C++ Primer第5版 第九章课后练习答案
合集《C++ Primer第5版》 课后练习答案 - 丸子球球 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
练习9.1
(a)list更合适,因为按照字典序插入到容器中代表需要在容器中间插入元素
(b)deque更合适,因为deque支持双端插入和删除
(c)无具体的插入删除操作,读取整数数量也是未知,可以选择vector
练习9.2
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::list<std::deque<int>> lq;
}
练习9.3
指向同一个容器的元素,或者尾后迭代器
end不在begin之前
练习9.4
bool find(vector<int>::const_iterator& begin, vector<int>::const_iterator& end, int i) {
while (begin != end) {
if (*begin == i)return true;
}
return false;
}
练习9.5
vector<int>::const_iterator& find(vector<int>::const_iterator& begin, vector<int>::const_iterator& end, int i) {
while (begin != end) {
if (*begin == i)return begin;
}
std::cerr << "don't find the num in the arrange";
return end;
}
练习9.6
在C++定义的容器类型中,只有vector和queue容器提供迭代器算数运算和除!=和==之外的关系运算
练习9.7
vector
练习9.8
读取
list
写入
list
练习9.9
cbegin返回的是const迭代器对象,begin不是
练习9.10
it1:vector
it2:constvector
it4:const vector
练习9.11
vector<int> v1;//空
vector<int> v2(v1);//v1的拷贝
vector<int> v3{ 0,1,2,3 };//初始化为初始化列表的拷贝
vector<int> v4(v3.begin(), v3.end());//初始化为迭代器之间元素的拷贝
vector<int> v5(10);//包含10个元素,每一个都被值初始化为0
vector<
练习9.12
接受一个容器创建其拷贝的构造函数:要求具有相同的容器类型,保存的是相同的元素类型
接受两个迭代器创建拷贝的构造函数:只要求迭代器范围内的元素类型相同
练习9.13
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> li{ 0,1,2,3 };
vector<double> vd(li.begin(), li.end());
for (auto i : vd)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
vector<int> vi{ 0,1,2,3 };
vector<double> vd2(vi.begin(), vi.end());
for (auto i : vd2)
cout << i << " ";
}
练习9.14
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<const char*> lc;
vector<string> vs;
vs.assign(lc.begin(), lc.end());
}
练习9.15
template<typename T>
bool check(const vector<T>& v1, const vector<T>& v2) {
return v1 == v2;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<string> vs1{ "012" };
vector<string> vs2{ "012","123" };
cout << (check(vs1, vs2) ? "相等" : "不相等");
}
练习9.16
template<typename T>
bool check(const list<T>& v1, const vector<T>& v2) {
if (v1.size() == v2.size()) {
auto j = v2.begin();
for (auto i = v1.begin(); i !=v1.end() ; i++,j++) {
if (*i != *j)return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<string> vs1{ "012" };
vector<string> vs2{ "012","123" };
cout << (check(vs1, vs2) ? "相等" : "不相等");
}
练习9.17
要求不是无序关联容器,c1和c2必须是相同类型的容器,且必须保存相同类型的元素
练习9.18
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::deque<string> ds;
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
ds.emplace_back(s);
s.clear();
}
for (auto it = ds.begin(); it != ds.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
练习9.19
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<string> ls;
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
ls.emplace_back(s);
s.clear();
}
for (auto it = ls.begin(); it != ls.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
练习9.20
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
list<int> li;
int i;
deque<int> di1, di2;
while (cin >> i) {
li.emplace_back(i);
}
for (auto it = li.begin(); it != li.end(); it++) {
if ((*it) % 2)di1.emplace_back(*it);
else di2.emplace_back(*it);
}
}
练习9.21
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<string> vst;
string word;
auto iter = vst.begin();
while (cin >> word) {
iter = vst.insert(iter, word);
}
}
将iter初始化为vst.begin(),第一次调用insert会将我们刚刚读入的string插入到iter所指向的元素之前的位置。
练习9.22
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<int> iv{ 0,1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int>::iterator iter = iv.begin(), mid = iv.begin() + iv.size() / 2;
int some_val = 0;
while (iter!=mid)
{
if (*iter == some_val)
iv.insert(iter, 2 * some_val);
}
}
该程序会在满足程序的情况下在vector开头插入元素,导致迭代器失效,应更新循环中的迭代器,并保证迭代器不会陷入无限循环
