1937.Codeforces Round 930 (Div. 2) - sol
20240301
由于笔者实力较弱,所以这只是 Div 2 的题解。
四年一次的比赛啊,还是要打。
Dashboard - Codeforces Round 930 (Div. 2) - Codeforces
A. Shuffle Party
You are given an array
. Initially, for each . The operation
for an integer is defined as follows:
- Let
be the largest divisor of which is not equal to itself. Then swap the elements and . Suppose you perform
for each in this exact order. Find the position of in the resulting array. In other words, find such that after performing these operations.
An integer is a divisor of if there exists an integer such that .
。
容易发现,换到的位置都是
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int N=2e5+5;
int n,T;
void sol(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--) if(n>=(1<<i)){cout<<(1<<i)<<'\n';break;}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>T;
while(T--) sol();
return 0;
}
B. Binary Path
You are given a
grid filled with zeros and ones. Let the number at the intersection of the -th row and the -th column be . There is a grasshopper at the top-left cell
that can only jump one cell right or downwards. It wants to reach the bottom-right cell . Consider the binary string of length consisting of numbers written in cells of the path without changing their order. Your goal is to:
- Find the lexicographically smallest
string you can attain by choosing any available path; - Find the number of paths that yield this lexicographically smallest string.
If two strings and have the same length, then is lexicographically smaller than if and only if in the first position where and differ, the string has a smaller element than the corresponding element in .
。
由于每一次只能往下和往右,所以其实我们只需要找到一个中断点,从这个点往下走即可。
而第一次找到的路径我们一定希望越远越好,也就是一直往右走,知道有一个位置右边是
这样我们就可以轻松找到最短的序列。
再来考虑出现次数,容易想到画图去解决问题。
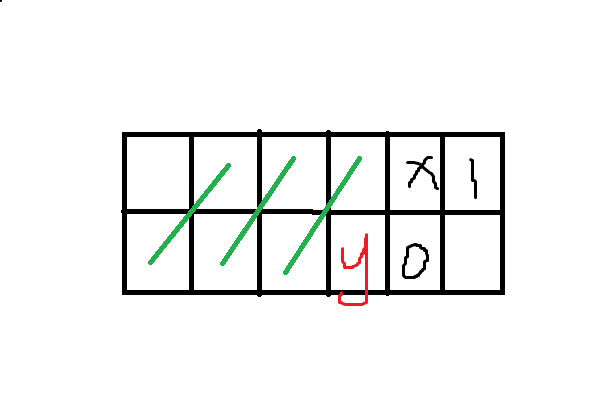
假设我们在
如果
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int N=2e5+5;
int n,T,tmp=0;
string s[2];
void sol(){
cin>>n>>s[0]>>s[1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<s[0][i];
if(i<n-1&&s[0][i+1]=='0') continue;
if(i<n-1&&s[0][i+1]==s[1][i]) continue;
tmp=i;break;
}
for(int i=tmp;i<n;i++) cout<<s[1][i];
cout<<'\n';
int cnt=1;
for(int i=tmp;i>0;i--){
if(s[0][i]==s[1][i-1]) ++cnt;
else break;
}
cout<<cnt<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>T;
while(T--) sol();
return 0;
}
C. Bitwise Operation Wizard
This is an interactive problem.
There is a secret sequence
, which is a permutation of . You need to find any two indices
and such that is maximized, where denotes the bitwise XOR operation. To do this, you can ask queries. Each query has the following form: you pick arbitrary indices
, , , and ( ). Next, the jury calculates and , where denotes the bitwise OR operation. Finally, you receive the result of comparison between and . In other words, you are told if , , or . Please find any two indices
and ( ) such that is maximum among all such pairs, using at most queries. If there are multiple pairs of indices satisfying the condition, you may output any one of them.
