VLFeat库实现KD-Tree算法
VLFeat库实现KD-Tree算法
K-D树(K-Dimensional Tree,即K维二叉树),K=1时,即是一棵普通的二叉树。常被用于高维空间中的搜索,比如范围搜索和最近邻搜索。考虑这样一种情况:
平面上有一堆散点,若想要找到与某一点最近的点,最朴素的办法就是逐一计算该点到其他点的距离,但算法会随着样本点的增大变得非常低效。使用2-D Tree能够比暴力搜索更快,并且随着散点集维度增加,KDTree的优势将更加明显。
本文档将介绍使用开源库VLFeat实现KDTree算法。
1 VLFeat库简介及配置
VLFeat,知名度略低于著名的计算机视觉/图像处理开源库OpenCV,VLFeat 开源库实现了大量的机器视觉算法,专门用于图像理解和局部特征提取和匹配。 算法包括 Fisher Vector、VLAD、SIFT、MSER、K-Means、分层 K-Means等。其使用 C 语言编写,提供 C 语言和 MATLAB 两种接口和详细的文档,可以在 windows,Mac 和 Linux 上使用。
首先,我们需要进入官网下载(VLFeat - 首页),并解压到本地。
然后,新建一个工程文件,随后开始配置:
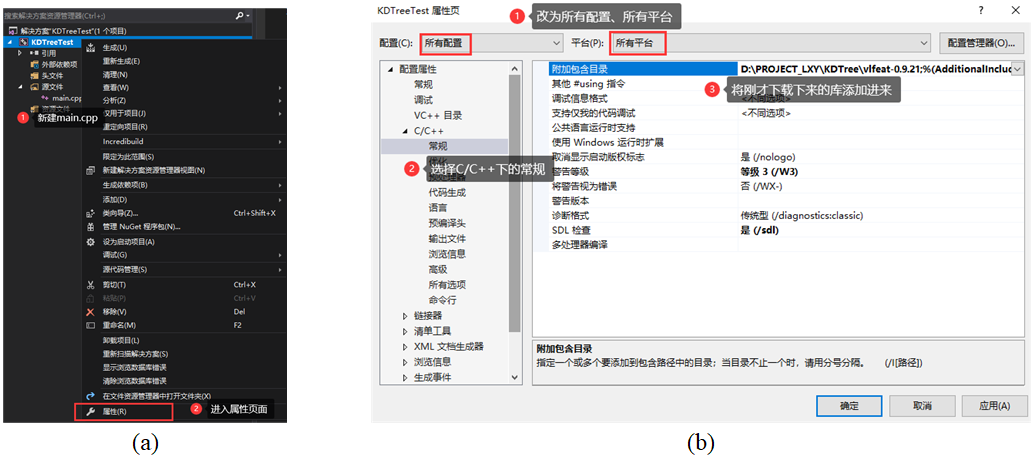
