一 、Github项目地址:https://github.com/GordonKowk/GatherTeam-Item
(上一链接包含一个 编译好的四则运算命令行运行文件)
https://github.com/JQJQ2019/TeamHomework
二、PSP表格
| Planning |
计划 |
45 |
60 |
| · Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
40 |
42 |
| Development |
开发 |
1090 |
1205 |
| · Analysis |
· 需求分析 |
60 |
70 |
| · Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
35 |
40 |
| · Design Review |
· 设计复审 |
50 |
60 |
| · Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 |
30 |
40 |
| · Design |
· 具体设计 |
80 |
85 |
| · Coding |
· 具体编码 |
700 |
750 |
| · Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
45 |
55 |
| · Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
90 |
105 |
| Reporting |
报告 |
120 |
150 |
| · Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
80 |
| · Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
30 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
40 |
| 合计 |
|
1255 |
1415 |
三、效能分析:
1)由于我们一开始是在每个函数自身调用main函数调试的,运算方法基本是放在专门类里面的,调用起来也不方便。有时候一个方法函数会在一个类里面出现两三次。所以我们最后做到要求功能后就对整个项目进行代码简化和性能优化。Algorithm就是我们对运算方法封装的一个类。多余和重复的代码去掉。
2)Problems_creator,Algroithm是整个项目运行的重点,占比例也最大。我们用到下面的函数查看它们的运行时间总和(没有出现在文件里)。
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis()
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
调试前生成代码时间:
调试优化后时间:
下文会展示Algorithm和Probelms_creator的关键代码
四、设计过程:
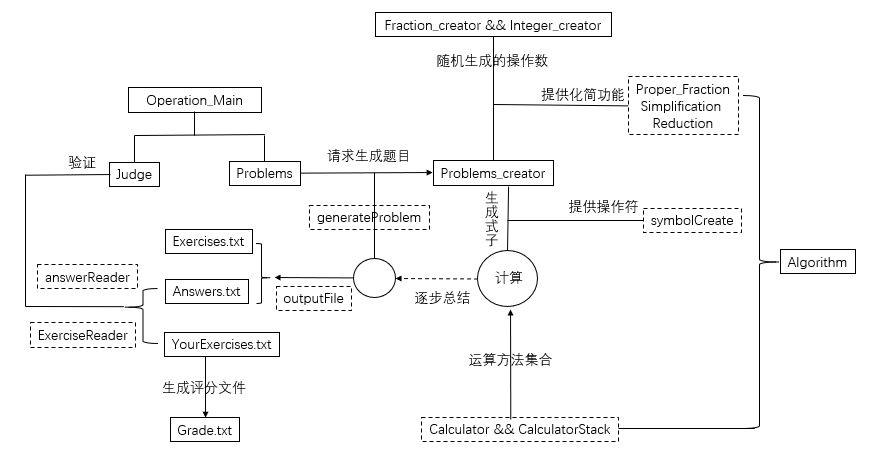
1)框架图:
![]()
2)我们一开始讨论了应该怎么去实现基本的数值运算。如果按照平常电脑支持的四则运算,整数int的加减乘除都是比较容易实现的,但是对于真分数,格式是要我们设计的,那么分数里面的各种数值 则需要一种算法支撑它们。所以我们最先讨论这个项目的操作数应该以怎样的形式出现,最后是选择了用整形数组的形式int[]{a,b,c}实现一个操作数。好处在于它整数部分,分子分母都是分开的,可以各自独立操作,但是这样会使得算法上的分类比较多。区分真分数和整数的标志在于数组的b,c值,如果都不为零,就是真分数,否则为整数。
3)随机生成是这个项目的核心部分。任何一个操作数,操作符以及它们的个数都是随机的。所以我们先考虑哪一种方法产生的式子可以符合我们操作数形式的运算。我们先让操作符个数和下标先确定下来。操作数的数量与操作符数量成+1关系,然后每次随机生成一个操作数,再在这个操作数后面添上一个操作符。考虑到假设用户是小学生,那么式子肯定都不全是真分数,所以我们让真分数和整数的生成几率平均下来。由于每个操作数生成的初始状态都是真分数,所以必须设置方法约分,区分整数和分数。
4)随机生成括号。括号有很多顺序问题。我们想到先在每生成一个操作数前便判断左括号的生成,右括号的生成要依赖左括号的数据。我们立下几个判断标志让括号生成的位置变得正确。譬如,头部标志head就是判断式子最开开头是否有括号,如果有,右括号就不能加在式子末尾;如果在最后右括号的数量不符合左括号的数量,Bracket Count标志便可以让剩下的右括号出现,并且Bracket Count还能避免出现e1-e2)(e3-e4的错误情况;far是用来判断左右括号距离必须有两个操作数以上……我们考虑到每一个情况,最后让括号能正确随机生成。
5)整个项目对于我们来说,最难的部分就是运算操作这部分。我们开始做运算方法时,首先做好最基本的四则运算,加减乘除,调试过程中两两操作数操作,寻找得到答案的方法,最后得出的四则运算会发现,每一中运算都有四种情况,符合我们整数数组的运算。但是要怎么用它们,何时用它们,才是更难得地方。我们运算过程用到几个栈,因为栈能方便整个数组的运算和化简。并且对于操作符,每一个操作符都有对应的下标,用下标运算会方便很多。