。
场上不会 C 的小丑。
发现直接讨论两个数是非常不好做的,所以我们可以一个一个来。
考虑我们可以通过
而在答案中选
进一步,我们可以通过与
而异或中,我们还要求
后两次的操作也都可以在
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+5;
int id[N],tmp1,tmp2,cnt=0,n,T;
char ch;
void sol(){
scanf("%d",&n);
tmp1=cnt=0;tmp2=-1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
printf("? %d %d %d %d\n",tmp1,tmp1,i,i);
fflush(stdout);
ch=getchar();
while(ch!='='&&ch!='<'&&ch!='>') ch=getchar();
if(ch=='<') tmp1=i;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i==tmp1) continue;
if(!cnt){id[++cnt]=i;continue;}
printf("? %d %d %d %d\n",tmp1,id[cnt],tmp1,i);
fflush(stdout);
ch=getchar();
while(ch!='='&&ch!='<'&&ch!='>') ch=getchar();
if(ch=='<') id[cnt=1]=i;
else if(ch=='=') id[++cnt]=i;
}
tmp2=id[1];
for(int i=2;i<=cnt;i++){
printf("? %d %d %d %d\n",tmp2,tmp2,id[i],id[i]);
fflush(stdout);
ch=getchar();
while(ch!='='&&ch!='<'&&ch!='>') ch=getchar();
if(ch=='>') tmp2=id[i];
}
printf("! %d %d\n",tmp1,tmp2);
fflush(stdout);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--) sol();
return 0;
}
D. Pinball
There is a one-dimensional grid of length
. The -th cell of the grid contains a character , which is either '<' or '>'. When a pinball is placed on one of the cells, it moves according to the following rules:
- If the pinball is on the
-th cell and is '<', the pinball moves one cell to the left in the next second. If is '>', it moves one cell to the right. - After the pinball has moved, the character
is inverted (i. e. if used to be '<', it becomes '>', and vice versa). - The pinball stops moving when it leaves the grid: either from the left border or from the right one.
You need to answer
independent queries. In the -th query, a pinball will be placed on the -th cell. Note that we always place a pinball on the initial grid. For each query, calculate how many seconds it takes the pinball to leave the grid. It can be shown that the pinball will always leave the grid within a finite number of steps.
。
这是一道简单题,主要就是去手玩一下走的过程。
建议自己多画几个样例,把走的路线画出来就知道怎么做了。
(不想写了,感觉也比较难以描述。)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=5e5+5;
int n,T,c[2],S[2][N],d[2][N];
char s[N];
int calc(int l,int r,int op){return S[op][r]-S[op][l-1];}
void sol(){
scanf("%lld%s",&n,s+1);c[0]=c[1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(s[i]=='>') ++c[0],S[0][c[0]]=S[0][c[0]-1]+i*2;
else ++c[1],S[1][c[1]]=S[1][c[1]-1]+i*2;
d[0][i]=c[0],d[1][i]=c[1];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(s[i]=='>'){
if(d[0][i]>c[1]-d[1][i]) printf("%lld ",calc(d[1][i]+1,c[1],1)-calc(d[0][i]-(c[1]-d[1][i]),d[0][i],0)+i+n+1);
else printf("%lld ",calc(d[1][i]+1,d[1][i]+d[0][i],1)-calc(1,d[0][i],0)+i);
}else{
if(d[0][i]<c[1]-d[1][i]+1) printf("%lld ",calc(d[1][i],d[1][i]+d[0][i],1)-calc(1,d[0][i],0)-i);
else printf("%lld ",calc(d[1][i],c[1],1)-i-calc(d[0][i]-(c[1]-d[1][i]),d[0][i],0)+n+1);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
signed main(){
scanf("%lld",&T);
while(T--) sol();
return 0;
}
E. Pokémon Arena
You are at a dueling arena. You also possess
Pokémons. Initially, only the -st Pokémon is standing in the arena. Each Pokémon has
attributes. The -th attribute of the -th Pokémon is . Each Pokémon also has a cost to be hired: the -th Pokémon's cost is . You want to have the
-th Pokémon stand in the arena. To do that, you can perform the following two types of operations any number of times in any order:
- Choose three integers
, , ( , , ), increase by permanently. The cost of this operation is . - Choose two integers
, ( , ) and hire the -th Pokémon to duel with the current Pokémon in the arena based on the -th attribute. The -th Pokémon will win if is greater than or equal to the -th attribute of the current Pokémon in the arena (otherwise, it will lose). After the duel, only the winner will stand in the arena. The cost of this operation is . Find the minimum cost you need to pay to have the
-th Pokémon stand in the arena.
