OpenCV图像金字塔
2016-03-18 18:37 GarfieldEr007 阅读(396) 评论(0) 收藏 举报图像金字塔
原理
Note
以下内容来自于Bradski和Kaehler的大作: Learning OpenCV 。
- 当我们需要将图像转换到另一个尺寸的时候, 有两种可能:
- 放大 图像 或者
- 缩小 图像。
- 尽管OpenCV 几何变换 部分提供了一个真正意义上的图像缩放函数(resize, 在以后的教程中会学到),不过在本篇我们首先学习一下使用 图像金字塔来做图像缩放, 图像金字塔是视觉运用中广泛采用的一项技术。
图像金字塔
- 一个图像金字塔是一系列图像的集合 - 所有图像来源于同一张原始图像 - 通过梯次向下采样获得,直到达到某个终止条件才停止采样。
- 有两种类型的图像金字塔常常出现在文献和应用中:
- 高斯金字塔(Gaussian pyramid): 用来向下采样
- 拉普拉斯金字塔(Laplacian pyramid): 用来从金字塔低层图像重建上层未采样图像
- 在这篇文档中我们将使用 高斯金字塔 。
高斯金字塔
-
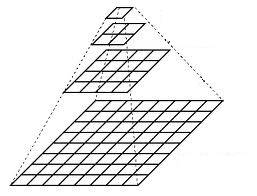
想想金字塔为一层一层的图像,层级越高,图像越小。
![Pyramid figure]()
-
每一层都按从下到上的次序编号, 层级
![(i+1)]() (表示为
(表示为 ![G_{i+1}]() 尺寸小于层级
尺寸小于层级 ![i]() (
(![G_{i}]() ))。
))。 -
为了获取层级为
![(i+1)]() 的金字塔图像,我们采用如下方法:
的金字塔图像,我们采用如下方法:-
将
![G_{i}]() 与高斯内核卷积:
与高斯内核卷积:![\frac{1}{16} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 4 & 6 & 4 & 1 \\ 4 & 16 & 24 & 16 & 4 \\ 6 & 24 & 36 & 24 & 6 \\ 4 & 16 & 24 & 16 & 4 \\ 1 & 4 & 6 & 4 & 1 \end{bmatrix}]()
-
将所有偶数行和列去除。
-
-
显而易见,结果图像只有原图的四分之一。通过对输入图像
![G_{0}]() (原始图像) 不停迭代以上步骤就会得到整个金字塔。
(原始图像) 不停迭代以上步骤就会得到整个金字塔。 -
以上过程描述了对图像的向下采样,如果将图像变大呢?:
- 首先,将图像在每个方向扩大为原来的两倍,新增的行和列以0填充(
![0]() )
) - 使用先前同样的内核(乘以4)与放大后的图像卷积,获得 “新增像素” 的近似值。
- 首先,将图像在每个方向扩大为原来的两倍,新增的行和列以0填充(
-
这两个步骤(向下和向上采样) 分别通过OpenCV函数 pyrUp 和 pyrDown 实现, 我们将会在下面的示例中演示如何使用这两个函数。
Note
我们向下采样缩小图像的时候, 我们实际上 丢失 了一些信息。
源码
本教程的源码如下,你也可以从 这里 下载
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
/// 全局变量
Mat src, dst, tmp;
char* window_name = "Pyramids Demo";
/**
* @函数 main
*/
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
/// 指示说明
printf( "\n Zoom In-Out demo \n " );
printf( "------------------ \n" );
printf( " * [u] -> Zoom in \n" );
printf( " * [d] -> Zoom out \n" );
printf( " * [ESC] -> Close program \n \n" );
/// 测试图像 - 尺寸必须能被 2^{n} 整除
src = imread( "../images/chicky_512.jpg" );
if( !src.data )
{ printf(" No data! -- Exiting the program \n");
return -1; }
tmp = src;
dst = tmp;
/// 创建显示窗口
namedWindow( window_name, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow( window_name, dst );
/// 循环
while( true )
{
int c;
c = waitKey(10);
if( (char)c == 27 )
{ break; }
if( (char)c == 'u' )
{ pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) );
printf( "** Zoom In: Image x 2 \n" );
}
else if( (char)c == 'd' )
{ pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) );
printf( "** Zoom Out: Image / 2 \n" );
}
imshow( window_name, dst );
tmp = dst;
}
return 0;
}
解释
-
让我们来回顾一下本程序的总体流程:
-
装载图像(此处路径由程序设定,用户无需将图像路径当作参数输入)
/// 测试图像 - 尺寸必须能被 2^{n} 整除 src = imread( "../images/chicky_512.jpg" ); if( !src.data ) { printf(" No data! -- Exiting the program \n"); return -1; } -
创建两个Mat实例, 一个用来储存操作结果(dst), 另一个用来存储零时结果(tmp)。
Mat src, dst, tmp; /* ... */ tmp = src; dst = tmp; -
创建窗口显示结果
namedWindow( window_name, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); imshow( window_name, dst ); -
执行无限循环,等待用户输入。
while( true ) { int c; c = waitKey(10); if( (char)c == 27 ) { break; } if( (char)c == 'u' ) { pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) ); printf( "** Zoom In: Image x 2 \n" ); } else if( (char)c == 'd' ) { pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) ); printf( "** Zoom Out: Image / 2 \n" ); } imshow( window_name, dst ); tmp = dst; }如果用户按 ESC 键程序退出。 此外,它还提供两个选项:
-
向上采样 (按 ‘u’)
pyrUp( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 )函数 pyrUp 接受了3个参数:
- tmp: 当前图像, 初始化为原图像 src 。
- dst: 目的图像( 显示图像,为输入图像的两倍)
- Size( tmp.cols*2, tmp.rows*2 ) : 目的图像大小, 既然我们是向上采样, pyrUp 期待一个两倍于输入图像( tmp )的大小。
-
向下采样(按 ‘d’)
pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 )类似于 pyrUp, 函数 pyrDown 也接受了3个参数:
- tmp: 当前图像, 初始化为原图像 src 。
- dst: 目的图像( 显示图像,为输入图像的一半)
- Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) :目的图像大小, 既然我们是向下采样, pyrDown 期待一个一半于输入图像( tmp)的大小。
-
注意输入图像的大小(在两个方向)必须是2的冥,否则,将会显示错误。
-
最后,将输入图像 tmp 更新为当前显示图像, 这样后续操作将作用于更新后的图像。
tmp = dst;
-
-
结果
翻译者
niesu@ OpenCV中文网站 <sisongasg@hotmail.com>
from: http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/doc/tutorials/imgproc/pyramids/pyramids.html#pyramids

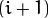 (表示为
(表示为 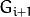 尺寸小于层级
尺寸小于层级  (
(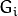 ))。
))。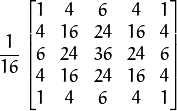
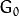 (原始图像) 不停迭代以上步骤就会得到整个金字塔。
(原始图像) 不停迭代以上步骤就会得到整个金字塔。 )
) , 因此向下采样不会产生错误(
, 因此向下采样不会产生错误(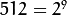 )。 原图像如下所示:
)。 原图像如下所示:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号