前端Vue框架-vuex状态管理详解
vuex理解
采用集中式存储管理模式。用来管理组件的状态,并以自定义规则去观测实时监听值得变化。
状态模式管理理解
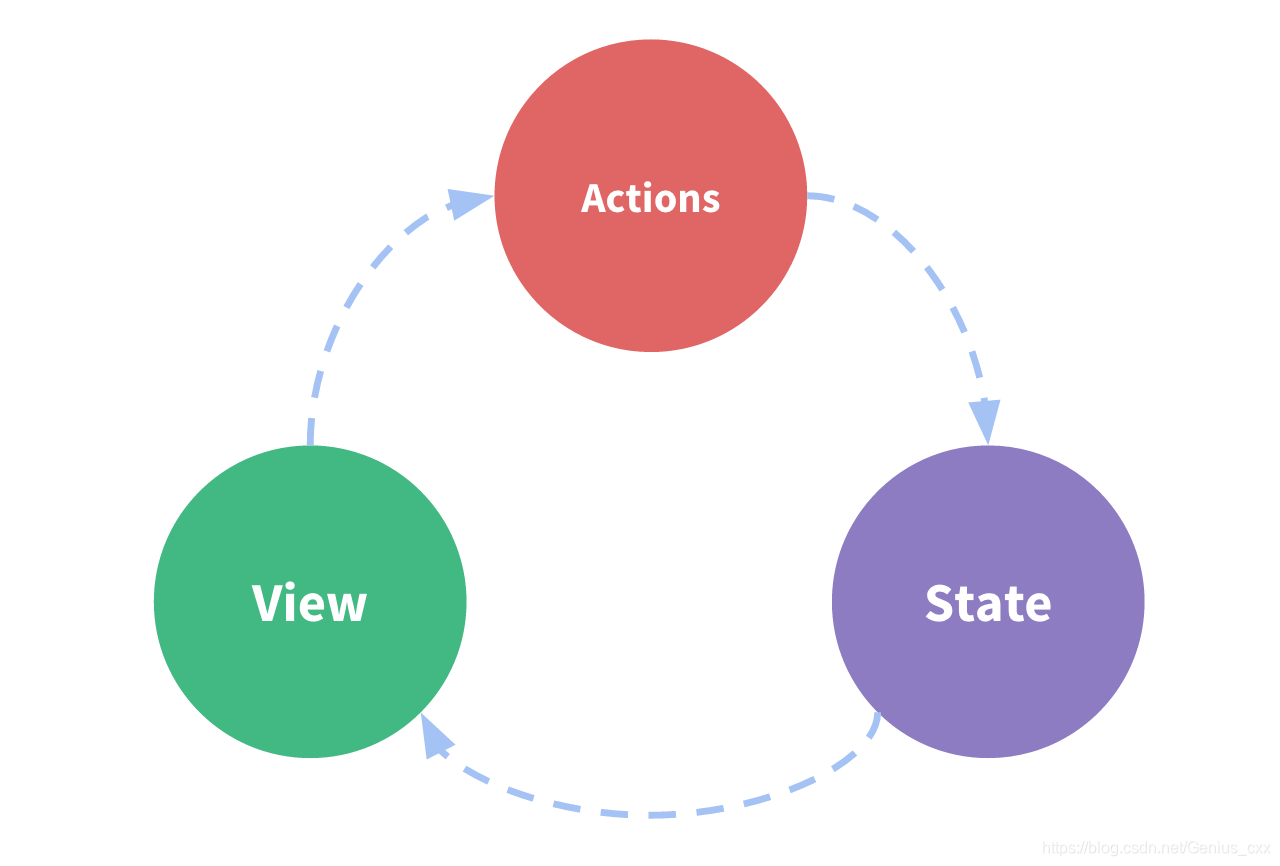
| 属性 | 理解 |
|---|---|
| state | 驱动应用的数据源 |
| view | 以声明的方式,将 state 映射到视图 |
| actions | 响应在 view(视图)上的用户输入导致的状态变化。 |
 |
new Vue({
// state 驱动应用的数据源
data(){
return {
count:0
}
},
// view 以声明的方式,将 state 映射到视图
template: `<div> {{ count }} </div>`,
// actions 响应在 view(视图)上的用户输入导致的状态变化。
methods: {
add(){
this.count ++
}
}
})
vuex安装引入
使用前需要下载vuex
npm install vuex --save
在我们的main.js文件中引入该文件,在文件里面添加 import store from ‘./store’;,再在vue实例全局引入store对象;
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from 'router'
import store from './stroe'
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
el:'#app',
store,
router,
componment:{ App },
template:'<App/>
})
然后在src目录下创建store目录,store目录下创建index.js编写以下代码
import Vue from 'vue' //引入vue
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex);
//创建Vuex实例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
})
export default store;//导出store
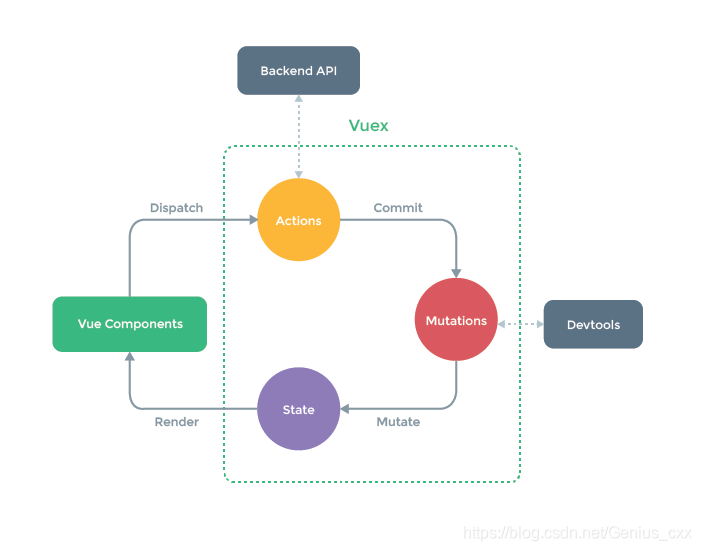
1.vuex四大核心属性
- state:数据源
我们需要保存的数据在这里定义并存储,可以在组件中通过this.$store.state来获取这些数据
首先在store目录下index.js编写以下代码
import Vue from 'vue' //引入vue
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex);
//创建Vuex实例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:1, //定义数据源
}
})
export default store;//导出store
然后在我们的任意组件中就可以使用this.$store.state方法获取我们的数据count
<template>
<div>
{{ this.$store.state.count }} //1.页面调用
{{ msg }} //2.方法赋值
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name : 'home',
data () {
return {
msg : null
}
},
mounted(){
this.msg = this.$store.state.count;
}
}
<script/>
- getters:计算属性
getters相当于vue中的computed计算属性,getters的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有他的依赖值发生改变时才会被重新计算,这里我们可以通过定义getters监听state中的值的变化,返回计算结果。
首先在store目录下index.js编写以下代码
import Vue from 'vue' //引入vue
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex);
//创建Vuex实例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:1, //定义数据源
},
getters:{
getStateCount: state => state.count+1 //观测
},
})
export default store;//导出store
在组件页面获取
<template>
<div>
{{ this.$store.state.count }} // count 值:1
{{ this.$store.getters.getStateCount }} //调用getters 值:2
</div>
</template>
- mutations:事件处理器
