域滤波:方框、高斯、中值、双边滤波
2016-01-09 14:19 GarfieldEr007 阅读(431) 评论(0) 收藏 举报邻域滤波(卷积)
邻域算子值利用给定像素周围像素的值决定此像素的最终输出。如图左边图像与中间图像卷积禅城右边图像。目标图像中绿色的像素由原图像中蓝色标记的像素计算得到。

通用线性邻域滤波是一种常用的邻域算子,输入像素加权得到输出像素:
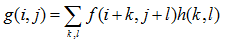
其中权重核 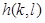 为“滤波系数”。上面的式子可以简记为:
为“滤波系数”。上面的式子可以简记为:

【方框滤波】
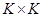 窗口中的像素值平均后输出,核函数为:
窗口中的像素值平均后输出,核函数为: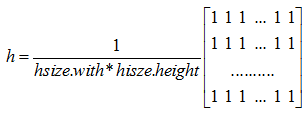
代码
- void cv::blur( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
- Size ksize, Point anchor, int borderType )
- {
- boxFilter( src, dst, -1, ksize, anchor, true, borderType );
- }
- cv::Ptr<cv::FilterEngine> cv::createBoxFilter( int srcType, int dstType, Size ksize,
- Point anchor, bool normalize, int borderType )
- {
- int sdepth = CV_MAT_DEPTH(srcType);
- int cn = CV_MAT_CN(srcType), sumType = CV_64F;
- if( sdepth <= CV_32S && (!normalize ||
- ksize.width*ksize.height <= (sdepth == CV_8U ? (1<<23) :
- sdepth == CV_16U ? (1 << 15) : (1 << 16))) )
- sumType = CV_32S;
- sumType = CV_MAKETYPE( sumType, cn );
- Ptr<BaseRowFilter> rowFilter = getRowSumFilter(srcType, sumType, ksize.width, anchor.x );
- Ptr<BaseColumnFilter> columnFilter = getColumnSumFilter(sumType,
- dstType, ksize.height, anchor.y, normalize ? 1./(ksize.width*ksize.height) : 1);
- return Ptr<FilterEngine>(new FilterEngine(Ptr<BaseFilter>(0), rowFilter, columnFilter,
- srcType, dstType, sumType, borderType ));
- }
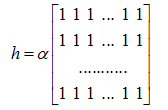
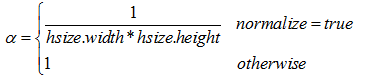
- blur( src, dst, Size( 1, 1 ), Point(-1,-1));
- blur( src, dst, Size( 4, 4 ), Point(-1,-1));
- blur( src, dst, Size( 8, 8 ), Point(-1,-1));
- blur( src, dst, Size( 16, 16 ), Point(-1,-1));
【高斯滤波】
常用的零均值离散高斯滤波器函数:
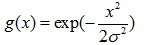
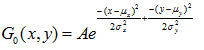
代码
- /****************************************************************************************\
- Gaussian Blur
- \****************************************************************************************/
- cv::Mat cv::getGaussianKernel( int n, double sigma, int ktype )
- {
- const int SMALL_GAUSSIAN_SIZE = 7;
- static const float small_gaussian_tab[][SMALL_GAUSSIAN_SIZE] =
- {
- {1.f},
- {0.25f, 0.5f, 0.25f},
- {0.0625f, 0.25f, 0.375f, 0.25f, 0.0625f},
- {0.03125f, 0.109375f, 0.21875f, 0.28125f, 0.21875f, 0.109375f, 0.03125f}
- };
- const float* fixed_kernel = n % 2 == 1 && n <= SMALL_GAUSSIAN_SIZE && sigma <= 0 ?
- small_gaussian_tab[n>>1] : 0;