①括号运算顺序是首要难题。我们必须保证抓准括号数量,括号类的操作数个数,运算顺序,还有不能在运算时出现操作数个数溢出和栈报空出错。所以我们想到逐步深入。我们从式子末端开始向前推,只要遇上右括号,就一直往里深入,直到其他操作符出现,这时候我们记录下括号个数,随后深入过程又会记录该括号内的操作数个数,直到遇上左括号,根据之前的判断标志,对完整的整个括号进行运算,把得出的结果入栈。所以整个流程下来,我们可以把式子的括号都去除了。还有一个问题,就是括号得出的结果如果立刻入栈会导致顺序出错,我们处理的方法是让一个static的数组保存这个函数,直到退出这个括号后,把下一个式子或括号的内容读入完整后再添加。
②加减乘除的优先级问题,我们曾考虑到是否要用哈希表去规定优先级,但是我们仍然没有摸索出适合我们整数数组运算的方法,所以我们换了一个方法,我们在运算过程中,对出现过的操作符(包括括号)进行判断,如果为乘除法,立刻两两运算,结果立刻入栈,如果不是则直接入栈。和括号运算一样,我们会实现去除乘除法,最后只剩下加减法。但是我们也注意到,单纯加减法,减法的位置会影响到你的运算顺序(主要看看你的出栈方向如何),这也是要考虑的
③剩下的加减,因为出入栈的缘故,最后栈元素的顺序和式子是一样的,所以我们最后不用考虑什么优先级,直接按顺序运算即可。
6)我们整个程序的生成结果就是两个txt文档,一个是题目,一个是答案,可以在题目上直接做大,判断函数能让用户选择自己做好的文件和程序原先生成的答案文件对比得出正确的错误个数。
五、程序关键代码:
题目生成函数随机Problems_creator()
public class Problems_creator {
private static final String[] ARITHMETIC_SYMBOL = {"+", "-", "*", "÷"};
//这里的"+", "-", "*", "÷","(",")"六个符号的下表各自为0,1,2,3,5,6
public static boolean W = false; //一个重要的判断标志
Algorithm AL = new Algorithm();
Fraction_creator FC = new Fraction_creator();
Integer_creator IC = new Integer_creator();
static int[] Numbers = {0,0,0};
static int BracketCount = 0; //括号统计数
static boolean head = false; //判断开头是否有括号
StringBuilder formula = new StringBuilder(); //可修改的String类式子
Stack<int[]> numStack = new Stack<>(); //操作数栈
Stack<Integer> symbolStack = new Stack<>(); //操作符栈
public String[] createProblem(int range){
Random S_random = new Random(); //符号数量随机数
Random I_OR_F_random = new Random(); //真分数与整数标志随机数
Random Bracket_random = new Random(); //括号生成随机数
int symbolCount = 1 + S_random.nextInt(3); //生成算数符号个数
int[] symbol = AL.symbolCreate(symbolCount, 4, S_random);//符号数组
int i = 0;
int far = 0; //括号距离,必须要大于0才能生成")"
//考虑到小学生的运算难度,不能全部生成真分数,所以这里随机生成的真分数和整数的概率都为50%
//左括号"("生成判断。
for( i=0; i<symbolCount+1; i++){
//左符号"("是不可以在最后一个操作数左右的。
if(i<symbolCount&&symbolCount!=1){
int Bracket = Bracket_random.nextInt(2);//Bracket为0可以生成括号
if( Bracket==0 && head==true && i==symbolCount-1);//可以生成括号同时,判断式子顶端是否有括号,如是,判断现在位置是否在倒数二个操作数
else if( Bracket==0 ){
formula.append("( ");
symbolStack.push(5);
if(i==0) head=true; //如果在式子顶端生成括号,立下标志
BracketCount++;far=0;
}else far=1;
}
int I_OR_F = I_OR_F_random.nextInt(2);
String Num = "";
String smb = "";
//真分数与整数的随机生成,各自几率50%
if (I_OR_F == 0){
int[] F = FC.Fraction(range);
F = AL.Proper_Fraction(F);
Num = AL.Simplification(F);
if( i!=symbolCount ) smb = ARITHMETIC_SYMBOL[symbol[i]];
numStack.push(F);
formula.append(Num+" ");
//右括号")"生成判断
if( i>0 && i<symbolCount-1 && symbolCount!=1){
