仅供参考,请指正
1、以下程序的功能是借助一个变量交换两个已知数据的值,程序中存在一些错误,修改这些错误并调试程序。

1 #include "iostream" 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main( ) 6 7 { 8 9 int x,y; 10 11 t=x; 12 13 x=y; 14 15 t=y; 16 17 cin>>x>>y>>endl; 18 19 cout<<"x="<<x<<"y="<<y<<endl; 20 21 system("pause"); 22 23 return 0; 24 25 }

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main( ) 5 { 6 int x,y,t;// 1.先定义后使用,t没有定义 7 8 cin>>x>>y;// 2.先赋值再交换,endl将换行符写入输出流 9 10 // 3.交换算法,是x放到临时变量,y赋值给x,再把临时变量里的x的值赋值给y 11 t=x; 12 x=y; 13 y=t; 14 15 cout<<"x="<<x<<",y="<<y<<endl; // 4.输出最好有个逗号分隔,更清晰一些 16 system("pause"); 17 return 0; 18 }
2、编写一个计算梯形面积的程序。要求梯形的上底、下底和高在定义变量时直接赋值

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main( ) 5 { 6 double a = 12,b = 15, h = 10;//初始化,即上底、下底和高在定义变量时直接赋值 7 cout<<(a+b)*h/2<<endl; //计算面积,不再定义面积变量了,直接输出 8 system("pause"); 9 return 0; 10 }
3、编写计算一个学生三门课平均成绩的程序,要求学生成绩从键盘输入

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main( ) 5 { 6 double a1,a2,a3; //定义3门课的成绩double变量 7 cin>>a1>>a2>>a3; 8 cout<<(a1+a2+a3)/3<<endl; //直接输出,不再定义平均成绩变量 9 system("pause"); 10 return 0; 11 }
4、输入直角坐标系中点P的坐标(x,y),若P点落在图中的阴影区域内,输出阴影部分面积,否则输出数据0


1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <cmath> 4 5 int main( ) 6 { 7 const double PI = 3.1415926; 8 double x,y; 9 double s = PI*(4*4 - 2*2); //阴影部分的面积 10 cin>>x>>y; 11 //如果p的坐标x,y在阴影内,直接输出阴影面积 12 if(fabs(x)>=2 && fabs(x)<=4 && fabs(y)>=2 && fabs(y)<=4) 13 cout<<s<<endl; 14 else 15 cout<<"0"<<endl; 16 system("pause"); 17 return 0; 18 }
5、任意输入3个整数数据,输出它们中最小的一个数

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main( ) 5 { 6 int a,b,c; 7 cin>>a>>b>>c; 8 int min = a<b?a:b; 9 min = min<c?min:c; 10 cout<<min<<endl; 11 system("pause"); 12 return 0; 13 }
6、将"fly"译成密码"iob"。编码规律:将字母a变成字母d,即变成其后的第3个字母,x变成a,y变成b, z变成c。

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main( ) 5 { 6 char c1 = 'f',c2 = 'l',c3 = 'y'; // fly 7 8 c1 = (c1+3-'a')%26 + 'a' ; // i 9 c2 = (c2+3-'a')%26 + 'a' ; // o 10 c3 = (c3+3-'a')%26 + 'a' ; // b 11 12 cout<<c1<<c2<<c3<<endl; // iob 13 system("pause"); 14 return 0; 15 }
7、以下程序的功能是求两个非0整数相除的商和余数。程序有几处错误,试找出它们加以修改,并上机验证修改结果

1 #include "iostream" 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 7 {int x,y,r1,r2; 8 9 cin>>x>>y; 10 11 if(x=0||y=0) 12 13 cout<<”input error”<<endl; 14 15 else 16 17 { if(x>y) 18 19 r1=x/y; 20 21 r2=x%y; 22 23 else 24 25 r1=y/x; 26 27 r2=y%x; 28 29 } 30 31 cout<<”商= ”<<r1<<” 余数= ”<<r2<<endl; 32 33 system("pause"); 34 35 return 0; 36 37 }

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 int x,y,r1,r2; 7 cin>>x>>y; 8 9 if(x==0||y==0)// 比较运算不是赋值 10 cout<<"input error"<<endl; // 引号英文 11 else 12 { 13 if(x>y){ 14 r1=x/y; 15 r2=x%y; 16 } 17 else{ 18 r1=y/x; 19 r2=y%x; 20 } 21 cout<<"商= "<<r1<<" 余数= "<<r2<<endl; //引号英文,不可以放到选择的外面 22 } 23 24 system("pause"); 25 return 0; 26 }
8、某商场购物时,若所选商品价值x在下述范围内,则实付金额y按如下折扣支付:用switch语句实现已知x求y
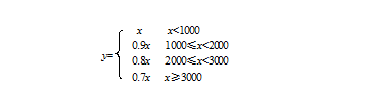

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 double x, y; 7 int n; 8 cin>>x; 9 10 if(x<1000) n = 10; 11 else if(x>=1000 && x<2000) n = 9; 12 else if(x>=2000 && x<3000) n = 8; 13 else n = 7; 14 15 switch(n) 16 { 17 case 10: 18 y = x;break; 19 case 9: 20 y = 0.9*x;break; 21 case 8: 22 y = 0.8*x;break; 23 case 7: 24 y = 0.7*x;break; 25 }; 26 27 cout<<y<<endl; 28 return 0; 29 }
9、编一模拟袖珍计算器的完整程序,运行结果见图。要求:输入两个操作数和一个操作符,根据操作符决定所做的运算
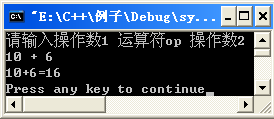

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include <cmath> 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 char ch; 8 double x,y,result; 9 cout<<"请输入操作数1"<<" 运算符op"<<" 操作数2"<<endl; 10 cin>>x>>ch>>y; 11 12 switch(ch) 13 { 14 case '+': 15 result = x+y; break; 16 case '-': 17 result = x-y; break; 18 case '*': 19 result = x*y; break; 20 case '/': 21 if(fabs(y)<1e-6){ 22 cout<<"input error"; 23 exit(0); 24 } 25 else 26 result = x/y; 27 break; 28 }; 29 30 cout<<x<<ch<<y<<"="<<result<<endl; 31 return 0; 32 }
10、以下程序求20以内的奇数和。程序有几处错误,试找出它们加以修改,并上机验证修改结果

