MySQL/mariadb知识点——操作篇(4)数据操作语句

INSERT插入数据
单挑记录插入
INSERT INTO tb_name (col1,col2,...) VALUES (val1,val2,...);
示例:
insert into tablename(字段1名称,字段2名称,......)values(字段1值,字段2值,...)
MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT students(id,name,ages,gender) VALUES (1,'tom',26,'M');
MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT students(name,ages,gender) VALUES ('jerry',19,'M');
MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT students(name,ages,gender) VALUES ('maria',19,'M');
MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT students SET name='ouyangfeng',ages=56,gender='M';
多条记录插入
INSERT INTO tb_name (col1,col2,...) VALUES (val1,val2,...)[,(val1,val2,...),...];
MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT students(name,ages,gender) VALUES ('xiaolongnv',18,'F'),('dongfangbubai',28,'F');
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students; +----+---------------+------+--------+ | id | name | ages | gender | +----+---------------+------+--------+ | 1 | tom | 26 | M | | 2 | jerry | 19 | M | | 3 | maria | 19 | M | | 4 | xiaolongnv | 18 | F | | 5 | dongfangbubai | 28 | F | | 6 | ouyangfeng | 56 | M | +----+---------------+------+--------+
从其他表查询数据保存到此表中
MariaDB [testdb]> ALTER TABLE students ADD address TEXT; #加个字段做测试用
MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT students(name,address) SELECT user,host FROM mysql.user;
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students; +----+---------------+------+--------+-----------+ | id | name | ages | gender | address | +----+---------------+------+--------+-----------+ | 1 | tom | 26 | M | NULL | | 2 | jerry | 19 | M | NULL | | 3 | maria | 19 | M | NULL | | 4 | xiaolongnv | 18 | F | NULL | | 5 | dongfangbubai | 28 | F | NULL | | 6 | ouyangfeng | 56 | M | NULL | | 7 | root | 0 | NULL | 127.0.0.1 | | 8 | root | 0 | NULL | ::1 | | 9 | | 0 | NULL | centos7 | | 10 | root | 0 | NULL | centos7 | | 11 | | 0 | NULL | localhost | | 12 | root | 0 | NULL | localhost | +----+---------------+------+--------+-----------+
UPDATE 修改数据
UPDATE tbl_name SET col1=value1,col2=value2,... WHERE col=value;
修改数据,主要通过where字句给定修改反而,而where字句的示例可以参考select常用语句;
示例:
MariaDB [testdb]> UPDATE students SET gender='F' WHERE id=3;
DELETE 删除数据
删除语句比较简单,主要是通过where字句给定删除范围,而where字句的示例可以参考select语句,删除前请确定给出条件没有任何问题,在不确定的情况下不要随意删除数据。
MariaDB [testdb]> DELETE FROM students WHERE name=''; #删除名字为空的记录 MariaDB [testdb]> TRUNCATE TABLE user; #情况表记录
注意:一定要有限制条件(WHERE | LIMIT),否则将修改所有行的指定字段
SELECT 数据查询
基础查询
1、选择
示例:
查询maria的信息
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students WHERE name='maria';
查询2到5号学生的信息
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students WHERE id BETWEEN 2 AND 5;
查询jerry和xiaolongnv的信息
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students WHERE name IN ('jerry','xiaolongnv');
查询年龄不为空的信息
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students WHERE gender IS NOT NULL;
查询姓名中包含'o'的信息
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students WHERE name LIKE '%o%';
2、投影
查询时给字段添加别名
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT user AS 用户,host AS 主机,password AS 密码 FROM mysql.user;
3、分组
示例
查询男生、女生年龄的平均值
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT gender,AVG(ages) FROM students GROUP BY gender;
只显示男生的平均年龄信息
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT gender,AVG(ages) FROM students GROUP BY gender HAVING gender='M';
4、排序
示例
按年龄排序,倒序显示
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY ages DESC;
按年龄排序,过滤年龄大于0的,正序排序,取前三条记录
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students WHERE ages > 0 ORDER BY ages LIMIT 3;
5、常用参数

1 AS:别名 2 WHERE:指明过滤条件以实现“选择”的功能 3 +, -, *, /, %:算术操作符 4 =, !=, <>, >, <, >=, <=:比较操作符 5 BETWEEN min_num AND max_num:在min_num和max_mun之间 6 IN (element1,element2,...):在element...中的 7 IS NULL:为空 8 IS NOT NULL:不为空 9 LIKE:做匹配,像。。。 10 %:任意长度的任意字符 11 _:单个任意字符 12 RLIKE:正则表达式,不建议用 13 REGEXP:同上 14 NOT, AND, OR, XOR:逻辑操作符 15 GROUP BY:根据指定的条件把查询结果进行“分组”以用于做“聚合”运算 16 AVG() 平均数 17 MAX() 最大数 18 MIN() 最小数 19 COUNT() 统计 20 SUM() 求和 21 HAVING :对分组聚合运算后的结果指定过滤条件。类似WHERE的作用,但只能在分组中使用 22 ORDER BY:排序 23 ASC:正序,默认 24 DESC:倒序 25 -KEYWORD:在排序时在关键字前加-可以避免把NULL排在前边 26 LIMIT [[offset,]row_count]:对查询的结果进行输出行数数量限制