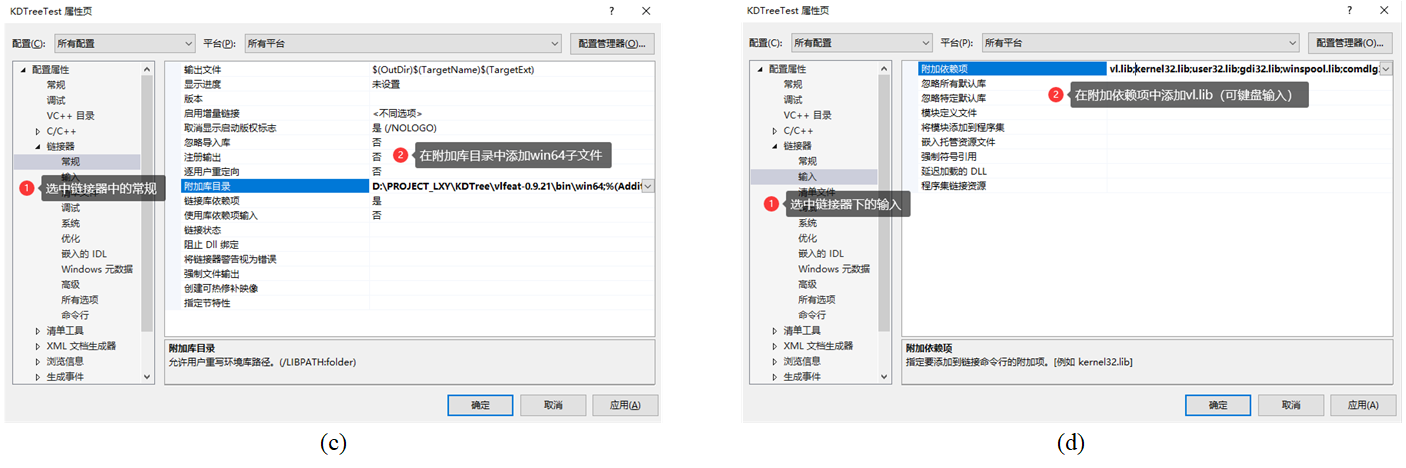
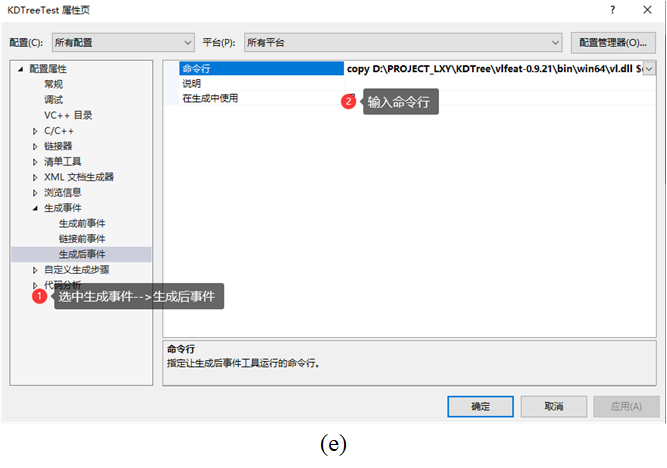
输入的命令行为:
copy D:\xxxxxx\vlfeat-0.9.21\bin\win64\vl.dll $(SolutionDir)x64\$(ConfigurationName)
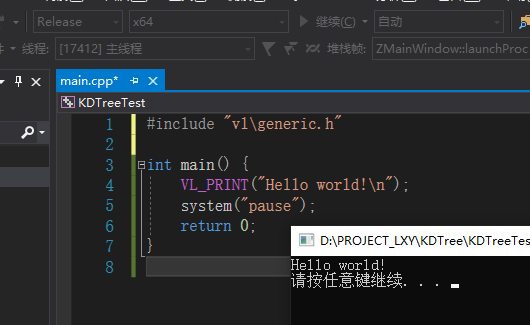
这样就配置完成了,我们在main.cpp中输入测试代码:
#include "vl\generic.h"
int main() {
VL_PRINT("Hello world!\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出为:
2 算法实现(Matlab)
(1)生成随机散点云、定义目标点
简单地说就是:在空间中有一堆散点,而我们要在茫茫多的散点中找到距离目标点(*)最近的几个。
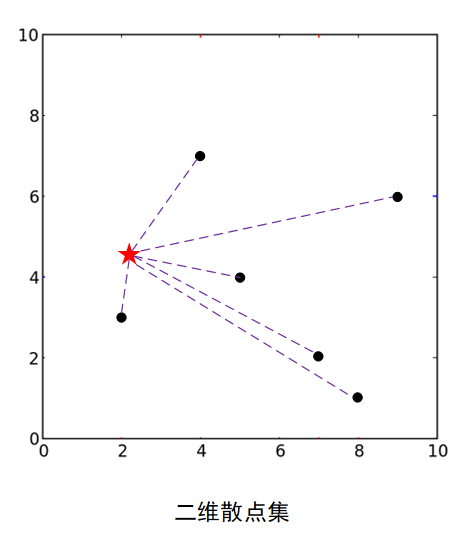
rand('state',0) ;
Q = single(rand(2,1)) ; %目标查询点
X = single(rand(2, 100)) ;%生成随机散点
(2)建树