int Bracket = Bracket_random.nextInt(2);
//BracketCount存在代表前面有"(",如果不加以判断会出现e1-e2)(e3-e4,是错误的
//far必须大于0,括号不能只括在一个操作数身上
if( Bracket==0 && far!=0 && BracketCount!=0){
formula.append(") ");
symbolStack.push(6);
BracketCount--;
if(BracketCount==0) far=0;
}
}
//head存在,式子最开头有左括号,式子最后就不能有右括号,并且在倒数第二个操作数后面加上剩下的右括号
if( head==true ){
if( BracketCount!=0 && i==symbolCount-1 ){
for (int n=0; n<BracketCount;n++){
formula.append(") ");
symbolStack.push(6);
}
}
}
//在最后补上剩下的右括号
else if ( BracketCount!=0 && i==symbolCount){
for (int n=0; n<BracketCount;n++){
formula.append(") ");
symbolStack.push(6);
}
}
if( i!=symbolCount ) formula.append(smb+" ");
else formula.append("= ");
if( i!=symbolCount ) symbolStack.push(symbol[i]);
}else {
int[] I = IC.Integer(range);
Num = I[0]+" ";
if(i!=symbolCount) smb = ARITHMETIC_SYMBOL[symbol[i]];
numStack.push(I);
formula.append(Num+" ");
if( i>0 && i<symbolCount-1 && symbolCount!=1){
int Bracket = Bracket_random.nextInt(2);
if(Bracket==0 && far!=0 && BracketCount!=0){
formula.append(") ");
symbolStack.push(6);
BracketCount--;
if(BracketCount==0) far=0;
}
}
if( head==true ){
if(BracketCount!=0 && i==symbolCount-1){
for (int n=0; n<BracketCount;n++){
formula.append(") ");
symbolStack.push(6);
}
}
}
else if (BracketCount!=0 && i==symbolCount){
for (int n=0; n<BracketCount;n++){
formula.append(") ");
symbolStack.push(6);
}
}
if(i!=symbolCount) formula.append(smb+" ");
else formula.append("= ");
if( i!=symbolCount ) symbolStack.push(symbol[i]);
}
}
//此时的formula如果不出现问题,是一个完整的式子
int[] n = AL.CalculatorStack(numStack, symbolStack);
n = AL.Proper_Fraction(n);
//字符串tail是这一条式子的答案
String tail = "";
tail = AL.Simplification(n);
BracketCount = 0;
String formulaRes[] = {formula.toString(), tail};
//formula不及时清空会出错
formula.replace(0, formula.length(),"");
//计算中途出现负数,formula就有问题,布尔W处理这种情况,W的修改可在Algorithm减法操作看得到
if(Problems_creator.W==true){
while(Problems_creator.W){
//不符合要求就重新在来一次
Problems_creator P = new Problems_creator();
formulaRes = P.createProblem(range);
}
}
return formulaRes;
}
运算方法集合Algorithm()
public class Algorithm {
//这是一个生成操作符号下表的函数
public int[] symbolCreate(int symbolCount,int Total, Random random){
int similar = 0;
int[] SCreate = new int[symbolCount];
for(int i = 0; i < symbolCount; i++){
SCreate[i] = random.nextInt(Total);
}
//保证所有的操作符号不会相同
for (int i : SCreate) {
if(SCreate[0] == i) similar++;
}
