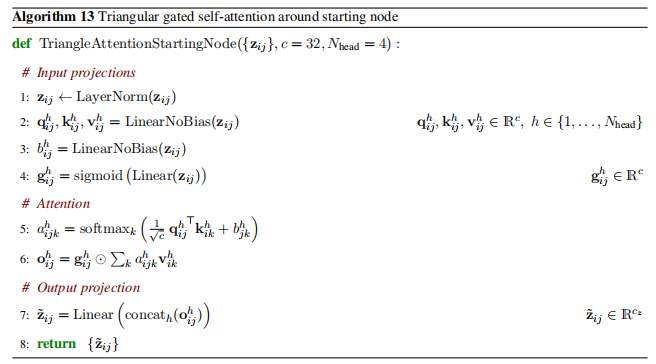
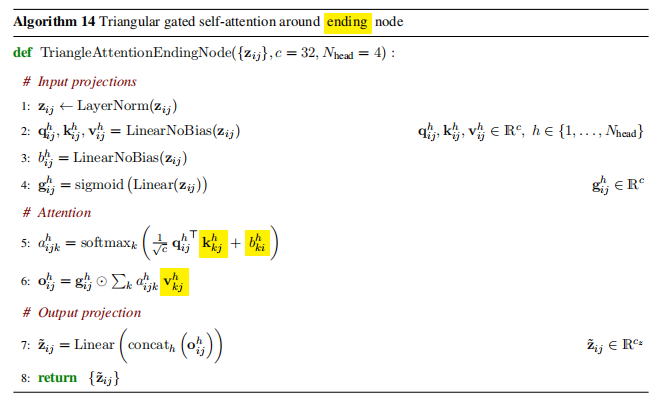
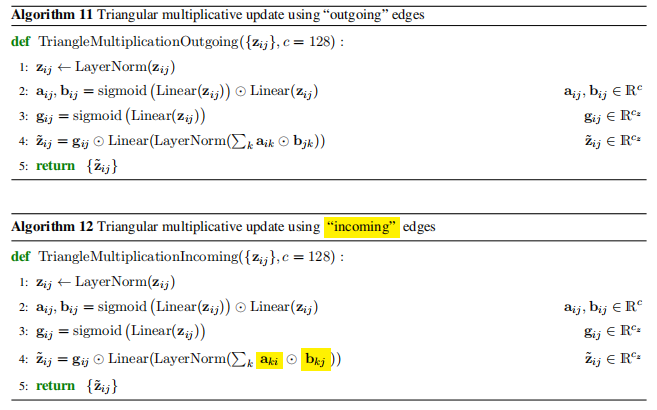
Triangle
class AxialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
dim,
heads,
row_attn = True,
col_attn = True,
accept_edges = False,
global_query_attn = False,
**kwargs
):
super().__init__()
assert not (not row_attn and not col_attn), 'row or column attention must be turned on'
self.row_attn = row_attn
self.col_attn = col_attn
self.global_query_attn = global_query_attn
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim = dim, heads = heads, **kwargs)
self.edges_to_attn_bias = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(dim, heads, bias = False),
Rearrange('b i j h -> b h i j')
) if accept_edges else None
def forward(self, x, edges = None, mask = None):
assert self.row_attn ^ self.col_attn, 'has to be either row or column attention, but not both'
b, h, w, d = x.shape
x = self.norm(x)
# axial attention
if self.col_attn:
axial_dim = w
mask_fold_axial_eq = 'b h w -> (b w) h'
input_fold_eq = 'b h w d -> (b w) h d'
output_fold_eq = '(b w) h d -> b h w d'
elif self.row_attn:
axial_dim = h
mask_fold_axial_eq = 'b h w -> (b h) w'
input_fold_eq = 'b h w d -> (b h) w d'
output_fold_eq = '(b h) w d -> b h w d'
x = rearrange(x, input_fold_eq)
if exists(mask):
mask = rearrange(mask, mask_fold_axial_eq)
attn_bias = None
if exists(self.edges_to_attn_bias) and exists(edges):
attn_bias = self.edges_to_attn_bias(edges)
attn_bias = repeat(attn_bias, 'b h i j -> (b x) h i j', x = axial_dim)
tie_dim = axial_dim if self.global_query_attn else None
out = self.attn(x, mask = mask, attn_bias = attn_bias, tie_dim = tie_dim)
out = rearrange(out, output_fold_eq, h = h, w = w)
return out
class TriangleMultiplicativeModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
*,
dim,
hidden_dim = None,
mix = 'ingoing'
):
super().__init__()
assert mix in {'ingoing', 'outgoing'}, 'mix must be either ingoing or outgoing'
hidden_dim = default(hidden_dim, dim)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.left_proj = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.right_proj = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.left_gate = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.right_gate = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.out_gate = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
# initialize all gating to be identity
for gate in (self.left_gate, self.right_gate, self.out_gate):
nn.init.constant_(gate.weight, 0.)