。
图论好题。
首先,
分析一下,考虑这样一种建图方式,对于每一个属性,我们都建立出
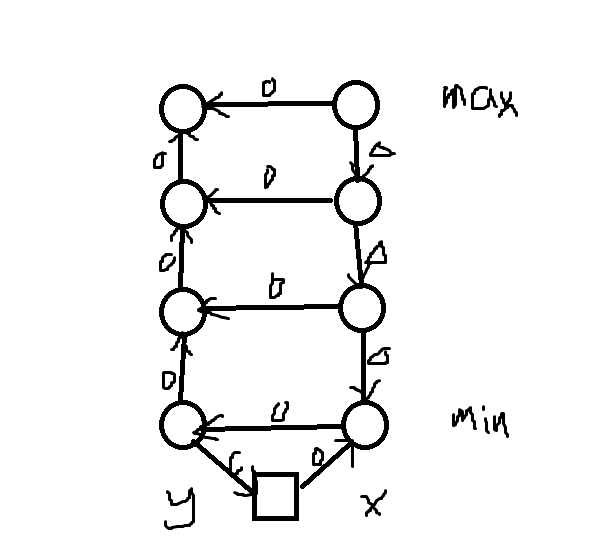
我们的两列点都是按照从大到小的顺序做的。
可以模拟一下,发现这样就变成了求
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
const int N=2e6+5;
const ll inf=1e18;
int n,m,c[N],idx=0,T;
ll dis[N];
vector<pair<int,ll>> G[N];
bool vis[N];
struct node{
int id,v;
bool operator <(const node &rhs) const{return v<rhs.v;}
};
vector<node> a[N];
ll dij(){
for(int i=1;i<=idx;i++) dis[i]=inf,vis[i]=false;
dis[1]=0;
priority_queue<pair<ll,int> > Q;
Q.push({0,1});
while(!Q.empty()){
int u=Q.top().se;Q.pop();
if(vis[u]) continue;
vis[u]=true;
for(auto i:G[u]){
ll w=i.se,v=i.fi;
if(dis[v]>dis[u]+w){
dis[v]=dis[u]+w;
Q.push({-dis[v],v});
}
}
}
return dis[n];
}
void sol(){
cin>>n>>m;idx=n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>c[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1,x;j<=m;j++) cin>>x,a[j].pb((node){i,x});
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
sort(a[i].begin(),a[i].end());
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) G[j].pb({idx+j,0}),G[idx+n+j].pb({j,c[j]}),G[idx+j].pb({idx+n+j,0});
for(int j=1;j<n;j++) G[idx+a[i][j].id].pb({idx+a[i][j-1].id,a[i][j].v-a[i][j-1].v});
for(int j=0;j+1<n;j++) G[idx+n+a[i][j].id].pb({idx+n+a[i][j+1].id,0});
idx+=2*n;a[i].clear();
}
cout<<dij()<<'\n';
for(int i=1;i<=idx;i++) G[i].clear();
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>T;
while(T--) sol();
return 0;
}
F. Bitwise Paradox
You are given two arrays
and of size along with a fixed integer . An interval
is called a good interval if , where denotes the bitwise OR operation. The beauty of a good interval is defined as . You are given
queries of two types:
- "1 i x": assign
; - "2 l r": find the minimum beauty among all good intervals
satisfying . If there is no suitable good interval, output instead. Please process all queries.
。
DS 好题。一篇认认真真的题解(上面的几道题都不认真)。
读完题目,发现这是一个与二进制相关的问题,
而容易发现,每组数据中
我们不难想到拆位,也就是对每一个二进制位分开来讨论。
现在再来看数据范围,直觉是可以去尝试 Poly log 的做法,
而用最普通的线段树来维护,问题就在于我们如何去 合并两个区间。
发现这是好做的,我们同样按照二进制位从高到低考虑,合并区间
设当前枚举到第
假设左区间从右往左第一个
-
如果
-
反之我们选择把
这样贪心地选择一定是不劣的,因为你总需要拓展一个,我们希望答案尽可能优。
而
-
如果把这一位选成
-
不选则继续往下枚举。
这样我们就可以做到两个区间的合并了,
实现中只需要维护一个区间每一位的
//S(l,r) 算区间 [l,r] 中 a_i 的最大值
sgt operator +(sgt Lp,sgt Rp){//合并区间 Lp 和 Rp
sgt res;
res.v=min(Lp.v,Rp.v),res.l=Lp.l,res.r=Rp.r;
//v 是当前区间的答案,l,r 是当前区间的左右界
int L=Lp.r,R=Rp.l,tmp=inf,_L,_R;bool fl=1;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--){
res.pre[i]=Lp.pre[i]?Lp.pre[i]:Rp.pre[i];//更新当前区间第 i 位的 P,不存在为 0
res.suf[i]=Rp.suf[i]?Rp.suf[i]:Lp.suf[i];//更新当前区间第 i 位的 Q,不存在为 0
if(!fl) continue;//高位无法满足条件直接跳过
if(!Lp.suf[i]&&!Rp.pre[i]){fl=!lim[i];continue;}//这一位无法为 1 满足条件
if(!lim[i]) _L=L,_R=R;
if(!Lp.suf[i]) R=max(R,Rp.pre[i]);
else if(!Rp.pre[i]) L=min(L,Lp.suf[i]);
