KMP 理解
例题
以字符串 ABABACA 为例
a
前缀:
后缀:
结果为0
ab
前缀:a
后缀: b
结果为0
aba
前缀:a ab
后缀: ba a
结果为1,此时 i=2,j=1
abab
前缀:a ab aba
后缀: bab ab b
结果为2,此时 i=3,j=2
ababa
前缀:a ab aba abab
后缀: baba aba ba a
结果为3,此时 i=4,j=3
ababac
前缀:a ab aba abab ababac
后缀: babac abac bac ac c
结果为0,此时 i=5,j=3,1,0
ababaca
前缀:a ab aba abab ababac ababaca
后缀: babaca abaca baca bac ac c
结果为1,此时 i=6,j=0
next数组结果:
0 0 0 1 2 3 0 1
总结
以i为尾,往前数对应值,即是相等的,前提是相等的情况下(废话!);
前缀:要第一个字母,不要最后一个字母;
后缀:不要第一个字母,要最后一个字母;
至于i+1,因为计算的是前缀和后缀的重合的值的长度,所以还需要加上1;
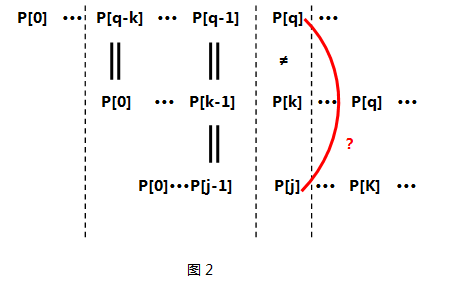
最重要的是
j = next[i - 1],比如说现在在 i 位置上不匹配,为了避免重复匹配,不想浪费之前 0 到 i-1 的匹配长度,也就是说要找以 0 开头,i-1 结尾的匹配的子串,就是说找字符串上 i-1 位置的重合长度,因为next数组存储的是前缀和后缀的重合长度,所以还需要 i-1-1,也就是找next[i-1-1]的值,此时我们再比较字符串上 i 和 j 位置的字符是否相等;
如果相等 j 就尽管移动,代表重合的长度,也就是说到了该位置不匹配,只需要向前移动next数组中对应的长度。

贴上代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> getNext(string str) {
int len = str.size();
int j = 0;
vector<int>next(len + 1);
next[0] = next[1] = 0;
// j表明相同的个数
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
while (j > 0 && str[i] != str[j]) {
j = next[j];
}
// 相同的个数
if (str[i] == str[j]) {
j++;
}
next[i+1] = j;
}
return next;
}
// 另一种写法
// vector<int> getNext2(string str) {
// int j = 0;
// int i = 1;
//
// vector<int> next(str.size());
// next[0] = 0; // 必须是0
//
// while (i < str.size()) {
// if (str[i] == str[j]) {
// j++;
// next[i] = j;
// i++;
// }
// else {
// if (j != 0) {
// j = next[j - 1];
// }
// else { // j 为 0
// next[i] = 0;
// i++;
// }
// }
// }
//
// return next;
//
// }
int search(string original, string find, vector<int> next) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < original.length(); ++i) {
while (j > 0 && original[i] != find[j]) {
j = next[j];
}
if (original[i] == find[j])
++j;
if (j == find.size()) {
return i - j + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
string o = "ABABACAAC";
string f = "ABABACA";
vector<int> next = getNext(f);
// next
int i = 1;
while (i < next.size()) {
cout << "next " << next[i] << endl;
i++;
}
//search
int result = search(o, f, next);
cout << "result " << result << endl;
return 0;
}

关注公众号:数据结构与算法那些事儿,每天一篇数据结构与算法



