Redis非阻塞IO复用模型
Redis线程模型(非阻塞IO复用模型)
Redis优点
- 基于内存,C语言编写-速度快
- 非阻塞的IO复用模型机制
- 单线程- 避免多线程的频繁上下文切换问题
- 丰富的数据结构 - 字符串、链表、哈希、集合、有序集合
文件事件处理器(file event handler)
Redis服务器是一个事件驱动程序
Redis基于Reactor模型开发了自己的网络事件处理器 - 文件事件处理器
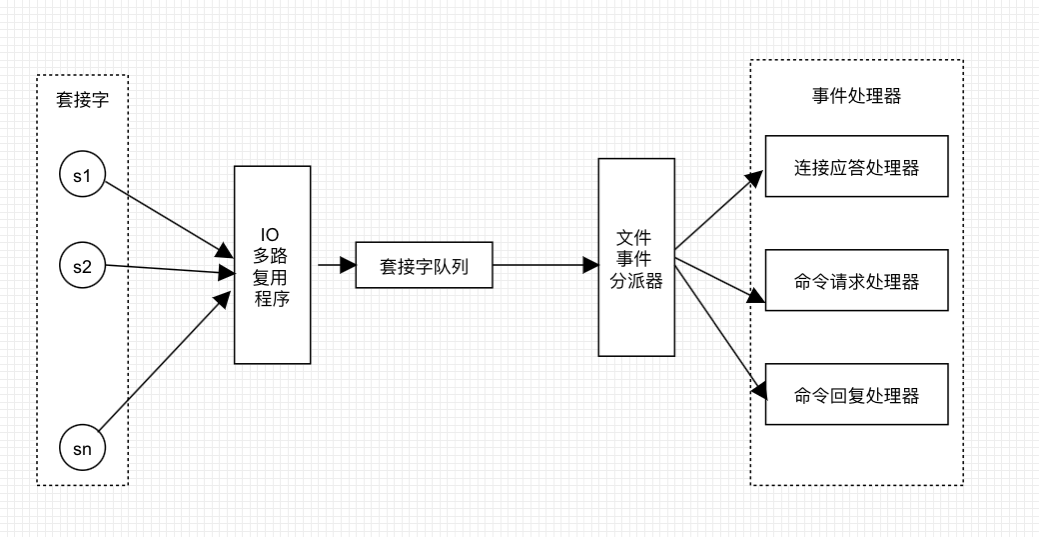
- 文件事件处理器使用I/O多路复用(multiplexing)同时监听多个套接字,并根据套接字目前执行的任务为套接字关联不同的事件处理器
- 当监听套接字准备好执行应答(accept)、读取(read)、写入(write)、关闭(close)等操作时,与操作所对应的文件事件就会产生,文件事件处理器就会调用套接字之前关联好的事件处理器来处理这些事件
文件事件处理器是单线程的,但是通过/O多路复用(multiplexing)同时监听多个套接字文件时期处理器既实现了高性能网络通讯模型,有保证了内部单线程设计的简单性
ae.h
/*
* 文件事件状态
*/
// 未设置
#define AE_NONE 0
// 可读
#define AE_READABLE 1
// 可写
#define AE_WRITABLE 2
Redis与客户端通信流程
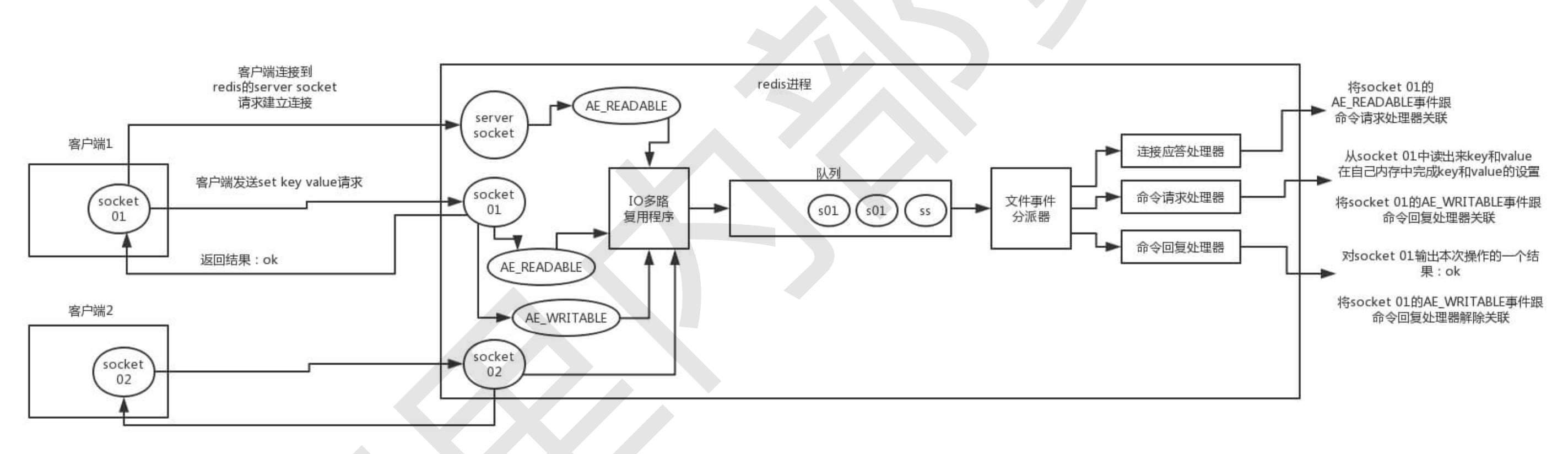
- 1.客户端 Socket01 向 Redis 的 Server Socket 请求建立连接,此时 Server Socket 会产生一个 AE_READABLE 事件,IO 多路复用程序监听到 server socket 产生的事件后,将该事件压入队列中。文件事件分派器从队列中获取该事件,交给连接应答处理器。连接应答处理器会创建一个能与客户端通信的 Socket01,并将该 Socket01 的 AE_READABLE 事件与命令请求处理器关联
- 2.此时客户端发送了一个 set key value 请求,此时 Redis 中的 Socket01 会产生 AE_READABLE 事件,IO 多路复用程序将事件压入队列,此时事件分派器从队列中获取到该事件,由于前面 Socket01 的 AE_READABLE 事件已经与命令请求处理器关联,因此事件分派器将事件交给命令请求处理器来处理。命令请求处理器读取 Socket01 的 set key value 并在自己内存中完成 set key value 的设置。操作完成后,它会将 Socket01 的 AE_WRITABLE 事件与命令回复处理器关联
- 3.如果此时客户端准备好接收返回结果了,那么 Redis 中的 Socket01 会产生一个 AE_WRITABLE 事件,同样压入队列中,事件分派器找到相关联的命令回复处理器,由命令回复处理器对 Socket01 输入本次操作的一个结果,比如 ok ,之后解除 Socket01 的 AE_WRITABLE 事件与命令回复处理器的关联
I/O多路复用
ae.c
/* Process every pending time event, then every pending file event
* (that may be registered by time event callbacks just processed).