建立KDTree实际上是一个不断划分的过程,选择方差最大的维度进行切分,然后选择这一维度上的中点/中位数(median)或者均值(mean)作为分割点。因此,只要数据散点确定,这棵树也就被确定下来了。使用上述分裂规则,将当前空间内数据一分为二,再在新的子集中递归切分过程,直到分割到叶子节点。
图中展示了二维/三维数据点的建树结果(按红、绿、蓝的顺序进行切分),这样一来,KD树将平面/空间划分成了许多子平面/空间,随后我们便能根据待查询的点、左/右子空间、以及分割点计算距离,从而规避逐一计算两点距离的庞大计算量。
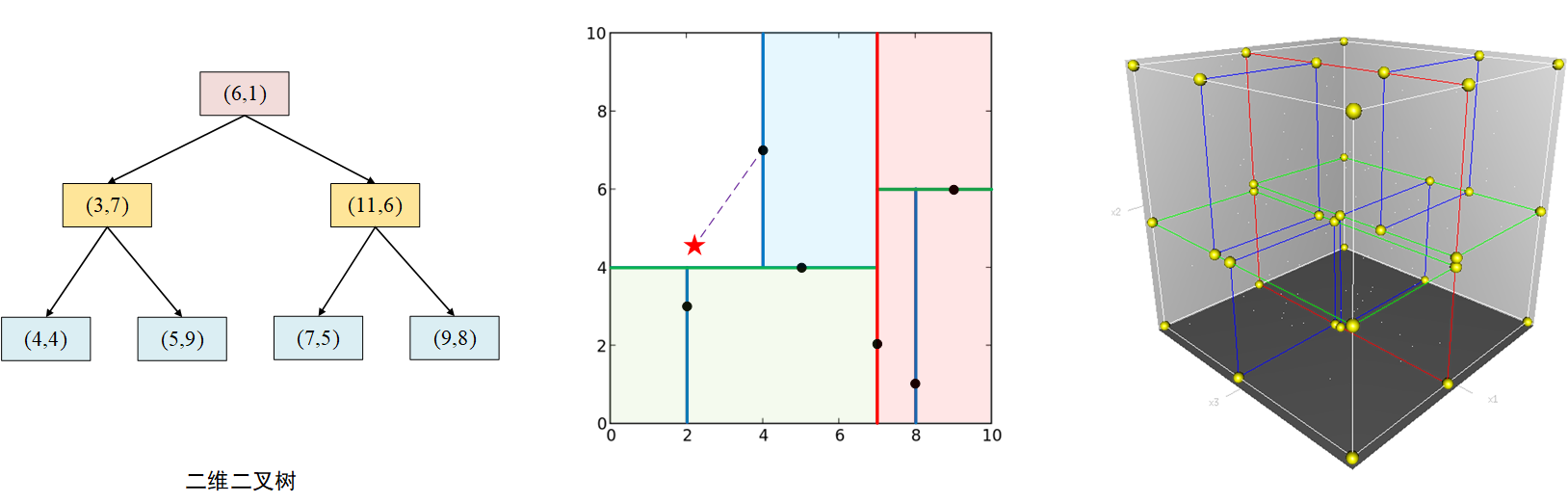
kdforest = vl_kdtreebuild (X, 'verbose','thresholdmethod', 'median') ;
(3)搜索&回溯
比如我们的目标点是(2,5),寻找它的最近邻点,得到的搜索路径为(7,2)\(\to\) (5,4)\(\to\)(4,7),因此我们得到的最近邻点为(4,7)。但是很明显,(2,3)这个点要更近,不过它被绿色这条分割线划到了对面(图①)。因此仅靠二叉树分割区域,然后把区域的上级分割点作为最邻近点是不准确的,需要通过回溯进行排查。需要注意,只有叶子节点才能作为最终的临近点去计算距离,也即搜索路径必须从根节点\(\to\)叶子节点,回溯本质是逆向\(\to\)正向的调校路径过程。