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 int n,sum; 6 for(n=1; ;n+=2); 7 sum=sum+n; 8 if(n==20) break; 9 cout<<"sum="<<sum<<endl; 10 system("pause"); 11 return 0; 12 }
11、编写程序将一个十进制整数按倒序形式输出。即若输入156,则输出651

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 int n; 6 cin>>n; 7 8 /* 9 //这段可以去掉尾部的0,比如120,输出21 10 while(n%10==0) 11 { 12 n/=10; 13 } */ 14 15 while(n) 16 { 17 cout<<n%10; 18 n/=10; 19 } 20 21 system("pause"); 22 return 0; 23 }
12、编一程序,显示出所有的水仙花数。所谓水仙花数,是指一个3位数,其各位数字立方和等于该数字本身。

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 for(int i = 100; i<=999; ++i ) 6 { 7 int a = i%10, b = i/10%10, c = i/100; 8 if(a*a*a + b*b*b + c*c*c == i) 9 cout<<i<<" "; 10 } 11 12 system("pause"); 13 return 0; 14 }
13、

1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<time.h> 4 int main() 5 { 6 srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //种子 7 8 int a = rand()%9 + 1; //随机产生1~9的数字 a 9 int n = 5 + rand()%5; //随机产生 5~9的数字 n 10 //cout<<a<<","<<n<<endl; 11 12 long temp=0,sum = 0; // 数据类型 long 13 for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)//计算sum 14 { 15 temp = temp*10+a; 16 sum += temp; 17 } 18 19 cout<<sum<<endl;//输出sum 20 21 system("pause"); 22 return 0; 23 }
14、随机产生10个30~100(包括30,100)的正整数,求它们的最大值、最小值、平均值,并显示整个数组的值和结果。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 int main() 5 { 6 srand(time(NULL)); 7 int max=30,min=100,sum=0; 8 int arr[10] = {0}; 9 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i){ 10 arr[i] = rand()%70 + 30; 11 sum += arr[i]; 12 if(arr[i]>max) 13 max =arr[i]; 14 if(arr[i]<min) 15 min = arr[i]; 16 } 17 18 printf("max=%d,min=%d,ave=%.2f\n",max,min,sum/10.0); 19 20 for(int j=0; j<10; ++j) 21 printf("%d ",arr[j]); 22 23 return 0; 24 }
15、随机产生20个学生的计算机课程的成绩(0~100),按照从大到小的顺序排序,分别显示排序前和排序后的结果

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 5 void SelectionSort(int *a,int left, int right); 6 int main() 7 { 8 srand(time(NULL)); 9 10 int arr[20] = {0}; 11 for(int i=0; i<20; ++i){ 12 arr[i] = rand()%100; 13 } 14 15 printf("排序前:\n"); 16 for(int j=0; j<20; ++j) 17 printf("%d ",arr[j]); 18 19 SelectionSort(arr,0,19); 20 21 printf("\n排序后:\n"); 22 for(int j=0; j<20; ++j) 23 printf("%d ",arr[j]); 24 25 return 0; 26 } 27 /*选择排序--递归*/ 28 void SelectionSort(int *a,int left, int right) 29 { 30 if(left<right){ 31 int j,t; 32 for(j=right; left<j; j--){ 33 if(a[j]<a[left])/*与最左边的比较*/ 34 t=a[left],a[left]=a[j],a[j]=t; 35 } 36 SelectionSort(a,j+1,right);/*递归*/ 37 } 38 }
16、随机产生10个数,输入1~10之间的正整数m,使数组元素右移m位,移出的元素再从左移入。如,假设原来的数组元素依次为:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10,假设m为2,则右移2位后的数组元素依次为:9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 int main() 5 { 6 srand(time(NULL)); 7 8 //1.随机产生1~10十个数 9 int arr1[10] = {0}; 10 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i){ 11 arr1[i] = rand()%10+1; 12 } 13 14 //2.输出产生的数组 15 printf("移动前:\n"); 16 for(int j=0; j<10; ++j) 17 printf("%d ",arr1[j]); 18 printf("\n"); 19 20 //3.输入移动的数据m 21 printf("\n请输入移动数据(1~10):\n"); 22 int arr2[10] = {0}; 23 int m; 24 scanf("%d",&m); 25 26 //4.复制移动覆盖的数 27 for(int i=0,j=10-m; j<10; ++i,++j) 28 arr2[i] = arr1[j]; 29 30 //5.原数组向右移动m位 31 for(int j=10-m; j>=0; --j) 32 arr1[j+m] = arr1[j]; 33 34 //6.保存的数拷贝回数组 35 for(int j=0; j<m; ++j) 36 arr1[j] = arr2[j]; 37 38 //7.打印移动后的数组 39 printf("\n移动后:\n"); 40 for(int j=0; j<10; ++j) 41 printf("%d ",arr1[j]); 42 43 return 0; 44 }
17、按由大到小的顺序输入10个int类型的数据将其存放在一个一维数组中,再输入一个整数到变量x,用二分法查找x是否是数组中的元素,若是,输出其在数组中的位置,否则输出不在数组中的提示。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int fun(int *arr,int left,int right,int x); 4 int main() 5 { 6 //输入数组数据 7 printf("\n请输入10个int型数据(从大到小有序输入):\n"); 8 int arr[10] = {0}; 9 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i){ 10 scanf("%d",&arr[i]); 11 } 12 13 //输入要查找的数据 14 printf("\n请输入要查找的数据:\n"); 15 int x; 16 scanf("%d",&x); 17 18 //查找x 19 int y = fun(arr,0,9,x); 20 if(y==-1){ 21 printf("x不在数组中\n"); 22 } 23 else{ 24 printf("x是数据的第%d元素\n",y+1); 25 } 26 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 int fun(int *arr,int left,int right,int x) 31 { 32 while(left<=right) 33 { 34 int mid = (left + right)/2; 35 //int mid = left + (right - left)/2; //防止溢出 36 if(arr[mid]>x) 37 left = mid+1; 38 else if(arr[mid]<x) 39 right = mid-1; 40 else 41 return mid; 42 } 43 return -1; 44 }
18、输入一个小于10的正整数n,显示具有如下形式的n行杨辉三角形。图中n=6


