hihoCoder1343 : Stable Members【BFS拓扑排序】
题目链接:https://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1343
#1343 : Stable Members
描述
Recently Little Hi joined an algorithm learning group. The group consists of one algorithm master and N members. The members are numbered from 1 to N. Each member has one or more other members as his mentors. Some members' mentor is the master himself.
Every week each member sends a report of his own learning progress and the reports collected from his pupils (if there is any) to his mentors. The group is so well designed that there is no loop in the reporting chain so no one receives his own report from his pupil. And finally the master gets every one's report (maybe more than once).
Little Hi notices that for some members their reporting routes to the master can be easily cut off by a single member's (other than the master and himself) absence from the reporting duty. They are called unstable members while the others are stable members. Given the reporting network of the group, can you find out how many members are stable?
Assume there are 4 members in the group. Member 1 and 2 both have the master as their only mentor. Member 3 has 2 mentors: member 1 and member 2. Member 4 has 1 mentor: member 3. Then member 4 is the only unstable member in the group because if member 3 is absent his learning report will be unable to be sent to the master.
输入
The first line contains an integer N, the number of members.
The i-th line of the following N lines describe the mentors of the i-th member. The first integer is Ki, the number of mentors of the i-th member. Then follows Ki integers A1 ... AN, which are his mentors' numbers. Number 0 indicates that the master is one of his mentor.
For 40% of the data, 1 ≤ N ≤ 1000.
For 100% of the data, 1 ≤ N ≤ 100000.
For 100% of the data, 1 ≤ Ki ≤ 10, Ki < N, 0 ≤ Ai ≤ N.
输出
Output the number of stable members.
- 样例输入
-
5 1 0 1 0 2 1 2 1 3 2 4 3 - 样例输出
-
3
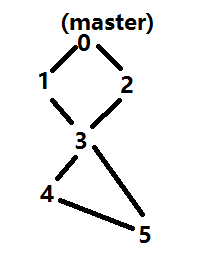 如左图所示,删掉点3,则4和5都无法连通到点0即master,所以4和5都是unstable点,1、2和3都是stable,所以最后答案为3个stable点。
如左图所示,删掉点3,则4和5都无法连通到点0即master,所以4和5都是unstable点,1、2和3都是stable,所以最后答案为3个stable点。
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N = 100001; 4 struct node { 5 int color = 0; 6 vector<int>s, p;//子节点、父节点 7 }a[N]; 8 bool unstable[N]; 9 bool all_colored(int v, int color) { 10 int num = a[v].p.size(); 11 bool flag = true; 12 for(int i = 0; flag && i < num; ++i) 13 flag &= (a[a[v].p[i]].color == color); 14 return flag; 15 } 16 void topo(int v) { 17 if(unstable[v]) return; 18 queue<int>q; 19 q.push(v); 20 a[v].color = v; 21 while(!q.empty()) { 22 int u = q.front(); q.pop(); 23 int num = a[u].s.size(); 24 for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { 25 int son = a[u].s[i]; 26 if(all_colored(son, v)) { 27 a[son].color = v; 28 unstable[son] = true; 29 q.push(son); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 int main() { 35 int n, k, i, v, ans = 0; 36 scanf("%d", &n); 37 for(i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { 38 scanf("%d", &k); 39 while(k--) { 40 scanf("%d", &v); 41 a[i].p.push_back(v); 42 a[v].s.push_back(i); 43 } 44 } 45 for(i = 1; i <= n; ++i) topo(i); 46 for(i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ans += unstable[i]; 47 printf("%d\n", n - ans); 48 return 0; 49 }