else{
if(S(Lp.suf[i],Lp.r)<=S(Rp.l,Rp.pre[i])) L=min(L,Lp.suf[i]);
else R=max(R,Rp.pre[i]);
}
if(!lim[i]) tmp=min(tmp,S(L,R)),L=_L,R=_R;//在不要求选 1 时选了 1,可以直接更新答案
}
if(fl) res.v=min(res.v,S(L,R));
res.v=min(res.v,tmp);
return res;
}
完成了区间合并,那么这道题就做完了。其实只要想到拆位,也就不难了。
实现中
const int N=2e5+5,inf=2e9;
int n,T,m,V,a[N],st[30][N],b[N],lg[N],lim[31];
void init(){
lg[1]=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) lg[i]=lg[i/2]+1;
for(int i=1;i<=lg[n]+1;i++)
for(int j=1;j+(1<<i)-1<=n;j++)
st[i][j]=max(st[i-1][j],st[i-1][j+(1<<(i-1))]);
}
int S(int l,int r){
int tmp=lg[r-l+1];
return max(st[tmp][l],st[tmp][r-(1<<tmp)+1]);
}
namespace SGT{
struct sgt{
int v,pre[31],suf[31],l,r;
}tr[N<<2];
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
#define lson l,mid,lc
#define rson mid+1,r,rc
sgt operator +(sgt Lp,sgt Rp){
sgt res;
res.v=min(Lp.v,Rp.v),res.l=Lp.l,res.r=Rp.r;
int L=Lp.r,R=Rp.l,tmp=inf,_L,_R;bool fl=1;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--){
res.pre[i]=Lp.pre[i]?Lp.pre[i]:Rp.pre[i];
res.suf[i]=Rp.suf[i]?Rp.suf[i]:Lp.suf[i];
if(!fl) continue;
if(!Lp.suf[i]&&!Rp.pre[i]){fl=!lim[i];continue;}
if(!lim[i]) _L=L,_R=R;
if(!Lp.suf[i]) R=max(R,Rp.pre[i]);
else if(!Rp.pre[i]) L=min(L,Lp.suf[i]);
else{
if(S(Lp.suf[i],Lp.r)<=S(Rp.l,Rp.pre[i])) L=min(L,Lp.suf[i]);
else R=max(R,Rp.pre[i]);
}
if(!lim[i]) tmp=min(tmp,S(L,R)),L=_L,R=_R;
}
if(fl) res.v=min(res.v,S(L,R));
res.v=min(res.v,tmp);
return res;
}
void pu(int p){tr[p]=tr[lc]+tr[rc];}
void Up(int p,int l){
tr[p].l=tr[p].r=l,tr[p].v=(b[l]>=V)?a[l]:inf;
for(int i=0;i<31;i++) tr[p].pre[i]=tr[p].suf[i]=((b[l]>>i)&1)?l:0;
}
void build(int l,int r,int p){
if(l==r) return Up(p,l);
build(lson),build(rson),pu(p);
}
void upd(int l,int r,int p,int x){
if(l==r) return Up(p,l);
x<=mid?upd(lson,x):upd(rson,x);pu(p);
}
sgt qry(int l,int r,int p,int x,int y){
if(x<=l&&y>=r) return tr[p];
if(y<=mid) return qry(lson,x,y);
if(x>mid) return qry(rson,x,y);
return qry(lson,x,y)+qry(rson,x,y);
}
}
using namespace SGT;
void sol(){
cin>>n>>V;
for(int i=0;i<31;i++) lim[i]=((V>>i)&1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i],st[0][i]=a[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>b[i];
init();build(1,n,1);
cin>>m;
while(m--){
int op,l,r;cin>>op>>l>>r;
if(op==1) b[l]=r,upd(1,n,1,l);
else{
sgt res=qry(1,n,1,l,r);
if(res.v==inf) cout<<"-1 ";
else cout<<res.v<<' ';
}
}
cout<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>T;
while(T--) sol();
return 0;
}
Conclusion
- 有关二进制的 DS 可以考虑 拆位,对每一位分别进行讨论。(F)
- 构造题可以考虑把每一个询问分开来考虑。(C)
- 图论边数过多时,我们可以考虑前缀和优化,也可以 对点按照权值排序,边权为
本文作者:H_W_Y
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/H-W-Y/p/18047267/cf1937
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步