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define N 100 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int a[N][N] = {0}; 9 int i, j, n = 6; 10 cin>>n; 11 12 for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ 13 a[i][1] = a[i][i] = 1; /*1.第一列和对角线的数都是1*/ 14 } 15 16 for(i=3;i<=n;i++) 17 { 18 for(j=2;j<=i-1;j++){ 19 a[i][j]=a[i-1][j-1]+a[i-1][j]; /*2.除两边的数, 等于左上/上两数之和*/ 20 } 21 } 22 23 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 24 { 25 cout<<setw((n-i)*3)<<' '; 26 27 for(j=1;j<=i;j++) 28 { 29 cout<<setw(6)<<a[i][j]; 30 } 31 32 cout<<endl; 33 } 34 35 return 0; 36 }
19、编写程序,将某一指定字符从一个已知的字符串中删除。假设已知字符串为“aaaasdfga”,将其中出现的'a'字母删除,删除后的字符串为“sdfg”

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define N 100 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 char arr[N] = "aaaasdfga"; 8 char *p = arr, *q = arr; 9 char ch = 'a'; 10 11 while(*p) 12 { 13 if(*p!=ch){ 14 *q++ = *p; 15 } 16 p++; 17 } 18 *q = '\0'; 19 20 cout<< arr << endl; 21 22 return 0; 23 }
20、编一个程序,输入一个字符串,将其倒序存放后输出。例如,假设原数组a的内容为“VISUAL C++PROGRAM”,倒序后数组a中的内容为“MAGORP++C LASUIV”。要求:不能借助另外一个数组实现倒序存放

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define N 100 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 char arr[N] = "VISUAL C++PROGRAM"; 9 char *p = arr, *q = arr + strlen(arr)-1; 10 gets(arr); 11 12 while(p < q) 13 { 14 char t = *p; 15 *p = *q; 16 *q = t; 17 p++,q--; 18 } 19 20 cout<< arr << endl; 21 22 return 0; 23 }
21、利用字符指针将输入的一个字符串中的大小写字母相互转换,并输出转换后的字符串的内容。如,假设输入的字符串的内容为“How are you”,则转换后的内容为“hOW ARE YOU”

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 char str[256] = ""; 7 cin.getline(str,256); 8 char *p = str; 9 10 while(*p) 11 { 12 if(*p>='a'&& *p<='z')//如果小写转大写 13 *p -= 32; 14 else if(*p>='A' && *p<='Z')//如果大写转小写 15 *p += 32; 16 p++; 17 } 18 19 cout<<str<<endl; 20 return 0; 21 }
22、利用字符指针将字符串s中从第n个字符开始的内容复制到字符串t中

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 char s[256] = ""; 7 char t[256] = ""; 8 cin.getline(s,256); 9 10 int n; 11 cin>>n; 12 char *p = s+n-1;//第n个字符开始,数组下标从0开始的 13 char *q = t; 14 15 while(*q++ = *p++); 16 17 cout<<t<<endl; 18 return 0; 19 }
23、利用指针将一个包含10个整数的数组中的最大最小元素进行交换,并输出交换后的内容。10个整数为随机产生的0~100之间的数。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <ctime> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 srand(time(NULL)); 8 int arr[10] = {0}; 9 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i){ //随机产生0~100的10个数 10 arr[i] = rand()%101; 11 } 12 13 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i){//打印10个随机数 14 cout<<arr[i]<<","; 15 } 16 17 int maxi=0,mini=0 ; //最大值下标、最小值下标 18 for(int *p = arr; p-arr<10; p++)//利用指针p扫描数组 19 { 20 if(*p<*(arr+mini)){ 21 mini = p - arr; //更新最小值下标 22 } 23 if(*p> *(arr+maxi)){ 24 maxi = p - arr; //更新最大值下标 25 } 26 } 27 cout<<endl; 28 29 //最大值 最小值交换 30 int t = *(arr+maxi); 31 *(arr+maxi) = *(arr+mini); 32 *(arr+mini) = t; 33 34 //交换后的数组,10个数 35 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i){ 36 cout<<arr[i]<<","; 37 } 38 return 0; 39 }
24、编一判断m是否为素数的函数,并在主函数中利用它输出十对最小的孪生素数。所谓孪生素数是指两个相差为2的素数,如3和5,11和13。程序运行结果见下图。函数形式为:bool isprime(int m)


1 #include "iostream" 2 using namespace std; 3 4 bool isprime(int m); 5 int main() 6 { 7 int two = 2, count = 0; 8 for(int j = 2; count<10; ++j){ 9 if(isprime(j) && isprime(j+two)){ 10 count++; 11 printf("(%d,%d)\n",j,j+two); 12 } 13 } 14 return 0; 15 } 16 bool isprime(int m){ 17 for(int i=2; i<m; ++i){ 18 if(m%i==0) 19 return false; 20 } 21 return true; 22 }
25、编一函数,功能为判断一字符串是否为回文,如果是回文则返回1,否则返回0。回文是指顺读和倒读都一样的字符串,如“deed”和“level”是回文。在主函数中对输入的字符串加以调用函数形式为:int huiwen(char s[])

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int huiwen(char s[]); 6 int main() 7 { 8 const int N = 100; 9 char s[N] = ""; 10 cin>>s; 11 if(huiwen(s)) 12 cout<<"是回文"<<endl; 13 else 14 cout<<"不是回文"<<endl; 15 return 0; 16 } 17 int huiwen(char s[]) 18 { 19 char *p = s, *q = s+strlen(s)-1; 20 while(p<q) 21 { 22 if(*p!=*q) 23 return 0; 24 p++, q--; 25 } 26 return 1; 27 }
26、函数的功能是将学生成绩从高分到低分排序,并统计优秀与不及格的人数。用下面两种方法实现:
(1)函数形式为:int fun1(int s[],int n,int *x)
要求优秀人数通过return返回,不及格人数通过指针参数返回结果。
(2)函数形式为:void fun2(int s[],int n,int &x,int &y)
要求优秀与不及格的人数通过引用参数返回结果。
分别编二个函数,学生人数从键盘输入。

