Hibernate 框架入门
接着上一篇的 Hibernate 框架 的了解,我们就继续学习 Hibernate 框架。这次就进入 Hibernate 框架的入门学习。
首先在学习 Hibernate 框架之前,我们要准备好我们需要的 jar 包。
下载 Hibernate 框架的 jar 链接: http://hibernate.org/
我是下载的是:
解压后可以看到其目录是:
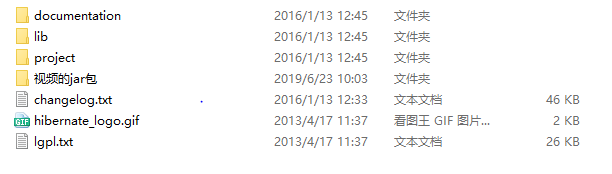
documentation:存放 Hibernate 的相关文件与 API 。
lib:存放 Hibernate 编译和运行所依赖的 jar 包, 其中 required 子目录下包含了运行 Hibernate 项目必须的 jar 包。
project:存放 Hibernate 各种相关的源代码与资源, project 目录下的 etc 目录非常重要,它里面有一些关于 Hibernate 的配置信息。
Hibernate 快速入门
使用 Hibernate 框架的三大步骤:
引入 jar 开发包
配置相关的 xml 文件
熟悉 API
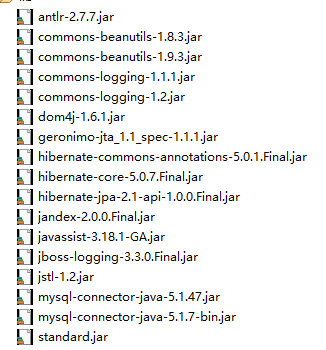
引入相关的 jar 包
在项目中引入 Hibernate 必须的 jar 包 和 数据库驱动包。如下图:
Hibernate 配置文件编写
Hibernate 通过读取默认的 XML 配置文件 hibernate.cfg.xml 加载数据库的配置信息,该默认文件默认存储于项目的 classpath 根目录下。
首先来看一下连接 Mysql 数据库所用的 XML 配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 数据库驱动 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class"> com.mysql.jdbc.Driver </property> <!-- 数据库url --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url"> jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate </property> <!-- 数据库连接用户名 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <!-- 数据库连接密码 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">111</property> <!-- 数据库方言 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect"> org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect </property> <!-- 将 sql 打印到控制台上 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 将sql 语句格式化 --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- ## auto schema export 自动导出表结构. 自动建表
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create 自动建表.每次框架运行都会创建新的表.以前表将会被覆盖,表数据会丢失.(开发环境中测试使用)
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop 自动建表.每次框架运行结束都会将所有表删除.(开发环境中测试使用)
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update(推荐使用) 自动生成表.如果已经存在不会再生成.如果表有变动.自动更新表(不会删除任何数据). #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate 校验.不自动生成表.每次启动会校验数据库中表是否正确.校验失败. --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 引入元数据 --> <mapping resource="cn/itheima/domain/Customer.hbm.xml" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
hibernate.cfg.xml 文件的根元素为 <hibernate-configuration> ,每一个 <session-factory> 元素可以有多个 <property> 和 <mapping> 子元素,通常情况下 <session-factory> 只有一个, 每一个 <session-factory> 对应一个数据库; <property> 元素用来配置 Hibernate 属性信息; <mapping> 元素用来配置持久化类映射文件的相对路径。
<property> 元素的常用属性及说明:
| 属性 | 说明 |
hibernate.connection.driver_class
|
设置数据库驱动 |
hibernate.connection.url
|
设置数据库连接的 URL |
hibernate.connection.username
|
设置连接数据库所使用的用户名 |
hibernate.connection.password
|
设置连接数据库所使用的密码 |
hibernate.dialect
|
设置连接数据库所使用的 Hibernate 方言 |
hibernate.show_sql
|
是否打印 SQL 语句 |
hibernate.format_sql
|
设置是否对 SQL 语句进行格式化 |
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto
|
设置自动建表 |
编写持久化类
对象 - 关系映射 ( ORM ) 是 Hibernate 的基础。 在 Hibernate 中, 持久化类是 Hibernate 操作的对象,它与数据库中的数据表相对应。在持久化类中,其属性信息与数据表中的字段相匹配。
下面看一个简单的持久化类:
package cn.hhh.domain; public class Customer { private Long cust_id; private String cust_name; private String cust_phone; public Customer() { super(); } public Customer(Long cust_id, String cust_name) { super(); this.cust_id = cust_id; this.cust_name = cust_name; } public Long getCust_id() { return cust_id; } public void setCust_id(Long cust_id) { this.cust_id = cust_id; } public String getCust_name() { return cust_name; } public void setCust_name(String cust_name) { this.cust_name = cust_name; } public String getCust_phone() { return cust_phone; } public void setCust_phone(String cust_phone) { this.cust_phone = cust_phone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer [cust_id=" + cust_id + ", cust_name=" + cust_name + "]"; } }
Customer 类为持久化类,此类中定义了用户的基本属性,并提供了相应的 getXXX() 与 setXXX() 方法。持久化类遵循 JavaBean 命名约定。由于持久化类只是一个普通的类,并没有特殊的功能,也就是说它不依赖任何对象( 没有实现任何接口,也没有继承任何类 ),又被称为 POJO 类。
Hibernate 编写持久化类的注意事项:
