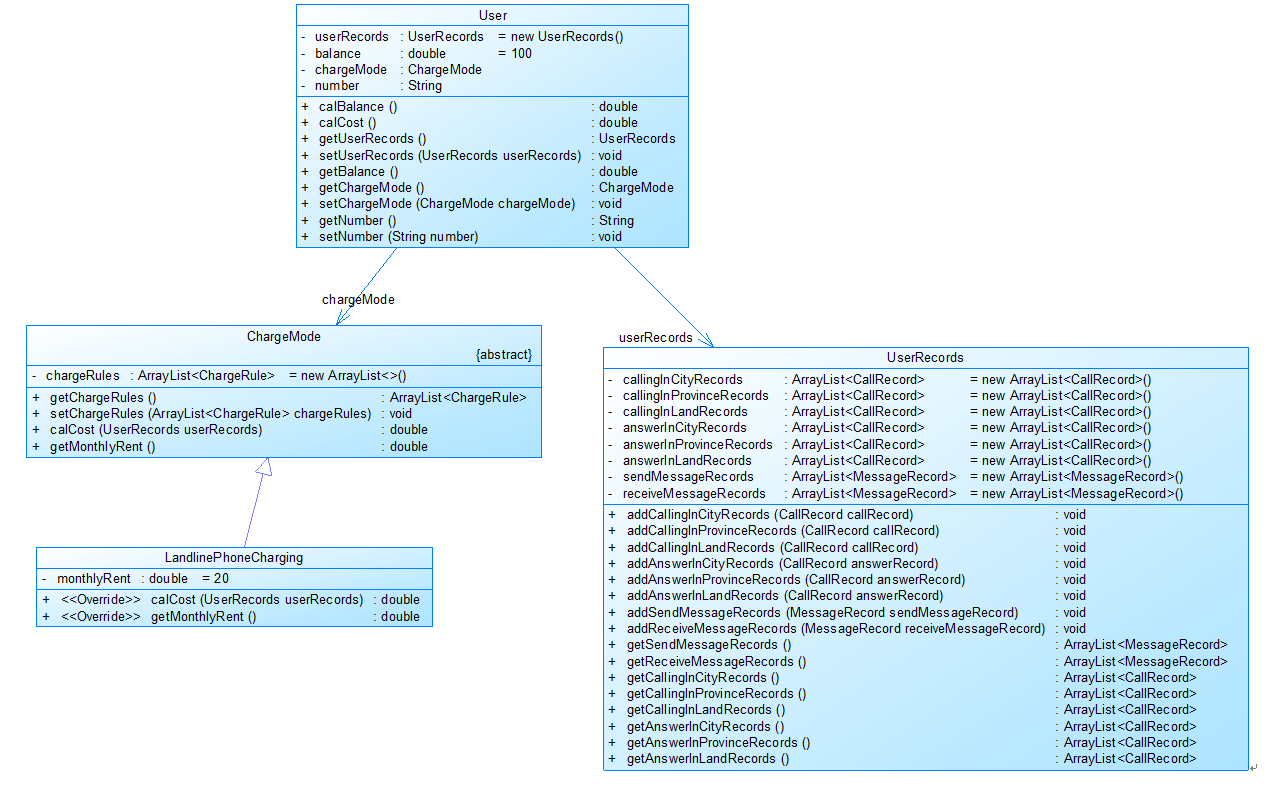
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
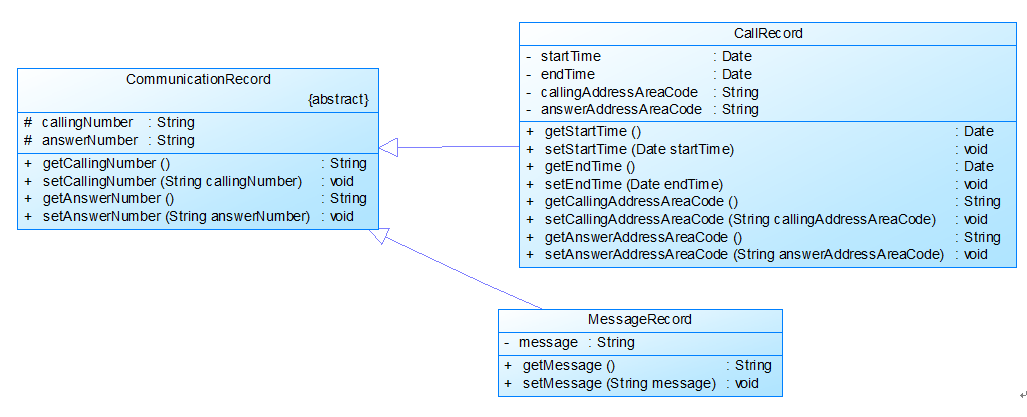
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。
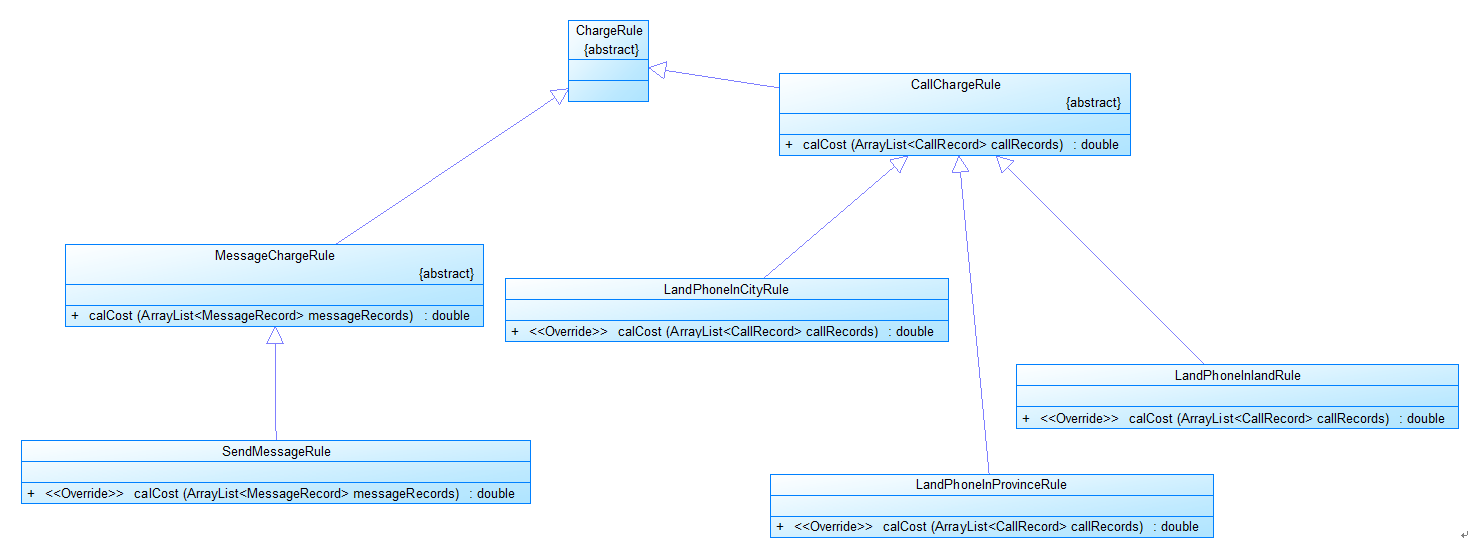
图3
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
SendMessageRule是发送短信的计费规则类,用于计算发送短信的费用。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-13811111111 1
t-13811111111 0791 13811111110 020 2022.1.3 08:00:00 2022.1.3 08:09:20
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
13811111111 3.0 82.0
代码:

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Locale; import java.text.ParseException; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Outputtool outputtool = new Outputtool(); Inputdeal inputdeal = new Inputdeal(); ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String input = in.nextLine(); while (!input.equals("end")) { if (1 == inputdeal.check(input)) { inputdeal.writeUser(users, input); } else if (2 == inputdeal.check(input)) { inputdeal.writeRecord(users, input); } input = in.nextLine(); } users.sort(new Comparator<User>() { @Override public int compare(User u1, User u2) { if (u1.getNumber().charAt(0) == '0' && u2.getNumber().charAt(0) != '0') { return -1; } else if (u1.getNumber().charAt(0) != '0' && u2.getNumber().charAt(0) == '0') { return 1; } if (Double.parseDouble(u1.getNumber()) > Double.parseDouble(u2.getNumber())) { return 1; } else { return -1; } } }); for (User u : users) { System.out.print(u.getNumber() + " "); outputtool.output(u.calCost()); System.out.print(" "); outputtool.output(u.calBalance()); System.out.println(); } } } abstract class ChargeMode { protected ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules = new ArrayList<>(); public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); public abstract double getMonthlyRent(); public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getChargeRules() { return chargeRules; } public void setChargeRules(ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules) { this.chargeRules = chargeRules; } } class UserRecords { private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<MessageRecord>(); private ArrayList<MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<MessageRecord>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void aaddAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord callRecord) { sendMessageRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addReceiveMessageRecords(MessageRecord callRecord) { receiveMessageRecords.add(callRecord); } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public void setCallingInCityRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords) { this.callingInCityRecords = callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public void setCallingInProvinceRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords) { this.callingInProvinceRecords = callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public void setCallingInLandRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords) { this.callingInLandRecords = callingInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public void setAnswerInCityRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords) { this.answerInCityRecords = answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public void setAnswerInProvinceRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords) { this.answerInProvinceRecords = answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public void setAnswerInLandRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords) { this.answerInLandRecords = answerInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() { return sendMessageRecords; } public void setSendMessageRecords(ArrayList<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords) { this.sendMessageRecords = sendMessageRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords() { return receiveMessageRecords; } public void setReceiveMessageRecords(ArrayList<MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords) { this.receiveMessageRecords = receiveMessageRecords; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) { sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords); } return sumCost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class MobilePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 15; public MobilePhoneCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) { sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords); } return sumCost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class Inputdeal { public int check(String input) { if (input.matches("[u]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s[0]") || input.matches("[u]-1[0-9]{10}\\s[1]")) { return 1; // } else if (input.charAt(0) == 'm') { // return 2; } else if (input.matches("(([t]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s" + "0[0-9]{9,11}\\s)|" + "([t]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s)|" + "([t]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s" + "0[0-9]{9,11}\\s)|" + "([t]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s))" + "((([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})\\.