1 #include "iostream" 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int fun1(int s[],int n,int *x); 6 void fun2(int s[],int n,int &x,int &y); 7 int main() 8 { 9 const int N = 100; 10 int s[N] = {0}; 11 int n; 12 cin>>n; 13 for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) 14 cin>>s[i]; 15 16 int x=0,y=0; 17 cout<<"优秀的人数:"<<fun1(s,n,&x)<<endl; 18 cout<<"不及格的人数:"<<x<<endl; 19 20 x=0,y=0; 21 fun2(s,n,x,y); 22 cout<<"优秀的人数:"<<y<<endl<<"不及格的人数:"<<x<<endl; 23 24 return 0; 25 } 26 int fun1(int s[],int n,int *x){ 27 int excellent=0; 28 * x = 0;// 29 for(int i=0; i<n-1; ++i){/*第0个元素有序,从第1个元素向右无序*/ 30 int max = s[i]; 31 int index = i; 32 for(int j = i+1; j<n; ++j){/*从i+1逐个比较*/ 33 if(max<s[j]){ /*是否比后面的小*/ 34 max = s[j]; 35 index = j; 36 } 37 } 38 if(index != i){/*找到了最大值才交换*/ 39 s[index] = s[i]; 40 s[i] = max; 41 } 42 } 43 for(int k=0; k<n; ++k){ 44 if(s[k]>=90) excellent++; 45 if(s[k]<60) (*x)++; 46 } 47 return excellent; 48 } 49 void fun2(int s[],int n,int &x,int &y){ 50 x=y=0; // 51 for(int i=0; i<n-1; ++i){/*第0个元素有序,从第1个元素向右无序*/ 52 int max = s[i]; 53 int index = i; 54 for(int j = i+1; j<n; ++j){/*从i+1逐个比较*/ 55 if(max<s[j]){ /*是否比后面的小*/ 56 max = s[j]; 57 index = j; 58 } 59 } 60 if(index != i){/*找到了最大值才交换*/ 61 s[index] = s[i]; 62 s[i] = max; 63 } 64 } 65 for(int k=0; k<n; ++k){ 66 if(s[k]>=90) y++; 67 if(s[k]<60) x++; 68 } 69 }
27、编一函数,功能为统计字符串中各个字母(不区分大、小写)出现的频率,同时找出频率出现最高的字母及次数,假设出现次数最多的字母只有一个。函数形式为:void freq(char s[],int p[],char &chmax,int &max)程序运行结果如下:
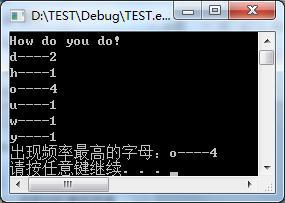

1 #include "iostream" 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void freq(char s[],int p[],char &chmax,int &max); 6 int main() 7 { 8 char chmax; 9 int max = 0; 10 const int N = 256; 11 int p[N] = {0}; 12 char s[N] = ""; 13 gets(s); 14 freq(s,p,chmax,max); 15 for(int i=0; i<N; ++i){ 16 if(p[i]) 17 printf("%c-----%d\n",i,p[i]); 18 } 19 printf("出现频率最高的字母:%c-----%d\n",chmax,max); 20 return 0; 21 } 22 void freq(char s[],int p[],char &chmax,int &max){ 23 char *q = s; 24 while(*q) 25 { 26 if(*q>='a'&&*q<='z'||*q>='A'&&*q<='Z') 27 { 28 if(*q<'a') 29 p[*q+32]++; 30 else 31 p[*q]++; 32 if(p[*q]>max){ 33 max = p[*q]; 34 chmax = *q; 35 } 36 } 37 q++; 38 } 39 }
28、编写递归函数int sum(int a[],int n),其功能是求长度为n的数组的累加和,在主函数中随机产生10个两位数,调用sum函数,求这10个数的和

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 int sum(int a[],int n); 5 int main( ) 6 { 7 srand(time(NULL)); 8 int arr[10] = {0}; 9 for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)//随机产生十个两位数的数组 10 arr[i] = rand()%100; 11 12 for(int j=0; j<10; ++j)//显示产生的数组 13 printf("%d ",arr[j]); 14 printf("\n"); 15 16 printf("%d\n", sum(arr,10));//调用递归函数sum求数组元素之和 17 return 0; 18 } 19 int sum(int a[],int n){ 20 if(n==1) 21 return a[0]; 22 else return a[n-1] + sum(a,n-1); 23 }
29、编写函数get_max,其功能是将字符串s中最大字符的地址返回,再编写一个主函数,调用该函数,将字符串s中从最大字符开始的子串中小写字母转换成大写字母,然后输出新字符串s。例如,假设s的内容为“qwertyou”,则从最大字符’y’开始的子串为“you”,处理后的s为“qwertYOU”。
函数形式为:char *get_max(char s[])

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define N 100 4 char *get_max(char s[]); 5 int main( ) 6 { 7 char s[N] = ""; 8 scanf("%s",s); 9 10 char *p = get_max(s); 11 while(*p) 12 { 13 if(*p>='a'&&*p<='z') 14 *p -= 32; 15 p++; 16 } 17 18 printf("%s\n", s); 19 return 0; 20 } 21 /* 22 char *get_max(char s[]){ 23 char ch = s[0]; 24 int i,maxi; 25 for(i=0; s[i]; ++i) 26 if(s[i]>ch){ 27 ch = s[i]; 28 maxi = i; 29 } 30 return &s[maxi]; 31 } 32 */ 33 char *get_max(char s[]){ 34 char *max = s; 35 for(char *p = s; *p; p++) 36 if( *p>*max ) max = p; 37 return max; 38 }
30、有一组关于学生成绩的信息,编写函数max,该函数返回值为分数最高的学生的信息(包括学号和分数)。再编写主函数对其进行调用并输出最高分者的信息。假设结构类型定义为:

1 struct student 2 3 { 4 5 char *num; 6 7 int score; 8 9 };