- CV_Assert( ktype == CV_32F || ktype == CV_64F );
- Mat kernel(n, 1, ktype);
- float* cf = (float*)kernel.data;
- double* cd = (double*)kernel.data;
- double sigmaX = sigma > 0 ? sigma : ((n-1)*0.5 - 1)*0.3 + 0.8;
- double scale2X = -0.5/(sigmaX*sigmaX);
- double sum = 0;
- int i;
- for( i = 0; i < n; i++ )
- {
- double x = i - (n-1)*0.5;
- double t = fixed_kernel ? (double)fixed_kernel[i] : std::exp(scale2X*x*x);
- if( ktype == CV_32F )
- {
- cf[i] = (float)t;
- sum += cf[i];
- }
- else
- {
- cd[i] = t;
- sum += cd[i];
- }
- }
- sum = 1./sum;
- for( i = 0; i < n; i++ )
- {
- if( ktype == CV_32F )
- cf[i] = (float)(cf[i]*sum);
- else
- cd[i] *= sum;
- }
- return kernel;
- }
- cv::Ptr<cv::FilterEngine> cv::createGaussianFilter( int type, Size ksize,
- double sigma1, double sigma2,
- int borderType )
- {
- int depth = CV_MAT_DEPTH(type);
- if( sigma2 <= 0 )
- sigma2 = sigma1;
- // automatic detection of kernel size from sigma
- if( ksize.width <= 0 && sigma1 > 0 )
- ksize.width = cvRound(sigma1*(depth == CV_8U ? 3 : 4)*2 + 1)|1;
- if( ksize.height <= 0 && sigma2 > 0 )
- ksize.height = cvRound(sigma2*(depth == CV_8U ? 3 : 4)*2 + 1)|1;
- CV_Assert( ksize.width > 0 && ksize.width % 2 == 1 &&
- ksize.height > 0 && ksize.height % 2 == 1 );
- sigma1 = std::max( sigma1, 0. );
- sigma2 = std::max( sigma2, 0. );
- Mat kx = getGaussianKernel( ksize.width, sigma1, std::max(depth, CV_32F) );
- Mat ky;
- if( ksize.height == ksize.width && std::abs(sigma1 - sigma2) < DBL_EPSILON )
- ky = kx;
- else
- ky = getGaussianKernel( ksize.height, sigma2, std::max(depth, CV_32F) );
- return createSeparableLinearFilter( type, type, kx, ky, Point(-1,-1), 0, borderType );
- }
- void cv::GaussianBlur( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, Size ksize,
- double sigma1, double sigma2,
- int borderType )
- {
- Mat src = _src.getMat();
- _dst.create( src.size(), src.type() );
- Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
- if( borderType != BORDER_CONSTANT )
- {
- if( src.rows == 1 )
- ksize.height = 1;
- if( src.cols == 1 )
- ksize.width = 1;
- }
- if( ksize.width == 1 && ksize.height == 1 )
- {
- src.copyTo(dst);
- return;
- }
- #ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
- if(sigma1 == 0 && sigma2 == 0 && tegra::gaussian(src, dst, ksize, borderType))
- return;
- #endif
- Ptr<FilterEngine> f = createGaussianFilter( src.type(), ksize, sigma1, sigma2, borderType );
- f->apply( src, dst );
- }
实验结果