if(similar == symbolCount && symbolCount != 1) return symbolCreate(symbolCount, Total, random);
else return SCreate;
}
//化简真分数的函数
public String Simplification(int[] F){
String Num = "";
F = Proper_Fraction(F);
if (F[2]!=0){
int reduction = Reduction(F[1], F[2]);
F[1] /= reduction;
F[2] /= reduction;
//真分数和整数的区别在于F[1]和F[2]是否为0,如都不是,便是真分数,否则为整数
//但是程序运算过程仍然会保留整数的0分母
if(F[1] == F[2]) {
if(F[0] == 0) Num = "1";
else Num = F[0]+"";
}else if (F[0] == 0){
if(F[1] == F[2]) Num = "1";
else Num = F[1] + "/" + F[2];
}
else if(F[1] == 0||F[2]==0) Num = F[0]+"";
else Num = F[0] + "'" + F[1] + "/" + F[2];
}else Num = F[0] + "";
return Num;
}
//最大公因数的函数
public int Reduction(int x,int y) {
while(true){
if(x % y == 0)
return y;
int temp = y;
y = x % y;
x = temp;
}
}
//形成真分数形式
public int[] Proper_Fraction(int[] F_Num){
int[] f_Num = F_Num;
int h = f_Num[0];
int x = f_Num[1];
int y = f_Num[2];
if(y==0||x==0) {
f_Num[0]=h;
f_Num[1]=0;
f_Num[2]=0;
return f_Num;
}
int n = x / y;
int sum = h+n;
if (x > y){
x = (x - n * y);
f_Num[0] = sum;
f_Num[1] = x;
f_Num[2] = y;
return f_Num;
}
else if (x == y) {
f_Num[0] = sum;
f_Num[1] = 0;
f_Num[2] = 0;
return f_Num;
}
else if (y == 1) {
f_Num[0] = sum+x;
f_Num[1] = 0;
f_Num[2] = 0;
return f_Num;
}
else if (x == 0) {
f_Num[0] = sum;
f_Num[1] = 0;
f_Num[2] = y;
return f_Num;
}
return f_Num;
}
/*整个程序最重要的运算函数
* 文件末尾保留main函数的注释,是用来做调试的
* 这个函数用整形数组int[]{a,b,c}的方式进行运算的
* a为整数部分,b为分子,c为分母
*/
public int[] CalculatorStack(Stack<int[]> numStack,Stack<Integer> symbolStack){
Stack<int[]> num = new Stack<>(); //需要用操作数计算而记录操作数的栈
Stack<Integer > symbol = new Stack<>(); //需要用操作符计算而记录操作符的栈
Stack<Integer > judge = new Stack<>(); //括号判断栈
int[] barcketRes = null;
while(!symbolStack.empty()){
int s = symbolStack.pop();
//右括号下表为"6",遇上了右括号,则继续往里面深推
if(s==6){
int j1 = 0;
judge.push(j1);
}
//左括号下表为"5",遇上了左括号,按规定算法运算
else if(s==5){
//把左括号右边的操作数入栈
if(!numStack.empty()){
int head[] = numStack.pop();
num.push(head);
}
//judge存在,既有括号,judge数值代表括号操作数个数
int j2 = judge.pop();
if(j2 ==1){
int[] n1 = num.pop();
int[] n2 = num.pop();
int s1 = symbol.pop();
int[] sum = Calculator(s1,n1,n2);
num.push(sum);
barcketRes = sum;
}else if(j2 ==2){
int[] sum = {0,0,0};
int[] n1 = num.pop();
int[] n2 = num.pop();
int[] n3 = num.pop();
int s1 = symbol.pop();
int s2 = symbol.pop();
//乘除法优先,然后判断减法位置,再弄加法,做出正确的算数过程
if(( s1==0&&s2==0 )|| s2==2 || s2==3 ){
sum = Calculator(s2,n2,n3);
sum = Calculator(s1,n1,sum);
