MKL库线性方程组求解(LAPACKE_?gesv)
LAPACK(Linear Algebra PACKage)库,是用Fortran语言编写的线性代数计算库,包含线性方程组求解(\(AX=B\))、矩阵分解、矩阵求逆、求矩阵特征值、奇异值等。该库用BLAS库做底层运算。
本示例将使用MKL中的LAPACK库计算线性方程组\(AX=B\)的解,并扩展使用此思路求逆矩阵的过程。首先介绍原理部分:
LU分解
引用自 LU分解 - 维基百科
对于方阵\(A\),其\(LU\)分解是将它分解成一个下三角矩阵\(L\)与上三角矩阵\(U\)的乘积,即\(A=LU\),
如一个\(3 \times 3\)的矩阵\(A\) ,其\(LU\)分解会写成下面的形式:
分解之后,由于\(L\)与\(U\)分别为下、上三角矩阵,再去求解\(X\)将变得更加简单。
然而,\(LU\)分解只适用于能用消去法处理的矩阵(比如左上角第一个元素为0时就无法消去)。
而\(PLU\)分解在加入置换矩阵\(P\)进行换行后,便可对任意实矩阵进行\(LU\)分解,此时\(A=P*L*U\)。
LAPACKE_sgesv计算线性方程组\(A*X = B\) 的解,其中 \(A\) 是$ N×N$ 矩阵,\(X\) 和 \(B\) 是 \(N×NRHS\) 矩阵。 将 \(A\) 分解为 \(A = P * L * U\),其中 \(P\) 是置换矩阵,\(L\)是单位下三角矩阵,\(U\)是上三角矩阵。 然后使用\(A\)的分解式来求解方程组\(A * X = B\)。
1 参数详解
lapack_int LAPACKE_sgesv( matrix_layout, // (input) 行优先(LAPACK_ROW_MAJOR)或列优先(LAPACK_COL_MAJOR)
n, // (input) 线性方程的个数,n>=0
nrhs, // (input) 矩阵B的列数,即线性方程组右端的项个数,nrhs>=0
a, // (input/output)系数矩阵A,维度为nxn
lda, // (input) A矩阵的第一维
ipiv, // (output) 置换矩阵,ipiv[i]表示矩阵A的第i行与第ipiv[i]行进行了交换
b, // (input/output)B矩阵
ldb // (input) B矩阵的第一维
);
2 定义线性方程组
Intel给出的官方示例为:
去求解\(AX=B\)的解\(X\)。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mkl_lapacke.h"
// 参数
#define N 5
#define NRHS 3
#define LDA N
#define LDB NRHS
MKL_INT n = N, nrhs = NRHS, lda = LDA, ldb = LDB, info;
MKL_INT ipiv[N];
float a[LDA*N] = {
6.80f, -6.05f, -0.45f, 8.32f, -9.67f,
-2.11f, -3.30f, 2.58f, 2.71f, -5.14f,
5.66f, 5.36f, -2.70f, 4.35f, -7.26f,
5.97f, -4.44f, 0.27f, -7.17f, 6.08f,
8.23f, 1.08f, 9.04f, 2.14f, -6.87f
};
float b[LDB*N] = {
4.02f, -1.56f, 9.81f,
6.19f, 4.00f, -4.09f,
-8.22f, -8.67f, -4.57f,
-7.57f, 1.75f, -8.61f,
-3.03f, 2.86f, 8.99f
};
3 执行求解过程
LAPACKE_sgesv( LAPACK_ROW_MAJOR, n, nrhs, a, lda, ipiv, b, ldb );
输出结果为:
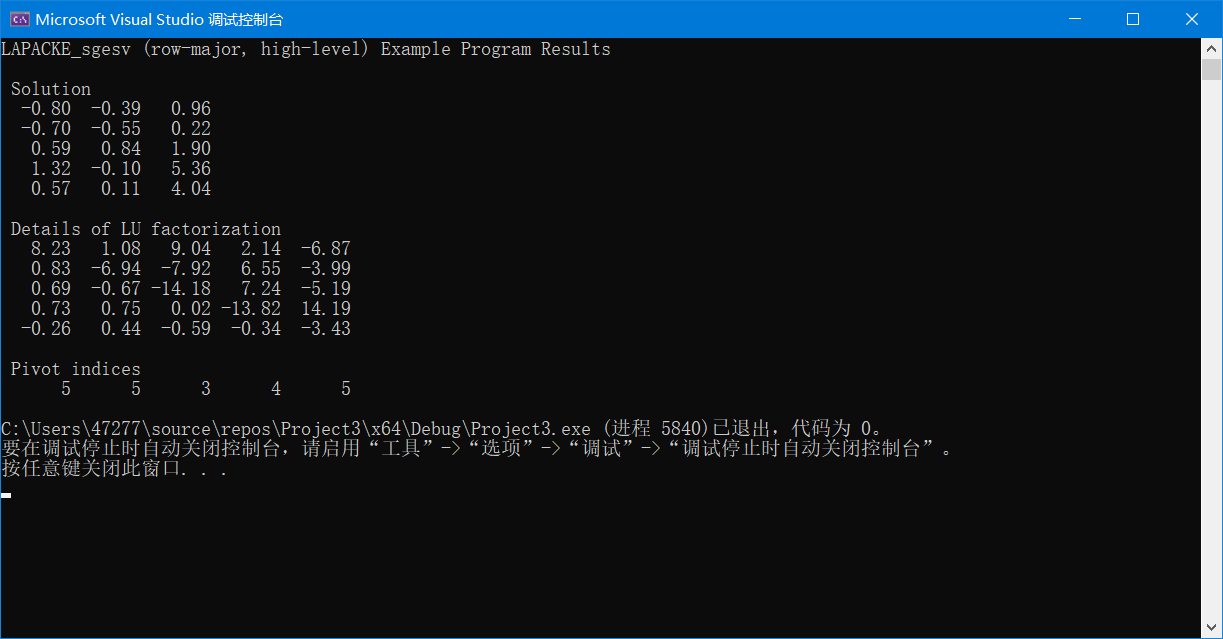
完整代码
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mkl_lapacke.h"
extern void print_matrix(const char* desc, MKL_INT m, MKL_INT n, float* a, MKL_INT lda);
extern void print_int_vector(const char* desc, MKL_INT n, MKL_INT* a);
#define N 5
#define NRHS 3
#define LDA N
#define LDB NRHS
int main() {
