转自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37970694/article/details/79485158
BatchNormalization(BN)的提出:paper[链接](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03167.pdf)
论文中对BN的解释:Making normalization a part of the model architecture and performing the normalization for each training mini-batch. 使用BN归一化的目的是使输入维持在0均值,单位方差。
caffe中的BN由两部分实现:batch_norm_layer和scale_layer,这两个层一起使用。关于为什么要结合两部分可参考百度回答:https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/621624946902864092.html,即batch_norm对输入进行归一化操作,scale对归一化后的输入进行尺度缩放和平移操作。
caffe 中为什么bn层要和scale层一起使用
这个问题bai首先你要理解batchnormal是做什么的du。它其实做了两件事zhi。
1) 输入归一化 x_norm = (x-u)/std, 其中u和std是个累计计算的均值和方dao差。
2)y=alpha×x_norm + beta,对归一化后的x进行比例缩放和位移。其中alpha和beta是通过迭代学习的。
那么caffe中的bn层其实只做了第一件事。scale层做了第二件事。
这样你也就理解了scale层里为什么要设置bias_term=True,这个偏置就对应2)件事里的beta。
1) 输入归一化 x_norm = (x-u)/std, 其中baiu和std是个du累计计算zhi的均值和方差。
2)y=alpha×x_norm + beta,对归一化后dao的x进行比例缩放和位移。其中alpha和beta是通过迭代学习的。
那么caffe中的bn层其实只做了第一件事,scale层做了第二件事,所以两者要一起使用。
一,在Caffe中使用Batch Normalization需要注意以下两点:
1. 要配合Scale层一起使用。
2. 训练的时候,将BN层的use_global_stats设置为false,然后测试的时候将use_global_stats设置为true。
二,基本公式梳理:
Scale层主要完成 top=alpha∗bottom+betatop=alpha∗bottom+beta的过程,则层中主要有两个参数alphaalpha与betabeta,
求导会比较简单。∂y∂x=alpha;∂y∂alpha=x;∂y∂beta=1。 需要注意的是alphaalpha与betabeta均为向量,针对输入的channelschannels进行的处理,因此不能简单的认定为一个floatfloat的实数。
三,具体实现该部分将结合源码实现解析scale层:
在Caffe proto中ScaleParameter中对Scale有如下几个参数:
1,基本成员变量,基本成员变量主要包含了Bias层的参数以及Scale层完成对应通道的标注工作。
2,基本成员函数,主要包含了LayerSetup,Reshape ,Forward和Backward ,内部调用的时候bias_term为true的时候会调用biasLayer的相关函数。
3,Reshape 调整输入输出与中间变量,Reshape层完成许多中间变量的size初始化。
4,Forward 前向计算,前向计算,在BN中国紧跟着BN的归一化输出,完成乘以alpha与+bias的操作,由于alpha与bias均为C的向量,因此需要先进行广播。
5,Backward 反向计算,主要求解三个梯度,对alpha 、beta和输入的bottom(此处的temp)。
一.公式
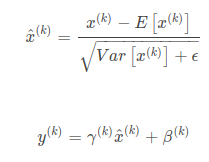
二.源码
2.1 层参数定义
BatchNorm层有3个参数: ①use_global_stats:在训练时设置为false(因为训练时,BN的作用对象是batch,而不是整个数据集),测试时设置为true;当为false 时批处理规范化使用当前batch的均值和标准差,采用滑动平均计算新的均值和方差;
为true时,强制使用模型中存储的BatchNorm层保存的全局均值与方差参数。 ②moving_average_fraction:滑动平均的系数。用来在训练阶段计算更新全局均值和标准差。 ③eps:公式中的小量,防止除以0 message BatchNormParameter { optional bool use_global_stats = 1; optional float moving_average_fraction = 2 [default = .999]; optional float eps = 3 [default = 1e-5]; } Scale层参数: ①axis:处理维度 ②FillerParameter:filler均值和方差的填充方式 ③bias_term:偏置项,是否学习bias(b):y=ax+b ④FillerParameter:bias_filler偏差的初始填充方式 message ScaleParameter { optional int32 axis = 1 [default = 1]; optional int32 num_axes = 2 [default = 1]; optional FillerParameter filler = 3; optional bool bias_term = 4 [default = false]; optional FillerParameter bias_filler = 5; }
2.2 BatchNorm层
(1)LayerSetUp模块
template <typename Dtype> void BatchNormLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { //获取BatchNormParameter参数 BatchNormParameter param = this->layer_param_.batch_norm_param(); //获取moving_average_fraction参数列表 moving_average_fraction_ = param.moving_average_fraction(); use_global_stats_ = this->phase_ == TEST; //如果参数列表里面定义了use_global_stats,则从参数列表获取 if (param.has_use_global_stats()) use_global_stats_ = param.use_global_stats(); //计算channels_ if (bottom[0]->num_axes() == 1) channels_ = 1; else channels_ = bottom[0]->shape(1); //获取参数列表里的eps参数 eps_ = param.eps(); if (this->blobs_.size() > 0) { LOG(INFO) << "Skipping parameter initialization"; } else { //初始化3个blob //前两个blob[0][1]的大小为channels_,第三个blob[2]的大小为1 this->blobs_.resize(3); vector<int> sz; //将channels_保存到sz中 sz.push_back(channels_); this->blobs_[0].reset(new Blob<Dtype>(sz)); this->blobs_[1].reset(new Blob<Dtype>(sz)); sz[0] = 1; this->blobs_[2].reset(new Blob<Dtype>(sz)); for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { caffe_set(this->blobs_[i]->count(), Dtype(0), this->blobs_[i]->mutable_cpu_data()); } } // Mask statistics from optimization by setting local learning rates // for mean, variance, and the bias correction to zero. for (int i = 0; i < this->blobs_.size(); ++i) { if (this->layer_param_.param_size() == i) { //新增参数 ParamSpec* fixed_param_spec = this->layer_param_.add_param(); fixed_param_spec->set_lr_mult(0.f); } else { CHECK_EQ(this->layer_param_.param(i).lr_mult(), 0.f) << "Cannot configure batch normalization statistics as layer " << "parameters."; } } }