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<int> iv{ 0,1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int>::iterator iter = iv.begin(), mid = iv.begin() + iv.size() / 2;
int some_val = 0;
while (iter!=mid)
{
if (*iter == some_val) {
iter = iv.insert(iter, 2 * some_val);
iter += 2;
}
else
iter++;
mid = iv.begin() + iv.size() / 2;
}
}
练习9.23
val,val2,val3和val4的值都相同
练习9.24
at:有未经处理的异常: Microsoft C++ 异常: std::out_of_range
下标运算符:vector subscript out of range
front:front() called on empty vector
begin:cant't dereference value-initialized vector iterator
练习9.25
elem1与elem2相等不会删除容器元素,如果elem2时尾后迭代器会删除所有elem1到elem2的所有元素(不包括elem2),如果elem1和elem2皆为尾后迭代器则不会删除元素
练习9.26
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int ia[] = { 0 ,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,55,89 };
vector<int> iv;
iv.assign(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
auto it = iv.begin();
while (it!=iv.end())
{
if (!(*it % 2))
it = iv.erase(it);
else it++;
}
list<int> il;
il.assign(ia, ia + sizeof(ia) / sizeof(int));
auto it2 = il.begin();
while (it2 != il.end())
{
if (*it2 % 2)
it2 = il.erase(it2);
else it2++;
}
}
练习9.27
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
forward_list<int> flst = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto prev = flst.before_begin(), curr = flst.begin();
while (curr != flst.end()) {
if (*curr % 2) {
curr = flst.erase_after(prev);
}
else {
prev = curr;
curr++;
}
}
}
练习9.28
void fl_find_insert(forward_list<string>& flst, string& s1, string& s2) {
auto prev = flst.before_begin(), curr = flst.begin();
while (curr != flst.end()) {
if (*curr == s1) {
flst.insert_after(prev, s2);
return;
}
else {
prev = curr;
++curr;
}
}
flst.insert_after(prev, s2);
}
练习9.29
vec.resize(100):调整vec大小为100,由于vec原来包含25个元素,将75个值为0的元素添加到vec末尾
vec.resize(10):调整vec大小为10,由于vec原来包含25个元素,将vec末尾15个元素删除
练习9.30
元素必须能进行值初始化,若为类类型元素则必须提供默认值或者默认构造函数
练习9.31
list迭代器没有递增递减的操作,需要修改为advance(iter, 2);
forward_list没有insert和erase操作需要修改
练习9.32
不合法,++递增符改变了iter的值,将产生未定义的行为。因为赋值运算符左右两端的运算对象都用到了iter,并且右侧的运算对象还改变了iter的值
练习9.33
迭代器失效
练习9.34
遍历容器,查找所有为奇数的元素并复制该元素插入到容器中,但因为只递增了一次导致程序只会卡在第一次找到奇数的时候
练习9.35
容器的size是指它已经保存的元素的数目
容器的capacity是在不分配新的内存空间的前提下他最多能保存多少元素
练习9.36
不可能,因为size必然小于等于capacity
练习9.37
list没有capacity是因为不要求空间是连续的
array没有capacity是因为array不允许修改空间大小
练习9.38
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<int> vec1;
int a;
while (cin >> a)
{
vec1.push_back(a);
cout << "vector的大小" << vec1.size() << endl;;
cout << "vector的容量" << vec1.capacity() << endl;
}
}
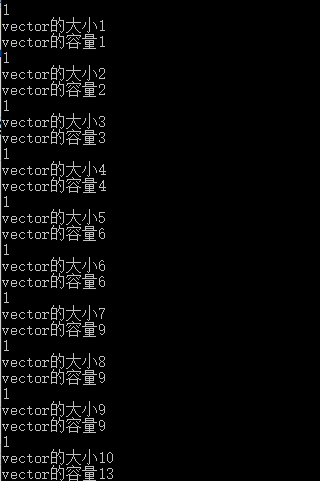
练习9.39
为vector分配1024个string元素的内存,传入值,然后插入容器一半数量的空string元素
练习9.40
256:1024
512:1024
1000:1536
1024:2304
练习9.41
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<char>cvec(10, 'c');
char *charray=new char[cvec.size()];
memcpy(charray, &cvec[0], cvec.size() * sizeof(char));
string s(charray);
}
练习9.42
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string s;
s.reserve(100);
char c;
while (cin >> c) {
s.push_back(c);
}
}
练习9.43
void str_find_replace(string& s, string& oldVal, string& newVal) {
auto it1 = s.begin(), it2 = newVal.begin(), it3 = newVal.end();
for (; it1 != s.end() - oldVal.size(); it1++) {
if (s.substr(it1 - s.begin(), oldVal.size()) == oldVal) {
s.erase(it1 - s.begin(), oldVal.size());
it1 = s.insert(it1, newVal.begin(), newVal.end());
it1 += newVal.size();
}
}
}
练习9.44
void str_find_replace(string& s, string& oldVal, string& newVal) {
auto it1 = s.begin(), it2 = newVal.begin(), it3 = newVal.end();
for (; it1 != s.end() - oldVal.size(); it1++) {
if (s.substr(it1 - s.begin(), oldVal.size()) == oldVal) {
s.replace(it1, it1 + oldVal.size(), newVal);
it1 += newVal.size();
}
}
}
练习9.45
string& last) {
s.insert(0, prev);