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define N 100 4 /* 结构体 */ 5 typedef struct student STUDENT; 6 struct student 7 { 8 char *num; 9 int score; 10 }; 11 /* 求最大分数学生的下标 */ 12 int fun(STUDENT arr[], int n) 13 { 14 int max = arr[0].score; 15 int maxi = 0; 16 for(int i=1; i<n; ++i) 17 if(arr[i].score>max){ 18 max = arr[i].score; 19 maxi = i; 20 } 21 return maxi; 22 } 23 24 int main() 25 { 26 STUDENT arr[N]; 27 printf("请输入学生人数:\n"); 28 int n; 29 scanf("%d",&n); 30 /* 输入n个学生的学号及分数 */ 31 printf("请输入学号、成绩:\n"); 32 for(int j=0; j<n; ++j){ 33 arr[j].num = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*10); 34 scanf("%s%d",arr[j].num,&arr[j].score); 35 } 36 /* 输出分数最大值 */ 37 int index = fun(arr,n); 38 printf("num=%s,score=%d\n",arr[index].num, arr[index].score ); 39 return 0; 40 }
31、编写程序,定义一个日期结构变量,计算某日期是本年度的第几天。提示:为简单起见,可定义一个存放12个月中每个月总天数的数组。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define N 100 4 /* 结构体 */ 5 typedef struct date DATE; 6 struct date 7 { 8 int year; 9 int month; 10 int day; 11 }; 12 /* 某日期是该年的第几天 */ 13 void fun(DATE d) 14 { 15 int months[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 16 int days = d.day; 17 if(d.year%4==0 && d.year%100!=0 ||d.year%400==0) 18 months[2]++; 19 for(int i=1; i<d.month; ++i) 20 days += months[i]; 21 printf("是%d年的第%d天\n",d.year,days); 22 } 23 24 int main() 25 { 26 DATE d; 27 printf("请输入日期(年/月/日):\n"); 28 scanf("%d/%d/%d",&d.year,&d.month,&d.day); 29 fun(d); 30 return 0; 31 }
32、编写函数deln,具有删除链表中第n个结点的功能。再编写主函数,按输入顺序建立不带头结点的职工信息单链表,然后调用del函数删除某个职工的信息,并输出删除后的职工信息表中的职工信息。假设链表结构如下:

1 struct staff 2 3 { 4 5 char num[6]; //职工工号 6 7 char name[20]; //职工姓名 8 9 double wage; //职工工资 10 11 };

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 /* node */ 5 typedef struct staff *STAFF; 6 struct staff 7 { 8 char num[6]; //职工工号 9 char name[20]; //职工姓名 10 double wage; //职工工资 11 STAFF next; 12 }; 13 14 /* makenode */ 15 STAFF makenode() 16 { 17 STAFF p = (STAFF)malloc(sizeof(struct staff)); 18 printf("请输入职工的工号、姓名、工资:\n"); 19 scanf("%s%s%lf",p->num,p->name,&p->wage); 20 p->next = NULL; 21 return p; 22 } 23 /* create */ 24 STAFF create(int m) 25 { 26 STAFF head,p; 27 head = p = makenode(); 28 while(--m) 29 { 30 p->next = makenode();//尾插 31 p = p->next; 32 } 33 return head; 34 } 35 /* print */ 36 void printlist(STAFF p) 37 { 38 while(p){ 39 printf("num=%s,name=%s,wag=%.2f\n",p->num,p->name,p->wage); 40 p= p->next; 41 } 42 printf("\n"); 43 } 44 /* deln */ 45 STAFF deln(STAFF head,int n) 46 { 47 STAFF p = head; 48 if(p==NULL) //链表为空 49 { 50 return NULL; 51 } 52 if(n==1)//删除的是头结点 53 { 54 head = head->next; 55 free(p); 56 } /* */ 57 else 58 { 59 STAFF q = p; 60 while(--n) 61 { 62 q = p; 63 p = p->next; 64 } 65 q->next = p->next; 66 free(p); 67 } 68 return head; 69 } 70 int main() 71 { 72 STAFF head = create(3);//创建有3个结点的单链表 73 printlist(head); //打印链表 74 head = deln(head,2); //删除链表的第2个元素 75 printlist(head); //打印链表 76 return 0; 77 }
33、从键盘输入一个字符串,要求将该字符串的内容按输入的相反顺序组织到一个不带表头结点的单链表中。假设输入的字符串为"abcdefg",则组织到链表中的内容为"gfedcba"

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #define N 100 5 /* node */ 6 typedef struct node *NODE; 7 struct node 8 { 9 char ch; //字符 10 NODE next; 11 }; 12 13 /* makenode */ 14 NODE makenode(char ch) 15 { 16 NODE p = (NODE)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); 17 p->ch = ch; 18 p->next = NULL; 19 return p; 20 } 21 22 /* print */ 23 void printlist(NODE p) 24 { 25 while(p){ 26 printf("%c",p->ch); 27 p= p->next; 28 } 29 printf("\n"); 30 } 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 char s[N] = ""; 35 scanf("%s",s); 36 int len = strlen(s); 37 38 NODE head,p; 39 head = p = makenode(s[len-1]); 40 for(int i=len-2; i>=0; --i){ 41 p->next = makenode(s[i]);//尾插 42 p = p->next; 43 } 44 printlist(head); 45 return 0; 46 }
34、编写程序,从键盘输入一串字符,要求将该串字符的倒序串先写入到文件f1.txt中,然后再将原字符串的内容接到该文件的末尾。例如,假设从键盘输入的字符串为“How do you do?”,则文件f1.txt的内容为:
?od uoy od woHHow do you do?

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #define N 256 4 int main() 5 { 6 FILE *fp; 7 fp = fopen("f1.txt","w"); 8 /* 1. */ 9 char s[N] = ""; 10 gets(s); 11 int len = strlen(s); 12 for(int i=len-1; i>=0; --i){ 13 fputc(s[i],fp); 14 } 15 /* 2. */ 16 fputs(s,fp); 17 fclose(fp); 18 return 0; 19 }
35、用记事本建立一个文本文件f2.txt,在该文件中任意存放一组整数。编写程序统计该文件中正整数、负整数和零的个数。(提示:用fscanf函数读取文件中的数据)