非线性滤波
线性滤波易于构造,且易于从频率响应的角度分析,但如果噪声是散粒噪声而非高斯噪声时线性滤波不能去除噪声。如图像突然出现很大的值,线性滤波只是转换为柔和但仍可见的散粒。这时需要非线性滤波。
简单的非线性滤波有 中值滤波, 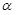 -截尾均值滤波,定义域滤波 和值域滤波 。
-截尾均值滤波,定义域滤波 和值域滤波 。
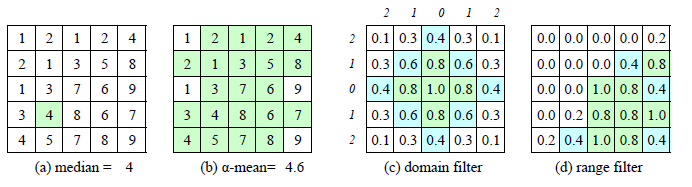
中值滤波选择每个邻域像素的中值输出; 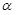 -截尾均值滤波是指去掉百分率为
-截尾均值滤波是指去掉百分率为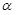 的最小值和最大值;定义域滤波中沿着边界的数字是像素的距离;值域就是去掉值域外的像素值。
的最小值和最大值;定义域滤波中沿着边界的数字是像素的距离;值域就是去掉值域外的像素值。
中值滤波代码
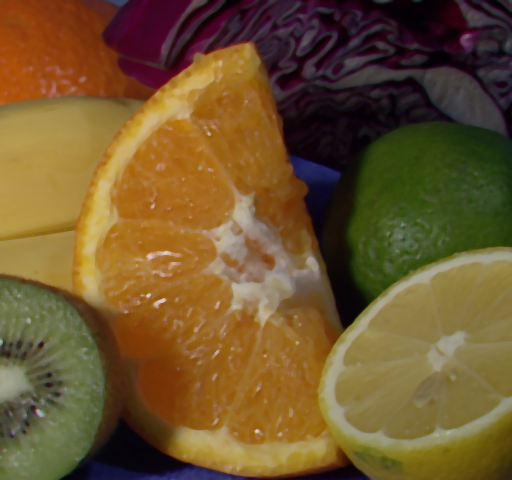
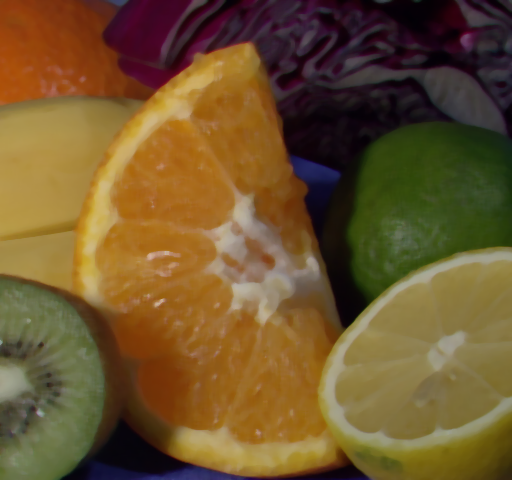
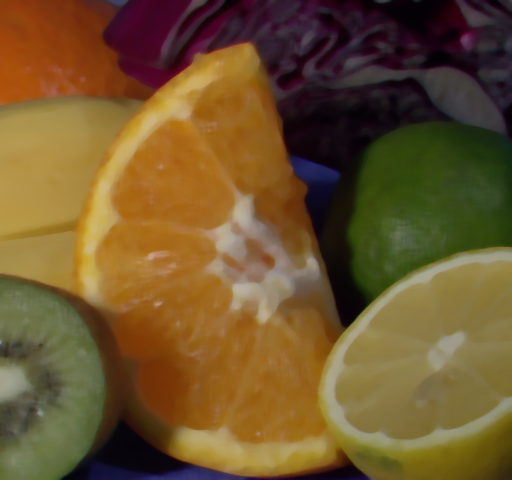