多表查询
在开始多表查询之前,我们对之前的表进行下手动扩展
MariaDB [testdb]> DELETE FROM students WHERE id BETWEEN 7 AND 12; MariaDB [testdb]> CREATE TABLE score (id TINYINT(2) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,score TINYINT(3)); MariaDB [testdb]> ALTER TABLE students ADD sid TINYINT(2); MariaDB [testdb]> UPDATE students SET sid=6 WHERE id=6; MariaDB [testdb]> INSERT score SET score=87; MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students; +----+---------------+------+--------+---------+------+ | id | name | ages | gender | address | sid | +----+---------------+------+--------+---------+------+ | 1 | tom | 26 | M | NULL | 1 | | 2 | jerry | 19 | M | NULL | 2 | | 3 | maria | 19 | F | NULL | 3 | | 4 | xiaolongnv | 18 | F | NULL | 4 | | 5 | dongfangbubai | 28 | F | NULL | 5 | | 6 | ouyangfeng | 56 | M | NULL | 6 | +----+---------------+------+--------+---------+------+ MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM score; +----+-------+ | id | score | +----+-------+ | 1 | 99 | | 2 | 98 | | 3 | 88 | | 4 | 68 | | 5 | 78 | | 6 | 87 | +----+-------+
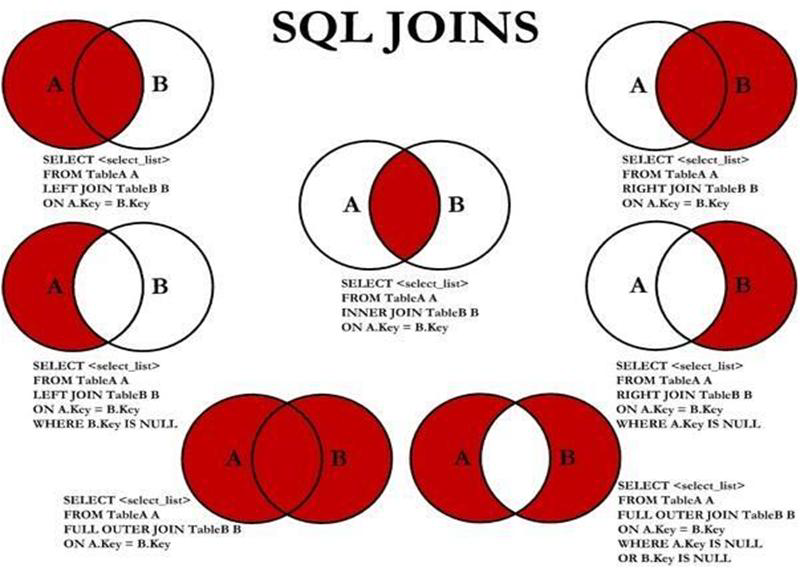
1、俩张表取交集
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students AS s,score AS o WHERE s.sid=o.id;
2、JOIN ON:交叉连接
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students JOIN score;
3、INNER JOIN ON:内连接
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT t.name,s.score FROM students AS t INNER JOIN score AS s ON t.sid=s.id; +---------------+-------+ | name | score | +---------------+-------+ | tom | 99 | | jerry | 98 | | maria | 88 | | xiaolongnv | 68 | | dongfangbubai | 78 | | ouyangfeng | 87 | +---------------+-------+
4、LEFT OUTER JOIN ON:左外连接
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT t.name,s.score FROM students AS t LEFT JOIN score AS s ON t.sid=s.id; #左外连接 +---------------+-------+ | name | score | +---------------+-------+ | tom | 99 | | jerry | 98 | | maria | 88 | | xiaolongnv | 68 | | dongfangbubai | 78 | | ouyangfeng | 87 | +---------------+-------+
5、RIGHT OUTER JOIN ON:右外连接
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students AS t RIGHT JOIN score AS s ON t.sid=s.id; #右外连接
6、UNION ON:完全外连接
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT name,address FROM students UNION
-> SELECT user,host FROM mysql.user;
+---------------+-----------+
| name | address |
+---------------+-----------+
| tom | NULL |
| jerry | NULL |
| maria | NULL |
| xiaolongnv | NULL |
| dongfangbubai | NULL |
| ouyangfeng | NULL |
| root | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | ::1 |
| | centos7 |
| root | centos7 |
| | localhost |
| root | localhost |
+---------------+-----------+
7、自连接
MariaDB [testdb]> ALTER TABLE students ADD tid TINYINT(2); #再加一个tid字段 MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT * FROM students; +----+---------------+------+--------+---------+------+------+ | id | name | ages | gender | address | sid | tid | +----+---------------+------+--------+---------+------+------+ | 1 | tom | 26 | M | NULL | 1 | 2 | | 2 | jerry | 19 | M | NULL | 2 | 1 | | 3 | maria | 19 | F | NULL | 3 | 4 | | 4 | xiaolongnv | 18 | F | NULL | 4 | 5 | | 5 | dongfangbubai | 28 | F | NULL | 5 | 4 | | 6 | ouyangfeng | 56 | M | NULL | 6 | 4 | +----+---------------+------+--------+---------+------+------+
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT s1.name AS studentname,s2.name AS teachername FROM students AS s1 INNER JOIN students AS s2 ON s1.id=s2.tid; +---------------+---------------+ | studentname | teachername | +---------------+---------------+ | jerry | tom | | tom | jerry | | xiaolongnv | maria | | dongfangbubai | xiaolongnv | | xiaolongnv | dongfangbubai | | xiaolongnv | ouyangfeng | +---------------+---------------+
子查询
子查询:在查询语句嵌套着查询语句,性能较差,基于某语句的查询结果再次进行的查询
1、用在WHERE子句中的子查询
- 用于比较表达式中的子查询;子查询仅能返回单个值
示例:
查询大于平均年龄的同学
MariaDB [testdb]> SELECT name,ages FROM students WHERE ages > (SELECT AVG(ages) FROM students);
- 用于IN中的子查询:子查询应该单键查询并返回一个或多个值从构成列表
2、用于FROM子句中的子查询
SELECT tb_alias.col1,... FROM (SELECT clause) AS tb_alias WHERE Clause;