MKL_INT n = N, nrhs = NRHS, lda = LDA, ldb = LDB, info;
MKL_INT ipiv[N];
float a[LDA * N] = {
6.80f, -6.05f, -0.45f, 8.32f, -9.67f,
-2.11f, -3.30f, 2.58f, 2.71f, -5.14f,
5.66f, 5.36f, -2.70f, 4.35f, -7.26f,
5.97f, -4.44f, 0.27f, -7.17f, 6.08f,
8.23f, 1.08f, 9.04f, 2.14f, -6.87f
};
float b[LDB * N] = {
4.02f, -1.56f, 9.81f,
6.19f, 4.00f, -4.09f,
-8.22f, -8.67f, -4.57f,
-7.57f, 1.75f, -8.61f,
-3.03f, 2.86f, 8.99f
};
printf("LAPACKE_sgesv (row-major, high-level) Example Program Results\n");
info = LAPACKE_sgesv(LAPACK_ROW_MAJOR, n, nrhs, a, lda, ipiv,
b, ldb);
if (info > 0) {
printf("The diagonal element of the triangular factor of A,\n");
printf("U(%i,%i) is zero, so that A is singular;\n", info, info);
printf("the solution could not be computed.\n");
exit(1);
}
print_matrix("Solution", n, nrhs, b, ldb);
print_matrix("Details of LU factorization", n, n, a, lda);
print_int_vector("Pivot indices", n, ipiv);
exit(0);
}
void print_matrix(const char* desc, MKL_INT m, MKL_INT n, float* a, MKL_INT lda) {
MKL_INT i, j;
printf("\n %s\n", desc);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) printf(" %6.2f", a[i * lda + j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_int_vector(const char* desc, MKL_INT n, MKL_INT* a) {
MKL_INT j;
printf("\n %s\n", desc);
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) printf(" %6i", a[j]);
printf("\n");
}
补充:矩阵求逆
简单来说,在使用以上API计算\(AX=B\),当\(B\)为单位矩阵时,\(X\)即为\(A^{-1}\)。
将上述案例中的
float b[LDB * N] = {
4.02f, -1.56f, 9.81f,
6.19f, 4.00f, -4.09f,
-8.22f, -8.67f, -4.57f,
-7.57f, 1.75f, -8.61f,
-3.03f, 2.86f, 8.99f
};
/**********改为**********/
#define NRHS 5
float b[LDB * N] = {
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
};
即可求解矩阵\(A\)的逆矩阵,输出为:
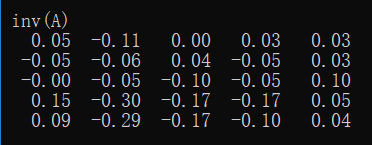
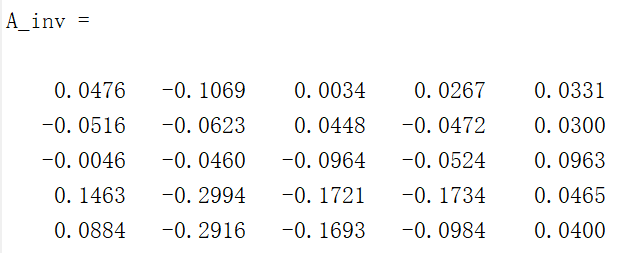
对比在Matlab中使用inv()函数求逆:
A = [ 6.80, -6.05, -0.45, 8.32, -9.67;
-2.11, -3.30, 2.58, 2.71, -5.14;
5.66, 5.36, -2.70, 4.35, -7.26;
5.97, -4.44, 0.27, -7.17, 6.08;
8.23, 1.08, 9.04, 2.14, -6.87];
A_inv=inv(A)
结果相同。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号