s.append(last);
}
练习9.46
string& last) {
s.insert(0, prev);
s.insert(s.size(), last);
}
练习9.47
只用find_first_of的
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string s = "ab2c3d7R4E6";
string numbers("0123456789");
auto pos = 0;
while ((pos = s.find_first_of(numbers, pos)) != string::npos) {
cout << s[pos++];
}
auto pos1 = 0, pos2 = 0;
while ((pos2 = s.find_first_of(numbers, pos1)) != string::npos) {
for (; pos1 != pos2; ++pos1)
cout << s[pos1];
++pos1;
}
if (pos1 != s.find_last_not_of(numbers))cout << s[pos1];
return 0;
}
只用find_first_not_of的
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string s = "ab2c3d7R4E6";
string numbers("0123456789");
auto pos1 = 0, pos2 = 0;
while ((pos2 = s.find_first_not_of(numbers, pos1)) != string::npos) {
for (; pos1 != pos2; ++pos1)
cout << s[pos1];
++pos1;
}
if (pos1 != s.find_last_not_of(numbers))cout << s[pos1];
auto pos = 0;
while ((pos = s.find_first_not_of(numbers, pos)) != string::npos){
cout << s[pos++];
}
return 0;
}
练习9.48
string::npos
练习9.49
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string ascender("bdfhklt"); //上出头部分单词
string descender("gjpqy"); //下出头部分单词
std::ifstream ifs(argv[1]);
string s, maxs;
auto max = 0;
string::size_type pos;
if (ifs)
{
while (!ifs.eof())
{
ifs >> s;
if (s.find_first_of(ascender) == string::npos & s.find_first_of(descender) == string::npos&s.size()>max) {
max = s.size();
maxs = s;
}
s.clear();
}
}
return 0;
}
练习9.50
计算整型值的string之和
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<string> strvec;
long long ll = 0;
for (const auto& it : strvec) {
ll += stoll(it);
}
cout << ll << endl;
return 0;
}
计算浮点值的string之和
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vector<string> strvec;
long double ld = 0;
for (const auto& it : strvec) {
ld += stold(it);
}
cout << ld << endl;
return 0;
}
练习9.51
#ifndef DATE_H_
#define DATE_H_
#include<string>
using std::string;
class Date
{
public:
Date(string&);
~Date();
private:
unsigned year;
unsigned month;
unsigned day;
void str_to_month(string &str,string::size_type& pos);
};
Date::Date(string &s)
{
string::size_type pos1, pos2;
if (pos1 = s.find_first_of(",/") == string::npos) {
pos1 = s.find_first_of(" ");
pos2 = s.find_last_of(" ");
str_to_month(s, pos1);
day = stoul(s.substr(pos1 + 1, pos2));
year = stoul(s.substr(pos2 + 1, s.size()));
}
else if (pos1 = s.find_first_of(",") == string::npos) {
pos1 = s.find_first_of("/");
pos2 = s.find_last_of("/");
str_to_month(s, pos1);
day = stoul(s.substr(pos1 + 1, pos2));
year = stoul(s.substr(pos2 + 1, s.size()));
}
else if (pos1 = s.find_first_of("/") == string::npos) {
pos1 = s.find_first_of(" ");
pos2 = s.find_last_of(",");
str_to_month(s, pos1);
day = stoul(s.substr(pos1 + 1, pos2));
year = stoul(s.substr(pos2 + 1, s.size()));
}
}
Date::~Date()
{
}
inline void Date::str_to_month(string& s, string::size_type& pos1)
{
if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Jan" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "January") {
month = 1;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Feb" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "February") {
month = 2;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Mar" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "March") {
month = 3;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Apr" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "April") {
month = 4;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "May" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "May") {
month = 5;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Jun" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "June") {