(((0?[13578]|1[02])\\.(0?" + "[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)\\.([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2\\.([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8]))))|(((" + "[0-9]{2})([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))\\.2\\.29))" + "\\s([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s" + "((([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})\\.((([13578]|1[02])\\.(" + "[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)\\.([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2\\.([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8]))))|(((" + "[0-9]{2})([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))\\.2\\.29))" + "\\s([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])")) { return 2; } return 0; } @SuppressWarnings("unused") private boolean validatet(String string) { if (!string.matches("^([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])$")) { return false; } return true; } public static boolean validate(String dateString) { // 使用正则表达式 测试 字符 符合 dddd.dd.dd 的格式(d表示数字) Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\d{4}+[\\.]\\d{1,2}+[\\.]\\d{1,2}+"); Matcher m = p.matcher(dateString); if (!m.matches()) { return false; } // 得到年月日 String[] array = dateString.split("\\."); int year = Integer.valueOf(array[0]); int month = Integer.valueOf(array[1]); int day = Integer.valueOf(array[2]); if (month < 1 || month > 12) { return false; } int[] monthLengths = new int[] { 0, 31, -1, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; if (isLeapYear(year)) { monthLengths[2] = 29; } else { monthLengths[2] = 28; } int monthLength = monthLengths[month]; if (day < 1 || day > monthLength) { return false; } return true; } /** 是否是闰年 */ private static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { return ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0); } public boolean judge(String input) { return false; } public void writeUser(ArrayList<User> users, String input) { User usernew = new User(); String[] inputs = input.split(" "); String num = inputs[0].substring(2); for (User i : users) { if (i.getNumber().equals(num)) { return; } } usernew.setNumber(num); int mode = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]); if (mode == 0) { usernew.setChargeMode(new LandlinePhoneCharging()); } else if (mode == 1) { usernew.setChargeMode(new MobilePhoneCharging()); } users.add(usernew); } public void writeRecord(ArrayList<User> users, String input) { String[] inputs = input.split(" "); User callu = null, answeru = null; CallRecord callrecord = new CallRecord(inputs); if (input.charAt(0) == 't') { String out = inputs[0]; String in = ""; if (inputs.length == 6) { in = inputs[1]; } else if (inputs.length == 7) { in = inputs[1]; } else if (inputs.length == 8) { in = inputs[2]; } for (User i : users) { if (i.getNumber().equals(out)) { callu = i; } if (i.getNumber().equals(in)) { answeru = i; } if (callu != null && answeru != null) { break; } } if (callu != null) { if (callrecord.getCallType().matches("^1[1-3]$")) { callu.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callrecord); } else if (callrecord.getCallType().matches("^2[1-3]$")) { callu.getUserRecords().addCallingInProvinceRecords(callrecord); } else { callu.getUserRecords().addCallingInLandRecords(callrecord); } } if (answeru != null) { if (callrecord.getCallType().matches("^[1-3]1$")) { answeru.getUserRecords().addAnswerInCityRecords(callrecord); } else if (callrecord.getCallType().matches("^[1-3]2$")) { answeru.getUserRecords().aaddAnswerInProvinceRecords(callrecord); } else { answeru.getUserRecords().addAnswerInLandRecords(callrecord); } } } else if (input.charAt(0) == 'm') { } } } abstract class CommunicationRecord { protected String callingNumber; protected String answerNumbe; public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumbe() { return answerNumbe; } public void setAnswerNumbe(String answerNumbe) { this.answerNumbe = answerNumbe; } } abstract class ChargeRule { abstract public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); } class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord { private Date startTime; private Date endTime; private String callingAddressAreaCode; private String answerAddressAreaCode; public String getCallType() { String type = ""; if (callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) { type = type.concat("1"); } else if (callingAddressAreaCode.matches("^079[023456789]$") || callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) { type = type.concat("2"); } else { type = type.concat("3"); } if (answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) { type = type.concat("1"); } else if (answerAddressAreaCode.matches("^079[023456789]$") || answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) { type = type.concat("2"); } else { type = type.concat("3"); } return type; } public CallRecord(String[] inputs) { super(); char type = inputs[0].charAt(0); inputs[0] = inputs[0].substring(2); String sd = null, st = null, ed = null, et = null; if (type == 't') { if (inputs.length == 6) { sd = inputs[2]; st = inputs[3]; ed = inputs[4]; et = inputs[5]; callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[0].substring(0, 4); answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[1].substring(0, 4); } else if (inputs.length == 7) { sd = inputs[3]; st = inputs[4]; ed = inputs[5]; et = inputs[6]; if (inputs[0].charAt(0) != '0') { if (inputs[2].length() == 10) { answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[2].substring(0, 3); } else { answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[2].substring(0, 4); } callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[1]; } else { if (inputs[0].length() == 10) { callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[0].substring(0, 3); } else { callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[0].substring(0, 4); } answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[2]; } } else if (inputs.length == 8) { sd = inputs[4]; st = inputs[5]; ed = inputs[6]; et = inputs[7]; callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[1]; answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[3]; } } else if (type == 'm') { } SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss", Locale.getDefault()); try { startTime = simpleDateFormat.parse(sd + " " + st); endTime = simpleDateFormat.parse(ed + " " + et); } catch (ParseException e) { } } public CallRecord(Date startTime, Date endTime, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerAddressAreaCode) { super(); this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } public Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } public void setStartTime(Date startTime) { this.startTime = startTime; } public Date getEndTime() { return endTime; } public void setEndTime(Date endTime) { this.endTime = endTime; } public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } if (call.getCallType().equals("11")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.1; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("12")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("13")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.6; } } return sumCost; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.6; } return sumCost; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } if (call.getCallType().equals("11")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.1; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("12")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.2; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("13")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.6; } for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } if (call.getCallType().equals("21")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("22")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("23")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } } return sumCost; } } class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord { private String message; public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } } class User { private UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); private double balance = 100; private ChargeMode chargeMode; private String number; public double calCost() { return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } public double calBalance() { return balance - chargeMode.getMonthlyRent() - chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } class Outputtool { @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public void output(double out) { BigDecimal numb = new BigDecimal(out); out = numb.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); System.out.print(out); } }
类图:
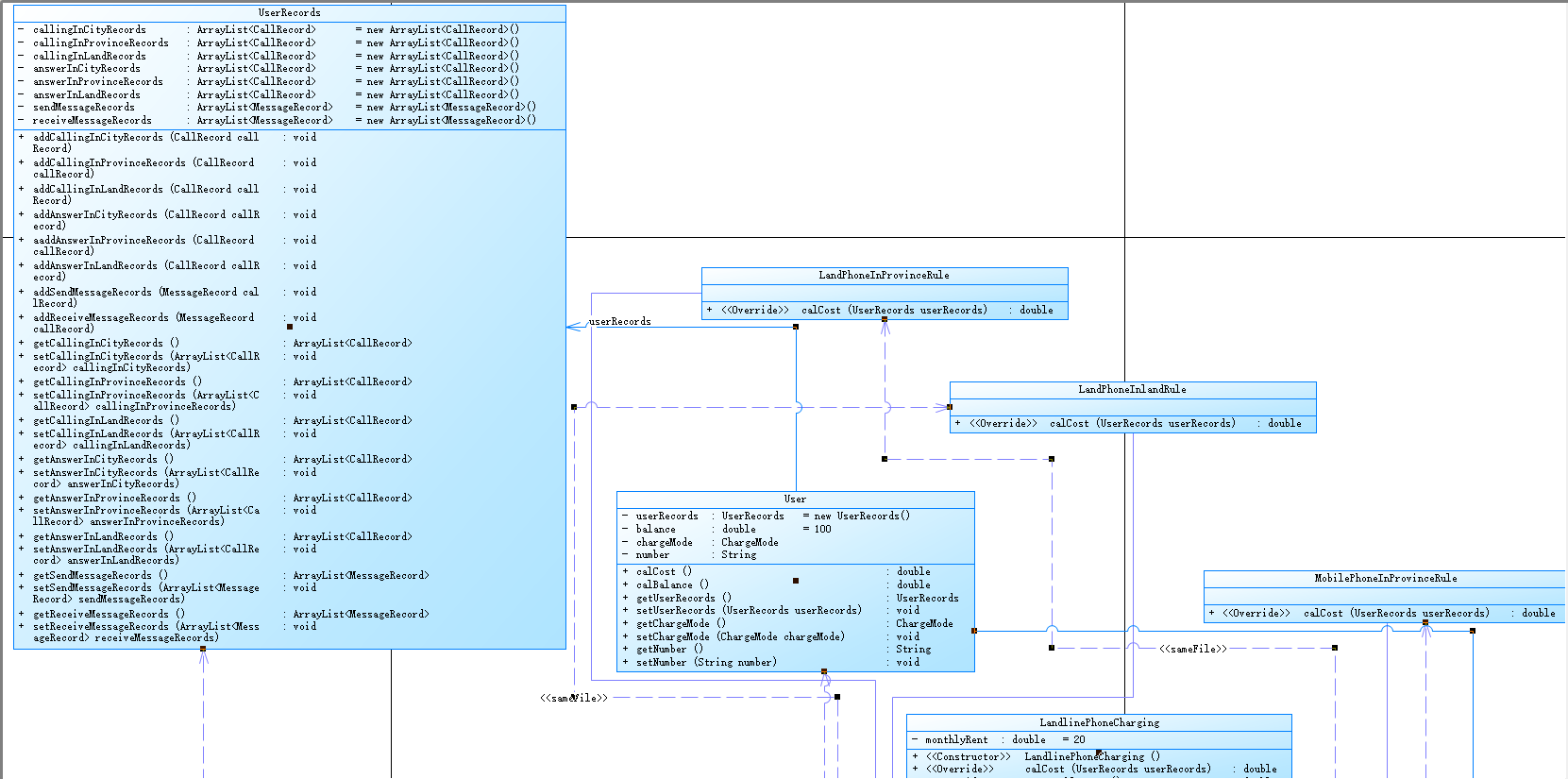
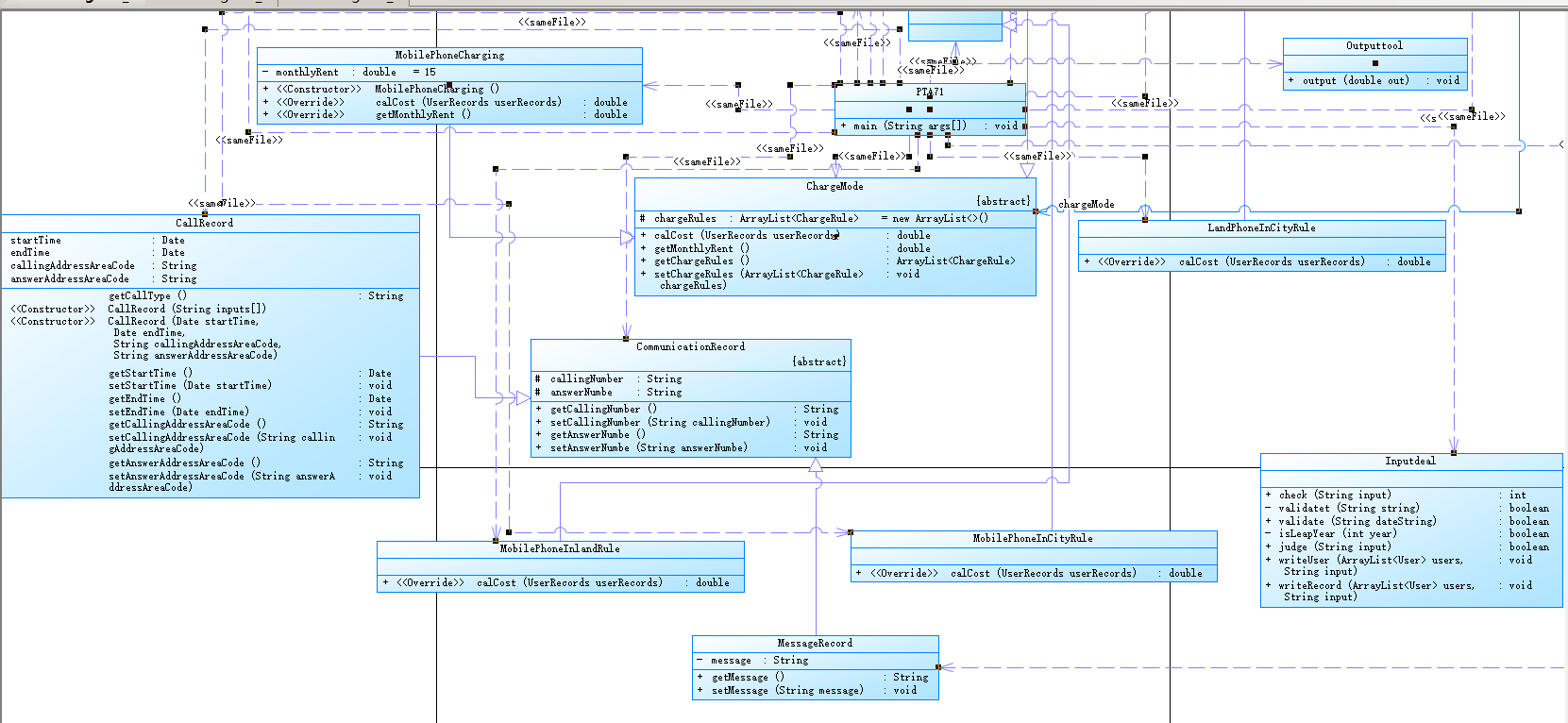
小结:本题总体来说和上次习题的第一题相差不多,但是增加了功能,因为隔着的时间比较长,所以重温代码还是花费了不少时间的。难度与之前持平,但是写起来的时候更熟练了一些。
2 、sdut-Collection-sort--C~K的班级(II)
经过不懈的努力,C~K终于当上了班主任。
现在他要统计班里学生的名单,但是C~K在教务系统中导出班级名单时出了问题,发现会有同学的信息重复,现在他想把重复的同学信息删掉,只保留一个,
但是工作量太大了,所以找到了会编程的你,你能帮他解决这个问题吗?