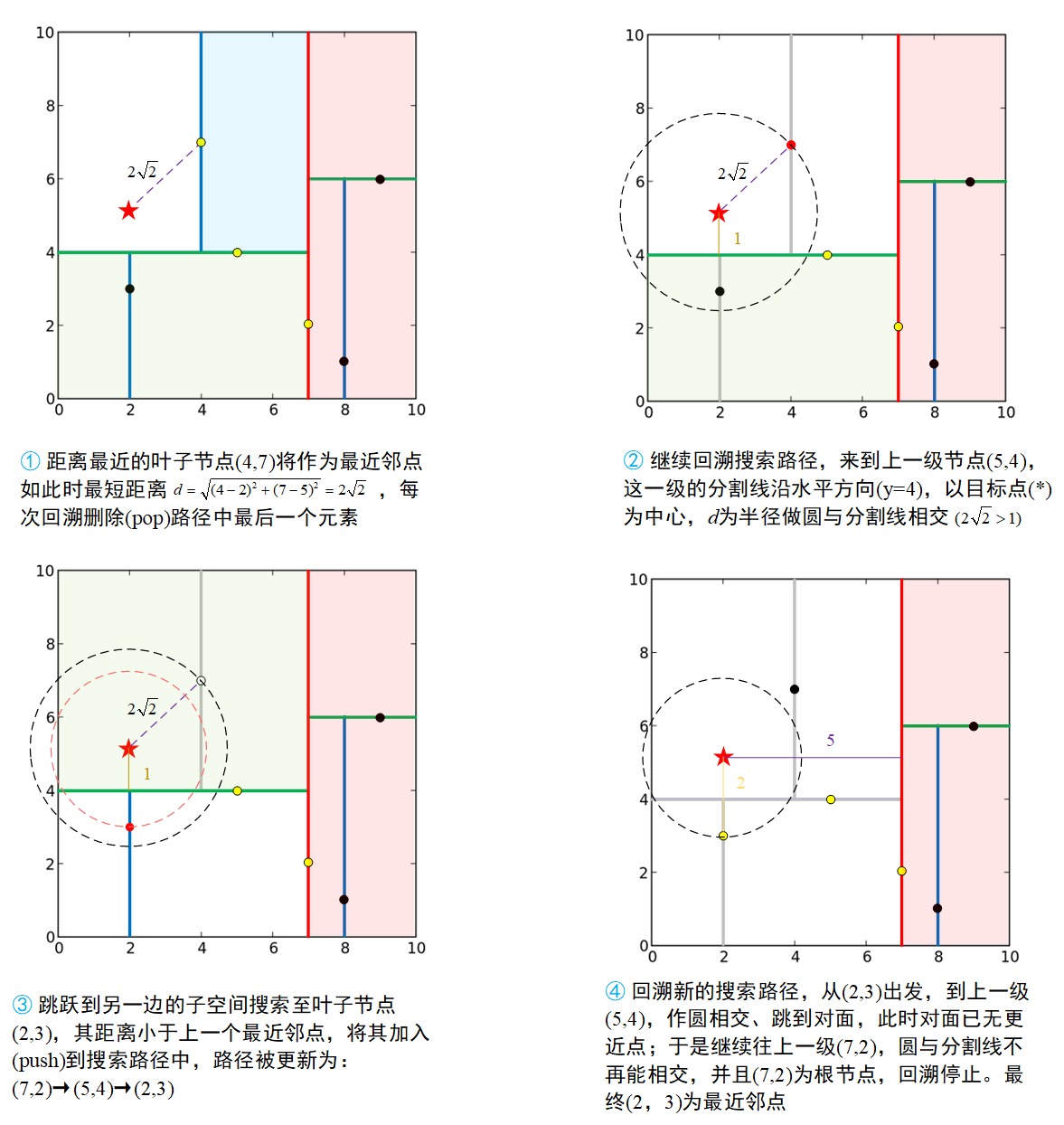
%回溯/查询
[i, d] = vl_kdtreequery (kdforest, X, Q, 'numneighbors', 10, 'verbose') ;
% 输出i为样本点的index,d为优选点距目标点的距离distance
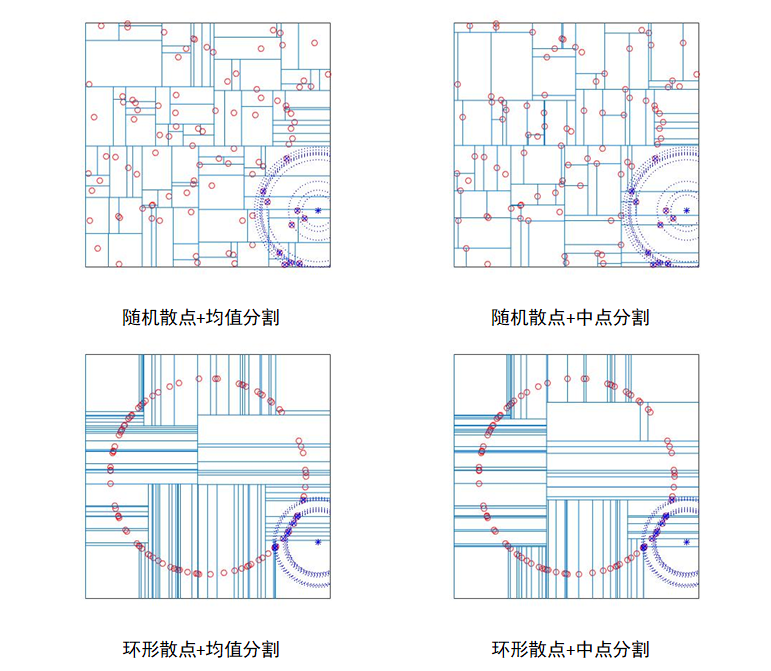
在整个过程完成之后,我们能够得到搜索结果。官方提供的教程中,对不同数据类型和分割规则作了演示:
3 转换至C/C++
VFLeat虽提供了开源C代码,好比给了一整箱零件,但离掌握函数的调用规则、搭建起一个完整的算法,还缺一张图纸。而这个图纸便是由上一章中由Matlab实现的部分。我们知道这套Matlab代码调用了开源库中的C零件,但是具体调用了哪些,怎么连接的,就需要用到MEX。
MEX搭建了Matlab与C之间的桥梁。它能够编译一个或多个用 MATLAB 数据 API 编写的 C++ 源文件并将其链接到当前文件夹中的二进制 MEX 文件中。通过MEX函数我们可以像调用内置函数一样,从 MATLAB 命令行调用 C 或 C++ 程序。比如,建树的函数vl_kdtreebuild:
-
Matlab "vlfeat-0.9.21\toolbox\misc\vl_kdtreebuild.m";