}else{
sum = Calculator(s1,n1,n2);
sum = Calculator(s2,sum,n3);
}
num.push(sum);
barcketRes = sum;
}
}
//没有括号直接入栈
else {
int[] n1 ;
if (barcketRes!=null){
n1=num.pop();
barcketRes=null;
}else n1= numStack.pop();
num.push(n1);
symbol.push(s);
//中途没有括号,自己却又被一个括号包围,judge增加距离
if(!judge.empty()){
int j3 = judge.pop();
j3++;
judge.push(j3);
}
}
}
//把剩下的操作数入栈
if(!numStack.empty()){
int[] r = numStack.pop();
num.push(r);
}
Stack<int[]> Num = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer > Symbol = new Stack<>();
//此时所有括号都去掉了,下面是运算所有的乘除法
while(!symbol.empty()){
int s = symbol.pop();
int[] n1= num.pop();
if(s==2||s==3){
int[] n2= num.pop();
int[] n = Calculator(s,n1,n2);
num.push(n);
}else{
Symbol.push(s);
Num.push(n1);
}
}
if(!num.empty()){
int[] n = num.pop();
Num.push(n);
}
//最后剩下的就是加减法
while(!Symbol.empty()){
int[] n1 = Num.pop();
int[] n2 = Num.pop();
int s = Symbol.pop();
int[] n3 = Calculator(s,n2,n1);
Num.push(n3);
}
int[] res = Num.pop();
return res;
}
/*适用于int[]{a,b,c}的四则运算
* 每个运算都有四个判断,分别为n1是整数,n2是整数,n1、n2均为整数和n1、n2均为真分数
*/
public int[] Calculator(int symbol,int[] n1,int[] n2){
Algorithm AL = new Algorithm();
int[] num = {0,0,0};
switch(symbol){
case 0:
if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]!=0&&n2[2]!=0)){
num[1] = n2[1];
num[2] = n2[2];
num[0] = n1[0]+n2[0];
}else if((n1[1]!=0&&n1[2]!=0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[1] = n1[1];
num[2] = n1[2];
num[0] = n1[0]+n2[0];
}else if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[0] = n1[0]+n2[0];
}else{
num[1] = ((n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*n2[2])+((n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1])*n1[2]);
num[2] = n1[2]*n2[2];
}
break;
case 1:
if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]!=0&&n2[2]!=0)){
n1[0]=n1[0]-1;
n1[1]=1;
n1[2]=1;
num[1] = ((n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*n2[2])-((n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1])*n1[2]);
num[2] = n1[2]*n2[2];
}else if((n1[1]!=0&&n1[2]!=0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
n2[0]=n2[0]-1;
n2[1]=1;
n2[2]=1;
num[1] = ((n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*n2[2])-((n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1])*n1[2]);
num[2] = n1[2]*n2[2];
}else if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[0] = n1[0]-n2[0];
}else{
