这篇记录的内容来自于Andrew Ng教授在coursera网站上的授课。
1.线性回归不适用于分类问题。
原因:1.单个样本对于线性回归可能会造成很大的影响。
2.函数的输出值可能非常大,非常离谱。
2.逻辑回归(logistic regression):一种分类算法。是广义线性回归,$h(x)=g(\theta^{T}x)$,其中
$g(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}$
被称为logistic函数,或sigmoid函数。
3.记号:$h_{\theta}(x)=P(y=1|x;\theta)$,即在theta参数和x的条件下,y等于1的概率。
4.决策边界(decision boundary):$h(x)=0$的解集,这是h函数、参数的属性,而不是数据集的属性。
5.逻辑回归可以像以前特征缩放一样使用多项式,这样就造成其可拟合很多类型的数据集。
6.逻辑回归问题:
h函数,$h_{\theta}{(x)}=\frac{1}{1+e^{-\theta^{T}x}}$
(x(i),y(i))第i样样本,输入为x,输出为y
最小化$\frac{1}{m}\sum{cost(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)}),y^{(i)})}$
可以发现,如果直接使用梯度下降法,非常容易会停留在局部最优值上,因此代价函数不能使用平方误差函数。
而我们的麻烦之处,正在于e次方上,我们便尝试使用对数函数来去掉它的影响。于是代价函数为:
$$cost(h_{\theta}(x),y)=\begin{cases}-log(h_{\theta}(x))if\quad y=1\\-log(1-h_{\theta}(x))if\quad y=0\end{cases}$$
条件不要搞反了。
为什么?
于是,$$J(\theta)=\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}{-y*log(h_{\theta}(x))-(1-y)log(1-h_{\theta}(x))}$$
$$=-\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}{y*log(h_{\theta}(x))+(1-y)log(1-h_{\theta}(x))}$$
我们知道,线性回归梯度下降的公式为$$\theta_{i}:=\theta_{i}-\alpha\sum_{j=1}^{m}{(h_{\theta}(x^{(j)})-y^{(j)})}x^{(j)}_{i}$$
对逻辑回归的误差函数求一下导,发现:
傻眼了吧?就是线性回归的式子。
7.多元逻辑回归(multi-class classification,one-vs-rest):用n个分类器。
8.除了线性回归以外,别想着自己亲手写出正确的、优秀的、高效的算法了。好好使用前人已经花费了心血的库。
1.欠拟合(underfitting):不能很好拟合训练数据。
2.过拟合(overfitting):很好地拟合了训练数据,但过度依赖,导致方差过大,实际预测效果很差。
3.正则化线性回归:$$J_{\theta}(x)=\frac{1}{2m}(\sum_{i=1}^{m}{(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2}+\lambda\sum_{i=1}^{n}{\theta_i^2})$$
不对$\theta_0$加以限制,这是传统。
能够调次数、均值归一化的双元、一对一逻辑回归:

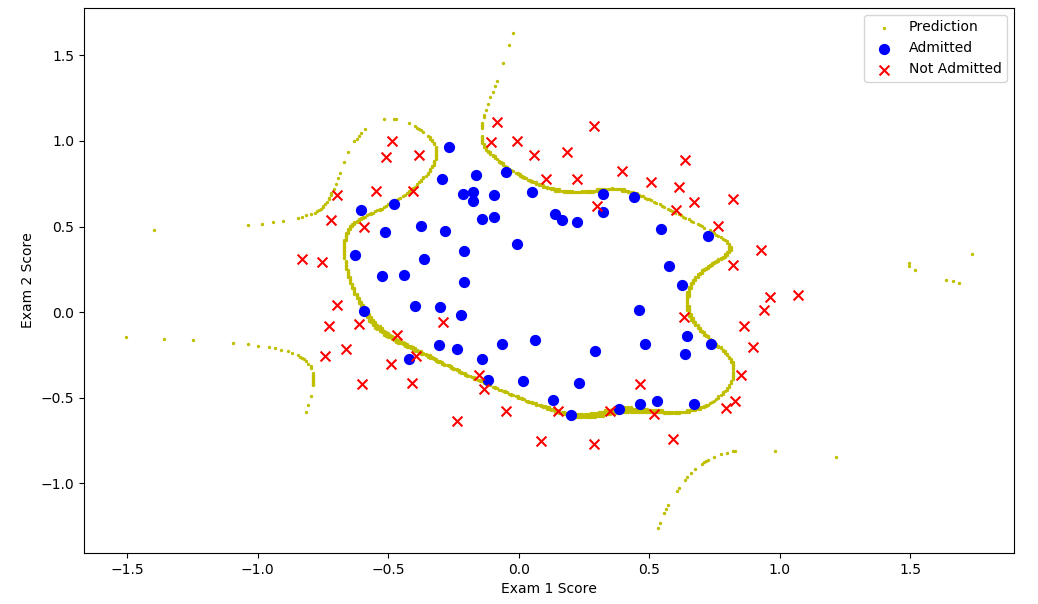
1 import numpy as np 2 import pandas as pd 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import math 5 import scipy.optimize as opt 6 7 ######################################################################sigmoid函数 8 def sigmoid(x): 9 return (1/(1+np.exp(-x))) 10 ######################################################################代价 11 def cost(theta,x,y): 12 theta=np.matrix(theta) 13 x=np.matrix(x) 14 y=np.matrix(y) 15 first=np.multiply(-y,np.log(sigmoid(x*theta.T))) 16 second=np.multiply(1-y,np.log(1-sigmoid(x*theta.T))) 17 return np.sum(first-second)/len(x) 18 ######################################################################更新函数 19 def gradient(theta,x,y): 20 theta=np.matrix(theta) 21 x=np.matrix(x) 22 y=np.matrix(y) 23 n=x.shape[1] 24 error=sigmoid(x*theta.T)-y 25 G=np.zeros(n) 26 for i in range(n): 27 temp=np.multiply(error,x[:,i]) 28 G[i]=np.sum(temp)/len(x) 29 return G 30 ######################################################################决策边界 31 def findBoundary(theta,type,mean,len): 32 Len=500 33 t1=np.linspace(-2,2,Len) 34 t2=np.linspace(-2,2,Len) 35 X=[] 36 Y=[] 37 n=theta[0].shape[0] 38 for i in range(Len): 39 for j in range(Len): 40 sum=theta[0][0] 41 x=t1[i] 42 y=t2[j] 43 for k in range(1,n): 44 sum+=(math.pow(x,type[k-1,0])*math.pow(y,type[k-1,1])-mean[k])*theta[0][k]/len[k] 45 if(abs(sum)<=0.1): 46 X.append(t1[i]) 47 Y.append(t2[j])###y特征没特征缩放 48 return X,Y 49 ######################################################################绘图 50 def plotData(positive,negative,theta,type,mean,len): 51 x,y=findBoundary(theta,type,mean,len) 52 fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8)) 53 ax.scatter(x,y,c="y",s=2,label="Prediction") 54 ax.scatter(positive['Exam 1'], positive['Exam 2'], s=50, c='b', marker='o', label='Admitted') 55 ax.scatter(negative['Exam 1'], negative['Exam 2'], s=50, c='r', marker='x', label='Not Admitted') 56 ax.legend() 57 ax.set_xlabel('Exam 1 Score') 58 ax.set_ylabel('Exam 2 Score') 59 plt.show() 60 ######################################################################处理数据 61 def dataProcess(data,type): 62 x=data.iloc[:,0] 63 y=data.iloc[:,1] 64 n=type.shape[0] 65 data2=pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((data.shape[0],n))) 66 mean=np.zeros(n+2) 67 len=np.zeros(n+2) 68 for i in range(n): 69 now=np.power(x,type[i,0])*np.power(y,type[i,1]) 70 mean[i+1]=np.mean(now) 71 len[i+1]=now.max()-now.min()+1 72 now=(now-mean[i+1])/len[i+1] 73 data2[i]=now 74 now=data.iloc[:,2] 75 mean[n+1]=0###这里不能特征缩放!!! 76 len[n+1]=1 77 data2[n]=data.iloc[:,2] 78 mean[0]=1 79 len[0]=1 80 data2.insert(0,"Ones",1) 81 return data2,mean,len 82 ######################################################################主函数 83 def main(): 84 path="ex2data2.txt" 85 G=[] 86 for i in range(0,5): 87 for j in range(0,5): 88 G.append([i,j]) 89 type=np.matrix(G) 90 source=pd.read_csv(path,header=None,names=['Exam 1','Exam 2','Admitted']) 91 data,mean,len=dataProcess(source,type) 92 m=data.shape[0] 93 n=data.shape[1] 94 x=np.matrix(data.iloc[:,0:n-1]) 95 y=np.matrix(data.iloc[:,n-1:n]) 96 theta=np.zeros(n-1) 97 vector=opt.fmin_tnc(func=cost,x0=theta,fprime=gradient,args=(x,y)) 98 ### 误差函数 初值 更新函数 样本 99 print(vector) 100 plotData(source[source["Admitted"].isin([1])],source[source["Admitted"].isin([0])],vector,type,mean,len) 101 ###################################################################### 102 if __name__=="__main__": 103 main()

过拟合:


 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号