-
MEX "vlfeat-0.9.21\toolbox\mex\mexw64\vl_kdtreebuild.mexw64";
-
C "vlfeat-0.9.21\toolbox\misc\vl_kdtreebuild.c";
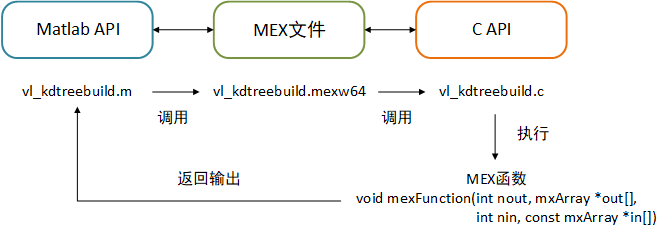
可以简单的将MEX理解为一种C与Matlab都能使用的语言,它有其独特的语法。比如,MEX函数库里的mexFunction()函数,它相当于C语言中的main()函数;用mxArray表示数组。更多关于MEX的介绍和用法可访问https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/call-mex-files-1.html。
原vl_kdtreebuild.c代码是用MEX书写:
void mexFunction(int nout, mxArray *out[], //输入及格式,
int nin, const mxArray *in[]) //输出及格式
{
enum {IN_DATA = 0, IN_END} ;
enum {OUT_TREE = 0} ;
int verbose = 0 ;
int opt ;
int next = IN_END ;
...
