循环计算过程(1pre1)
RNN 最典型的应用就是利用历史数据预测下一时刻将发生什么,即根据以前见过的历史规律做预测
例子:

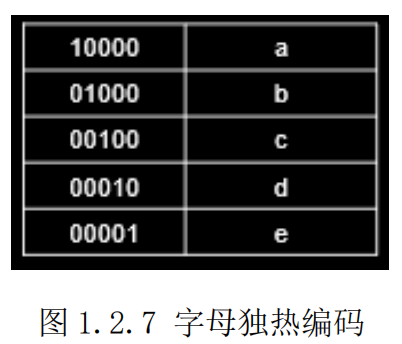
计算机不认识字母,只能处理数字。所以需要我们对字母进行编码。这里假设使用独热编码(实际中可使用其他编码方式),编码结果如图1.2.7所示。
词向量空间:

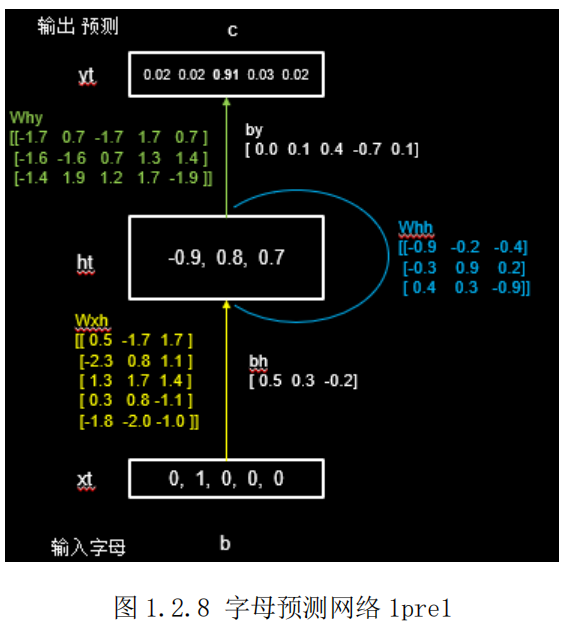
假设使用一层 RNN 网络,记忆体的个数选取 3,则字母预测的网络如图 1.2.8所示。假设输入字母 b,即输入𝑥𝑡为[0,1,0,0,0],这时上一时刻的记忆体状态信息ℎ𝑡−1 为 0。由上文理论知识不难得到:
h𝑡 = tanh( 𝑥𝑡𝑤𝑥ℎ+ℎ𝑡−1wℎh + 𝑏) =tanh([−2.3 0.8 1.1 ] + 0 + [ 0.5 0.3 − 0.2]) =tanh[−1.8 1.1 0.9 ] = [−0.9 0.8 0.7]
这个过程可以理解为脑中的记忆因为当前输入的事物而更新了。
输出y𝑡 是把提取到的时间信息通过全连接进行识别预测的过程,是整个网络的输出层。不难知道,
y𝑡 = softmax(ℎ𝑡𝑤ℎ𝑦 + 𝑏y) = softmax([−0.7 − 0.6 2.9 0.7 −0.8] + [ 0.0 0.1 0.4 − 0.7 0.1]) = softmax([−0.7 − 0.5 3.3 0.0 − 0.7]) =[0.02 0.02 0.91 0.03 0.02 ] 。
可见模型认为有 91%的可能性输出字母 c ,所以循环网络输出了预测结果 c。

构建模型:一个具有 3 个记忆体的循环层+一层全连接->Compile->fit->summary。
input_word = 'abcde'
# 单词映射到数值id的字典
w_to_id = {'a': 0, 'b': 1, 'c': 2, 'd': 3, 'e': 4}
# id编码为one_hot
id_to_onehot = {0: [1., 0., 0., 0., 0.], 1: [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.], 2: [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], 3: [0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
4: [0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]}
x_train = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']],
id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']]]
y_train = [w_to_id['b'], w_to_id['c'], w_to_id['d'], w_to_id['e'], w_to_id['a']]