*
* 处理所有已到达的时间事件,以及所有已就绪的文件事件。
*
* Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event
* fires, or when the next time event occurs (if any).
*
* 如果不传入特殊 flags 的话,那么函数睡眠直到文件事件就绪,
* 或者下个时间事件到达(如果有的话)。
*
* If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns.
* 如果 flags 为 0 ,那么函数不作动作,直接返回。
*
* if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_ALL_EVENTS ,所有类型的事件都会被处理。
*
* if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_FILE_EVENTS ,那么处理文件事件。
*
* if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_TIME_EVENTS ,那么处理时间事件。
*
* if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set the function returns ASAP until all
* the events that's possible to process without to wait are processed.
* 如果 flags 包含 AE_DONT_WAIT ,
* 那么函数在处理完所有不许阻塞的事件之后,即刻返回。
*
* The function returns the number of events processed.
* 函数的返回值为已处理事件的数量
*/
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
/* Note that we want call select() even if there are no
* file events to process as long as we want to process time
* events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready
* to fire. */
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL;
struct timeval tv, *tvp;
// 获取最近的时间事件
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))
shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop);
if (shortest) {
// 如果时间事件存在的话
// 那么根据最近可执行时间事件和现在时间的时间差来决定文件事件的阻塞时间
long now_sec, now_ms;
/* Calculate the time missing for the nearest
* timer to fire. */
// 计算距今最近的时间事件还要多久才能达到
// 并将该时间距保存在 tv 结构中
aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms);
tvp = &tv;
tvp->tv_sec = shortest->when_sec - now_sec;
if (shortest->when_ms < now_ms) {
tvp->tv_usec = ((shortest->when_ms+1000) - now_ms)*1000;
tvp->tv_sec --;
} else {
tvp->tv_usec = (shortest->when_ms - now_ms)*1000;
}
// 时间差小于 0 ,说明事件已经可以执行了,将秒和毫秒设为 0 (不阻塞)
if (tvp->tv_sec < 0) tvp->tv_sec = 0;
if (tvp->tv_usec < 0) tvp->tv_usec = 0;
} else {
// 执行到这一步,说明没有时间事件
// 那么根据 AE_DONT_WAIT 是否设置来决定是否阻塞,以及阻塞的时间长度
/* If we have to check for events but need to return
* ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout
* to zero */
if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) {
// 设置文件事件不阻塞
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else {
/* Otherwise we can block */
// 文件事件可以阻塞直到有事件到达为止
tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */
}
}
// 处理文件事件,阻塞时间由 tvp 决定
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
// 从已就绪数组中获取事件
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
/* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed
* event removed an element that fired and we still didn't
* processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */
// 读事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
// rfired 确保读/写事件只能执行其中一个
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
// 写事件
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
// 执行时间事件
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS)
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}
/* Wait for milliseconds until the given file descriptor becomes
* writable/readable/exception
*
* 在给定毫秒内等待,直到 fd 变成可写、可读或异常
*/
int aeWait(int fd, int mask, long long milliseconds) {
struct pollfd pfd;
int retmask = 0, retval;
memset(&pfd, 0, sizeof(pfd));
pfd.fd = fd;
if (mask & AE_READABLE) pfd.events |= POLLIN;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) pfd.events |= POLLOUT;
if ((retval = poll(&pfd, 1, milliseconds))== 1) {
if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) retmask |= AE_READABLE;
if (pfd.revents & POLLOUT) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (pfd.revents & POLLERR) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE;
if (pfd.revents & POLLHUP) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE;
return retmask;
} else {
return retval;
}
}
/*
* 事件处理器的主循环
*/
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
// 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,那么运行它
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 开始处理事件
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS);
}
}
aeApiPoll()函数
编译时会自动选择系统中性能最高的I/O多路复用函数库作为Redis的I/O多路复用程序
文件事件的处理器
- 连接应答处理器
networking.c/acceptTcpHandler
- 命令请求处理器
networking.c/readQueryFrom
- 命令回复处理器
networking.c/sendReplyToClient
不要用狭隘的眼光看待不了解的事物,自己没有涉及到的领域不要急于否定.
每天学习一点,努力过好平凡的生活.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号