forest = vl_kdforest_new (dataType, dimension, numTrees, distance) ; //C函数,存在kdtree.c中
vl_kdforest_set_thresholding_method (forest, thresholdingMethod) ;
...
}
于是,我们可以根据MEX代码,根据其特定的数据格式与语法,转换成C/C++语言,从而仿制出一个C版的Demo。
*之后跳过MEX-->C/C++的转换、翻译过程,直接展示可使用的C/C++代码。
(1)生成随机散点云、定义目标点
在实际运用过程中,这部分通常是从外部输入的文件,此处我们直接用rand()函数生成10000组随机散点。并设置待搜寻的目标点为(30,50)。
#define NUM 10000
srand(7);
double *xpoint = (double*)calloc(NUM,sizeof(double));
double *ypoint = (double*)calloc(NUM, sizeof(double));
for(int i = 0; i<NUM; i++){
xpoint[i] = ((double)rand() / RAND_MAX) * 200.0 - 100.0; //生成随机二维散点
ypoint[i] = ((double)rand() / RAND_MAX) * 200.0 - 100.0;
}
double xdist = 30.0; //目标位置
double ydist = 50.0;
(2)建树
在mex代码中,提供了许多可调的参数。我们可以根据后续地实际需要增加判断语句去一一实现这些参数。首先,声明一个接受建树参数的结构体:
/*
vlmxOption options [] = { //带引号的是Matlab的用法,使用变量名的则是C
{"Verbose", 0, opt_verbose },
{"ThresholdMethod", 1, opt_threshold_method },
{"NumTrees", 1, opt_num_trees },
{"Distance", 1, opt_distance },
{0, 0, 0 }
} ;
*/
typedef struct BuildKdtreeParametert{
int num_trees;
}BuildKdtreeParametert;
随后借助Vl方法,创建可供C/C++调用的建树函数:
/**********************************************
函数功能:根据现有数据创建KD树(2D)
输入:
xpoint X坐标
ypoint Y坐标
nsample 样本个数
bkparameter 参数列表
输出:
forest VlKD树对象
备注:
函数中出现的所有以Vl为开头的关键字为VLFeat提供的类型或方法
**************************************************/
VlKDForest *kdtreebuild2D(double *xpoint, double *ypoint, unsigned int nsample, BuildKdtreeParametert bkparameter) {
if((xpoint==NULL)||(ypoint==NULL)||(nsample==0)){
return NULL;
}
vl_size numData = nsample; // 样本个数
vl_size Dimension = 2; // 样本维度
vl_size dataType = VL_TYPE_DOUBLE; // 数据类型
vl_size numTrees = 1; // 树棵数
VlVectorComparisonType distance = VlDistanceL2; //L2距离
int thresholdingMethod = VL_KDTREE_MEDIAN; //中位数作为分割点
double *data = NULL;
data=(double*)calloc(nsample*2,sizeof(double));
for(int i = 0; i < nsample; i++){ //两列数据合并为一列,为了满足后续接口
data[2 * i] = xpoint[i];
data[2 * i + 1] = ypoint[i];
}//end for(int i = 0; i < nsample; i++)
VlKDForest *forest;
forest = vl_kdforest_new(dataType, Dimension, numTrees, distance); //创建一颗新的KDTree
vl_kdforest_set_thresholding_method(forest, VL_KDTREE_MEDIAN); // 按照规则分割树
vl_kdforest_build(forest, numData, data); //建树
return forest;
}
(3)搜索&回溯
同样的,我们先声明参数列表,并创建一个最近邻属性结构体:
typedef struct FindKdtreeParameter{
int numneighbors;
}FindKdtreeParameter;
typedef struct NearstPointSet{ //Nearst
vector<double> xPoint;
vector<double> yPoint;
vector<double> distance;
int nSample;
}NearstPointSet;
移植搜索方法:
/**********************************************
函数功能:根据建好的KD树(2D)进行回溯,寻找最近的n个点
输入:
forest VlKD树对象,即上一步建好的树
xpoint X坐标
ypoint Y坐标