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 使x_train符合SimpleRNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处整个数据集送入,送入样本数为len(x_train);输入1个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为1; 表示为独热码有5个输入特征,每个时间步输入特征个数为5
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 1, 5))
y_train = np.array(y_train)
# 逐层搭建网络,设计一个3个记忆体的循环层+一个全连接层
model = tf.keras.Sequential([SimpleRNN(3), Dense(5, activation='softmax')])
# 配置训练方法
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
)
# 设置模型保存路径
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_1pre1.ckpt"
# 判断保存的模型是否存在
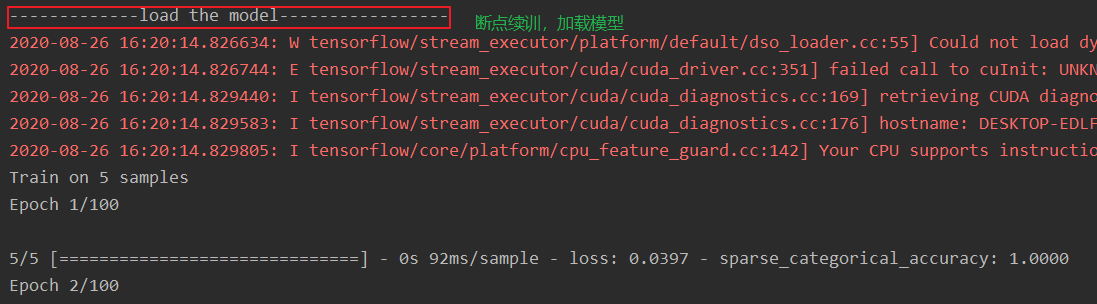
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('------------------load the model-------------------')
# 读取模型
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
# 保存模型,借助tensorflow给出的回调函数,直接保存参数和网络
'''
monitor 配合 save_best_only 可以保存最优模型,包括:训练损失最小模型、测试损失最小模型、训练准确率最高模型、测试准确率最高模型等。
'''
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss' # 由于fit没有给出测试集,不计算测试集准确率,根据loss,保存最优模型
)
# 执行训练过程
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=100, callbacks=[cp_callback])
# 对网络结构参数的统计
model.summary()
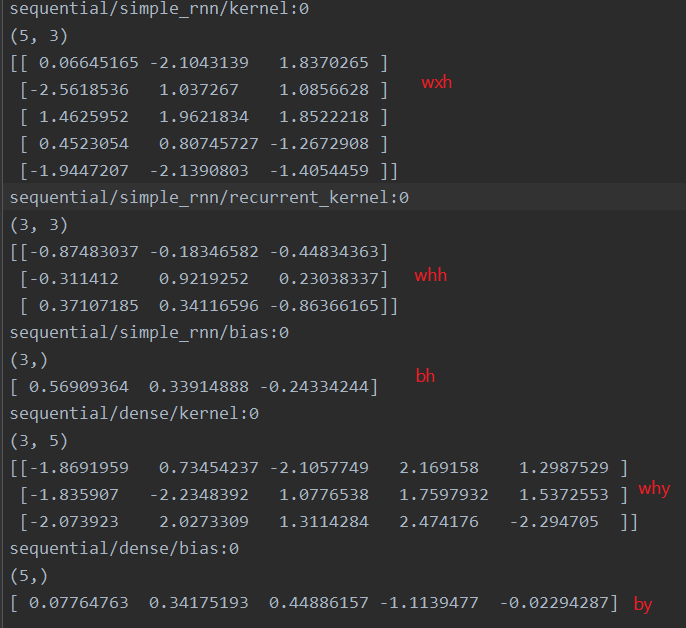
# 参数提取,写到weights.txt文本中
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w')