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int main() 3 { 4 FILE *fp; 5 fp = fopen("f2.txt","r"); 6 7 int plus=0, minus=0, zero=0,num; 8 9 while(!feof(fp)) 10 { 11 fscanf(fp,"%d",&num); 12 if(num>0) 13 plus++; 14 if(num<0) 15 minus++; 16 if(num==0) 17 zero++; 18 } 19 printf("正数=%d,负数=%d,零=%d\n",plus,minus,zero); 20 21 fclose(fp); 22 return 0; 23 }
36、将从键盘输入的N个学生的学号和成绩存入到文件student.dat中。再从文件中读取学生的信息,求出最高分、最低分和总分。N可通过符号常量自行定义大小。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #define N 4 3 4 typedef struct student STUDENT; 5 struct student{ 6 char no[20]; 7 double score; 8 }stu[N]; 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 FILE *fp; 13 /* 写入 */ 14 fp = fopen("student.dat","w"); 15 for(int i=0; i<N; ++i){ 16 scanf("%s%lf",stu[i].no,&stu[i].score); 17 } 18 fwrite(stu, sizeof(STUDENT),4,fp); 19 fclose(fp); 20 /* 读取 */ 21 fp = fopen("student.dat","r"); 22 STUDENT st[N];//也可以直接用stu 23 fread(st, sizeof(STUDENT),4,fp);//读取到st 24 /* 处理 */ 25 double max = st[0].score,min=st[0].score,total = st[0].score; 26 for(int j=1; j<N; ++j){ 27 total += st[j].score; 28 if(st[j].score>max) 29 max = st[j].score; 30 if(st[j].score<min) 31 min = st[j].score; 32 } 33 printf("max=%.2f,min=%.2f,total=%.2f\n",max,min,total); 34 fclose(fp); 35 return 0; 36 }
37、设计一个点类(Point),具有数据成员x,y(点的坐标),以及设置、输出数据成员及求两点之间距离的功能。再编写主函数对该类进行测试。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cmath> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Point{ 6 double x,y; 7 public: 8 Point(double x,double y){ 9 this->x = x; 10 this->y = y; 11 } 12 double distance( const Point &p){ 13 return sqrt((x-p.x)*(x-p.x)+(y-p.y)*(y-p.y)); 14 } 15 }; 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 Point p1(2,3),p2(4,5); 20 cout<<p1.distance(p2)<<endl; 21 return 0; 22 }
38、设计一个字符串类(Mystring),除具有一般的输入输出字符串的功能外,还要求具有计算字符串长度、连接两个字符串等功能,其中求字符串长度和连接字符串功能不能直接调用字符串处理函数。再编写主函数对该类进行测试

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define N 256 4 class Mystring{ 5 char *p; 6 long length; 7 public: 8 Mystring(); 9 void input(); 10 void show(); 11 long stringLength(); 12 Mystring& operator+(Mystring &s); 13 }; 14 /* 无参构造函数 */ 15 Mystring::Mystring() 16 { 17 p = new char[N]; 18 length = 0; 19 } 20 /* 输入字符串(并计算长度) */ 21 void Mystring::input() 22 { 23 cin>>p; 24 char *t = p; 25 while(*t) {t++,length++;} 26 } 27 /* 显示字符串 */ 28 void Mystring::show() 29 { 30 cout<<p<<endl; 31 } 32 /* 输出字符串长度 */ 33 long Mystring::stringLength() 34 { 35 return length ; 36 } 37 /* +运算符重载(连接两个字符串) */ 38 Mystring& Mystring::operator+(Mystring &s){ 39 char *t1 = p,*t2 = s.p; 40 while(*t1) t1++; 41 while(*t1++=*t2++); 42 return *this; 43 } 44 int main() 45 { 46 Mystring s1,s2; 47 cout<<"请输入字符串1:"; 48 s1.input(); 49 cout<<"请输入字符串2:"; 50 s2.input(); 51 cout<<"输出字符串1:"; 52 s1.show(); 53 cout<<"输出字符串1长度:"; 54 cout<<s1.stringLength()<<endl; 55 cout<<"连接2个字符串并输出\n"; 56 s1 = s1+s2; 57 s1.show(); 58 return 0; 59 }
39、设计一个分数类Fraction。该类的数据成员包括分子fz和分母fm;类中还包括如下成员函数:
(1)构造函数,用于初始化分子和分母。
(2)成员函数print,将分数以 "fz/fm" 的形式输出。
(3)成员函数Reduction,用于对分数的分子和分母进行约分。
再编写主函数对该类进行测试。