num[1] = ((n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*n2[2])-((n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1])*n1[2]);
num[2] = n1[2]*n2[2];
}
//一个很重要的判断标志,如果计算途中一出现负数,布尔函数W会让式子重新在生成一次
if(num[1]<0||num[0]<0) Problems_creator.W=true;
else Problems_creator.W=false;
break;
case 2:
if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]!=0&&n2[2]!=0)){
num[1] = n1[0]*(n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1]);
num[2] = n2[2];
}else if((n1[1]!=0&&n1[2]!=0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[1] = (n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*n2[0];
num[2] = n1[2];
}else if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[0] = n1[0]*n2[0];
}else{
num[1] = (n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*(n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1]);
num[2] = n1[2]*n2[2];
}
break;
case 3:
if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]!=0&&n2[2]!=0)){
num[1] = n1[0]*n2[2];
num[2] = (n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1]);
}else if((n1[1]!=0&&n1[2]!=0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[1] = n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1];
num[2] = n1[2]*n2[0];
}else if((n1[1]==0||n1[2]==0)&&(n2[1]==0||n2[2]==0)){
num[1]=n1[0];
num[2]=n2[0];
}else{
num[1] = (n1[0]*n1[2]+n1[1])*n2[2];
num[2] = n1[2]*(n2[0]*n2[2]+n2[1]);
}
break;
default:break;
}
num = AL.Proper_Fraction(num);
return num;
}
问题生成函数Problems()
public void ConstructProblem(){
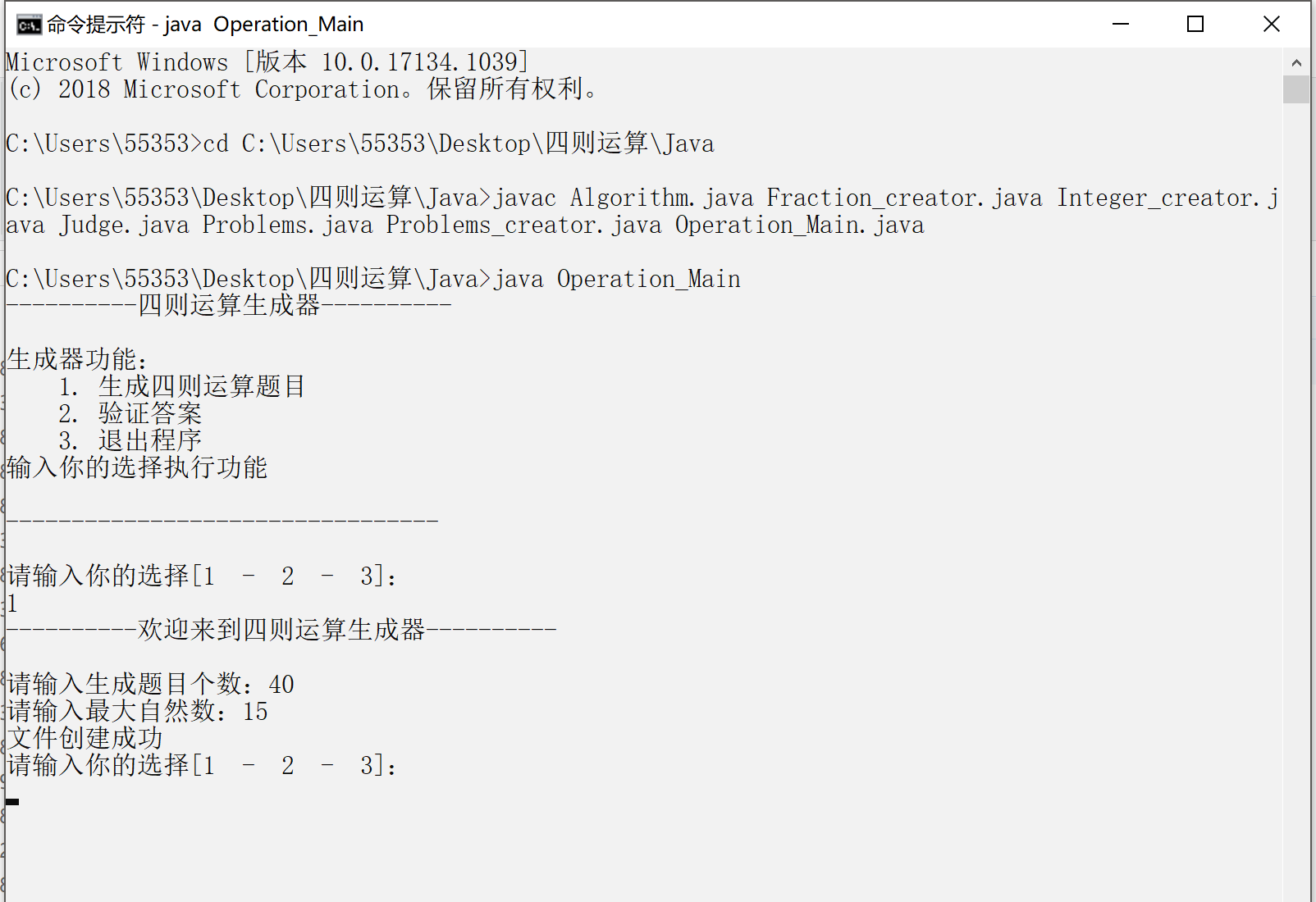
System.out.println("----------欢迎来到四则运算生成器----------\n");
try {
//用户输入生成的题目个数和自然数取值范围
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入生成题目个数:");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入最大自然数:");
int range = scanner.nextInt();
generateProblem(num, range);
}catch (InputMismatchException e){
System.out.println("请输入数字。\n\n\n");
ConstructProblem();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件创建失败");
}
}
/**
* @param num
* @param range
* @throws IOException
*/
public void generateProblem(int num, int range) throws IOException {
//文件会在项目根目录生成
File exercises = new File("Exercises.txt");
File answers = new File("Answers.txt");
//如果原来存在文件,先删除
if (exercises.exists() || answers.exists()){
exercises.delete();
answers.delete();
//这里我弄这两个输出的原因是因为两台电脑运行的状态不一样,这一一个解决办法
System.out.println(exercises.createNewFile());
System.out.println(answers.createNewFile());
}
