AOP-方法拦截器-笔记
方法拦截器的继承层次图:
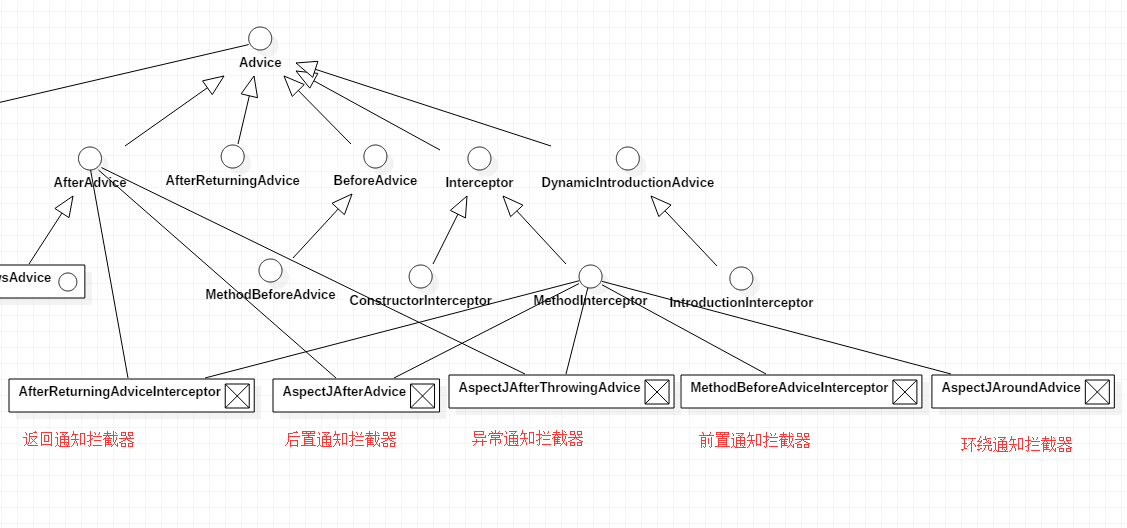
这些拦截器具体长什么样??
一、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
这个拦截器只有一个属性就是前置通知。需要注意的是前置通知和返回通知的拦截器才会持有的通知的引用,也就是拦截器会有一个属性是前置通知或返回通知。其他三个既是通知又是拦截器。如:AspectJAfterAdvice 既是通知又是拦截器,AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice、AspectJAroundAdvice也同样既是通知又是拦截器。
/** * Interceptor to wrap am {@link org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice}. * Used internally by the AOP framework; application developers should not need * to use this class directly. * * @author Rod Johnson */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { private MethodBeforeAdvice advice;//前置通知 /** * Create a new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor for the given advice. * @param advice the MethodBeforeAdvice to wrap *///构造器 public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) { Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null"); this.advice = advice; } //注意:前置通知拦截器是在调用proceed()方法之前调用前置通知方法的。而返回通知拦截器是在调用proceed()方法之后才调用返回通知方法的。后置通知也是在proceed()方法之后,但还是它在finally块中,因为后置通知不管是否抛异常都要执行。 @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() );//首先调用前置通知方法。 return mi.proceed();//然后调用proceed()方法。 } }
二、AspectJAfterAdvice
既是通知又是拦截器,所以它不需要持有通知的引用。
/** * Spring AOP advice wrapping an AspectJ after advice method. * * @author Rod Johnson * @since 2.0 */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable { public AspectJAfterAdvice( Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) { super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif); } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { try { return mi.proceed();//先调用的proceed()方法。 } finally { invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);//因为是后置通知,所以不管程序有没有抛异常都会执行后置通知方法。所以后置通知方法方法finally中调用。 } } @Override public boolean isBeforeAdvice() { return false; } @Override public boolean isAfterAdvice() { return true; } }
三、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
返回通知拦截器。持有一个返回通知的引用。
/** * Interceptor to wrap am {@link org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice}. * Used internally by the AOP framework; application developers should not need * to use this class directly. * * @author Rod Johnson */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable { private final AfterReturningAdvice advice;//持有一个返回通知的引用 /** * Create a new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor for the given advice. * @param advice the AfterReturningAdvice to wrap */ public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) { Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null"); this.advice = advice; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { Object retVal = mi.proceed();//先调用proceed()方法,如果proceed()方法抛出了异常那么程序就中断了,无法执行返回通知方法了。 this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());//返回通知方法,上面的proceed()方法抛异常则无法执行。 return retVal; } }
四、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
既是通知又是拦截器。没有持有异常通知的引用。异常通知方法在catch块中执行。
/** * Spring AOP advice wrapping an AspectJ after-throwing advice method. * * @author Rod Johnson * @since 2.0 */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable { public AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice( Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) { super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif); } //省略掉一些代码 @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { try { return mi.proceed(); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) { invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);//如果抛出异常,在catch块中调用异常通知方法。 } throw ex; } } //省略掉一些代码。 }
五、AspectJAroundAdvice
既是通知又是拦截器。稍后。。。。。。。。。
/** * Spring AOP around advice (MethodInterceptor) that wraps * an AspectJ advice method. Exposes ProceedingJoinPoint. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.0 */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { public AspectJAroundAdvice( Method aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) { super(aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif); } @Override public boolean isBeforeAdvice() { return false; } @Override public boolean isAfterAdvice() { return false; } @Override protected boolean supportsProceedingJoinPoint() { return true; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) { throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi); } ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi; ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi); JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi); return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null); } /** * Return the ProceedingJoinPoint for the current invocation, * instantiating it lazily if it hasn't been bound to the thread already. * @param rmi the current Spring AOP ReflectiveMethodInvocation, * which we'll use for attribute binding * @return the ProceedingJoinPoint to make available to advice methods */ protected ProceedingJoinPoint lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(ProxyMethodInvocation rmi) { return new MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint(rmi); } }
六、目标方法对应的通知方法拦截器链是如何创建的