输入格式:
第一行输入一个N,代表C~K导出的名单共有N行(N<100000).
接下来的N行,每一行包括一个同学的信息,学号 姓名 年龄 性别。
输出格式:
第一行输出一个n,代表删除重复名字后C~K的班级共有几人。
接下来的n行,输出每一个同学的信息,输出按照学号从小到大的顺序。
输入样例:
6
0001 MeiK 20 M
0001 MeiK 20 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
0000 blf2 22 F
输出样例:
3
0000 blf2 22 F
0001 MeiK 20 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
代码:

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; public class Main{ String name; String num; int age; char sex; Main(String num,String name,int age,char sex){ this.name=name; this.num=num; this.age=age; this.sex=sex; } public String toString(){ return num+" "+name+" "+age+" "+sex; } public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner i=new Scanner(System.in); HashMap<String,Main> a=new HashMap<String,Main>(); int n=i.nextInt(); for(int b=0;b<n;b++){ Main s=new Main(i.next(),i.next(),i.nextInt(),i.next().charAt(0)); a.put(s.num,s); } Set<String> c=a.keySet(); ArrayList<String>list=new ArrayList<String>(c); Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(list.size()); for(String b:list){ System.out.println(a.get(b)); } i.close(); } }
类图:
小结:将学生的信息转化为了字符串,通过比较字符串是否相同来删除重复学生信息。
3 、阅读程序,按照题目需求修改程序
功能需求:
使用集合存储3个员工的信息(有序);
通过迭代器依次找出所有的员工。
提示:学生复制以下代码到编程区,并按需求进行调试修改。
// 1、导入相关包
//定义员工类
class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee() {
super();
}
public Employee(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
//主函数
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、创建有序集合对象
Collection c ;
// 创建3个员工元素对象
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String employeeName = sc.nextLine();
int employeeAge = sc.nextInt();
Employee employee = new Employee(employeeName, employeeAge);
c.add(employee);
}
// 2、创建迭代器遍历集合
Iterator it;
//3、遍历
while (it.hasnext) {
//4、集合中对象未知,向下转型
Employee e = it.next();
System.out.println(e.getName() + "---" + e.getAge());
}
}
}
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
zs
10
ls
20
ww
30
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
zs---10
ls---20
ww---30
代码:

import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; class Employee { private String name; private int age; public Employee() { super(); } public Employee(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } } //主函数 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建有序集合对象 ArrayList<Employee> c=new ArrayList<Employee>(); // 创建3个员工元素对象 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String employeeName = sc.nextLine(); int employeeAge = sc.nextInt(); Employee employee = new Employee(employeeName, employeeAge); c.add(employee); } // 2、创建迭代器遍历集合 Iterator it=c.iterator(); //3、遍历 while (it.hasNext()) { //4、集合中对象未知,向下转型 Employee e =(Employee)it.next(); System.out.println(e.getName() + "---" + e.getAge()); } } }

小结:从类图中可以看出,本次实验并不复杂,并且题目中已经给出了代码主体,进行修改与补充即可。
PTA8
1 、电信计费系列3-短信计费
实现一个简单的电信计费程序,针对手机的短信采用如下计费方式:
1、接收短信免费,发送短信0.1元/条,超过3条0.2元/条,超过5条0.3元/条。
2、如果一次发送短信的字符数量超过10个,按每10个字符一条短信进行计算。
输入:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市手机用户开户的信息,每行一个用户。
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐 3-手机短信计费)
例如:u-13305862264 3
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题只针对类型3-手机短信计费。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的短信信息,短信的格式:
m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容 (短信内容只能由数字、字母、空格、英文逗号、英文句号组成)
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi.
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you.