# model.trainable_variables 返回模型中可训练的参数
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.shape)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy())+'\n')
file.close()
############################################### show ###############################################
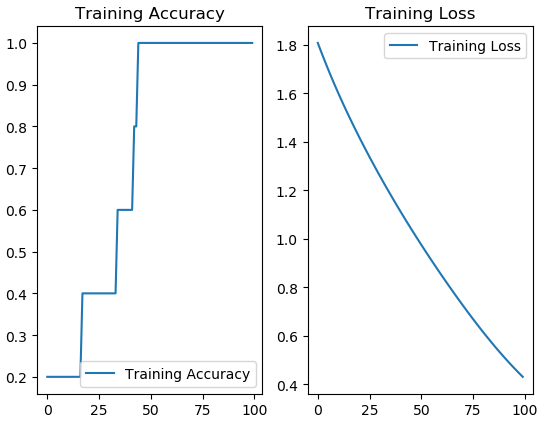
# 显示训练集和验证集的acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.title('Training Accuracy') # 图标题
plt.legend() # 图例
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss') # 图标题
plt.legend() # 图例
plt.show()
############### predict #############
preNum = int(input('input the number of test alphbet:'))
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1 = input("input test alphabet:")
# 变成模型需要的输入
alphabet = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id[alphabet1]]]
# 使alphabet符合SimpleRNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处验证效果送入了1个样本,送入样本数为1;输入1个字母出结果,所以循环核时间展开步数为1; 表示为独热码有5个输入特征,每个时间步输入特征个数为5
alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1, 1, 5))
result = model.predict([alphabet])
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
pred = int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
输出结果:
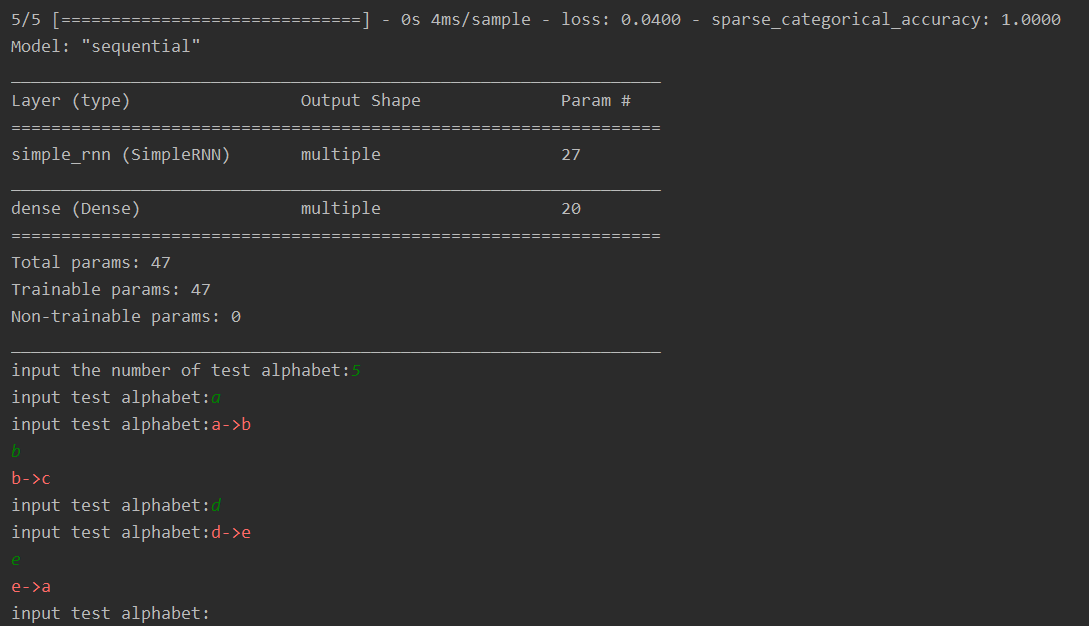
模型已经保存下来了
weights.txt内容
再运行一次,就是断点续训,就是利用上次保存模型的最优的参数,再次训练
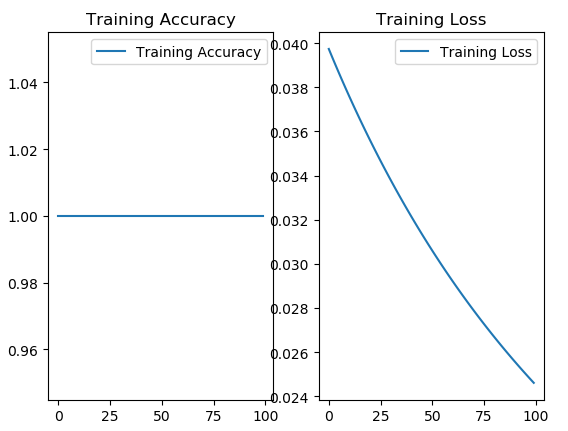
可以看到模型已经训练的非常好了。