1、声明一个默认的、无参的构造方法。 Hibernate 在创建持久化类时, 通过默认且没有参数的构造方法进行实例化,所以必须要提供一个无参的构造方法。
2、类的声明是非 final 类型的。如果 Hibernate 的持久化类声明为 final 类型,那么将不能使用延迟加载等设置,因为 Hibernate 的延迟加载通过代理实现;它要求持久化类非 final 的。
3、拥有一个标识属性。标识属性通常对应数据表中的主键。此属性是可选的。为了更好地使用 Hibernate ,推荐加入此属性。
4、为属性声明访问器。 Hibernate 在加载持久化类时,需要对其进行创建并赋值,所以在持久化类中属性声明 getXXX() 与 setXXX() 方法,这些方法为 public 类型。
编写持久化类对应的映射文件
Hibernate 的映射文件与持久化类相互对应,映射文件指定持久化类与数据表之间的映射关系,如数据表的主键生成策略、字段的类型、一对一关联关系等。它与持久化类的关系密切,两者之间相互关联。在 Hibernate 中,映射文件的类型为 .xml 格式,其命名格式规范为 “ 持久化类名.hbm.xml ”。
创建 Customer 持久化类的映射文件,其命名为 Customer.hbm.xml 。代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="cn.hhh.domain"> <class name="Customer" table="cst_customer" > <id name="cust_id"> <generator class="native" /> </id> <property column="cust_name" name="cust_name" /> <property column="cust_phone" name="cust_phone" /> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<hibernate-mapping> 元素:是 Hibernate 映射文件的根元素,其他元素嵌入在 <hibernate-mapping> 元素内,其常用属性主要有 package 属性,用于指定的包名。
<class> 元素:用于指定持久化类和数据表的映射。 其 name 属性指定持久化类的完整类名; table 属性指定数据库中对应的数据表的表名,如果不指定 table 属性, Hibernate 将使用类名作为表名。
在 <class> 元素中包含一个 <id> 元素及多个 <property> 元素,其中 <id> 元素对应数据表中的标识,指定持久化类的 OID 和表的主键的映射; <property> 元素描述数据表中的字段属性。
<id> 元素:通过 name 属性指定持久化类中的属性,设置数据表中的主键。其子元素 <generator> 元素用于配置数据表主键的生成策略。其主键生成策略说明如下表:
| 标识生成策略 | 说明 |
| identity | 主键自增。由数据库来维护主键值。录入时不需要指定主键。 |
| increment | 主键自增。由hibernate来维护。每次插入前会先查询表中id最大值,+1作为新主键值。 |
| sequence | Oracle中的主键生成策略。 |
| hilo | 高低位算法。主键自增。由hibernate来维护。开发时不使用。 |
| native | hilo+sequence+identity 自动三选一 |
| uuid | 产生随机字符串作为主键。主键类型必须为String类型 。 |
| assigned | 自然主键生成策略。由 Java 应用程序负责生成。 |
<property> 元素:用于配置数据表中字段的属性信息。常用配置属性及说明如下表:
| 属性名称 | 说明 |
| name | 指定持久化类中的属性名称 |
| column | 指定数据表中的字段名称 |
| type | 指定数据表中的字段类型 |
| not-null | 指定数据表字段的非空属性,它是一个布尔值 |
| length | 指定数据表中的字段长度 |
| unique | 指定数据表中字段值是否唯一,它是一个布尔值 |
| lazy | 设置延迟加载 |
在实际开发过程中,可以省略 column 及 type 属性的配置,在尚未配置它们的情况下, Hibernate 默认使用持久化类中的属性名及属性类型去映射数据表中的字段名和类型。
编写 Hibernate 的初始化类
Hibernate 的运行离不开 Session 对象, 对于数据的增、删、改、查都要用到 Session , 而 Session 对象依赖于 SessionFactory 对象,它需要通过 SessionFactory 进行获取。
下面测试一个例子,保存一个客户到数据库中去。
package cn.hhh.test; public class DemoTest { @Test //保存客户 public void test() { Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();//加载 Hibernate 配置文件 SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();//创建SessionFactory 对象 Session session = sf.openSession();//获取 session Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();//打开事务 Customer c = new Customer(); c.setCust_name("小明"); c.setCust_phone("12345678910"); session.save(c); tx.commit(); session.close(); }
}
这就是使用 Hibernate 框架保存的例子。
根据 id 查询一个客户的测试例子:
package cn.hhh.test; public class DemoTest { @Test //保存客户 public void test() { Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();//加载 Hibernate 配置文件 SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();//创建SessionFactory 对象 Session session = sf.openSession();//获取 session Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();//打开事务 Customer c = new Customer(); Customer c = session.get(Customer.class , 1L );//查询客户 System.out.println(c); tx.commit(); session.close(); } }
编写通用的工具类,代码如下:
package cn.hhh.utils; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; public class HibernateUtils { private static Configuration cfg; private static SessionFactory factory; static{ cfg = new Configuration().configure(); factory = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); } public static Session openSession(){ Session session = factory.openSession(); return session; } public static Session getCurrentSession(){ Session session = factory.getCurrentSession(); return session; } }
这里面都是使用 Hibernate 最基本的操作。要掌握好。 特别是 怎么配置,怎么编写持久化类。下一篇文章就让我们继续深入了解 Hibernate 的其他功能和其他操作。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号