注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
输出:
根据输入的详细短信信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月短信费用(精确到小数点后2位,单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条短信信息均单独计费后累加,不是将所有信息累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
本题只做格式的错误判断,无需做内容上不合理的判断,比如同一个电话两条通讯记录的时间有重合、开户号码非南昌市的号码、自己给自己打电话等,此类情况都当成正确的输入计算。但时间的输入必须符合要求,比如不能输入2022.13.61 28:72:65。
本题只考虑短信计费,不考虑通信费用以及月租费。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3:
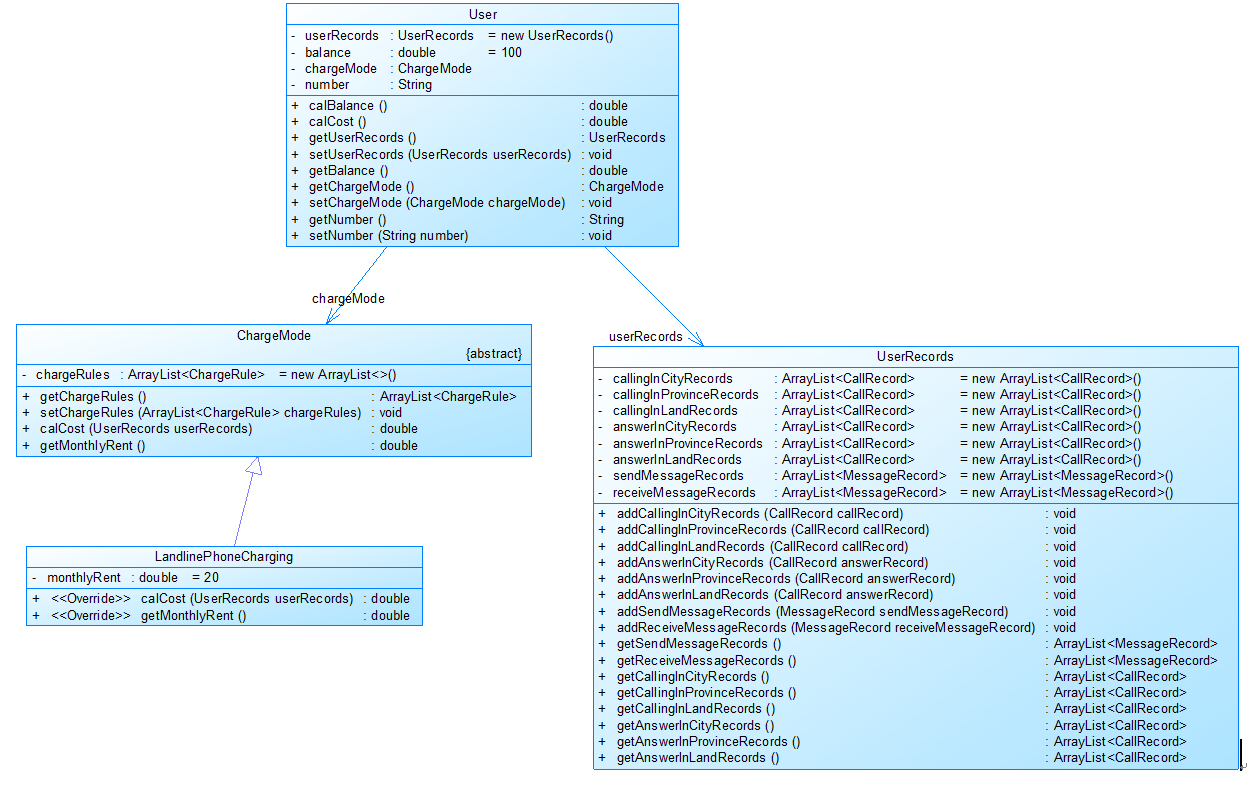
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
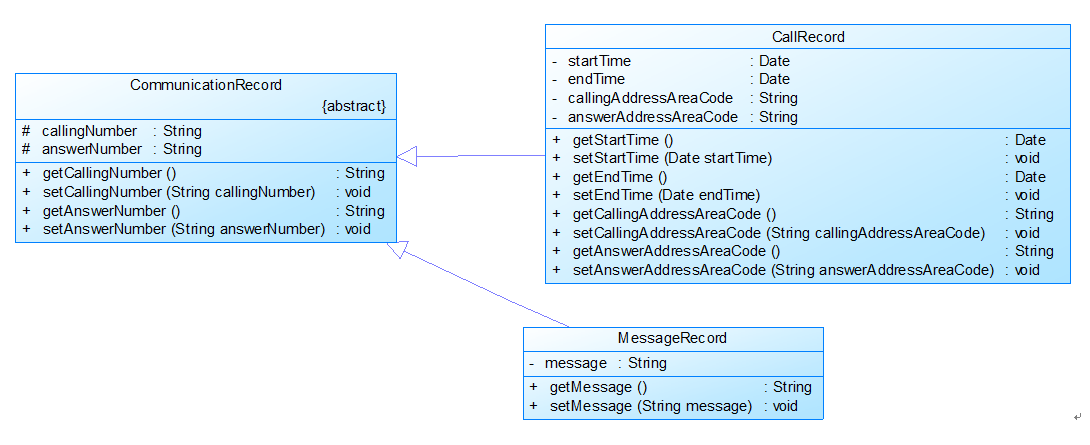
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
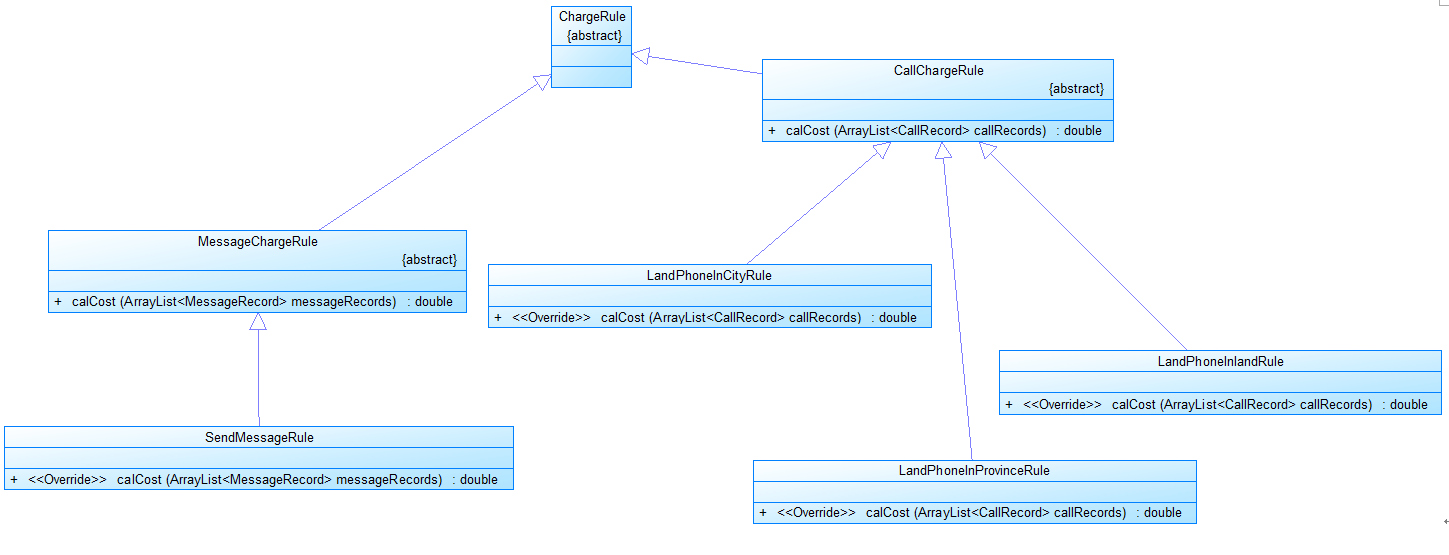
图3
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
SendMessageRule是发送短信的计费规则类,用于计算发送短信的费用。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-18907910010 3
m-18907910010 13305862264 aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
18907910010 0.3 99.7
### 输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-18907910010 3
m-18907910010 13305862264 aaaaaaaaaaaa
m-18907910010 13305862264 aaaaaaa.