(2)Reshape模块
template <typename Dtype> void BatchNormLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { if (bottom[0]->num_axes() >= 1) CHECK_EQ(bottom[0]->shape(1), channels_); //输出形状和输入形状相同 top[0]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]); vector<int> sz; sz.push_back(channels_); //初始化mean_,variance_,temp_,x_norm_,batch_sum_multiplier_ mean_.Reshape(sz);//通道数,即channel值大小,存储的是均值 variance_.Reshape(sz);//通道数,即channel值大小,存储的是方差值 temp_.ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]);//temp_中存储的是减去mean_后的每一个数的方差值。 x_norm_.ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]); sz[0] = bottom[0]->shape(0); batch_sum_multiplier_.Reshape(sz);//batch_size 大小 //定义spatial_sum_multiplier_的形状 int spatial_dim = bottom[0]->count()/(channels_*bottom[0]->shape(0));//图像height*width if (spatial_sum_multiplier_.num_axes() == 0 || spatial_sum_multiplier_.shape(0) != spatial_dim) { sz[0] = spatial_dim; spatial_sum_multiplier_.Reshape(sz); //multiplier_data=spatial_dim Dtype* multiplier_data = spatial_sum_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data(); //分配一副图像的空间 //初始化spatial_sum_multiplier中的值为1*multiplier_data即saptial_dim caffe_set(spatial_sum_multiplier_.count(), Dtype(1), multiplier_data); //初始化值为 1, } //初始化num_by_chans_ = channels_*bottom[0]->shape(0) int numbychans = channels_*bottom[0]->shape(0); //batch_size*channel if (num_by_chans_.num_axes() == 0 || num_by_chans_.shape(0) != numbychans) { sz[0] = numbychans; num_by_chans_.Reshape(sz); //初始化batch_sum_multiplier_值为1 batch_sum_multiplier_ batch_size大小的空间,也是辅助在计算mean_时,将所要图像的相应的通道值相加。 caffe_set(batch_sum_multiplier_.count(), Dtype(1), batch_sum_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data()); //分配空间,初始化为 1,分配空间,初始化为 1, } }
(3)Forward_cpu模块
template <typename Dtype> void BatchNormLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { //输入blob:bottom_data const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data(); //输出blob:top_data Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data(); //batch的数量N(num)*C*H*W int num = bottom[0]->shape(0); //N*C*H*W/N*C=H*W,即spatial_dim=H*W int spatial_dim = bottom[0]->count()/(bottom[0]->shape(0)*channels_); if (bottom[0] != top[0]) { //如果bottom和top的值不相等,则把bottom的值赋给top caffe_copy(bottom[0]->count(), bottom_data, top_data); } if (use_global_stats_) { //如果使用已经计算好的mean和variance //mean保存在blobs_[0]中,variance保存在blobs_[1]中 const Dtype scale_factor = this->blobs_[2]->cpu_data()[0] == 0 ? 0 : 1 / this->blobs_[2]->cpu_data()[0]; caffe_cpu_scale(variance_.count(), scale_factor, this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(), mean_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_scale(variance_.count(), scale_factor, this->blobs_[1]->cpu_data(), variance_.mutable_cpu_data()); } else { //否则需要自己计算均值和方差 // 最终num_by_chans_=channels_*spatial_dim //num_by_chans_=1./(num*spatial_dim) * bottom_data *spatial_sum_multiplier_ //bottom_data=num*channels_*(spatial_dim),即N*C*(H*W) //spatial_sum_multiplier_=spatial_dim caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1. / (num * spatial_dim), bottom_data, spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); //计算均值mean_=num_by_chans_*batch_sum_multiplier caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, num, channels_, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., mean_.mutable_cpu_data()); } // subtract mean //num_by_chans=1*batch_sum_multiplier_*mean_=channels*spatial_dim=mean_ caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num, channels_, 1, 1, batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), mean_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); //top_data=top_data - num_by_chans_*spatial_sum_multiplier_ //=top_data-mean_*spatial_dim=(x-E(x))^2 //=top_data-channels_*spatial_dim*spatial_dim caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1, -1, num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 1., top_data); if (!use_global_stats_) { // compute variance using var(X) = E((X-EX)^2) //将top_data的值保存到temp_中 caffe_sqr<Dtype>(top[0]->count(), top_data, temp_.mutable_cpu_data()); // (X-EX)^2 caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1. / (num * spatial_dim), temp_.cpu_data(), spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, num, channels_, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., variance_.mutable_cpu_data()); // E((X_EX)^2) // compute and save moving average //blobs_[2]=(moving_average_fraction_*blobs_[2])+1 this->blobs_[2]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] *= moving_average_fraction_; this->blobs_[2]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] += 1; //blobs_[0]=1*mean_+moving_average_fraction_*blobs_[0] caffe_cpu_axpby(mean_.count(), Dtype(1), mean_.cpu_data(), moving_average_fraction_, this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_data()); int m = bottom[0]->count()/channels_; Dtype bias_correction_factor = m > 1 ? Dtype(m)/(m-1) : 1; caffe_cpu_axpby(variance_.count(), bias_correction_factor, variance_.cpu_data(), moving_average_fraction_, this->blobs_[1]->mutable_cpu_data()); } // normalize variance //计算variances_=variance_+eps_ caffe_add_scalar(variance_.count(), eps_, variance_.mutable_cpu_data()); //求根号:公式中的分母 caffe_sqrt(variance_.count(), variance_.cpu_data(), variance_.mutable_cpu_data()); // replicate variance to input size //扩展variance到输入的每个batch上 caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num, channels_, 1, 1, batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), variance_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., temp_.mutable_cpu_data()); //top_data=top_data/temp_,即公式(1) caffe_div(temp_.count(), top_data, temp_.cpu_data(), top_data); // TODO(cdoersch): The caching is only needed because later in-place layers // might clobber the data. Can we skip this if they won't? //将最终计算结果保存在x_norm_中,在反向传播时调用 caffe_copy(x_norm_.count(), top_data, x_norm_.mutable_cpu_data()); }
(4)Backward_cpu模块
反向传播公式推导:(来自论文)
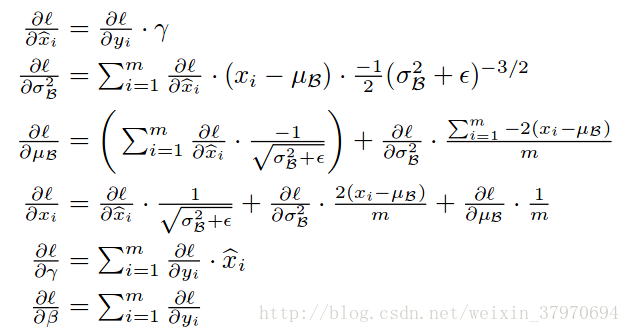
template <typename Dtype> void BatchNormLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top, const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) { const Dtype* top_diff; if (bottom[0] != top[0]) { top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff(); } else { caffe_copy(x_norm_.count(), top[0]->cpu_diff(), x_norm_.mutable_cpu_diff()); top_diff = x_norm_.cpu_diff(); } Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff(); if (use_global_stats_) { caffe_div(temp_.count(), top_diff, temp_.cpu_data(), bottom_diff); return; } const Dtype* top_data = x_norm_.cpu_data(); int num = bottom[0]->shape()[0]; int spatial_dim = bottom[0]->count()/(bottom[0]->shape(0)*channels_); // if Y = (X-mean(X))/(sqrt(var(X)+eps)), then // // dE(Y)/dX = // (dE/dY - mean(dE/dY) - mean(dE/dY \cdot Y) \cdot Y) // ./ sqrt(var(X) + eps) // // where \cdot and ./ are hadamard