nn.init.constant_(gate.bias, 1.)
if mix == 'outgoing':
self.mix_einsum_eq = '... i k d, ... j k d -> ... i j d'
elif mix == 'ingoing':
self.mix_einsum_eq = '... k j d, ... k i d -> ... i j d'
self.to_out_norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_dim)
self.to_out = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim)
def forward(self, x, mask = None):
assert x.shape[1] == x.shape[2], 'feature map must be symmetrical'
if exists(mask):
mask = rearrange(mask, 'b i j -> b i j ()')
x = self.norm(x)
left = self.left_proj(x)
right = self.right_proj(x)
if exists(mask):
left = left * mask
right = right * mask
left_gate = self.left_gate(x).sigmoid()
right_gate = self.right_gate(x).sigmoid()
out_gate = self.out_gate(x).sigmoid()
left = left * left_gate
right = right * right_gate
out = einsum(self.mix_einsum_eq, left, right)
out = self.to_out_norm(out)
out = out * out_gate
return self.to_out(out)
计算过程的举例
为了详细说明如何更新 3 行 3 列矩阵中第 ( (1, 1) ) 元素的过程,我将使用伪代码中的逻辑,并结合您提供的代码来解释。我们假设当前矩阵为 ( Z ),其中 ( z_{ij} ) 代表矩阵中第 ( i ) 行第 ( j ) 列的元素。
假设的输入矩阵
设有一个 3x3 矩阵 ( Z ):
\(
Z = \begin{bmatrix}
z_{11} & z_{12} & z_{13} \\
z_{21} & z_{22} & z_{23} \\
z_{31} & z_{32} & z_{33}
\end{bmatrix}
\)
我们来讨论如何更新 ( z_{11} ) 这个元素。
步骤 1: 层归一化
首先对矩阵中的每个元素进行层归一化:
\(
z_{ij} \leftarrow \text{LayerNorm}(z_{ij})
\)
步骤 2: 计算投影和门控
将每个 ( z_{ij} ) 通过线性映射得到 ( a_{ij} )、( b_{ij} ) 和 ( g_{ij} ):
\(
a_{ij}, b_{ij} = \text{sigmoid}(\text{Linear}(z_{ij}))
\)
\(
g_{ij} = \text{sigmoid}(\text{Linear}(z_{ij}))
\)
步骤 3: 混合操作(选择 ingoing 或 outgoing)
假设我们选择了 “ingoing” 模式,对应于 Algorithm 12。
在这种情况下,我们想更新 ( z_{11} ) 需要使用伪代码中的:
\(
\tilde{z}_{11} = g_{11} \odot \text{Linear}(\text{LayerNorm}(\sum_k a_{k1} \odot b_{k1}))
\)
具体步骤计算 ( \tilde{z}_{11} )
-
计算 ( a_{k1} ) 和 ( b_{k1} ):
对于每个 ( k )(这里 ( k = 1, 2, 3 )),分别计算:- ( a_{11}, b_{11} = \text{sigmoid}(\text{Linear}(z_{11})) )
- ( a_{21}, b_{21} = \text{sigmoid}(\text{Linear}(z_{21})) )
- ( a_{31}, b_{31} = \text{sigmoid}(\text{Linear}(z_{31})) )
-
计算 ( g_{11} ):
\( g_{11} = \text{sigmoid}(\text{Linear}(z_{11})) \) -
混合计算:
将 ( k ) 的结果相乘后求和:
\( \text{sum} = a_{11} \odot b_{11} + a_{21} \odot b_{21} + a_{31} \odot b_{31} \) -
归一化和线性变换:
\( \text{out} = \text{Linear}(\text{LayerNorm}(\text{sum})) \) -
应用门控 ( g_{11} ):
\( \tilde{z}_{11} = g_{11} \odot \text{out} \)
代码中的实现细节
在代码中,self.mix_einsum_eq 控制了不同模式下的混合计算:
- “ingoing”:
'... k j d, ... k i d -> ... i j d'- 当
einsum运算时,形如a_{k1}和b_{k1}相乘,然后累加得到更新的 ( z_{11} )。
- 当
- “outgoing”:
'... i k d, ... j k d -> ... i j d'(如果选择了这个模式,则会使用类似 Algorithm 11 的方式更新)
总结
更新矩阵 ( Z ) 中 ( z_{11} ) 的过程:
- 先对矩阵进行归一化处理。
- 计算 ( a )、( b ) 和 ( g ) 投影。
- 根据模式进行“ingoing”或“outgoing”混合操作。
- 计算归一化后的线性变换并乘以 ( g_{11} )。
- 得到最终的 ( \tilde{z}_{11} )。
这样,通过伪代码和实际实现的对比,可以看到 ( (1, 1) ) 元素如何通过这种方式被更新。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号