if (!exercises.createNewFile() && !answers.createNewFile()){
FileOutputStream exercisesOutput = new FileOutputStream(exercises);
PrintStream exercisesPrintStream = new PrintStream(exercisesOutput);
FileOutputStream answersOutput = new FileOutputStream(answers);
PrintStream answersPrintStream = new PrintStream(answersOutput);
Problems_creator PC = new Problems_creator();
String[] problem = new String[2];
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++){
//题目生成的方法
problem = PC.createProblem(range);
outputFile(i, problem, exercisesPrintStream, answersPrintStream);
}
exercisesOutput.close();
answersOutput.close();
exercisesPrintStream.close();
answersPrintStream.close();
System.out.println("文件创建成功 ");
}
}
//题目序号
public void outputFile(int i, String problem[], PrintStream... var){
try {
var[0].println(i + "、 " + problem[0]);
var[1].println(i + "、 " + problem[1]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("程序内部出错了");
}
}
判断函数Judge()
//这里继承JFrame是因为文本选择框方法得构造函数需要它
public class Judge extends JFrame{
//文件路径名
static String path = null;
static String name = null;
public void start(){
//用户可以通过命令行手动输入文件路径或者打开文件选择框
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String exerciseFilePath = null;
String answerFilePath = null;
System.out.println("输入 Choose 可以打开文本选择器");
System.out.print("请输入待验证答案路径:");
if(scanner.next().equals("Choose")){
FileDialog filedialog = new FileDialog(this,"打开",FileDialog.LOAD);
filedialog.setVisible(true);
this.path = filedialog.getDirectory();
this.name = filedialog.getFile();
System.out.println(this.path+this.name);
exerciseFilePath = this.path+this.name;
}
System.out.print("请输入程序生成答案文件路径:");
if(scanner.next().equals("Choose")){
FileDialog filedialog = new FileDialog(this,"打开",FileDialog.LOAD);
filedialog.setVisible(true);
this.path = filedialog.getDirectory();
this.name = filedialog.getFile();
System.out.println(this.path+this.name);
answerFilePath = this.path+this.name;
}
else answerFilePath = scanner.next();
try {
//exerciseAnswers和answers是两个读入文本的方法
List<String> exerciseAnswers = exerciseFileReader(exerciseFilePath);
List<String> answers = answerReader(answerFilePath);
List<String> correct = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> wrong = new ArrayList<>();
int min = Math.min(exerciseAnswers.size(), answers.size());
int num = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++){