product and elementwise division, // respectively, dE/dY is the top diff, and mean/var/sum are all computed // along all dimensions except the channels dimension. In the above // equation, the operations allow for expansion (i.e. broadcast) along all // dimensions except the channels dimension where required. // sum(dE/dY \cdot Y) caffe_mul(temp_.count(), top_data, top_diff, bottom_diff); caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1., bottom_diff, spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, num, channels_, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., mean_.mutable_cpu_data()); // reshape (broadcast) the above caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num, channels_, 1, 1, batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), mean_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., bottom_diff); // sum(dE/dY \cdot Y) \cdot Y caffe_mul(temp_.count(), top_data, bottom_diff, bottom_diff); // sum(dE/dY)-sum(dE/dY \cdot Y) \cdot Y caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, channels_ * num, spatial_dim, 1., top_diff, spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, num, channels_, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., mean_.mutable_cpu_data()); // reshape (broadcast) the above to make // sum(dE/dY)-sum(dE/dY \cdot Y) \cdot Y caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num, channels_, 1, 1, batch_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), mean_.cpu_data(), 0., num_by_chans_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num * channels_, spatial_dim, 1, 1., num_by_chans_.cpu_data(), spatial_sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 1., bottom_diff); // dE/dY - mean(dE/dY)-mean(dE/dY \cdot Y) \cdot Y caffe_cpu_axpby(temp_.count(), Dtype(1), top_diff, Dtype(-1. / (num * spatial_dim)), bottom_diff); // note: temp_ still contains sqrt(var(X)+eps), computed during the forward // pass. caffe_div(temp_.count(), bottom_diff, temp_.cpu_data(), bottom_diff); }
2.3 Scale层
Scale层主要完成top(y)=alpha*bottom(x)+beta
反向传播求导:∂y∂x=alpha;∂y∂alpha=x;∂y∂beta=1∂y∂x=alpha;∂y∂alpha=x;∂y∂beta=1
(1)LayerSetUp层
template <typename Dtype> void ScaleLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { //获取scale层参数列表 const ScaleParameter& param = this->layer_param_.scale_param(); if (bottom.size() == 1 && this->blobs_.size() > 0) { LOG(INFO) << "Skipping parameter initialization"; } else if (bottom.size() == 1) { // scale is a learned parameter; initialize it axis_ = bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(param.axis()); const int num_axes = param.num_axes(); CHECK_GE(num_axes, -1) << "num_axes must be non-negative, " << "or -1 to extend to the end of bottom[0]"; if (num_axes >= 0) { CHECK_GE(bottom[0]->num_axes(), axis_ + num_axes) << "scale blob's shape extends past bottom[0]'s shape when applied " << "starting with bottom[0] axis = " << axis_; } this->blobs_.resize(1); const vector<int>::const_iterator& shape_start = bottom[0]->shape().begin() + axis_; const vector<int>::const_iterator& shape_end = (num_axes == -1) ? bottom[0]->shape().end() : (shape_start + num_axes); vector<int> scale_shape(shape_start, shape_end); this->blobs_[0].reset(new Blob<Dtype>(scale_shape)); FillerParameter filler_param(param.filler()); if (!param.has_filler()) {//填充方式和填充值 // Default to unit (1) filler for identity operation. filler_param.set_type("constant"); filler_param.set_value(1); } shared_ptr<Filler<Dtype> > filler(GetFiller<Dtype>(filler_param)); filler->Fill(this->blobs_[0].get()); } if (param.bias_term()) {//是否需要bias LayerParameter layer_param(this->layer_param_); layer_param.set_type("Bias"); BiasParameter* bias_param = layer_param.mutable_bias_param(); bias_param->set_axis(param.axis()); if (bottom.size() > 1) { bias_param->set_num_axes(bottom[1]->num_axes()); } else { bias_param->set_num_axes(param.num_axes()); } bias_param->mutable_filler()->CopyFrom(param.bias_filler()); bias_layer_ = LayerRegistry<Dtype>::CreateLayer(layer_param); bias_bottom_vec_.resize(1); bias_bottom_vec_[0] = bottom[0]; bias_layer_->SetUp(bias_bottom_vec_, top); if (this->blobs_.size() + bottom.size() < 3) { // case: blobs.size == 1 && bottom.size == 1 // or blobs.size == 0 && bottom.size == 2 bias_param_id_ = this->blobs_.size(); this->blobs_.resize(bias_param_id_ + 1); this->blobs_[bias_param_id_] = bias_layer_->blobs()[0]; } else { // bias param already initialized bias_param_id_ = this->blobs_.size() - 1; bias_layer_->blobs()[0] = this->blobs_[bias_param_id_]; } bias_propagate_down_.resize(1, false); } this->param_propagate_down_.resize(this->blobs_.size(), true); }
(2)Reshape层
template <typename Dtype> void ScaleLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { //获取scale层参数列表 const ScaleParameter& param = this->layer_param_.scale_param(); Blob<Dtype>* scale = (bottom.size() > 1) ? bottom[1] : this->blobs_[0].get(); axis_ = (scale->num_axes() == 0) ? 0 : bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(param.axis()); CHECK_GE(bottom[0]->num_axes(), axis_ + scale->num_axes()) << "scale blob's shape extends past bottom[0]'s shape when applied " << "starting with bottom[0] axis = " << axis_; for (int i = 0; i < scale->num_axes(); ++i) { //维度保持相同 CHECK_EQ(bottom[0]->shape(axis_ + i), scale->shape(i)) << "dimension mismatch between bottom[0]->shape(" << axis_ + i << ") and scale->shape(" << i << ")"; } outer_dim_ = bottom[0]->count(0, axis_);//N scale_dim_ = scale->count();//C inner_dim_ = bottom[0]->count(axis_ + scale->num_axes());//H*W if (bottom[0] == top[0]) { // in-place computation同址运算 temp_.ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]); } else {//若输入与输出大小不等,则将输入的值赋给输出 top[0]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]); } sum_result_.Reshape(vector<int>(1, outer_dim_ * scale_dim_)); const int sum_mult_size = std::max(outer_dim_, inner_dim_); sum_multiplier_.Reshape(vector<int>(1, sum_mult_size)); if (sum_multiplier_.cpu_data()[sum_mult_size - 1] != Dtype(1)) { caffe_set(sum_mult_size, Dtype(1), sum_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data()); } if (bias_layer_) { bias_bottom_vec_[0] = top[0]; bias_layer_->Reshape(bias_bottom_vec_, top); } }
(3)Forward_cpu模块
template <typename Dtype> void ScaleLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu( const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data(); if (bottom[0] == top[0]) { // In-place computation; need to store bottom data before overwriting it. // Note that this is only necessary for Backward; we could skip this if not // doing Backward, but Caffe currently provides no way of knowing whether // we'll need to do Backward at the time of the Forward call. caffe_copy(bottom[0]->count(), bottom[0]->cpu_data(), temp_.mutable_cpu_data()); } const Dtype* scale_data = ((bottom.size() > 1) ? bottom[1] : this->blobs_[0].get())->cpu_data(); Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data(); for (int n = 0; n < outer_dim_; ++n) { for (int d = 0; d < scale_dim_; ++d) { const Dtype factor = scale_data[d]; caffe_cpu_scale(inner_dim_, factor, bottom_data, top_data); bottom_data += inner_dim_; top_data += inner_dim_; } } if (bias_layer_) { bias_layer_->Forward(bias_bottom_vec_, top); } }
(4)Backward_cpu模块