#include <iostream> using namespace std; #define N 256 class Fraction{ private: int fz,fm; public: /* 构造 */ Fraction(int z,int m){ fz = z; fm = m; } /* 输出 */ void print(){ Reduction(); cout<<fz<<"/"<<fm<<endl; } private: /* 约分 */ void Reduction(){ int t = fz<fm?fz:fm; while(fz%t!=0||fm%t!=0) t--; fz /= t; fm /= t; } }; int main() { Fraction f(12,16); f.print(); return 0; }
课程相关
1、十进制正整数进制转化成八进制数(递归)
1 void convert(int n) 2 { 3 if(n>0) 4 { 5 convert(n/8);//base==8 6 cout<<n%8; 7 } 8 }
2、寻数组最大元素地址
int *maxaddr(int a[],int n) { int *max=a; for(int *p=a;p<a+n;p++) if(*p>*max) max=p; return max; }
3、设计一个字符串类(Mystring)
1 #include <cstdlib> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int strlen(const char * s) 5 { int i = 0; 6 for(; s[i]; ++i); 7 return i; 8 } 9 void strcpy(char * d,const char * s) 10 { 11 int i = 0; 12 for( i = 0; s[i]; ++i) 13 d[i] = s[i]; 14 d[i] = 0; 15 16 } 17 int strcmp(const char * s1,const char * s2) 18 { 19 for(int i = 0; s1[i] && s2[i] ; ++i) { 20 if( s1[i] < s2[i] ) 21 return -1; 22 else if( s1[i] > s2[i]) 23 return 1; 24 } 25 return 0; 26 } 27 void strcat(char * d,const char * s) 28 { 29 int len = strlen(d); 30 strcpy(d+len,s); 31 } 32 class MyString 33 { 34 int len; 35 char * str; 36 public: 37 MyString (const char *s) :len(strlen(s)) 38 { 39 str=new char[len+1]; 40 strcpy(str,s); 41 } 42 MyString(const MyString &s):len(strlen(s.str)) 43 { 44 str=new char[len+1]; 45 strcpy(str,s.str); 46 } 47 48 //MyString () {str="\0";len=0;} 49 MyString () {str=NULL;len=0;} 50 //~MyString(){if (len!=0) delete []str;} 51 ~MyString(){if (str) delete []str;} 52 //重载<< 53 //friend ostream & operator<<(ostream & o,const MyString & s) 54 //{ 55 // o<<s.str; 56 // return o; 57 //} 58 59 //重载<< 60 friend ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const MyString &s) 61 { 62 if(s.str)os << s.str; 63 return os; 64 } 65 friend int operator <(MyString &s1,MyString &s2) 66 { 67 if(*(s1.str)<*(s2.str)) return 1; 68 else return 0; 69 } 70 friend int operator >(MyString &s1,MyString &s2) 71 { 72 if(*(s1.str)>*(s2.str)) return 1; 73 else return 0; 74 } 75 friend int operator ==(MyString &s1,MyString &s2) 76 { 77 if(*(s1.str)==*(s2.str)) return 1; 78 else return 0; 79 } 80 char * operator()(int start ,int len) 81 { 82 char*tem=new char[len]; 83 int i ; 84 for( i=0;i<len;++i) 85 tem[i]=str[i+start]; 86 tem[i]=0; 87 return tem; 88 } 89 //重载= 90 //MyString & operator =(const MyString &s) 91 //{ 92 // if (this==&s) return *this; 93 // delete [] str; 94 // str=new char[s.len+1]; 95 // strcpy(str,s.str); 96 // return *this; 97 //} 98 99 //重载= 100 MyString & operator=(const MyString & x) 101 { 102 if(str == x.str) 103 return *this; 104 if(str) 105 delete[] str; 106 if(x.str){ 107 str = new char[strlen(x.str)+1]; 108 strcpy(str,x.str); 109 } 110 else 111 str = NULL; 112 return *this; 113 } 114 //多余的字符串转对象 115 //MyString & operator =(const char *s) 116 //{ 117 // if (len>0)delete []str; 118 // len=strlen(s); 119 // str=new char[len+1]; 120 // strcpy(str,s); 121 // return *this; 122 //} 123 124 125 //对象相加 126 //MyString operator +(MyString &s) 127 //{ 128 // static MyString s1; 129 // if (s1.len>0) delete []s1.str; 130 // s1.len=len+s.len; 131 // s1.str=new char[s1.len]; 132 // strcpy(s1.str,str); 133 // strcat(s1.str,s.str); 134 // return s1; 135 //} 136 137 //对象相加 138 MyString operator+(const MyString &ms) 139 { 140 MyString temp; 141 temp.str = new char[strlen(str) + strlen(ms.str)+1]; 142 strcpy(temp.str, str); 143 strcat(temp.str, ms.str); 144 return temp; 145 } 146 147 //多余的对象与字符串相加 148 //MyString operator +(char *s) 149 //{ 150 // static MyString s1; 151 // if (s1.len>0) delete []s1.str; 152 // s1.len=len+strlen(s); 153 // s1.str=new char[s1.len]; 154 // strcpy(s1.str,str); 155 // strcat(s1.str,s); 156 // return s1; 157 //} 158 159 // 160 MyString & operator +=(const char* s) 161 { 162 len=len+strlen(s); 163 char*p=new char[len]; 164 strcpy(p,str); 165 strcat(p,s); 166 if(len>0) delete []str; 167 str=p; 168 return *this; 169 } 170 //字符串与对象相加 171 //friend MyString & operator +(const char*s,MyString &s2) 172 //{ 173 // static MyString s1; 174 // if (s1.len>=0) delete []s1.str; 175 // s1.len=strlen(s)+s2.len; 176 // s1.str=new char[s1.len]; 177 // strcpy(s1.str,s); 178 // strcat(s1.str,s2.str); 179 // return s1; 180 //} 181 //字符串与对象相加 182 friend MyString operator+(const char*str, const MyString &ms) 183 { 184 MyString temp(str);//字符串转对象 185 temp = temp + ms; 186 return temp; 187 } 188 // 189 char &operator [](int i) 190 { 191 return str[i]; 192 } 193 }; 194 195 196 int CompareString( const void * e1, const void * e2) 197 { 198 MyString * s1 = (MyString * ) e1; 199 MyString * s2 = (MyString * ) e2; 200 if( * s1 < *s2 ) 201 return -1; 202 else if( *s1 == *s2) 203 return 0; 204 else if( *s1 > *s2 ) 205 return 1; 206 } 207 int main() 208 { 209 MyString s1("abcd-"),s2,s3("efgh-"),s4(s1); 210 MyString SArray[4] = {"big","me","about","take"}; 211 cout << "1. " << s1 << s2 << s3<< s4<< endl; 212 s4 = s3; 213 s3 = s1 + s3; 214 cout << "2. " << s1 << endl; 215 cout << "3. " << s2 << endl; 216 cout << "4. " << s3 << endl; 217 cout << "5. " << s4 << endl; 218 cout << "6. " << s1[2] << endl; 219 s2 = s1; 220 s1 = "ijkl-"; 221 s1[2] = 'A' ; 222 cout << "7. " << s2 << endl; 223 cout << "8. " << s1 << endl; 224 s1 += "mnop"; 225 cout << "9. " << s1 << endl; 226 s4 = "qrst-" + s2; 227 cout << "10. " << s4 << endl; 228 s1 = s2 + s4 + " uvw " + "xyz"; 229 cout << "11. " << s1 << endl; 230 qsort(SArray,4,sizeof(MyString),CompareString); 231 for( int i = 0;i < 4;i ++ ) 232 cout << SArray[i] << endl; 233 //s1的从下标0开始长度为4的子串 234 cout << s1(0,4) << endl; 235 //s1的从下标5开始长度为10的子串 236 cout << s1(5,10) << endl; 237 return 0; 238 }