当我们调用目标方法时,程序会将调用目标方法的任务转交给JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法来执行。在invoke方法中根据目标方法为其创建拦截器链。也就是这个目标方法一共对应多少个通知方法,为每个通知方法建一个通知,然后将这些通知再包装成拦截器(其实有写通知本身就是拦截器),最后将这些拦截器组成一条拦截器链。拦截器链构建好以后就是执行通知方法和目标方法了。
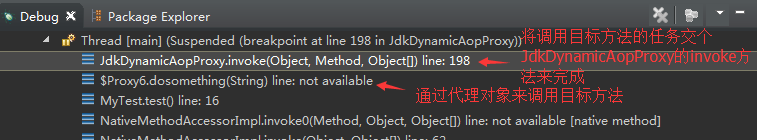
下面是JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法的代码(这个方法的代码都很重,只是这里讨论拦截器是如何创建的,所以删掉了部分代码):
/** * Implementation of {@code InvocationHandler.invoke}. * <p>Callers will see exactly the exception thrown by the target, * unless a hook method throws an exception. */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { MethodInvocation invocation; Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Class<?> targetClass = null; Object target = null; try { //省略部分代码// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, // in case it comes from a pool. target = targetSource.getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } // Get the interception chain for this method.这行代码执行创建拦截器链的操作,将目标方法和所属对象的类对象作为参数 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); // Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation. if (chain.isEmpty()) { //省略 } else { // We need to create a method invocation... invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); } //省略掉部分代码return retVal; } finally { //省略 } }
上面的代码中调用了AdvisedSupport的方法,如下:
/** * Determine a list of {@link org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor} objects * for the given method, based on this configuration. * @param method the proxied method * @param targetClass the target class * @return List of MethodInterceptors (may also include InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatchers) */ public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method); List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);//先从缓存里查看目标方法对应的拦截器链是否已经存在,如果不存在则创建拦截器链。 if (cached == null) { cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(//缓存中没有,所以要创建拦截器链,这个任务交给了AdvisorChainFactory来完成。 this, method, targetClass); this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);//拦截器链创建好以后放到缓存中以便下次使用 } return cached;//返回拦截器链。 }
下面看看AdvisorChainFactory是如何创建的拦截器链的。(AdvisorChainFactory是接口,它有一个实现类DefaultAdvisorChainFactory)
/** * A simple but definitive way of working out an advice chain for a Method, * given an {@link Advised} object. Always rebuilds each advice chain; * caching can be provided by subclasses. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Rod Johnson * @author Adrian Colyer * @since 2.0.3 */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable { @Override public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { // This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first, // but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list. List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);//创建一个拦截器链,也就是一会儿创建的拦截器会放到这个链条中。 Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass()); boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass); AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance(); //Advisor对象是单例非懒加载的,所以他们在bean工厂初始化的时候就已经实例化好了。每一个Advisor中包含的一个通知和一个切点,
//因此现在要把目标方法对应的所有通知组成拦截器链,可以从Advisor中取出通知,再将通知封装到拦截器中(有些通知本身就是拦截器,以直接转化为拦截器类型就可以) for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {//循环目标方法对应的所有Advisor对象,将每个Advisor中的通知封装到拦截器中。 if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { // Add it conditionally. PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
//判断是否预过滤,或是Advisor中的这个通知是否适用于(或者说是否想匹配)目标对象。 if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { //我一开始会奇怪为什么以一个Advisor作为参数却获得一个拦截器数组,不是应该一个Advisor对应一个拦截器吗??
//en。。。。确实是一个Advisor对应一个拦截器。所以它每次返回来的数组都只有一个元素。
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);//标记一 MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
//刚才是判断通知是否跟目标对象匹配,但是跟目标对象匹配不一定跟目标对象中的目标方法匹配呀,所以这里还需要判断是否与目标方法匹配。 if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) { if (mm.isRuntime()) {//是否是运行时的 // Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method // isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains. for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) { interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm)); } } else { interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));//将拦截器添加到拦截器链末尾。 } } } } else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } else { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } return interceptorList;//返回拦截器链。 }
看看上述代码中标记一处的代码是如何实现的,这个代码在DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry中
@Override public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException { List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3); Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();//从Advisor中取出通知 if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) { interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);//如果通知本身是就是拦截器,那么进行类型转换变成拦截器。 } for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) { if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {//通知本身不是拦截器,将通知封装到拦截器当中。 interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)); } } if (interceptors.isEmpty()) { throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice()); } return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);//返回 }


