poj1330 lca 最近公共祖先问题学习笔记
首先推荐两个博客网址:
http://dongxicheng.org/structure/lca-rmq/
http://scturtle.is-programmer.com/posts/30055.html
[转]tarjan算法的步骤是(当dfs到节点u时):
1 在并查集中建立仅有u的集合,设置该集合的祖先为u
1 对u的每个孩子v:
1.1 tarjan之
1.2 合并v到父节点u的集合,确保集合的祖先是u
2 设置u为已遍历
3 处理关于u的查询,若查询(u,v)中的v已遍历过,则LCA(u,v)=v所在的集合的祖先
举例说明(非证明):
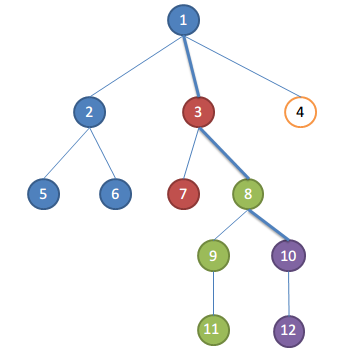
假设遍历完10的孩子,要处理关于10的请求了
取根节点到当前正在遍历的节点的路径为关键路径,即1-3-8-10
集合的祖先便是关键路径上距离集合最近的点
比如此时:
1,2,5,6为一个集合,祖先为1,集合中点和10的LCA为1
3,7为一个集合,祖先为3,集合中点和10的LCA为3
8,9,11为一个集合,祖先为8,集合中点和10的LCA为8
10,12为一个集合,祖先为10,集合中点和10的LCA为10
你看,集合的祖先便是LCA吧,所以第3步是正确的
道理很简单,LCA(u,v)便是根至u的路径上到节点v最近的点
为什么要用祖先而且每次合并集合后都要确保集合的祖先正确呢?
因为集合是用并查集实现的,为了提高速度,当然要平衡加路径压缩了,所以合并后谁是根就不确定了,所以要始终保持集合的根的祖先是正确的
关于查询和遍历孩子的顺序:
wikipedia上就是上文中的顺序,很多人的代码也是这个顺序
但是网上的很多讲解却是查询在前,遍历孩子在后,对比上文,会不会漏掉u和u的子孙之间的查询呢?
不会的
如果在刚dfs到u的时候就设置u为visited的话,本该回溯到u时解决的那些查询,在遍历孩子时就会解决掉了
这个顺序问题就是导致我头大看了很久这个算法的原因,也是絮絮叨叨写了本文的原因,希望没有理解错= =
对于这道题
题意:求最近公共祖先lca
下面是学来的tarjan代码
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <cmath> 7 #include <ctime> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 class Edge 12 { 13 public: 14 int to; 15 int next; 16 }e[11000]; 17 18 int n,T,cnt; 19 int f[11000],depth[11000],anc[11000],p[11000]; 20 bool visited[11000],In[11000]; 21 22 inline void Add_edge(const int & x,const int & y) 23 { 24 e[++cnt].to=y; 25 e[cnt].next=p[x]; 26 p[x]=cnt; 27 return ; 28 } 29 30 inline int get_anc(const int &x) 31 { 32 return f[x]==x ? x:f[x]=get_anc(f[x]); 33 } 34 35 inline void Union(const int & x,const int & y) 36 { 37 int S,T; 38 S=get_anc(x); 39 T=get_anc(y); 40 if(S==T)return ; 41 if(depth[S]<=depth[T]) 42 f[S]=T,depth[S]+=depth[T]; 43 else 44 f[T]=S,depth[T]+=depth[S]; 45 return ; 46 } 47 48 void Dfs(const int &S,const int d) 49 { 50 int i; 51 depth[S]=d; 52 for(i=p[S];i;i=e[i].next) 53 { 54 Dfs(e[i].to,d+1); 55 } 56 57 return ; 58 } 59 60 int Lca_tarjan(const int & s,const int & t,const int & u) 61 { 62 int i,temp; 63 64 anc[u]=u; 65 for(i=p[u];i;i=e[i].next) 66 { 67 temp=Lca_tarjan(s,t,e[i].to); 68 if(temp)return temp; 69 Union(u,e[i].to); 70 anc[get_anc(u)]=u; 71 } 72 73 visited[u]=true; 74 if(s==u&&visited[t]) 75 return anc[get_anc(t)]; 76 if(t==u&&visited[s]) 77 return anc[get_anc(s)]; 78 79 return 0; 80 } 81 82 inline void Init() 83 { 84 cnt=0; 85 memset(depth,0,sizeof(depth)); 86 memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited)); 87 memset(anc,0,sizeof(anc)); 88 memset(p,0,sizeof(p)); 89 memset(e,0,sizeof(e)); 90 memset(In,0,sizeof(In)); 91 92 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) 93 { 94 f[i]=i; 95 } 96 97 return ; 98 } 99 100 int main() 101 { 102 //freopen("1330.in","r",stdin); 103 104 int i,x,y,s,t,S; 105 106 scanf("%d",&T); 107 while(T--) 108 { 109 scanf("%d",&n); 110 Init(); 111 for(i=1;i<n;++i) 112 { 113 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 114 Add_edge(x,y); 115 In[y]=true; 116 } 117 118 for(S=1;S<=n;++S) 119 if(!In[S])break; 120 121 scanf("%d%d",&s,&t); 122 Dfs(S,1); 123 printf("%d\n",Lca_tarjan(s,t,S)); 124 } 125 126 return 0; 127 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号