m-18907910010 13305862264 bb,bbbb
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
18907910010 0.5 99.5
代码:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Locale; import java.text.ParseException; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Outputtool out=new Outputtool(); Inputdeal inp=new Inputdeal(); ArrayList<User> un=new ArrayList<User>(); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String s=input.nextLine(); while(!s.equals("end")){ if(inp.check(s)==1){ inp.writeUser(un,s); } else if(inp.check(s)==2){ inp.writeRecord(un,s); } s=input.nextLine(); } un.sort(new Comparator<User>(){ public int compare(User u1,User u2){ if(u1.getNumber().charAt(0)=='0'&&u2.getNumber().charAt(0)!='0'){ return -1; } else if(u1.getNumber().charAt(0)!='0'&&u2.getNumber().charAt(0)=='0'){ return 1; } if(Double.parseDouble(u1.getNumber())>Double.parseDouble(u2.getNumber())){ return 1; } else{ return -1; } } }); for(User u:un){ System.out.print(u.getNumber()+" "); out.output(u.calCost()); System.out.print(" "); out.output(u.calBalance()); System.out.println(); } } } abstract class ChargeMode { protected ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules = new ArrayList<>(); public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); public abstract double getMonthlyRent(); public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getChargeRules() { return chargeRules; } public void setChargeRules(ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules) { this.chargeRules = chargeRules; } } class UserRecords { private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); private ArrayList<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<MessageRecord>(); private ArrayList<MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<MessageRecord>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void aaddAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord callRecord) { sendMessageRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addReceiveMessageRecords(MessageRecord callRecord) { receiveMessageRecords.add(callRecord); } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public void setCallingInCityRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords) { this.callingInCityRecords = callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public void setCallingInProvinceRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords) { this.callingInProvinceRecords = callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public void setCallingInLandRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords) { this.callingInLandRecords = callingInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public void setAnswerInCityRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords) { this.answerInCityRecords = answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public void setAnswerInProvinceRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords) { this.answerInProvinceRecords = answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public void setAnswerInLandRecords(ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords) { this.answerInLandRecords = answerInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() { return sendMessageRecords; } public void setSendMessageRecords(ArrayList<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords) { this.sendMessageRecords = sendMessageRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords() { return receiveMessageRecords; } public void setReceiveMessageRecords(ArrayList<MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords) { this.receiveMessageRecords = receiveMessageRecords; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) { sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords); } return sumCost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class MobilePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 15; public MobilePhoneCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) { sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords); } return sumCost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class MobilePhoneMassageCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 0; public MobilePhoneMassageCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new MobilePhoneMessageRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) { sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords); } return sumCost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class Inputdeal { public int check(String input) { if (input.matches("[u]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s[0]") || input.matches("[u]-1[0-9]{10}\\s[13]")) { return 1; } else if (input.matches("[m]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "[0-9a-zA-Z\\s\\.,]+")) { return 2; } return 0; } public void writeUser(ArrayList<User> users, String input) { User usernew = new User(); String[] inputs = input.split(" "); String num = inputs[0].substring(2); for (User i : users) { if (i.getNumber().equals(num)) { return; } } usernew.setNumber(num); int mode = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]); if (mode == 0) { usernew.setChargeMode(new LandlinePhoneCharging()); } else if (mode == 1) { usernew.setChargeMode(new MobilePhoneCharging()); } else if (mode == 3) { usernew.setChargeMode(new