【双边滤波】
双边滤波的思想是抑制与中心像素值差别太大的像素,输出像素值依赖于邻域像素值的加权合:
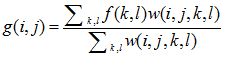
权重系数 取决于定义域核

和依赖于数据的值域核

的乘积。相乘后会产生依赖于数据的双边权重函数:
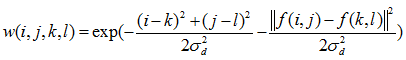
双边滤波源码
- /****************************************************************************************\
- Bilateral Filtering
- \****************************************************************************************/
- namespace cv
- {
- static void
- bilateralFilter_8u( const Mat& src, Mat& dst, int d,
- double sigma_color, double sigma_space,
- int borderType )
- {
- int cn = src.channels();
- int i, j, k, maxk, radius;
- Size size = src.size();
- CV_Assert( (src.type() == CV_8UC1 || src.type() == CV_8UC3) &&
- src.type() == dst.type() && src.size() == dst.size() &&
- src.data != dst.data );
- if( sigma_color <= 0 )
- sigma_color = 1;
- if( sigma_space <= 0 )
- sigma_space = 1;
- double gauss_color_coeff = -0.5/(sigma_color*sigma_color);
- double gauss_space_coeff = -0.5/(sigma_space*sigma_space);
- if( d <= 0 )
- radius = cvRound(sigma_space*1.5);
- else
- radius = d/2;
- radius = MAX(radius, 1);
- d = radius*2 + 1;
- Mat temp;
- copyMakeBorder( src, temp, radius, radius, radius, radius, borderType );
- vector<float> _color_weight(cn*256);
- vector<float> _space_weight(d*d);
- vector<int> _space_ofs(d*d);
- float* color_weight = &_color_weight[0];
- float* space_weight = &_space_weight[0];
- int* space_ofs = &_space_ofs[0];
- // initialize color-related bilateral filter coefficients
- for( i = 0; i < 256*cn; i++ )
- color_weight[i] = (float)std::exp(i*i*gauss_color_coeff);
- // initialize space-related bilateral filter coefficients
- for( i = -radius, maxk = 0; i <= radius; i++ )
- for( j = -radius; j <= radius; j++ )
- {
- double r = std::sqrt((double)i*i + (double)j*j);
- if( r > radius )
- continue;
- space_weight[maxk] = (float)std::exp(r*r*gauss_space_coeff);
- space_ofs[maxk++] = (int)(i*temp.step + j*cn);
- }
- for( i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
- {
- const uchar* sptr = temp.data + (i+radius)*temp.step + radius*cn;
- uchar* dptr = dst.data + i*dst.step;
- if( cn == 1 )
- {
- for( j = 0; j < size.width; j++ )
- {
- float sum = 0, wsum = 0;
- int val0 = sptr[j];
- for( k = 0; k < maxk; k++ )
- {
- int val = sptr[j + space_ofs[k]];
- float w = space_weight[k]*color_weight[std::abs(val - val0)];
- sum += val*w;
- wsum += w;
- }
- // overflow is not possible here => there is no need to use CV_CAST_8U
- dptr[j] = (uchar)cvRound(sum/wsum);
- }
- }
- else
- {
- assert( cn == 3 );
- for( j = 0; j < size.width*3; j += 3 )
- {
- float sum_b = 0, sum_g = 0, sum_r = 0, wsum = 0;
- int b0 = sptr[j], g0 = sptr[j+1], r0 = sptr[j+2];
- for( k = 0; k < maxk; k++ )
- {
- const uchar* sptr_k = sptr + j + space_ofs[k];
- int b = sptr_k[0], g = sptr_k[1], r = sptr_k[2];
- float w = space_weight[k]*color_weight[std::abs(b - b0) +
- std::abs(g - g0) + std::abs(r - r0)];
- sum_b += b*w; sum_g += g*w; sum_r += r*w;
- wsum += w;
- }
- wsum = 1.f/wsum;
- b0 = cvRound(sum_b*wsum);
- g0 = cvRound(sum_g*wsum);
- r0 = cvRound(sum_r*wsum);
- dptr[j] = (uchar)b0; dptr[j+1] = (uchar)g0; dptr[j+2] = (uchar)r0;
- }
- }
- }
- }
双边滤波调用
- bilateralFilter(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int d, double sigmaColor, double sigmaSpace,
- int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );
参考文献:
Richard Szeliski 《Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications》
http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/MANDUCHI1/Bilateral_Filtering.html
《The OpenCV Tutorials》 Release 2.4.2
《The OpenCV Reference Manual 》 Release 2.4.2









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号