template <typename Dtype> void ScaleLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top, const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) { if (bias_layer_ && this->param_propagate_down_[this->param_propagate_down_.size() - 1]) { bias_layer_->Backward(top, bias_propagate_down_, bias_bottom_vec_); } const bool scale_param = (bottom.size() == 1); Blob<Dtype>* scale = scale_param ? this->blobs_[0].get() : bottom[1]; if ((!scale_param && propagate_down[1]) || (scale_param && this->param_propagate_down_[0])) { const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff(); const bool in_place = (bottom[0] == top[0]); const Dtype* bottom_data = (in_place ? &temp_ : bottom[0])->cpu_data(); // Hack: store big eltwise product in bottom[0] diff, except in the special // case where this layer itself does the eltwise product, in which case we // can store it directly in the scale diff, and we're done. // If we're computing in-place (and not doing eltwise computation), this // hack doesn't work and we store the product in temp_. const bool is_eltwise = (bottom[0]->count() == scale->count()); Dtype* product = (is_eltwise ? scale->mutable_cpu_diff() : (in_place ? temp_.mutable_cpu_data() : bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff())); caffe_mul(top[0]->count(), top_diff, bottom_data, product); if (!is_eltwise) { Dtype* sum_result = NULL; if (inner_dim_ == 1) { sum_result = product; } else if (sum_result_.count() == 1) { const Dtype* sum_mult = sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(); Dtype* scale_diff = scale->mutable_cpu_diff(); if (scale_param) { Dtype result = caffe_cpu_dot(inner_dim_, product, sum_mult); *scale_diff += result; } else { *scale_diff = caffe_cpu_dot(inner_dim_, product, sum_mult); } } else { const Dtype* sum_mult = sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(); sum_result = (outer_dim_ == 1) ? scale->mutable_cpu_diff() : sum_result_.mutable_cpu_data(); caffe_cpu_gemv(CblasNoTrans, sum_result_.count(), inner_dim_, Dtype(1), product, sum_mult, Dtype(0), sum_result); } if (outer_dim_ != 1) { const Dtype* sum_mult = sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(); Dtype* scale_diff = scale->mutable_cpu_diff(); if (scale_dim_ == 1) { if (scale_param) { Dtype result = caffe_cpu_dot(outer_dim_, sum_mult, sum_result); *scale_diff += result; } else { *scale_diff = caffe_cpu_dot(outer_dim_, sum_mult, sum_result); } } else { caffe_cpu_gemv(CblasTrans, outer_dim_, scale_dim_, Dtype(1), sum_result, sum_mult, Dtype(scale_param), scale_diff); } } } } if (propagate_down[0]) { const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff(); const Dtype* scale_data = scale->cpu_data(); Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff(); for (int n = 0; n < outer_dim_; ++n) { for (int d = 0; d < scale_dim_; ++d) { const Dtype factor = scale_data[d]; caffe_cpu_scale(inner_dim_, factor, top_diff, bottom_diff); bottom_diff += inner_dim_; top_diff += inner_dim_; } } } }
2.4 caffe中BN层的使用
BN层的设定一般是按照Conv->BatchNorm->Scale->ReLu的顺序,需要注意的是caffe实现中的use_global_stats参数在训练时设置为false,在测试时设置为true,因为在训练时,bn的作用对象是一个batch_size,而不是整个训练数据集,如果没有将其设置为false,有可能会造成bn后数据更加偏离中心点,导致训练loss出现NAN或87.3365的问题。如果没有设置use_global_stats参数,caffe会自动匹配该值:true/false。
layer { name: "conv" type: "Convolution" bottom: "data" top: "conv" param{ lr_mult:1 decay_mult:1 } param{ lr_mult:2 decay_mult:0 } convolution_param{ num_output:32 kernel_size:5 weight_filler{ type:"xavier" } bias_filler{ type:"constant" } } } layer { name: "BatchNorm" type: "BatchNorm" bottom: "conv" top: "conv1" param { lr_mult: 0 decay_mult: 0 } param { lr_mult: 0 decay_mult: 0 } param { lr_mult: 0 decay_mult: 0 } } layer { name: "scale" type: "Scale" bottom: "conv1" top: "conv2" scale_param { bias_term: true } } layer{ name:"relu1" type:"ReLU" bottom:"conv2" top:"conv3" }




