25. K 个一组翻转链表 + 链表的翻转
25. K 个一组翻转链表
25. K 个一组翻转链表
题目描述
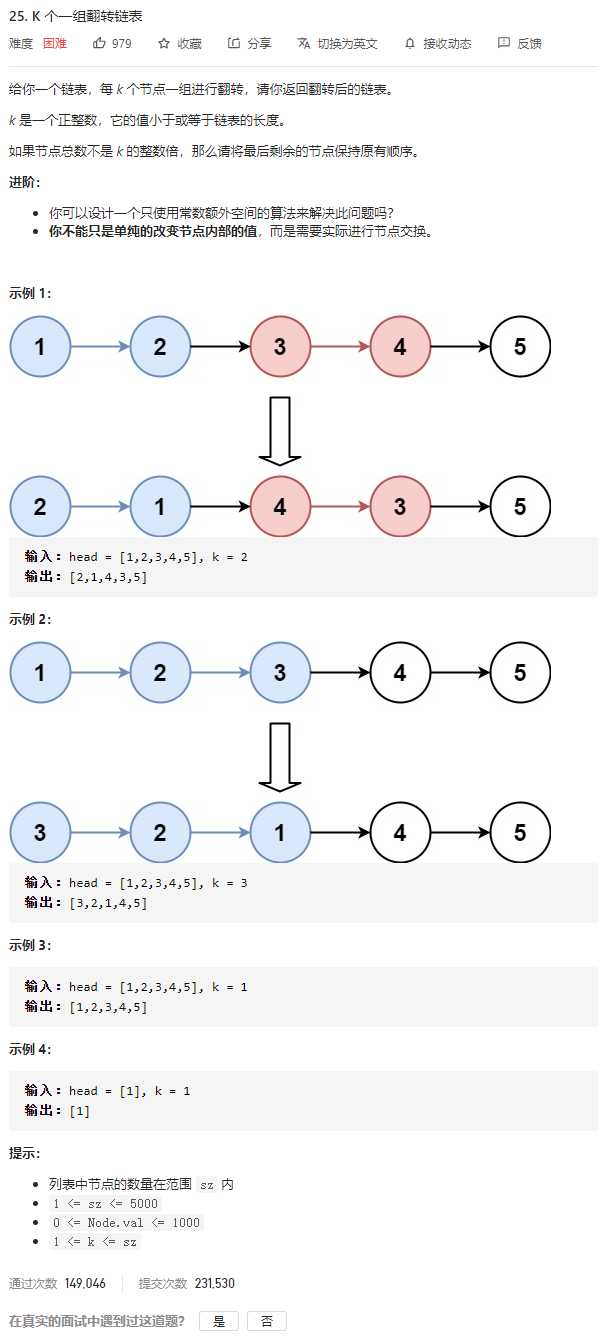
题解分析
- 这题的主要解决思路就是链表的翻转,关键是要找到每次翻转的头结点和尾结点。
- 外层是一个while(true)循环,内存找到本次需要翻转的k个结点的左右边界。
代码实现
解法一:迭代法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dumyHead = new ListNode(0);//创建虚拟头结点
dumyHead.next = head;
ListNode pre = dumyHead;
while(head != null){
ListNode temp = pre;
for(int i=0; i<k; i++){//判断剩下的链表是否够k个结点
temp = temp.next;
if(temp == null)
return dumyHead.next;//直接返回链表
}
ListNode next = temp.next;
ListNode[] res = reverseLink(head, temp);
head = res[0];//头结点
temp = res[1];//尾结点
pre.next = head;
temp.next = next;
pre = temp;
head = temp.next;//新的头结点
}
return dumyHead.next;
}
/*
翻转头结点和尾结点之间的这段链表
*/
public ListNode[] reverseLink(ListNode head, ListNode tail){
ListNode pre = tail.next;//这里很关键,前置结点设置为尾结点的下一个结点
ListNode current = head;
while(pre != tail){//注意这里是pre不等于尾结点
ListNode temp = current.next;
current.next = pre;
pre = current;
current = temp;
}
return new ListNode[]{tail, head};
}
}
解法二:递归法
- 与反转链表题目类似,本题也可以使用递归法来实现,只不过实现的步骤稍微有些麻烦。
- 递归方法中,每次返回的是子递归的新头节点newHead,在递归之后,需要将当前头节点head的next指针指向子递归的头节点。
- 需要注意的是,在递归边界中,如果遇到了head为null或者head.next为null,都需要返回head表示无法翻转空节点或者单个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode tail = head;
for(int i=0; i<k-1; i++){
tail = tail.next;
if(tail == null){
return head;
}
}
ListNode[] temp = reverse(head, tail);
ListNode newHead = temp[0];
head.next = reverseKGroup(temp[1].next, k);
return newHead;
}
private ListNode[] reverse(ListNode slow, ListNode fast){
ListNode pre = fast.next;
ListNode now = slow;
while(pre != fast){
ListNode temp = now.next;
now.next = pre;
pre = now;
now = temp;
}
return new ListNode[]{fast, slow};
}
}
Either Excellent or Rusty