numpoint 样本个数
xdist 目标点X坐标
ydist 目标点Y坐标
findkdtreeparameter 参数列表
输出:
nps NearstPointSet对象,最近的n个点的属性
**************************************************/
NearstPointSet kdtreefind2D(VlKDForest *forest, double *xpoint, double *ypoint, int numpoint, double xdist, double ydist, FindKdtreeParameter findkdtreeparameter) {
NearstPointSet nps; //定义一些基础变量
VlKDForestNeighbor *neighbors = NULL;
double *qurey = NULL;
int numneighbors = findkdtreeparameter.numneighbors;
int indexTemp = 0;
double distanceTemp = 0.0;
qurey=(double*)calloc(2,sizeof(double));
neighbors = (VlKDForestNeighbor*)calloc(numneighbors,sizeof(VlKDForestNeighbor));
qurey[0] = xdist; //查询点(或目标点)
qurey[1] = ydist;
vl_kdforest_query(forest, neighbors, numneighbors, qurey); //执行搜索操作
for (int i = 0; i < numneighbors; i++){ //按指定需求输出最近的n个点
indexTemp = neighbors[i].index;
distanceTemp =neighbors[i].distance;
if((indexTemp>=0)&&(indexTemp<numpoint)){ //按索引存回坐标与距离
nps.xPoint.push_back(xpoint[indexTemp]);
nps.yPoint.push_back(ypoint[indexTemp]);
nps.distance.push_back(distanceTemp);
}//end if((indexTemp>=0)&&(indexTemp<numpoint)
}//end for (int i = 0; i < numneighbors; i++)
nps.nSample = nps.xPoint.size(); //搜索到的满足条件的点数
return nps;
}
(4)执行程序
BuildKdtreeParameter bkp;
bkp.num_trees = 1; //树棵树
VlKDForest *forest = kdtreebuild2D(xpoint, ypoint, NUM,bkp);
FindKdtreeParameter fkp;
fkp.numneighbors = 10; //挑选最近的10个点
NearstPointSet p1 = kdtreefind2D(forest, xpoint, ypoint, NUM, xdist, ydist,fkp);
//打印最近的那个点坐标和距离
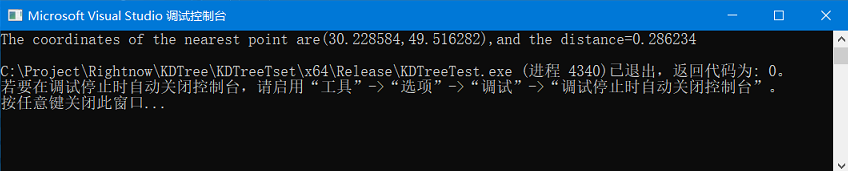
printf("The coordinates of the nearest point are(%f,%f),and the distance=%f\n", p1.xPoint[0], p1.yPoint[0],p1.distance[0]);
将得到以下输出:
完整代码
I KD-Tree.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define PI 3.141592654
#define EPS 0.000001
#define N 2
#include "vl\generic.h"
#include"vl\kdtree.h"
using namespace std;
typedef struct BuildKdtreeParameter{
int num_trees;
}BuildKdtreeParameter;
typedef struct FindKdtreeParameter{
int numneighbors;
}FindKdtreeParameter;
typedef struct NearstPointSet{ //Nearst
vector<double> xPoint;
vector<double> yPoint;
vector<double> distance;
int nSample;
}NearstPointSet;
VlKDForest *kdtreebuild2D(double *xpoint,double *ypoint,unsigned int nsample, BuildKdtreeParameter bkparameter); //build Kdtree Object
NearstPointSet kdtreefind2D(VlKDForest *forest,double *xpoint,double *ypoint,int numpoint,double xdist,double ydist, FindKdtreeParameter findkdtreeparameter);//estimate Nearest Point Set Of aim point ;
II KD-Tree.cpp
#include"KD-Tree.h"
//建树
VlKDForest *kdtreebuild2D(double *xpoint, double *ypoint, unsigned int nsample, BuildKdtreeParameter bkparameter) {