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define N 256 5 class Mystring{ 6 char *p; 7 static char *temp; 8 public: 9 Mystring(); 10 ~Mystring(); 11 long stringLength(); 12 Mystring& operator=(const char *t); 13 14 friend char* operator+(Mystring &s1,Mystring &s2); 15 friend char* operator+(char *s1,Mystring &s2); 16 friend istream &operator>>( istream &in, Mystring &s ); 17 friend ostream &operator<<( ostream &out, Mystring &s ); 18 }; 19 char* Mystring::temp = new char[N]; 20 /* 无参构造函数 */ 21 Mystring::Mystring() 22 { 23 p = new char[N]; 24 } 25 /* 析构函数 */ 26 Mystring::~Mystring() 27 { 28 if(p) delete p; 29 } 30 /* 输出字符串长度 */ 31 long Mystring::stringLength() 32 { 33 return strlen(p) ; 34 } 35 /* +运算符重载(连接字符串与对象) */ 36 char* operator+(char *s1,Mystring &s2){ 37 if(s1==Mystring::temp){ 38 strcat(s1,s2.p); 39 } 40 return s1; 41 } 42 /* +运算符重载(连接两个对象)*/ 43 char* operator+(Mystring &s1,Mystring &s2){ 44 strcat(strcpy(Mystring::temp,s1.p),s2.p); 45 return Mystring::temp; 46 } 47 /* =运算符重载(char*转对象引用)*/ 48 Mystring& Mystring::operator=(const char *t){ 49 strcpy(this->p,t); 50 return *this; 51 } 52 /* 友元函数,重载>>输入字符串 */ 53 istream &operator>>( istream &in, Mystring &s ) 54 { 55 in>>s.p; 56 return in; 57 } 58 /* 友元函数,重载<<输出字符串 */ 59 ostream &operator<<( ostream &out, Mystring &s ) 60 { 61 out<<s.p; 62 return out; 63 } 64 int main() 65 { 66 cout<<"请输入3个字符串:\n"; 67 Mystring s1,s2,s3,s4; 68 cin>>s1>>s2>>s3; 69 cout<<"连接3个字符串并输出:\n"; 70 cout<<s1+s2+s3<<endl; 71 cout<<"连接3个字符串并赋值给字符串4,并输出:\n"; 72 s4 = s1+s2+s3; 73 cout<<s4<<endl; 74 cout<<"输出字符串1:\n"; 75 cout<<s1<<endl; 76 cout<<"输出字符串1长度:\n"; 77 cout<<s1.stringLength()<<endl; 78 return 0; 79 }
4、将一个字符串中的大小写字母相互转换后写入文件alp.txt中
1 #define N 100 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 FILE *fp; 8 int i; 9 char s[N]; 10 fp =fopen("alp.txt","w");//1.只写打开一个文件 11 if (fp == NULL) 12 { 13 cout << "can't open alp.txt" << endl; 14 exit(0); 15 } 16 gets(s); 17 i=0; //2. i 赋初值 18 while (s[i] != '\0') 19 { 20 if (s[i] >= 'a'&&s[i] <= 'z') 21 s[i] = s[i] - 'a' + 'A'; 22 else if(s[i] >= 'A'&& s[i] <= 'Z')//3. else if 23 s[i] = s[i] - 'A' + 'a'; 24 i++; 25 } 26 fputs(s,fp);//4.写文件 27 fclose(fp); 28 system("pause"); 29 return 0; 30 }
5、定义了一个日期类,具有设置日期、判断闰年、输出日期等功能。程序对2018年8月23日进行测试。
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Tdate 4 { 5 private: //1. 6 int year,month,day; 7 public: 8 void setdate(int y,int m,int d) 9 {year=y; month=m; day=d;} 10 int isleapyear()//要求为闰年时函数的返回值为1,否则为0 11 { 12 if(year%400==0||(year%4==0&&year%100!=0)) 13 return 1; 14 else 15 return 0; 16 } 17 void print(); 18 }; 19 void Tdate::print() //2. 20 {cout<<year<<"."<<month<<"."<<day<<endl;} 21 22 int main() 23 { 24 Tdate *date1; 25 date1 = new Tdate(); //3. 26 date1->setdate(2018,8,23); 27 date1->print(); 28 if(date1->isleapyear()) //4. 29 cout<<"leap year."<<endl; 30 else 31 cout<<"not leap year."<<endl; 32 system("pause"); 33 return 0; 34 }
6、某球类比赛根据第一阶段的积分情况将8支队伍分成两组再进行第二阶段的比赛,分组原则是:积分第1名分在A组,第2名分在B组,第3名分在A组,第4名分在B组,依次类推。
1 #define N 8 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 struct Team 5 { 6 char name[30]; 7 int score; 8 }; 9 int main() 10 { 11 Team t[N], t1[N/2], t2[N/2]; 12 int i, j,imax; 13 for (i = 0; i < N; i++) 14 cin >> t[i].name >> t[i].score; 15 /* 交换排序 */ 16 for (i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) 17 { 18 imax = i;//1. 19 for (j = imax + 1; j < N; j++) 20 if (t[imax].score<t[j].score) //2. 21 imax = j; 22 if (imax != i) 23 { 24 Team temp = t[i];//3. 25 t[i] = t[imax]; 26 t[imax] = temp; 27 } 28 } 29 for (i = 0; i < N; i++) 30 if (i%2==0) //4. 31 t1[i/2] = t[i]; 32 else 33 t2[i/2] = t[i]; 34 cout << "A组队伍及积分:" << endl; 35 for (i = 0; i < N / 2; i++) 36 cout << t1[i].name << ' '<<t1[i].score <<endl; 37 cout << "B组队伍及积分:" << endl; 38 for (i = 0; i < N / 2; i++) 39 cout << t2[i].name << ' ' << t2[i].score<<endl; 40 system("pause"); 41 return 0; 42 }
7、函数invert的功能是将字符串s倒序存放。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 void invert(char s[]);//1. 7 char s[100]; 8 cin>>s; 9 invert(s);//2. 10 cout<<s<<endl; 11 system("pause"); 12 return 0; 13 } 14 void invert(char s[]) 15 { 16 int i,len; 17 char ch; 18 len=strlen(s); //3. 19 for(i=0;i<len/2;i++) 20 { 21 ch=s[i]; 22 s[i]=s[len-1-i];//4. 23 s[len-1-i]=ch; 24 } 25 }
8、验证“满足公式 p=n*n+n+41 (n是正整数)的p一定是素 数”这个说法的不正确性。
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int fun(int p) 4 { 5 int n; 6 for (n=2; p%n != 0; n++);//1. 7 return n==p; //2. 8 } 9 int main() 10 { 11 int n = 1, p; 12 do 13 { 14 p = n * n + n + 41; 15 if (!fun(p)) //3. 16 break; 17 n++; //4. 18 } while (1); 19 cout<< p<<"="<<n<<"*"<<n<<"+"<<n<<"+41不是素数,故结论不正确"<<endl; 20 system("pause"); 21 return 0; 22 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号