month = 6;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Jul" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "July") {
month = 7;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Aug" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "August") {
month = 8;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Sept" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "September") {
month = 9;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Oct" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "October") {
month = 10;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Nov" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "November") {
month = 11;
}
else if (s.substr(0, pos1) == "Dec" || s.substr(0, pos1) == "December") {
month = 12;
}
else {
month = stoul(s.substr(0, pos1));
}
}
练习9.52
unsigned get_operator_level(const char& c) {
if (c == ')')return 4;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/')return 3;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-')return 2;
else return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string s("(11+21)*13-(62+21)/53");
string ns;
stack<char> chars;
stack<long> numbers;
bool other = true;
for (const auto&c:s) {
if (isdigit(c)) {
ns.insert(ns.end(), c);
}
else if(chars.empty()||c=='('){
chars.push(c);
}
else if (c != ')') {
while (!chars.empty() & get_operator_level(chars.top()) >= get_operator_level(c)) {
ns.insert(ns.end(), chars.top());
chars.pop();
}
chars.push(c);
ns.insert(ns.end(), ' ');
}
else {
while (chars.top() != '(') {
ns.insert(ns.end(), chars.top());
chars.pop();
}
chars.pop();
}
}
while (!chars.empty()) {
ns.insert(ns.end(), chars.top());
chars.pop();
}
for (const auto& c : ns) {
if (isdigit(c) & other) {
long num = 0;
if (!numbers.empty()) {
num = numbers.top();
numbers.pop();
}
num = num * 10 + c - '0';
numbers.push(num);
}
else if (isdigit(c)) {
numbers.push(c - '0');
other = true;
}
else if (isspace(c)) {
other = false;
}
else {
long num1, num2;
num2 = numbers.top();
numbers.pop();
num1 = numbers.top();
numbers.pop();
if (c == '+')numbers.push(num1 + num2);
else if (c == '-')numbers.push(num1 - num2);
else if (c == '*')numbers.push(num1 * num2);
else if (c == '/')numbers.push(num1 / num2);
other = false;
}
}
return 0;
}
unsigned get_operator_level(const char& c) {
if (c == ')')return 4;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/')return 3;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-')return 2;
else return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string s("(11+21)*13-(62+21)/53");
string ns;
stack<char> chars;
stack<long> numbers;
bool other = true;
for (const auto&c:s) {
if (isdigit(c)) {
ns.insert(ns.end(), c);
}
else if(chars.empty()||c=='('){
chars.push(c);
}
else if (c != ')') {
while (!chars.empty() & get_operator_level(chars.top()) >= get_operator_level(c)) {
ns.insert(ns.end(), chars.top());
chars.pop();
}
chars.push(c);
ns.insert(ns.end(), ' ');
}
else {
while (chars.top() != '(') {
ns.insert(ns.end(), chars.top());
chars.pop();
}
chars.pop();
}
}
while (!chars.empty()) {
ns.insert(ns.end(), chars.top());
chars.pop();
}
for (const auto& c : ns) {
if (isdigit(c) & other) {
long num = 0;
if (!numbers.empty()) {
num = numbers.top();
numbers.pop();
}
num = num * 10 + c - '0';
numbers.push(num);
}
else if (isdigit(c)) {
numbers.push(c - '0');
other = true;
}
else if (isspace(c)) {
other = false;
}
else {
long num1, num2;
num2 = numbers.top();
numbers.pop();
num1 = numbers.top();
numbers.pop();
if (c == '+')numbers.push(num1 + num2);
else if (c == '-')numbers.push(num1 - num2);
else if (c == '*')numbers.push(num1 * num2);
else if (c == '/')numbers.push(num1 / num2);
other = false;
}
}
return 0;
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)