if (exerciseAnswers.get(i).equals(answers.get(i))) correct.add(String.valueOf(num++));
else wrong.add(String.valueOf(num++));
}
File grade = new File("Grade.txt");
if (grade.exists()){
grade.delete();
}
//这里我弄这两个输出的原因是因为两台电脑运行的状态不一样,这一一个解决办法
System.out.println(!grade.createNewFile());
if (!grade.createNewFile()){
FileOutputStream gradeOutput = new FileOutputStream(grade);
PrintStream gradePrintStream = new PrintStream(gradeOutput);
//以逗号隔开每个题目编号,然后统一后呈现
String corrects = String.join(",", correct);
System.out.println("Correct:" + correct.size() +
" (" + corrects + ")");
gradePrintStream.println("Correct:" + correct.size() +
" (" + corrects + ")");
String wrongs = String.join(",", wrong);
System.out.println("Wrong:" + wrong.size() +
" (" + wrongs + ")");
gradePrintStream.println("Wrong:" + wrong.size() +
" (" + wrongs + ")");
}
System.out.println("判定完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读入异常");
}
}
public List<String> exerciseFileReader(String path) throws IOException {
BufferedReader exerciseReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String exerciseAnswer = "";
List<String> exerciseAnswers = new ArrayList<>();
while ((exerciseAnswer = exerciseReader.readLine()) != null){
//去掉题目,留下答案
String[] split = exerciseAnswer.split("= ");
if (split.length >= 2){
exerciseAnswers.add(split[1]);
}else {
exerciseAnswers.add(" ");
}
}
return exerciseAnswers;
}
public List<String> answerReader(String path) throws IOException {
BufferedReader answerReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String answer = "";
List<String> answers = new ArrayList<>();
while ((answer = answerReader.readLine()) != null){
//去掉编号
String[] split = answer.split(" ");
answers.add(split[1]);
}
return answers;
}
六、测试结果:
1)用命令行运行的主界面:
![]()
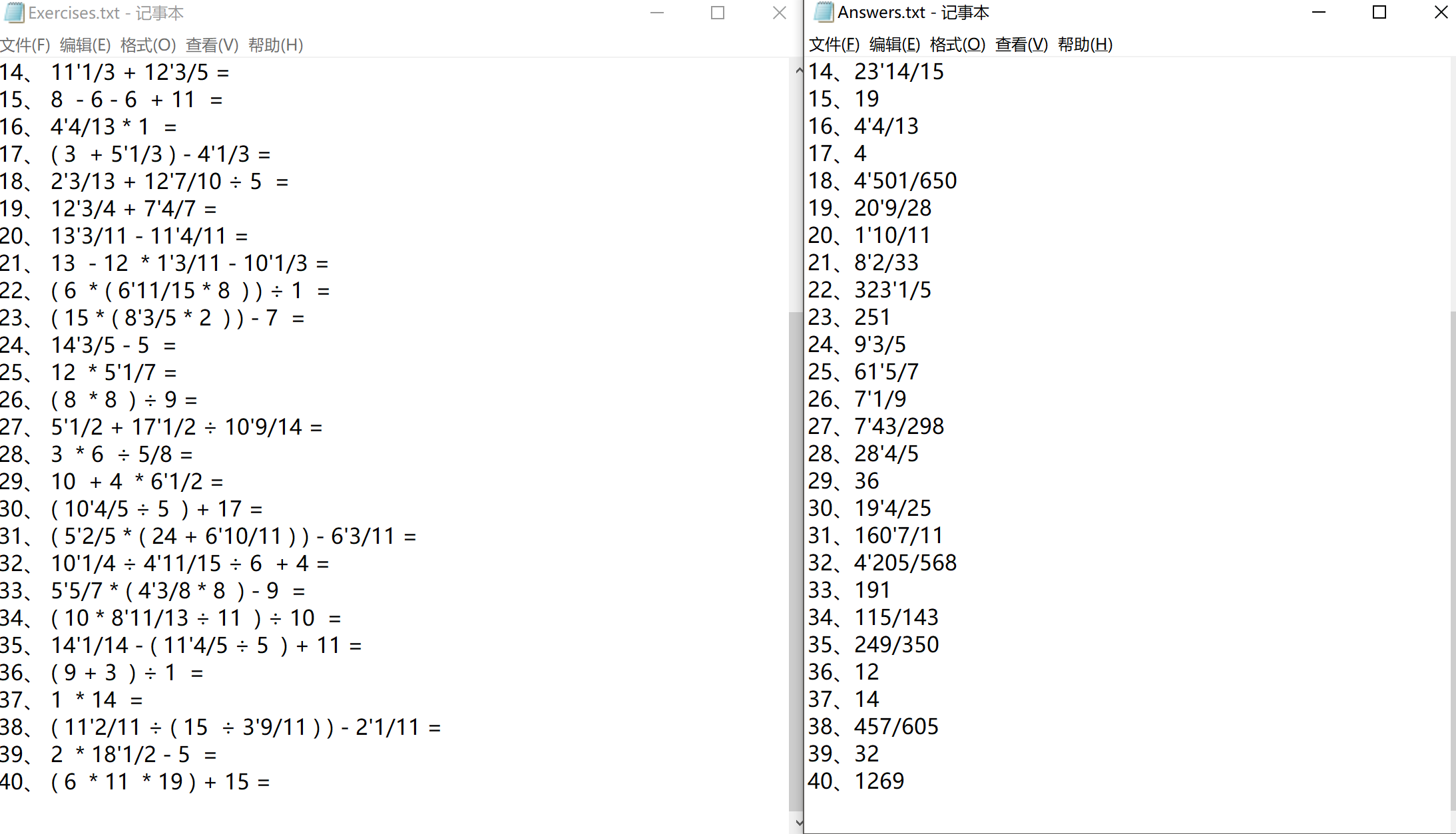
2)生成的文件如图:
![]()
![]()
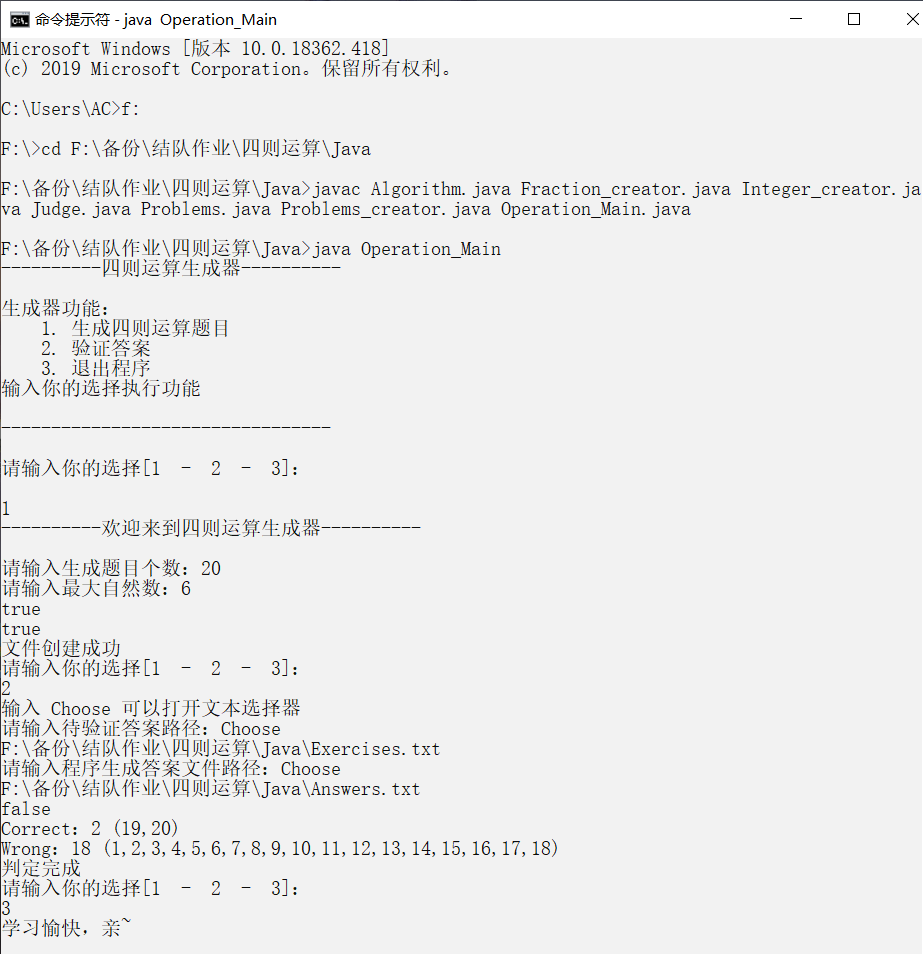
3)检查可用文件时可以用文件选择框&&输入错误后的提示&&检验过程
![]()
![]()
![]()
这里重新从头演示一次
![]()
![]()
![]()
七、项目小结
做集队项目,不得不说是一件新鲜而且兴奋的事情。以前没有合作打代码的经验,平时我们会一起学习打代码,所以交流起来的意见会更加相近。虽然一开始我们就讨论过要用什么方法去做,就像我们选用了整数数组的方法去运算一样,但是设计中经常出现过很多问题,不得不在每一个方法函数调用main函数取调试,甚至想过放弃这个方向,但是还是坚持下来,但是我们已经确定了操作数形式,就按这个方向走下去。而且集队项目给我们一个很大的感触就是我们不会像一个人做项目那么枯燥,灵感枯竭,我们能感受到的是很多的交流,一起攻破难关的成就感。譬如对于式子的统计函数,我们连续两天都泡在咖啡厅一直寻找最好的办法,不断修改,不断调试。甚至在写博客的时候程序出现问题,两台电脑运行效果不一样,我们也连忙赶在一起修复它。这次的项目制作让我们收获很多
项目成员:温治乾 3117002323 郭家豪3117004652





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号