if((xpoint==NULL)||(ypoint==NULL)||(nsample==0)){
return NULL;
}
vl_size numData = nsample; // number of sample
vl_size Dimension = 2; // number of point dimension
vl_size dataType = VL_TYPE_DOUBLE; // Define size of data
vl_size numTrees = 1; // number of kd-tree
VlVectorComparisonType distance = VlDistanceL2; //L2 distance
int thresholdingMethod = VL_KDTREE_MEDIAN;
double *data = NULL;
data=(double*)calloc(nsample*2,sizeof(double));
for(int i = 0; i < nsample; i++){ //data to point
data[2 * i] = xpoint[i];
data[2 * i + 1] = ypoint[i];
}//end for(int i = 0; i < nsample; i++)
VlKDForest *forest;
forest = vl_kdforest_new(dataType, Dimension, numTrees, distance);
vl_kdforest_set_thresholding_method(forest, VL_KDTREE_MEDIAN);
vl_kdforest_build(forest, numData, data);
return forest;
}
//回溯
NearstPointSet kdtreefind2D(VlKDForest *forest, double *xpoint, double *ypoint, int numpoint, double xdist, double ydist, FindKdtreeParameter findkdtreeparameter) {
NearstPointSet nps;
VlKDForestNeighbor *neighbors = NULL;
double *qurey = NULL;
int numneighbors = findkdtreeparameter.numneighbors;
int indexTemp = 0;
double distanceTemp = 0.0;
qurey=(double*)calloc(2,sizeof(double));
neighbors = (VlKDForestNeighbor*)calloc(numneighbors,sizeof(VlKDForestNeighbor));
qurey[0] = xdist;
qurey[1] = ydist;
vl_kdforest_query(forest, neighbors, numneighbors, qurey);
for (int i = 0; i < numneighbors; i++){
indexTemp = neighbors[i].index;
distanceTemp =neighbors[i].distance;
if((indexTemp>=0)&&(indexTemp<numpoint)){
nps.xPoint.push_back(xpoint[indexTemp]);
nps.yPoint.push_back(ypoint[indexTemp]);
nps.distance.push_back(distanceTemp);
}//end if((indexTemp>=0)&&(indexTemp<numpoint)
}//end for (int i = 0; i < numneighbors; i++)
nps.nSample = nps.xPoint.size();
return nps;
}
III main.cpp
#include"KD-Tree.h"
#define NUM 10000
int main() {
srand(7);
double *xpoint = (double*)calloc(NUM,sizeof(double));
double *ypoint = (double*)calloc(NUM, sizeof(double));
for(int i = 0; i<NUM; i++){
xpoint[i] = ((double)rand() / RAND_MAX) * 200.0 - 100.0;
ypoint[i] = ((double)rand() / RAND_MAX) * 200.0 - 100.0;
}
double xdist = 30.0;
double ydist = 50.0;
BuildKdtreeParameter bkp;
bkp.num_trees = 10;
VlKDForest *forest = kdtreebuild2D(xpoint, ypoint, NUM, bkp);
FindKdtreeParameter fkp;
fkp.numneighbors = 10;
NearstPointSet p1 = kdtreefind2D(forest, xpoint, ypoint, NUM, xdist, ydist, fkp);
printf("The coordinates of the nearest point are(%f,%f),and the distance=%f\n", p1.xPoint[0], p1.yPoint[0],p1.distance[0]);
return 0;
}
参考:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号