【Java】使用线程解决生产者与消费者问题
Box.java
package LearnJava16.sczandxfz;
public class Box {
// 定义一个成员变量
private int milk;
// 定义一个成员变量表示奶箱状态
private boolean status = false;
// 提供存储牛奶和获取牛奶的操作
public synchronized void put(int milk) {
// 如果有牛奶,等待消费
if (status) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 如果没有就生产
this.milk = milk;
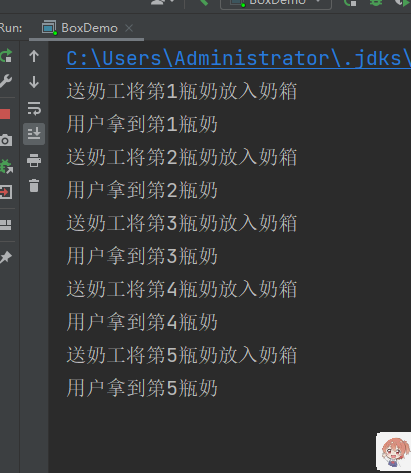
System.out.println("送奶工将第" + this.milk + "瓶奶放入奶箱");
// 生产完毕,修改奶箱状态
status=true;
// 唤醒其他线程
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void get() {
// 如果没有牛奶,等待生产
if (!status){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 如果有牛奶就消费
System.out.println("用户拿到第" + this.milk + "瓶奶");
// 消费完毕,修改状态
status=false;
// 唤醒其他线程
notifyAll();
}
}Producer.java
package LearnJava16.sczandxfz;
public class Producer implements Runnable{
private Box b;
public Producer(Box b) {
this.b=b;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
b.put(i);
}
}
}Customer.java
package LearnJava16.sczandxfz;
public class Customer implements Runnable{
private Box b;
public Customer(Box b) {
this.b=b;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
b.get();
}
}
}BoxDemo.java
package LearnJava16.sczandxfz;
public class BoxDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建奶箱对象
Box b=new Box();
Producer p=new Producer(b);
Customer c=new Customer(b);
Thread t1=new Thread(p);
Thread t2=new Thread(c);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:木子欢儿,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/HGNET/p/16206941.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号