MobilePhoneMassageCharging()); } users.add(usernew); } public void writeRecord(ArrayList<User> users, String input) { String[] inputs = input.split(" "); inputs[0] = inputs[0].substring(2); User callu = null, answeru = null; String out = inputs[0]; String in = ""; if (inputs.length == 6) { in = inputs[1]; } else if (inputs.length == 7) { in = inputs[1]; } else if (inputs.length == 8) { in = inputs[2]; } else { in = inputs[1]; } for (User i : users) { if (i.getNumber().equals(out)) { callu = i; } if (i.getNumber().equals(in)) { answeru = i; } if (callu != null && answeru != null) { break; } } if (input.charAt(0) == 'm') { MessageRecord messageRecord = new MessageRecord(input); if (callu != null) { callu.getUserRecords().addSendMessageRecords(messageRecord); ; } if (answeru != null) { callu.getUserRecords().addReceiveMessageRecords(messageRecord); } } } } abstract class CommunicationRecord { protected String callingNumber; protected String answerNumbe; public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumbe() { return answerNumbe; } public void setAnswerNumbe(String answerNumbe) { this.answerNumbe = answerNumbe; } } abstract class ChargeRule { abstract public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); } class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord { private Date startTime; private Date endTime; private String callingAddressAreaCode; private String answerAddressAreaCode; public String getCallType() { String type = ""; if (callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) { type = type.concat("1"); } else if (callingAddressAreaCode.matches("^079[023456789]$") || callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) { type = type.concat("2"); } else { type = type.concat("3"); } if (answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) { type = type.concat("1"); } else if (answerAddressAreaCode.matches("^079[023456789]$") || answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) { type = type.concat("2"); } else { type = type.concat("3"); } return type; } public CallRecord(String[] inputs) { super(); char type = inputs[0].charAt(0); String sd = null, st = null, ed = null, et = null; if (type == 't') { if (inputs.length == 6) { sd = inputs[2]; st = inputs[3]; ed = inputs[4]; et = inputs[5]; callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[0].substring(0, 4); answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[1].substring(0, 4); } else if (inputs.length == 7) { sd = inputs[3]; st = inputs[4]; ed = inputs[5]; et = inputs[6]; if (inputs[0].charAt(0) != '0') { if (inputs[2].length() == 10) { answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[2].substring(0, 3); } else { answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[2].substring(0, 4); } callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[1]; } else { if (inputs[0].length() == 10) { callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[0].substring(0, 3); } else { callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[0].substring(0, 4); } answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[2]; } } else if (inputs.length == 8) { sd = inputs[4]; st = inputs[5]; ed = inputs[6]; et = inputs[7]; callingAddressAreaCode = inputs[1]; answerAddressAreaCode = inputs[3]; } } else if (type == 'm') { } SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss", Locale.getDefault()); try { startTime = simpleDateFormat.parse(sd + " " + st); endTime = simpleDateFormat.parse(ed + " " + et); } catch (ParseException e) { } } public CallRecord(Date startTime, Date endTime, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerAddressAreaCode) { super(); this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } public Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } public void setStartTime(Date startTime) { this.startTime = startTime; } public Date getEndTime() { return endTime; } public void setEndTime(Date endTime) { this.endTime = endTime; } public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } if (call.getCallType().equals("11")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.1; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("12")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("13")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.6; } } return sumCost; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.6; } return sumCost; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } if (call.getCallType().equals("11")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.1; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("12")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.2; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("13")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.6; } for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) { double distanceS = (-call.getStartTime().getTime() + call.getEndTime().getTime()) / 1000; if (distanceS < 0) { continue; } double distanceM = (int) distanceS / 60; if (distanceS % 60 != 0) { distanceM += 1; } if (call.getCallType().equals("21")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("22")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } else if (call.getCallType().equals("23")) { sumCost += distanceM * 0.3; } } return sumCost; } } class MobilePhoneMessageRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; int number = 0; for (MessageRecord m : userRecords.getSendMessageRecords()) { int length = m.getMessage().length(); if (length <= 10) { number++; } else { number += length / 10; if (length % 10 != 0) { number++; } } } if (number <= 3) { sumCost = number * 0.1; } else if (number <= 5) { sumCost = 0.3 + 0.2 * (number - 3); } else { sumCost = 0.7 + 0.3 * (number - 5); } return sumCost; } } class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord { private String message; public MessageRecord(String input) { super(); this.message = input.substring(26); } public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } } class User { private UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); private double balance = 100; private ChargeMode chargeMode; private String number; public double calCost() { return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } public double calBalance() { return balance - chargeMode.getMonthlyRent() - chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } class Outputtool { @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public void output(double out) { BigDecimal numb = new BigDecimal(out); out = numb.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue(); System.out.print(out); } }
类图:


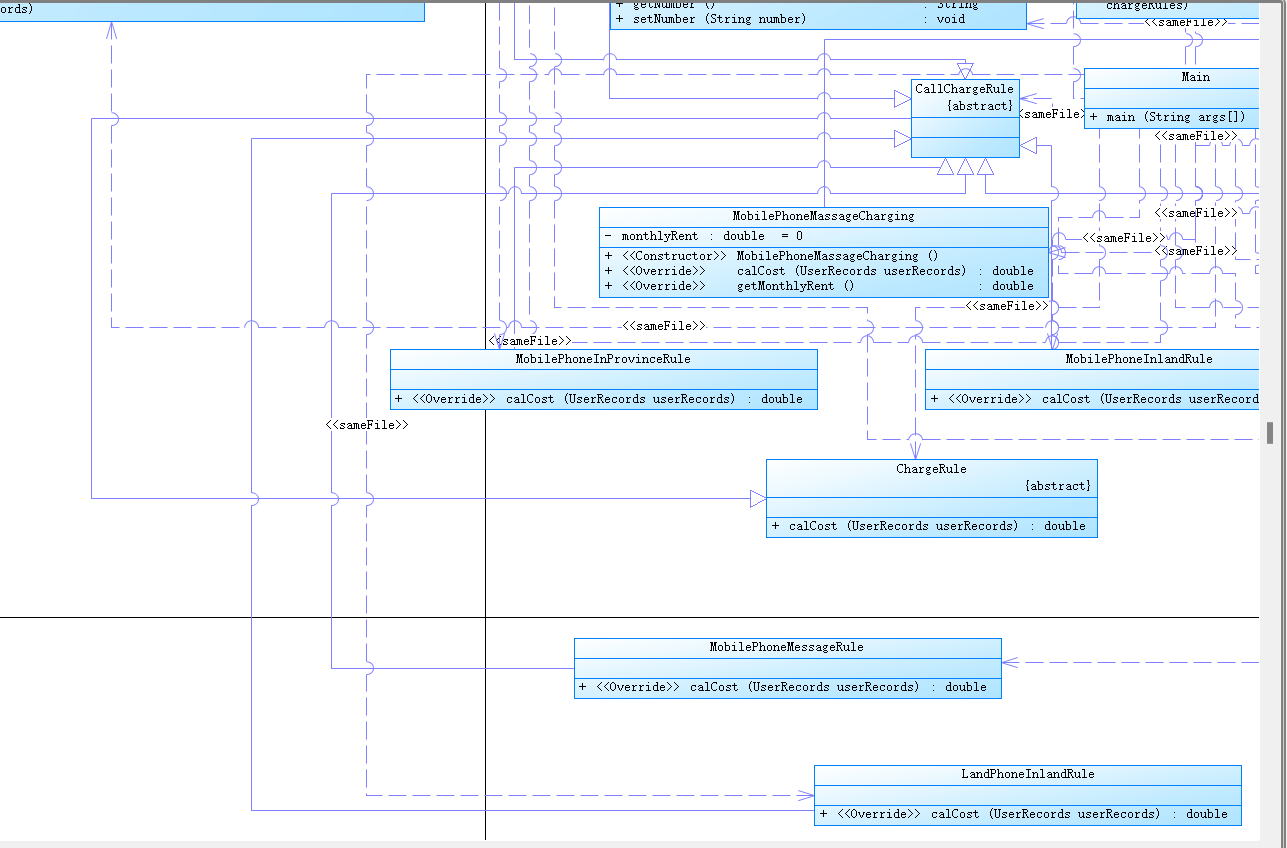
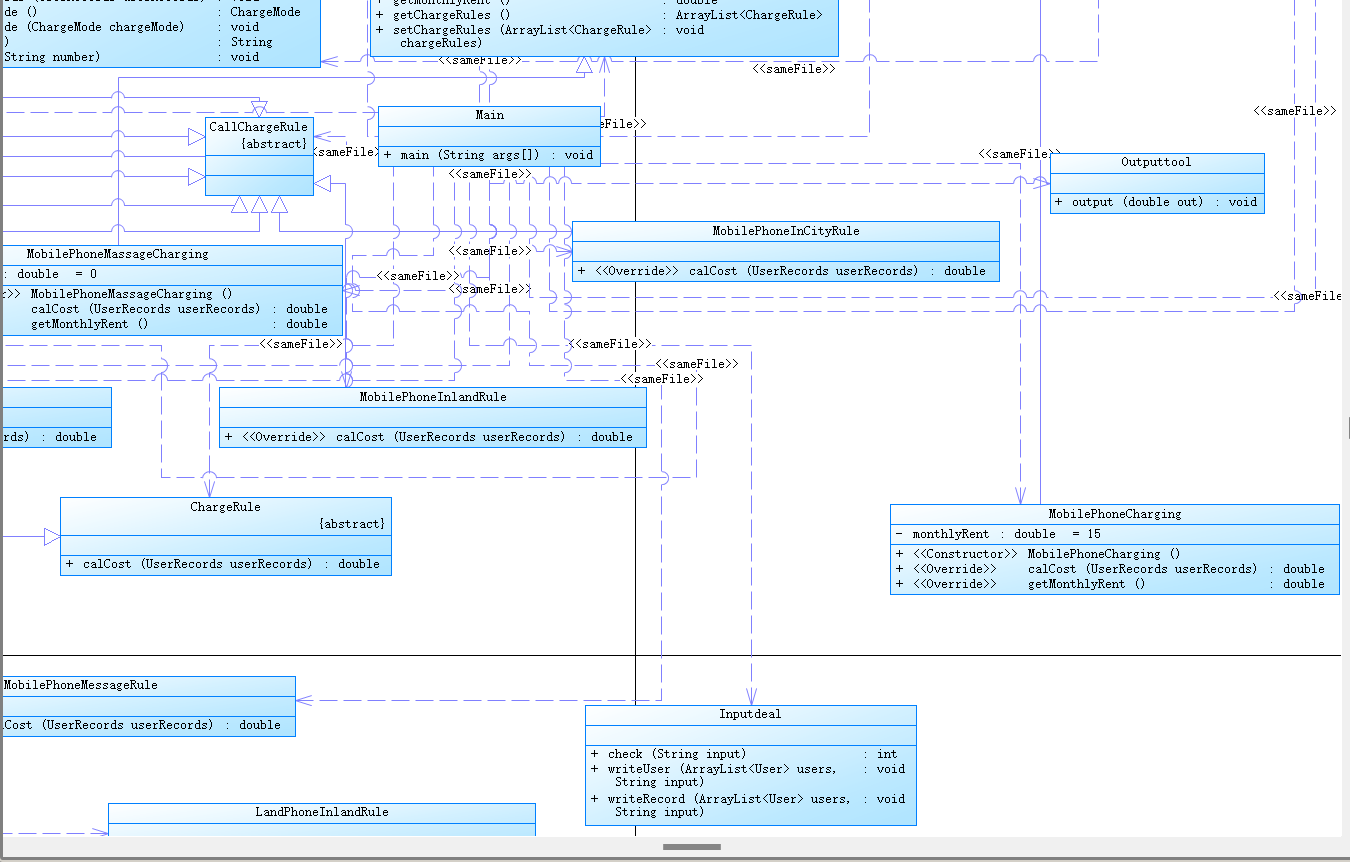
小结:本次实验较为顺利,有了前两次的基础,熟悉各种规则后写代码会容易很多,大部分从前边进行粘贴就可以。写本次实验的时候偶尔前边的部分会报错,可以进行单元测试找到是哪部分出了问题,大多数时候都是因为变量问题,和前边代码产生冲突。
2 、编写一个类Shop(商店)、内部类InnerCoupons(内部购物券)
编写一个类Shop(商店),该类中有一个成员内部类InnerCoupons(内部购物券),可以用于购买该商店的牛奶(假设每箱牛奶售价为50元)。要求如下:
(1)Shop类中有私有属性milkCount(牛奶的箱数,int类型)、公有的成员方法setMilkCount( )和getMilkCount( )分别用于设置和获取牛奶的箱数。
(2)成员内部类InnerCoupons,有公有属性value(面值,int类型),一个带参数的构造方法可以设定购物券的面值value,一个公有的成员方法buy( )要求输出使用了面值为多少的购物券进行支付,同时使商店牛奶的箱数减少value/50。
(3)Shop类中还有成员变量coupons50(面值为50元的内部购物券,类型为InnerCoupons)、coupons100(面值为100元的内部购物券,类型为InnerCoupons)。
(4)在Shop类的构造方法中,调用内部类InnerCoupons的带参数的构造方法分别创建上面的购物券coupons50、coupons100。
在测试类Main中,创建一个Shop类的对象myshop,从键盘输入一个整数(大于或等于3),将其设置为牛奶的箱数。假定有顾客分别使用了该商店面值为50的购物券、面值为100的购物券各消费一次,分别输出消费后商店剩下的牛奶箱数。
输入格式:
输入一个大于或等于3的整数。
输出格式:
使用了面值为50的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩XX箱
使用了面值为100的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩XX箱
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
使用了面值为50的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩4箱
使用了面值为100的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩2箱
代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); Shop shop=new Shop(in.nextInt()); shop.coupons50.buy(); System.out.println("牛奶还剩" + shop.getMilkCount() + "箱"); shop.coupons100.buy(); System.out.println("牛奶还剩" + shop.getMilkCount() + "箱"); } } class Shop{ private int milkCount; InnerCoupons coupons50=new InnerCoupons(50); InnerCoupons coupons100=new InnerCoupons(100); public Shop(int milkCount){ super(); this.milkCount=milkCount; } class InnerCoupons{ public int value; public InnerCoupons(int value){ this.value=value; } public void buy(){ System.out.println("使用了面值为" +value + "的购物券进行支付"); milkCount=milkCount-value/50; } } public int getMilkCount(){ return milkCount; } public void setMilkCount(int milkCount){ this.milkCount=milkCount; } }
类图:
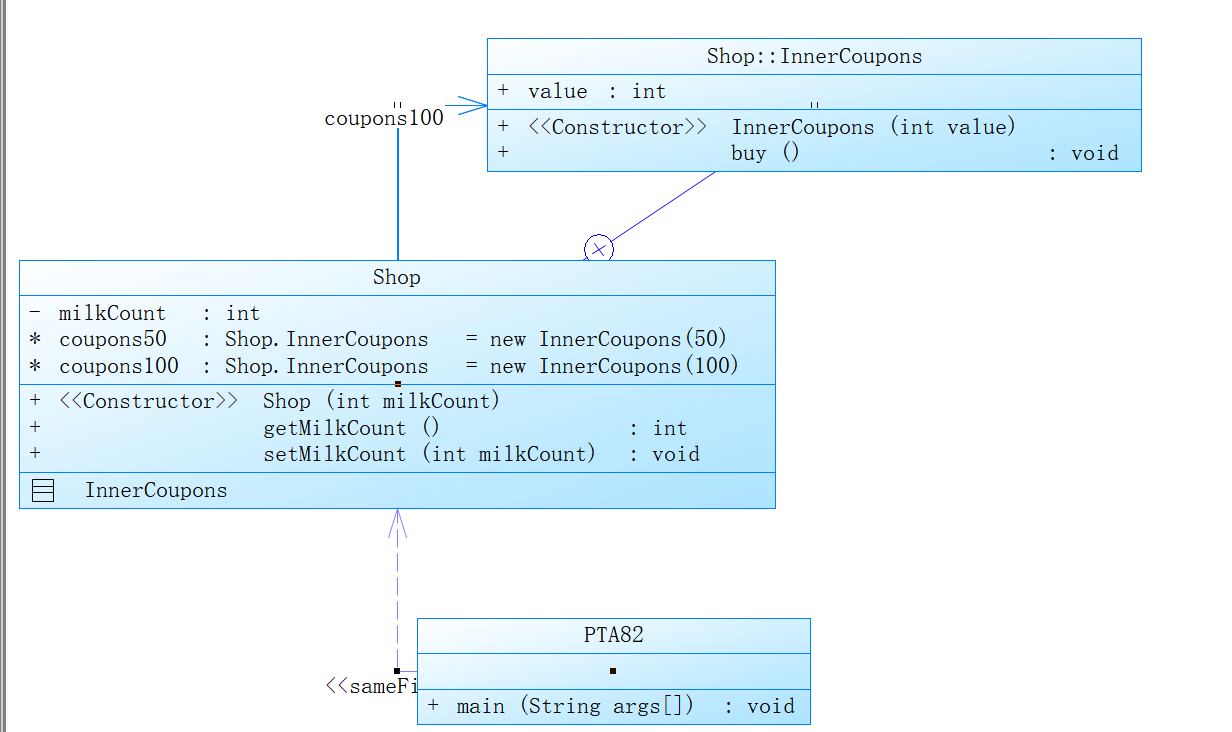
小结:还是老问题,注意审题。刚开始并没有想写getCount方法,输出的时候直接get用户输入的牛奶箱数,用100元券的时候count-2,查看编译结果的时候发现答案错误,还有测试点没有通过,用测试案例进行了测试,发现输出部分有问题,进行了修改并添加了getCount方法。
3 、动物发声模拟器(多态)
设计一个动物发生模拟器,用于模拟不同动物的叫声。比如狮吼、虎啸、狗旺旺、猫喵喵……。
定义抽象类Animal,包含两个抽象方法:获取动物类别getAnimalClass()、动物叫shout();
然后基于抽象类Animal定义狗类Dog、猫类Cat和山羊Goat,用getAnimalClass()方法返回不同的动物类别(比如猫,狗,山羊),用shout()方法分别输出不同的叫声(比如喵喵、汪汪、咩咩)。
最后编写AnimalShoutTest类测试,输出:
猫的叫声:喵喵
狗的叫声:汪汪
山羊的叫声:咩咩
其中,在AnimalShoutTestMain类中,用speak(Animal animal){}方法输出动物animal的叫声,在main()方法中调用speak()方法,分别输出猫、狗和山羊对象的叫声。
请在下面的【】处添加代码。
//动物发生模拟器. 请在下面的【】处添加代码。
public class AnimalShoutTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
Dog dog = new Dog();
Goat goat = new Goat();
speak(cat);
speak(dog);
speak(goat);
}
//定义静态方法speak()
【】
}
//定义抽象类Animal
【】class Animal{
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义猫类Cat,并重写两个抽象方法
class Cat 【】{
【】
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义狗类Dog,并重写两个抽象方法
class Dog 【】{
【】
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义山羊类Goat,并重写两个抽象方法
class Goat 【】{
【】
【】
}
输入样例:
输出样例:
猫的叫声:喵喵
狗的叫声:汪汪
山羊的叫声:咩咩
代码:

public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Cat cat=new Cat(); Dog dog=new Dog(); Goat goat=new Goat(); speak(cat); speak(dog); speak(goat); } static void speak(Animal animal){ System.out.print(animal.getAnimalClass()+"的叫声:"); animal.shout(); } } abstract class Animal{ abstract void shout(); abstract String getAnimalClass(); } class Cat extends Animal{ void shout(){ System.out.println("喵喵"); } String getAnimalClass(){ return "猫"; } } class Dog extends Animal{ void shout(){ System.out.println("汪汪"); } String getAnimalClass(){ return "狗"; } } class Goat extends Animal{ void shout(){ System.out.println("咩咩"); } String getAnimalClass(){ return "山羊"; } }
类图:

小结:本次实验先定义了动物类作为父类,羊狗猫为三个子类,继承于父类,可硬省去很多重复冗杂的步骤,因为已经由父类统一定义。在非主类的类中,我们需要做的只有获取用户输入动物的类,然后输出他们的叫声,最后在主类中调用输出方法。难度不大,也要注意题目要求,当然用我们刚开始学java时的技术也能写,但是测试点不会完全正确,需要符合题目要求。
总结:
三次习题的侧重点都在于电信计费,通过写代码让我们熟悉继承,多态,接口等相关知识。当然写题的过程并不是都很顺利,基础知识我还有一些地方掌握的并不熟练,包括接口的运用,我会在课下时间及时夯实基础,看幕课的同时复习课上所学知识。