数据我们在页面是获取到了,但是如果我们需要修改count值怎么办?如果需要修改store中的值唯一的方法就是提交mutation来修改。
简单事件实例,还是在store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue' //引入vue
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex);
//创建Vuex实例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:1, //定义数据源
},
getters:{
getStateCount: state => state.count+1 //观测
},
mutations:{
add:state => state.count++,
red:state => state.count--
}
})
export default store;//导出store
组件中使用this.$store.commit(‘mutations事件名称’)调用该方法
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ count }}<p/>
<p>
<button @click='add'></button>
<button @click='red'></button>
</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name : 'home',
data () {
return {
count: 1,
}
},
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
},
methods: {
add(){
this.$store.commit('add')
},
red(){
this.$store.commit('red')
},
}
</script>
- actions: 可以给组件使用的函数,用来驱动事件处理器 mutations
通过以上学习我们学会了如何修改state中的值。但是,官方并不建议我们这样直接去修改store里面的值,而是让我们去提交一个actions,在actions中提交mutation再去修改状态值。
因此我们需要先定义一个actions去提交mutation的函数。
import Vue from 'vue' //引入vue
import Vuex from 'vuex' //引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex);
//创建Vuex实例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:1, //定义数据源
},
getters:{
getStateCount: state => state.count+1 //观测
},
mutations:{
add:state => state.count++,
red:state => state.count--
},
actions:{
addFn(context) {
context.commit('add');
},
redFn(context) {
context.commit('red')
}
})
export default store;//导出store
然后编辑组件文件,虽然效果相同,但是还是要严格遵从官方写法。
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ count }}<p/>
<p>
<button @click='addFn'></button>
<button @click='redFn'></button>
</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name : 'home',
data () {
return {
count: 1,
}
},
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
},
methods: {
addFn(){
this.$store.dispatch('addFn')
},
redFn(){
this.$store.dispatch('redFn')
},
}
</script>
- vuex还有一个属性 modules :存放模块化的数据(不是必须的)
2.vuex拓展
- mapState
- mapGetters
- mapActions
在我们开发过程中会频繁调用store中的方法和数据,此时使用this.$store.state等写法就会显得很臃肿,所有这里介绍mapState、mapGetters、mapActions。
在我们需要使用vuex状态管理的组件中引入。
import { mapState、mapGetters、mapActions } from 'vuex';
.
.
.
computed:{
...mapState({
count : state => state.count
})
}
此时我们页面使用count调用效果相同。



